The ecology of the Waves public chain has been borrowed from Terra to a certain extent, but it faces a lot of problems and the support ratio is low.
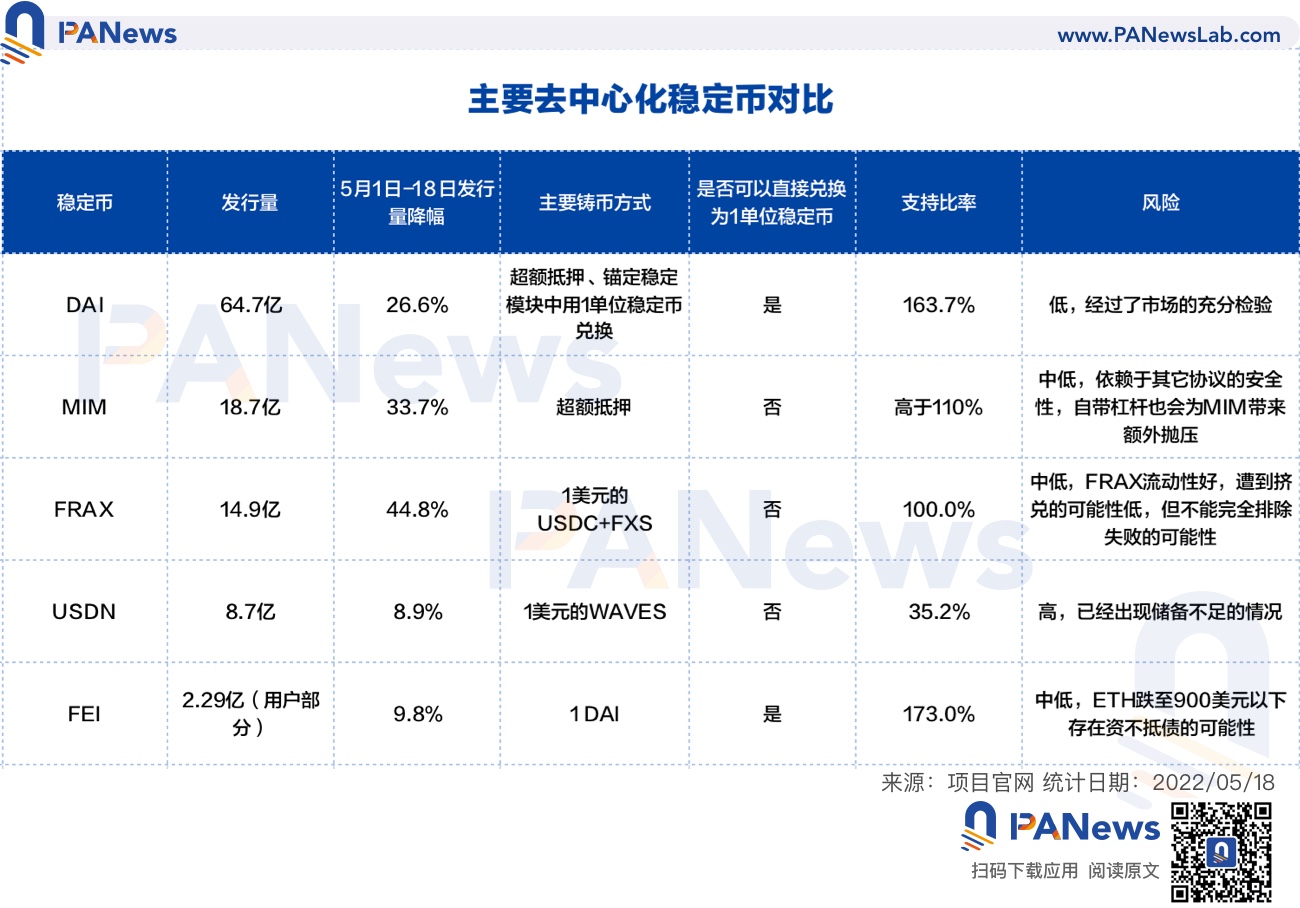
After the UST storm, decentralized stablecoins were hit hard across the board. As of May 18, the circulation of DAI and FRAX dropped by 26.6% and 44.8% respectively this month . UST was once the most successful decentralized stablecoin, and some decentralized stablecoins also partially refer to UST in terms of mechanism. The following will introduce the commonly used decentralized stablecoins and analyze their risks.
TL;DR
At present, the commonly used decentralized stablecoins have corresponding mortgage assets or reserves, most of which are commonly used assets such as ETH or stablecoins, and a small part include assets with large fluctuations such as FXS and WAVES.
USDN has already experienced under-collateralization, and most of USDN is idle in Vires, which is similar to the situation of Terra, and the risk is relatively high.
DAI has been fully tested by the market and has a clear liquidation mechanism. Even in the case of bad debts caused by the 3.12 plunge two years ago, the price of DAI is still higher than $1, with the lowest risk.
Although the vast majority of Fei Protocol's PCV is ETH, it needs ETH to fall below $900 to become insolvent.
The data of FRAX is healthy, the liquidity is sufficient, and the possibility of project failure caused by a death spiral is relatively low.
DAI/MIM
MakerDAO is one of the earliest DeFi projects. Users can deposit assets into Maker Vaults and mint the stablecoin DAI in an over-collateralized manner. According to Dai Stats, the circulation of DAI has dropped from $8.81 billion on May 1 to $6.47 billion now.

With the expansion of the protocol, MakerDAO now supports minting DAI in a variety of ways.
1. Overcollateralization. DAI is minted in the form of over-collateralization of encrypted assets. The collateral can be commonly used cryptocurrencies such as ETH and W BTC , or LP tokens such as Uniswap USDC-ETH. This is one of the main methods of minting DAI.
2. Anchoring and stabilizing the module. The anchoring stability module allows users to directly exchange DAI with USDC, USDP, and GUSD, three centralized stablecoins, and the DAI issued in this way exceeds 46% of the total amount of DAI, and DAI and centralized stablecoins are getting closer . The introduction of the stable anchor module provides an additional way for DAI to be minted and withdrawn. Based on the current data, it is equivalent to providing about $3 billion in liquidity for DAI without slippage.
3. Real assets. Over-collateralized real assets are used to cast DAI. Currently, there are only more than 30 million DAI issued in this way.
4. Direct deposit module (D3M). Allow the agreement to generate DAI instantly and deposit it into a supported third-party lending pool without traditional collateral. The purpose is to ensure that the floating interest rate in the lending agreement is lower than the target interest rate determined by Maker governance. About 118 million DAI was minted in this way.
Cryptocurrency over-collateralization and anchoring stability module are the main casting methods of DAI in MakerDAO. These two methods have also passed the test of time. MakerDAO limits the amount of DAI minted in each method, and the risk is low. DAI is used in hundreds of DeFi projects, forming its own moat.
MIM in Abracadabra Money is similar to DAI, and it is minted in an over-collateralized manner, supporting interest-earning assets in agreements such as Yearn as collateral. The circulation of MIM exceeds 1.8 billion, the leverage is higher, and the risk is higher than that of MakerDAO.
Frax
Frax is a part-algorithmic stablecoin. Mining FRAX requires a part of USDC and a part of FXS (Frax's governance token). The protocol allows users to mint 1 FRAX with 1 USDC+FXS, and also allows burning 1 FRAX to redeem 1 USD USDC+FXS. The proportion of USDC is called the mortgage rate, and FXS corresponds to the algorithm part. If the demand for FRAX is high, the proportion of the algorithm part will increase; if the demand for FRAX is insufficient, the proportion of the algorithm part will decrease. From May 1 to the present, the circulation of FRAX has dropped from 2.7 billion to 1.49 billion, a drop of 44.8%.

Theoretically, Frax also has the possibility of spiral death during a run, and several Frax fork projects have failed, but Frax has been running stably for more than a year. Compared with its fork projects and UST, the risk of FRAX Relatively small.
1. The mortgage rate of Frax is currently 89%. There are more stable currency reserves in the agreement. The impact of destroying and minting FRAX on the price of FXS is smaller than that of UST and LUNA in Terra.
2. The FRAX+3Crv pool has a TVL of more than US$1.3 billion, of which FRAX is 740 million and 3Crv is 570 million; Uniswap V3 also has a liquidity of US$176 million in FRAX. The liquidity of FRAX is very good, and the vast majority of FRAX provides liquidity in various DEXs. Frax has accumulated a large amount of Convex governance token CVX, and Convex controls the distribution of Curve rewards through veCRV, so Frax can distribute rewards to its users through Curve, and there is no such agreement as the Anchor of the Terra ecology to accumulate a large amount of futures. Stablecoins exploited.
3. Frax has restrictions on casting and burning, and the circulation of FRAX is more stable. New FRAX can only be minted when the price of FRAX is higher than $1.0033, and can be redeemed through the agreement when the price of FRAX is lower than $0.9933.
4. Frax has profitability. Through the "Algorithmic Market Operation Controller" (AMOs), the reserves are used for the mining of agreements such as Curve. Currently, the agreement has obtained a profit of 37.85 million US dollars through AMOs. The agreement calculates the actual mortgage rate regularly. If the actual mortgage rate is higher than the theoretical value due to the way AMOs earn income, the agreement will use the excess funds to mint FRAX and buy FXS for destruction. This will not only help expand the scale of FRAX, but also reduce the cost of FXS supply, which also reduces the participation of arbitrageurs.
Since its launch, Frax has been continuously improving, such as learning from its fork project at the beginning, and now the overall risk is low. In addition to the USD stablecoin FRAX, Frax also launched the FPI which tracks the CPI.
USDN
The ecology of the Waves public chain and the mechanism of the algorithmic stablecoin USDN of the Neutrino protocol have borrowed from Terra to a certain extent. Users can realize the swap between 1 USD WAVES token and 1 USDN in Neutrino. The initial circulation of USDN is 100 million pieces. The part unlocked from the contract circulates in the market, and the unlocked part is credited to the total supply. The WAVES tokens exchanged by users for USDN are included in the reserve, and Neutrino cannot issue or destroy them. As the price of WAVES fluctuates, the mortgage rate corresponding to the WAVES reserve can range from 0 to positive infinity. If the mortgage rate is lower than 1, it needs to rely on the auction governance token NSBT to adjust.
USDN has continued to maintain a slight unanchor, and the current price is $0.976. Neutrino’s official website shows that USDN issuance is 870 million, while the corresponding WAVES reserve value is 306 million US dollars, and the mortgage rate is only 35.16%.

According to data from CoinGecko, the circulation of WAVES is 100 million pieces, and the market value of WAVES corresponding to US$6.44 is US$644 million; the price of NSBT is US$21.83, with a market value of US$59.32 million. The market value of USDN has exceeded the sum of the market value of WAVES and NSBT.
The pledge income of USDN is provided by the LPoS (Lease Proof of Stake) consensus algorithm of the Waves blockchain, generated by the pledge of WAVES tokens in the reserve, and distributed to pledgers of USDN.
Vires Finance is a lending protocol of the Waves ecosystem, which allows loans between WAVES, USDN, USDT, USDC, BTC, ETH and other tokens. The data shows that there are about 689 million USDN deposits in Vires Finance, and only 25 million borrowings. More than 76% of USDN is idle in Vires Finance, and this part of USDN can also receive Neutrino’s pledge rewards.

Vires provides a scenario where the stablecoins USDT and USDC are used as collateral to borrow USDN and WAVES to short. However, almost all USDT and USDC have been borrowed at present, and these depositors may not be able to redeem their collateral, and there is a greater risk.
USDN and the entire Waves ecology are facing greater risks. USDN has insufficient reserves, and a run may cause WAVES to spiral down. A large number of deposits are idle in Vires Finance, which is similar to Anchor, and the pledge reward of USDN has dropped significantly. If you want to deposit stablecoins USDT and USDC, and borrow USDN and WAVES to go short, you may also face the risk of not being able to redeem USDT and USDC.
FEI
Fei Protocol allows users to mint the algorithmic stablecoin FEI with $1 assets, and also allows users to redeem FEI for $1 assets. It promotes the concept of PCV (protocol control value), and various assets held by the protocol can be used to generate revenue.
At the beginning, FEI was minted with ETH, but now it has been changed to DAI, and the vast majority of assets in PCV are still ETH. According to the official website data of Fei Protocol, the FEI minted by the agreement is about 300 million, and the FEI minted by users is about 230 million. The assets held by PCV are worth US$398 million, of which ETH accounts for 73.3%, DAI accounts for 8.7%, and LUSD accounts for 7.6%.

Theoretically, if the price of ETH continues to fall sharply, Fei Protocol may also be insolvent. According to the calculation of PCV assets and the issuance of FEI, the price of ETH needs to fall below $900 to become insolvent.
0
Author: PA line
 Alex
Alex
 Alex
Alex Brian
Brian Alex
Alex Hui Xin
Hui Xin Kikyo
Kikyo Brian
Brian Joy
Joy Hui Xin
Hui Xin Joy
Joy Brian
Brian