Author: Hotcoinglobalofficial Source: medium
EigenLayer, a re-staking protocol based on the Ethereum network, proposes to use ETH staked for Ethereum network verification to share security and capital efficiency with other protocols, while providing additional interest to protocol participants. Driven by concepts such as AVS, re-staking, and the points system, a huge ecosystem has gradually formed. From the beginning of 2024 to now, EigenLayer's TVL has increased by 12 times, attracting about $160 million in investment from crypto VCs including a16z, and quickly rising to the second place in the total TVL ranking of DeFi protocols, second only to Lido. Recently, with the launch of the EigenLayer mainnet, it has aroused heated discussions and widespread attention in the industry.
1. Overview of EigenLayer
EigenLayer is an Ethereum-based re-staking protocol that allows ETH that has been staked on the Ethereum network to increase the security of the network by re-staking. That is, users who have pledged ETH can choose to join the EigenLayer smart contract to re-stake their ETH and extend cryptoeconomic security to other applications on the network. At the same time, it will provide additional benefits to network participants. This process not only improves the efficiency of capital utilization, but also enhances the overall security of the network.
EigenLayer supports the secure operation of other blockchain protocols and applications by utilizing ETH that has been staked on Ethereum. This process is called restaking. Restaking allows Ethereum validators to use some or all of their staked ETH to support other Active Validation Services (AVS), such as bridge protocols, sequencers, and oracles. These services usually require their own staking and verification mechanisms to ensure network security, but through EigenLayer's restaking function, they can obtain Ethereum-level security without attracting a large amount of capital themselves.
Through restaking, the original single-purpose staked capital can support multiple networks at the same time, thereby improving the capital efficiency and security of the entire ecosystem. This mechanism does not require additional native tokens, just ETH or Liquid Staking Tokens (LST), such as stETH, rETH, etc., to participate in the staking verification process of AVS.
EigenLayer's features and advantages are as follows:
1. Establish a new security sharing model: EigenLayer's innovation is that it brings a new security sharing model to Ethereum, allowing different blockchain protocols to share Ethereum's security infrastructure without having to build a huge network of verification nodes themselves, greatly reducing the startup cost of new blockchain protocols. In addition, re-staking also increases the anti-attack ability of the entire network, because attacking any protected protocol requires overcoming the security protection increased by re-staking.
2. Improve ETH capital efficiency: The re-staking mechanism introduced by EigenLayer improves the liquidity and efficiency of capital use. Now the same ETH can serve multiple networks at the same time. While enjoying the original staking income, users can also get additional rewards for participating in other AVS protocols. It brings greater flexibility and scalability to the Ethereum network and the entire blockchain ecosystem.
3. Lower the threshold for participation: Through the re-staking mechanism, small stakers can also participate in the security of the Ethereum network. Stakers do not have to have the full staking threshold of 32 ETH, and individual stakers can also participate in the form of Liquidity Staking Tokens (LST). EigenLayer supports LST, such as stETH, which represents the staking rights of the original ETH and can be freely circulated and used in DeFi projects.
4. Improve decentralization: By allowing small amounts of pledges, EigenLayer further decentralizes the contributor base of network security and reduces dependence on large pledgers, which helps prevent potential centralization risks and validator monopoly. In addition, the design of EigenLayer also encourages broader community participation and governance, making the blockchain network more democratic and decentralized.
2. Design principles of EigenLayer
1. Re-staking: In the EigenLayer ecosystem, re-staking provides security guarantees shared with Ethereum, which is the foundation of the entire EigenLayer. Participants re-stake their ETH on Ethereum to the EigenLayer network, and these ETH serve as security capital to support the security and operation of the network. Stakers will receive double benefits from the verification of the native Ethereum network and AVS.
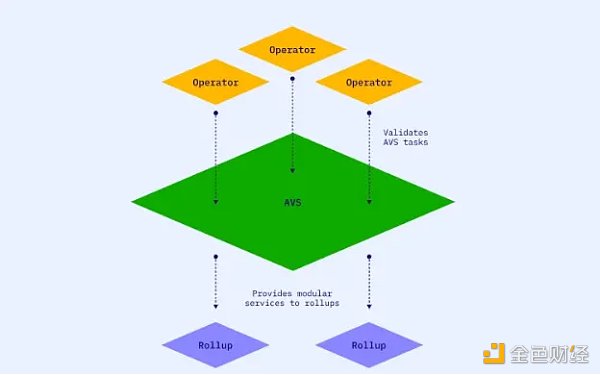
2. Active Verification Service (AVS): Active Verification Service (AVS) uses these re-staked ETH to enhance its service functions. AVS is a special service or application that runs on EigenLayer and directly uses these re-staked funds to provide enhanced network services. These services can include a variety of functions such as computing, storage, and data processing. AVS can be compared to middleware or modules, such as new blockchains, DA layers, virtual machines, oracle networks, cross-chain bridges, and other projects. AVS can provide data services for DeFi, games, and wallets.
3.Rollups: In the EigenLayer ecosystem, Rollups, as a solution for Ethereum Layer 2, benefit from the modular services provided by AVS. For example, through services such as EigenDA (EigenLayer's super data availability service), Rollups can achieve super-scaling of data processing, which greatly increases its ability to process large-scale data.
4. Operators: Operators play a key role in the EigenLayer ecosystem. They perform various verification tasks, which in turn rely on the pledged ETH as a security guarantee, which is also the basis for AVS to rely on. The responsibilities of operators include, but are not limited to, verifying transactions, executing smart contracts, and maintaining network security. Their work ensures that AVS can operate reliably and provide support for upper-layer applications and services.
5. Safeguards: Considering the additional risks that may be caused by re-staking, EigenLayer has introduced a number of risk control mechanisms. For example, for security issues that may be caused by AVS, EigenLayer has designed a system called "Decentralized Validator Cluster" (DVC) to disperse risks and ensure that even if some AVS have problems, it will not affect the security of the entire network. In order to ensure the normal operation of the network and the security of the pledged capital, EigenLayer implements a slashing mechanism for pledgers who operate improperly. Slashing refers to the method that EigenLayer will use to ensure the honesty of AVS operators. If validators act maliciously, they will face the risk of having their pledges revoked.
6. Points mechanism: EigenLayer has introduced an internal points system, which will award one EigenLayer point every hour for each ETH deposited by each re-staker. The purpose of this method is to measure the user's contribution to the network, and the number of points reflects the activity and duration of their pledge. Although the EigenLayer team has not yet clearly specified the specific use of points, nor has it announced any details about the launch of EigenLayer tokens, many users continue to re-stake and look forward to possible token airdrops based on points in the future. This shows that users have expectations and confidence in the future development of EigenLayer.
3. EigenLayer re-staking methods
Currently, EigenLayer supports two re-staking methods: Liquid Restaking and Native Restaking.
1. Liquid Restaking
Allows staking of Liquid Staking Tokens (LST), which are pledge certificates issued by LSP (Liquid Staking Protocol) that represent the rights and interests of the original ETH pledge and can be freely circulated and used in various decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, without affecting the pledger's pledge status and reward collection on Ethereum. LSP solves some of the limitations of Ethereum network staking, and users can participate in Ethereum network verification and collect verification rewards with less than 32 ETH of capital. At the same time, it allows the use of LST in DeFi protocols to generate additional income, or by selling LST on the market without waiting for the unstaking period, effectively providing the same benefits as unstaking. For example, Lido Finance is the most well-known LSP at present, and the LST issued by Lido Finance is stETH. EigenLayer accepts user pledged stETH, making it an infrastructure to ensure the security of AVS.
Currently, EigenLayer supports a total of 12 types of LST for liquid re-staking, including stETH, swETH, mETH, stETH, wbETH, rETH, sfrxETH, cbETH, osETH, oETH, lsETH, ankrETH.
EigenLayer only accepts LST re-staking deposits during a specific time period, or limits the incentives and governance participation rights obtained by a single LST from EigenLayer to a maximum of 33%. To date, EigenLayer's LST re-staking limit has been increased five times. On April 16, EigenLayer announced the cancellation of all deposit limits for LST and reopened the deposit window, allowing ETH to be re-staked through EigenPod on the EigenLayer application.
2. Local re-staking
Local re-staking is a more direct method. The staker uses the staked ETH directly for EigenLayer's smart contract, that is, the Ethereum PoS node validator connects the ETH staked in the network to EigenLayer to participate in the verification process of AVS. Performing local re-staking requires staking at least 32 ETH, and participants need to directly manage an Ethereum node, which provides a higher entry barrier than liquid re-staking.
Since ETH is directly used in EigenLayer's smart contracts, local re-staking provides higher security. The pledged assets are directly exposed to the penalty standards of Ethereum and AVS, which increases the protection of capital. Compared with liquid re-staking, local re-staking does not involve any intermediate tokens, which reduces the risks caused by token volatility or mismanagement. But its disadvantage is that the liquidity of funds is low, and it may take longer to unlock and transfer assets.
Fourth, EigenLayer Ecological Status and Project Inventory
Currently, the EigenLayer ecosystem has begun to support multiple AVS and has been integrated with multiple well-known DeFi protocols and other blockchain services. It allows different types of staking proofs (such as LST and local ETH) to support these services, so that capital can be used more efficiently.
On April 10, EigenLayer announced the official launch of the blockchain mainnet. The release was also accompanied by the EigenLayer team's launch of the data availability (DA) service EigenDA. At the end of February, a16z announced an investment of $100 million in EigenLayer, making it a crypto unicorn with a valuation of tens of billions. As of April 18, according to DefiLlama data, EigenLayer TVL has exceeded $12.8 billion.
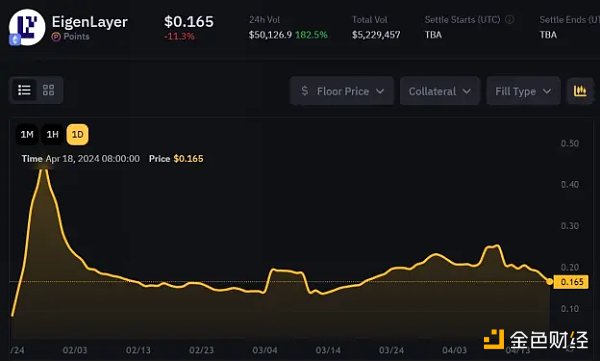
As of April 18, EigenLayer has distributed approximately 4.2 billion points to all re-stakers. The trading price of each EigenLayer point in the over-the-counter market Whales Market is $0.165.
(I) Eigenlayer Ecosystem AVS Project Inventory
Currently, there are 13 AVS announced by EigenLayer. EigenDA, as the first AVS launched, was developed by Eigen Labs to help other blockchain protocols store transaction data and other information. AVS outside of EigenDA will be able to "register" with the protocol, but they are not yet fully deployed.

1. EigenDA: EigenDA is the first AVS on EigenLayer, which provides efficient, ultra-large-scale throughput data availability services for Rollups. Through the shared cryptoeconomic security provided by EigenLayer's re-stakeholders, EigenDA makes Rollups cheaper and more efficient when processing large-scale data. On April 18, EigenLayer announced that it had lowered the staking threshold for EigenDA validator nodes from 320 ETH to 96 ETH. EigenLayer said the change would allow more new validators to participate in EigenDA's AVS validation service.
2. Aethos: Aethos is a policy engine for smart contracts that abstracts pre-transaction calculations while maintaining decentralization. Aethos makes contract execution more efficient and secure by simplifying the pre-processing of smart contracts.
3. AltLayer: AltLayer is a decentralized inter-layer network designed for Rollups. It uses EigenLayer to achieve fast finality and guarantees data availability through EigenDA, thereby optimizing interoperability and performance between Rollups.
4. Blockless: Blockless is a verifiable computing engine that is economically incentivized through a re-staking mechanism. It provides a decentralized verification platform for complex calculations, enhancing the transparency and credibility of the calculation results.
5. Drosera Network: Drosera Network creates a strong and responsive collective of first responders through re-staking, focusing on decentralized verification. This provides a new way for emergency response and security verification for the network.
6. Espresso: Espresso is a decentralized serialization service that uses re-staking to achieve alignment and strong economic security on Ethereum. It guarantees the order and consistency of transaction execution.
7. Ethos: Ethos is a security coordination layer that uses the security of re-staking ETH to power Cosmos. It enhances the security and efficiency of cross-chain interactions.
8. Hyperlane: Hyperlane uses EigenLayer to enhance message security for inter-chain application developers, providing security for inter-application communication through the economic security of re-staking.
9. Lagrange: Lagrange creates a secure and scalable light client dedicated to OP Rollups through re-staking. It improves the accessibility and responsiveness of the network through light clients.
10. Near: Near aims to build a fast finality layer to improve composability and liquidity in the Ethereum Rollup ecosystem. This helps to improve the efficiency of cross-Rollup operations.
11. Omni: Omni is a low-latency interoperable network that connects all Ethereum Rollups through re-staking, ensuring the security and efficient operation of the entire network.
12. Silence Laboratories: Silence Laboratories is building authentication libraries and SDKs based on multi-party computing (MPC), which are agnostic to technology stacks and devices, improving the security and flexibility of the network.
13. Witness Chain: Witness Chain is a monitoring network that uses re-staking for proof, focusing on the security and proof position of Rollup. By providing the function of proving diligence and position, it enhances the monitoring and verification capabilities of the network.
(II) Eigenlayer Ecosystem Rollups Project Inventory
Rollups projects use EigenLayer's technology to achieve fast finality and efficient data availability, further expanding its blockchain solutions. Currently, there are 9 integrated Layer 2 solutions. Among them, AltLayer is both AVS and Rollup project.

1. Caldera: Caldera is a modular blockchain platform that allows developers to deploy Rollups with EigenDA services in one click. This platform greatly reduces the technical threshold for developers by simplifying the deployment process, allowing more innovations and applications to be launched quickly.
2. Celo: Celo was originally an independent layer 1 network, and is now using EigenDA to transform into Ethereum's second layer Rollup. Through this transformation, Celo can better integrate into the Ethereum ecosystem while improving the performance and scalability of its network.
3. Cyber: Cyber is a modular layer 2 network designed for social and mass adoption, using EigenDA to optimize data processing and user experience. Cyber aims to promote the application of blockchain technology in the field of social media through efficient data services.
4. Layer N: Layer N is a layer 2 network designed to accelerate decentralized finance (DeFi), and also uses EigenDA to improve data processing capabilities. With this technical support, Layer N aims to provide higher efficiency and better scalability for DeFi applications.
5. Mantle: Mantle was developed by BitDAO and is a modular Rollup using EigenDA. This project provides users with an efficient and powerful blockchain platform by combining the resources of BitDAO and the technology of EigenDA.
6. Movement: The Movement network consists of a series of modular blockchains based on the Move language, which also uses EigenDA technology. This design enables Movement to provide flexibility while ensuring efficient data processing and security.
7. Polymer Labs: Polymer Labs is a Rollup that combines the Cosmos SDK and the OP stack, using EigenDA for data availability services and settlement in Ethereum. This multi-technology integrated solution provides its users with diverse application scenarios and strong network support.
8. Versatus: Versatus is a project in cooperation with EigenDA, aiming to introduce the world's first stateless Rollup into the Ethereum ecosystem. This innovative Rollup design brings new development potential to the Ethereum ecosystem through efficient data processing and unique network structure.
(III) Eigenlayer Ecosystem LRP Related Project Inventory
The Liquid Restaking Protocol (LRP) is a key component in the EigenLayer ecosystem, designed to attract and increase user participation in a flexible and efficient manner. LRP allows users to deposit ETH or LST (liquid staking tokens) and re-stake on EigenLayer on behalf of the user, which provides users with a more flexible way to participate in the EigenLayer ecosystem. Users can choose to re-stake through the LRP platform without directly participating in the complex staking process, including earning EigenLayer points and additional points provided by the platform.
To prove the user's deposit and participation, LRP will issue LRT, which are tokens representing the user's staked share in LRP. LRT not only serves as a certificate of the holder's assets, but can also be freely traded in the DeFi market, providing additional liquidity and income opportunities, thereby further increasing income on the basis of EigenLayer points. Representative LRT-related projects include Ether.fi, Kelp DAO, EigenPie, Pendle Finance, and Gearbox, etc.
1.Ether.fi:Ether.fi, as a member of the EigenLayer ecosystem, initially started as part of LSP, but soon demonstrated its breadth of application in the DeFi field through its innovative eETH and weETH tokens. These two tokens not only ensure compatibility with mainstream DeFi protocols through the repurchase mechanism and reward nature of the design, but also enhance user participation and liquidity of pledged assets through the EigenLayer points farm.
2.Kelp DAO: Kelp DAO provides users with an attractive staking and re-staking scenario through its unique re-staking solution and Kelp Miles points system. Its development reflects the efforts of the LRP ecosystem to improve user experience and reduce transaction costs, especially when high Gas fees and network congestion often hinder user experience.
3.EigenPie: EigenPie, as part of the MagPie ecosystem, focuses on aggregating governance tokens and influencing DeFi protocol decisions. Its strategy is to diversify risks and optimize the liquidity and usability of tokens through independent re-staking methods. This is particularly critical to promoting the long-term sustainable development of the protocol. 4.Pendle Finance: Pendle Finance has partnered with Ether.fi to launch Ether.fi's eETH as the first LRT available on its platform. Ether.fi has designed a system to distribute EigenLayer points and Ether.fi loyalty points to users who hold YT tokens for eETH (YT-eETH). This enables users to buy YT-eETH that is close to expiration (which is getting cheaper) and accumulate interest and points until that date.
5. Gearbox: Gearbox is a leveraged yield protocol where borrowers leverage their positions by depositing pledged assets in a credit account and assets borrowed from the protocol. Gearbox has launched a leveraged points strategy through cooperation with the LRP protocol. Gearbox allows EigenLayer points and LRP local points to be accumulated in a credit account and sent to the borrower's wallet, providing users with up to 9 times leverage points.
V. EigenLayer Ecosystem Risks and Challenges
As a re-staking layer built on Ethereum, EigenLayer provides innovative solutions for blockchain technology, but it is also accompanied by many risks and challenges.
1. Technical implementation risks: The implementation of EigenLayer is highly dependent on complex technical solutions, including the stability and security of smart contracts. Smart contract vulnerabilities or protocol-level security issues may lead to serious financial losses. In addition, since EigenLayer is directly integrated with Ethereum's node ecosystem, any imperfections in technical execution may affect its overall security and efficiency. 2. Market acceptance: Although EigenLayer provides an innovative re-staking solution, market acceptance remains an important uncertainty. The volatility of the crypto market may affect the value of the pledged assets, and the market's acceptance of this emerging technology will directly affect the liquidity and widespread application of EigenLayer. 3. Centralization risk: The re-staking model may lead to the concentration of capital in a small number of efficient validators, which may further aggravate the centralization trend and form a market monopoly, thus posing a threat to the decentralized principle of the Ethereum ecosystem.
4. Possibility of consensus split: If EigenLayer's operating mode directly intervenes in Ethereum's node ecology, it may affect Ethereum's social consensus. If handled improperly, it may lead to community splits or even chain forks.
5. Risk of AVS: EigenLayer provides additional functions and services through its AVS (Active Verification Service), but the security and efficiency of these services depend on the reliability and technical implementation of the operator. Any operational failure may cause losses to the staked ETH. For AVS, which requires very high network security, re-staking may not provide sufficient protection, which may affect the trust and adoption rate of these services.
VI. EigenLayer Ecological Development Outlook
EigenLayer has gradually evolved from the concept of sharing Ethereum network security and generating additional income to a large ecosystem to meet the needs of infrastructure builders and investors, which has aroused great interest and high expectations in the infrastructure industry and the crypto market.
1. Expansion of AVS: Following the launch of EigenDA, EigenLayer will introduce more AVS and provide more customized services, such as enhanced data processing capabilities, more efficient transaction verification, etc., thereby expanding its service scope and influence.
2. Security enhancement: By implementing advanced security measures and audit mechanisms such as penalty mechanisms, ensure that the operation of AVS is not affected by malicious attacks or vulnerabilities.
3. Cross-chain integration: Develop cross-chain solutions that allow EigenLayer to not only serve Ethereum, but also interoperate with other major blockchains, enhancing its market applicability and user base. Cooperate with more blockchain and crypto projects to achieve technical interoperability and improve overall network performance.
4. Ecosystem expansion: Establish partnerships with more ecological projects such as DeFi, DAO, and NFT platforms, and bring value to these platforms by providing efficient re-pledge solutions.
5. Integration of emerging technologies: Explore the possibility of combining emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things with EigenLayer technology to create new application models.
6. Competition and cooperation: As the largest liquidity pledge protocol in the Ethereum ecosystem, Lido not only pledges the most ETH, but also has many node operators. Perhaps these direct conflicts of interest between EigenLayer and Lido will also make Lido rethink its business model and sustainability, and EigenLayer will also need some time to gradually fill in the missing modules.
As more and more blockchain and crypto projects seek to reduce startup costs through shared security models, EigenLayer's re-staking model may become an important direction for future blockchain network security architecture. In addition, it may also promote the emergence of new economic models and investment opportunities, especially in the fields of DeFi and cross-chain operations. It not only brings innovation and value to the Ethereum network, but also provides power and direction for the entire blockchain ecosystem.
Hotcoin pays close attention to the development of the EigenLayer ecosystem and the re-staking track, and has launched high-quality assets such as ALT, ETHFI, OMNI, NEAR, CYBER, and PENDLE. For crypto investment, come to Hotcoin, where you can get the hottest high-quality assets first and be one step ahead!
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance




