Source: Zepin Macroeconomics
On January 20, 2025, Trump will be officially sworn in as the President of the United States. At present, Trump has started the nomination of cabinet members and important officials. The new cabinet's governing ideas are gradually becoming clear, and its China policy is gradually becoming clear.
After Trump returns to the White House, where will Sino-US relations go? How should China respond?

1 Overview of the US Cabinet
The United States pursues a "separation of powers" system. The two houses of Congress, the Supreme Court and the president respectively enjoy legislative power, judicial power and executive power. The Constitution limits the role of each branch through a system of checks and balances. The Supreme Court has the power to declare that laws enacted by Congress or actions taken by the President are not in accordance with the Constitution; while Congress can impeach the President, the federal judiciary and judges.
The President can propose legislation to Congress, and has the power to veto laws passed by Congress,and has the power to nominate candidates for Supreme Court Justices;He can bypass Congress and exercise the right to conclude foreign treaties independently by signing executive orders.
The President's Executive Office and the Cabinet assist the President in governing.
The structure of the President's Executive Office began in 1939,when President Roosevelt established the Executive Office during his second term, which consists of the Office of the President and the Bureau of the Budget.
Thereafter, administrative agencies such as the Council of Economic Advisers, the Homeland Security Council, the Office of the United States Trade Representative, and the Office of Homeland Security were established through presidential executive orders and other means.Currently, the members of the Executive Office include staff, consultants, and personnel and agencies directly responsible to the President, and the office isheaded by the White House Chief of Staff.Generally speaking, except for cabinet-level leaders, members of the President's Executive Office do not need to be reviewed by the Senate.
The presidential cabinet structure began in 1789. It is more of an institution to assist the president in his administration. It is generally composed of the vice president and 15 cabinet ministers as the main members, including the vice president, secretary of state, secretary of the treasury, secretary of defense, attorney general, secretary of the interior, secretary of agriculture, secretary of commerce, secretary of labor, secretary of health and human services, secretary of housing and urban development, secretary of transportation, secretary of energy, secretary of education, secretary of veterans affairs, secretary of homeland security, etc.
The president will promote some officials to the cabinet level as needed, including the White House Chief of Staff, the Director of the Environmental Protection Agency, the Director of the Office of Management and Budget, the Director of National Intelligence, the Trade Representative, the Ambassador to the United Nations, the Chairman of the Council of Economic Advisers, the Director of the Small Business Administration, etc. In his last term, Trump nominated the Director of National Intelligence and the Director of Central Intelligence to join the cabinet, and disqualified the Chairman of the Council of Economic Advisers; Biden nominated the Director of the Office of Science and Technology Policy to join the cabinet during his term, and disqualified the Ambassador to the United Nations.
2 Panoramic view of Trump and his cabinet's thoughts
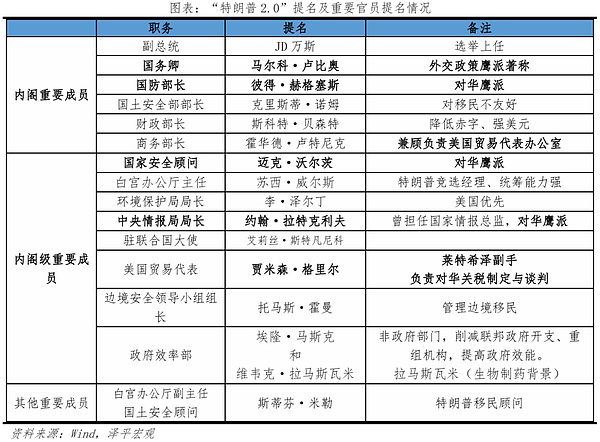
On November 6, Trump announced that he had won the election and launched the nomination of "Trump 2.0" cabinet members and important officials.As of November 23, the prototypes of the teams in the fields of diplomacy, defense, justice, and internal affairs have basically taken shape.
In the field of national diplomacy and security, Marco Rubio was nominated as Secretary of State, and Mike Waltz was nominated as National Security Advisor, sending a tough signal to China. Pete Hegseth was nominated as Secretary of Defense, Kristi Noem was nominated as Secretary of Homeland Security, and Tom Homan was nominated as the head of national border affairs ("Border Czar"); Elise Stefanik was nominated as the US Ambassador to the United Nations, and Steve Witkoff was nominated as the Middle East Envoy; John Ratcliffe was nominated as the Director of the Central Intelligence Agency, and Tulsi Gabbard was nominated as the Director of National Intelligence.
In the field of domestic affairs, Susie Wells was nominated as the White House Chief of Staff (Chief of Staff), and Stephen Miller was nominated as the Deputy Director of the White House Office; Lee Zeldin was nominated as the Director of the Environmental Protection Agency, Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy were nominated to lead the Department of Government Efficiency, and Matt Gates was nominated as the Attorney General.
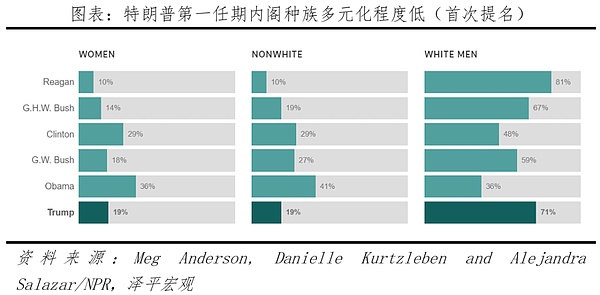
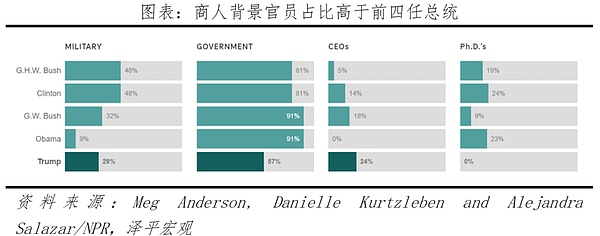
Among the officials nominated by Trump, the proportion of candidates with business and media backgrounds is higher than that of previous presidents, the cabinet has a low degree of racial diversity, and the proportion of white men is relatively high, which was also reflected in the previous term. Looking back at the early nominations of presidential cabinets from Reagan to Trump (first term), Trump's cabinet team has the highest proportion of white men, is inclusive of women, but the proportion is low, and the degree of racial diversity is low; in addition, the proportion of officials with business backgrounds is relatively high, and the proportion of government officials is relatively low.
The turnover rate of cabinet members in the previous term was high. Trump replaced three chiefs of staff, three secretaries of homeland security, and two secretaries of defense due to "disagreements" and other issues. This time, Trump places more emphasis on and prefers candidates who are "highly ideologically consistent with him, or more extreme in ideology" to enhance his executive power in the fields of trade, immigration, and military over the next four years. Among the nominees, Secretary of State Rubio, CIA Director Ratcliffe, Secretary of Defense Hegseth, and National Security Advisor Waltz advocate a tough stance against China, which may intensify the conflict between China and the United States in the fields of trade, finance, technology, military, and geopolitics.


Specifically,
1) Secretary of State candidate Marco Rubio, responsible for the Trump administration's foreign and international affairs. Rubio is "interventionist" and "hawkish", with rich diplomatic experience and a tough attitude. He once supported the US invasion of Iraq, sanctions on Iran, and supported Israel.
In recent years, Rubio has been a comprehensive hawk on China, covering finance, trade, human rights and other fields, and believes that China's rise threatens the status of the United States. In 2021, he initiated a proposal to ban Chinese companies that threaten national security from being listed on US stock exchanges; interfered with human rights and called for a boycott of imported Xinjiang products; criticized the US government for allowing China to join the WTO; and believed that China's diplomatic behavior and the "Belt and Road" initiative are threatening the US hegemony. In November, Rubio published an article in The Economist saying that the United States should end the Russian-Ukrainian war and the Middle East war and turn its strategic goals to China.
2) Mike Waltz, a candidate for National Security Advisor, does not require Senate confirmation and is directly appointed by the president. Trump believes that Waltz is a defender of "peace through strength." Waltz served in the US Army and was stationed in Afghanistan, the Middle East and Africa. He has rich military experience; he served as the director of defense policy for Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld and Robert Gates, and served former Vice President Dick Cheney as a counterterrorism adviser.
Both Waltz and Rubio represent the hawkish stance on China within the Republican Party, believing that China is an "existential threat".In 2020, as a member of the House China Special Committee, he released a more than 140-page "China Task Force Report", covering ideology, supply chain, national security, technology, economic energy, competition and other matters. The report includes 82 key points and 400 forward-looking recommendations. In addition, it is proposed to prohibit the US Federal Savings Plan (TSP) from investing in China and Russia, etc.; and supports establishing good relations with Asian allies to constrain China.
3) White House Chief of Staff candidate Susie Wells, who is deeply trusted by Trump, will be the first woman in American history to be appointed as the White House Chief of Staff. She has relatively rich communication and management experience, but lacks political experience. Susie Wells has served in the Republican campaign for a long time. Politico once described her as a "fearsome and little-known politician". She served in the Reagan campaign in 1980, and helped businessman Rick Scott be elected governor of Florida in 2010, ending Democratic control. She participated in Trump's campaign in 2016 and was responsible for Florida operations. In 2018, Trump appointed her to help Ron Sanders run for governor of Florida. In 2021, she served as CEO of Trump's "Save America" campaign and in 2022, she served as Trump's campaign manager. On November 7, Trump nominated Susie Wells as the White House Chief of Staff, responsible for the affairs of the President's Executive Office. 4) Howard Lutnick, a candidate for Secretary of Commerce, has a business background and is the chairman and CEO of Cantor Fitzgerald and BGC Group. Held several fundraising events for Trump in the 2020 and 2024 elections. Political advocacy, supports Trump's policy of imposing broad tariffs and high tariffs, encouraging cryptocurrencies and the return of manufacturing. Lutnick is also responsible for the Office of the United States Trade Representative, implementing the "tariff and trade agenda", and ensuring the smooth implementation of Trump's promises such as "general tariffs", "fighting unfair trade", and "repatriation of manufacturing". Trump will have more systematic regulation in economic and trade negotiations, tariff trade, export promotion, and unfair competition in the future.
5) US Trade Representative candidate Jamison Greer, has a legal background and was responsible for domestic corporate trade relief issues, import and export compliance, and investment security affairs at King & Spalding Law Firm. From 2017 to 2021, he served as Deputy to Trade Representative Lighthizer, responsible for the formulation and negotiation of tariffs on China. Trump believes that Greer can control the huge US trade deficit and defend the manufacturing, agricultural and service industries.
6) Scott Bessant, the candidate for the Minister of Finance, has a business background and is the founder of the global macro investment company Key Square
Group. In 2016, he donated $1 million to Trump's presidential campaign; in 2024, he held several fundraising events for Trump, making an important contribution to his victory. Bessant suggested that Shinzo Abe's "three arrows" plan be included in Trump's economic policy blueprint, calling for deregulation, increased energy production, reducing the deficit to 3%, and stimulating the US GDP to 3%. It is worth noting that Bessant's advocacy is inconsistent with Trump's "weak dollar to promote exports" strategy, and Trump may weaken the power of the Minister of Finance in the field of trade. 7) Peter Hegseth, candidate for Secretary of Defense, has a background of "military + media person". He is responsible for national security and military strategic affairs, and supervises military and defense situations. He has a military and media background, is conservative, and pays attention to veterans' benefits. He has a high influence in Fox News. He is a co-host of "Fox & Friends Weekend" and a retired soldier who participated in the Iraq War and the Afghanistan War. He has interviewed Trump twice on Fox TV and has become one of Trump's biggest defenders. 8) John Ratcliffe, candidate for Director of the Central Intelligence Agency, is responsible for the work of US intelligence agencies. He served as the Director of National Intelligence in the Trump administration and has a tough attitude towards China. Ratcliffe once emphasized in a column in the Wall Street Journal that China is "the biggest threat to the United States and the biggest threat to democracy and freedom in the world since World War II."
9) Tom Homan, the head of national border affairs, served as the acting director of Immigration and Customs Enforcement during Trump's first term.
10) Kristi Noem, the candidate for the Department of Homeland Security, is responsible for national security, emergency management and immigration policy and supports Trump's immigration policy.
11) Trump has established a new Department of Government Efficiency, co-led by Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy. The department aims to cut federal government spending, reorganize agencies, and improve government efficiency. However, the president "cannot unilaterally reorganize government agencies" and needs to "apply to Congress for the right to reorganize." The reorganization and abolition issues may face opposition from both parties, making it difficult to advance.
Elon Musk, is a businessman, the founder of SpaceX, CEO of Tesla, owner of X (formerly Twitter), and co-founder of OpenAI. The business sector involves commercial aerospace, new energy vehicles, social platforms, artificial intelligence, infrastructure, banking and other fields, and is relatively friendly to China. CCTV news reports show that Musk's business sector is heavily dependent on federal government contracts and rules. The Biden administration has been quite cold to him in the past four years. In early 2024, Musk announced his support for Trump's campaign and became the second largest individual donor, donating more than $110 million, playing an important role in propaganda in seven swing states. For this reason, Trump's attitude towards electric vehicles changed from opposition to support. From a political standpoint, Musk advocates streamlining federal government agencies and cutting federal staff, believing that it can save "US$2 trillion in government budget."
Vivek Ramaswamy, is an Indian businessman, involved in biotechnology and finance, and is a good friend of Vice President Vance. From a political standpoint, Ramaswamy opposes the equal rights movement and LGBT. He promised during his campaign to fire 75% of federal employees and abolish five agencies including the Department of Education and the FBI.
12) Stephen Miller, candidate for deputy director of the White House Office. He served as a senior policy adviser and has an extreme right and anti-immigrant political stance. He was the main person in charge of the "Muslim" ban and one of the main developers of the wall and family separation policies.
3 Trump 2.0 Administration: America First, Containment of China
The Republican Party pursues "isolationism" and "America First" in diplomacy. During his last term, Trump changed the foreign policy of the Obama era, fought on all sides and offended allies.
Trump launched a trade war against China and exerted extreme pressure. Sino-US trade frictions continue to escalate, and the United States has launched an all-out war with China in terms of technology, diplomacy, geopolitics, international public opinion, and finance.
Tax benefits are collected through the trade war and manufacturing is brought back to China. Section 301 investigations were launched, multiple rounds of tariffs were imposed, and the "poison pill clause" was signed in the "US-Canada-Mexico Free Trade Agreement" to target China.
Using the technology war to curb China's innovative vitality,suppressing high-tech companies such as Huawei and DJI; proposing a clean network plan to cut off ties with China in the fields of operators, app stores, applications, cloud services, and submarine cables; signing an executive order to prohibit any transactions between the United States and TikTok, WeChat, and its parent companies ByteDance and Tencent; and imposing visa restrictions on employees of Chinese technology companies.
Using geopolitical wars to disrupt the peaceful and stable development environment in China and its surrounding areas,passing the "Hong Kong Autonomy Act" to interfere in China's Taiwan affairs and challenge sovereignty and territorial integrity; and imposing sanctions on countries that are relatively friendly to China.
In the field of international organizations and rules,the United States does not recognize China's market economy and developing country status, and unilaterally pressures the WTO to modify international rules.
In the field of international public opinion,it controls the public opinion of Western traditional media and emerging social media, and joins allies to discredit China's international image and discredit China's "Belt and Road" initiative.
In his second term, Trump's domestic goal is still to "repatriate manufacturing" and promote employment, and his foreign policy will continue to be "America First".With the advantage of holding a majority of seats in the Senate and the House of Representatives, Trump can more smoothly implement the large-scale general tariff policy and promote related bills.
Specifically,
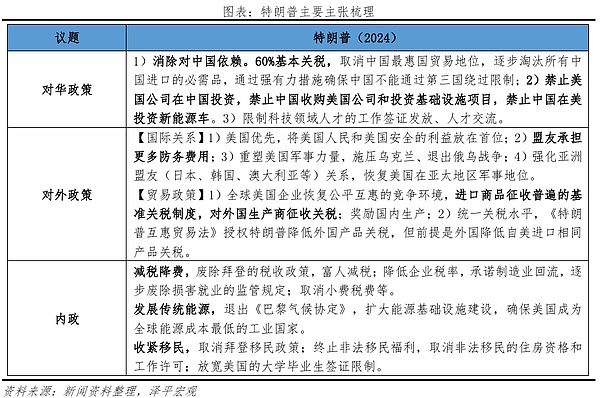
1) At the China level, increase tariffs and strategic decoupling. In the field of trade, a 60% basic tariff will be imposed, China's most-favored-nation trade status will be cancelled, and all necessities imported from China, especially biopharmaceutical products, will be gradually phased out; strong measures will be taken to ensure that China cannot bypass restrictions on exports to the United States through third countries. In the field of investment, American companies are prohibited from investing in China, China is prohibited from acquiring American companies and investing in infrastructure projects, and China is prohibited from investing in new energy vehicles in the United States. In the field of talent, the issuance of work visas and talent exchanges for talents in the field of science and technology will be restricted, and the source of research funds for universities will be investigated. In the field of geopolitics, sovereignty will be interfered with, and relations with Asian allies (Japan, South Korea, Australia, etc.) will be strengthened to restrict China's development. The most fundamental and essential thing is to curb China's rise and maintain US hegemony. 2) In the international trade level, based on "America First", Trump imposed a 10%-20% tariff to force trading partners to reduce tariffs on US products, accelerate the recovery and return of manufacturing, and promote US employment. Including opposing the Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement (TPP); raising tariffs indiscriminately and imposing "basic tariffs" on all countries; further raising tariffs on countries that implement "unfair" trade practices; implementing the "Trump Reciprocal Trade Act" to ensure that American products receive the lowest tariff level in all countries.
3) At the level of international relations and national security, Trump insists on reshaping military power and letting allies bear military expenses; opposes war, and shifts military strategic goals to the Asia-Pacific region, repairs relations with North Korea, maintains relations with Asia-Pacific allies, and has a better attitude towards allies such as Japan, South Korea, and Australia than European allies.
4) At the domestic level, tax cuts and fee reductions, promises to gradually abolish regulatory regulations that harm employment; supports increasing domestic energy production, abolishing Biden's tax policies, and reducing corporate tax rates to reduce inflation. Develop traditional energy, withdraw from the Paris Climate Agreement; expand energy infrastructure construction. Crack down on illegal immigration, implement stricter immigration policies, and cancel illegal immigrant benefits.
4 Containment of China is a consensus between the two parties in the United States. The trade war is expected to heat up. How should China respond?
Since the establishment of diplomatic relations between China and the United States in 1979, Sino-US relations can be divided into three stages: 1) Win-win cooperation (1979-2000): Later, in order to promote China's move towards the Western model, free economy, and gain access to the Chinese market, the United States wooed China and supported China's accession to the WTO. The two parties are generally friendly to China, and engagement with China is a consensus.
2) Competition and Cooperation (2000-2008):China and the United States have both competition and cooperation. In 2000, the Republican Party's platform proposed that "China is a strategic competitor of the United States, not a strategic partner." However, after the 9/11 incident, the United States needed to cooperate with China to fight terrorism, and the United States implemented a "engagement" and "containment" strategy against China. The two parties had differences in their positioning on China during this period. The Republican Party's attitude towards China turned to a mixture of toughness and wooing. The Democratic Party advocated continued engagement with China, believing that the deterioration of Sino-US relations would harm the national security interests of the United States, but also paid attention to China's human rights issues.
3) Strategic Containment (2008-Present):The United States was hit hard by the financial crisis, the gap between the rich and the poor widened, and anti-globalization rose. At the same time, China surpassed Japan to become the world's second largest economy, proposed the "Belt and Road" initiative, and the South China Sea conflict intensified. The United States returned to the Asia-Pacific and implemented the "Asia-Pacific Rebalancing" to comprehensively contain China. The two parties have reached a consensus on China again, that is, to contain China. The United States believes that China is a state capitalist in terms of economy, mercantilism in terms of trade, and neo-expansionism in international relations.
The two parties in the United States have reached a consensus on being tough on China, which has nothing to do with who is elected as the US president. The "National Defense Strategy Report" released by the Trump administration at the end of 2017 has defined my country as a "strategic competitor". Its "U.S. Strategic Approach to the People's Republic of China" released in 2020 further clarified that the nature of Sino-US relations is great power competition and the strategic thinking of containing China. In the future, the existing attitude will continue and new measures to contain China will be continuously introduced. On May 20, 2020, the White House released the "U.S. Strategic Approach to the People's Republic of China", clarifying that the nature of Sino-US relations is great power competition. The Democratic Party platform released on July 21 stressed that "the Democratic Party will take active action against China and any country that attempts to weaken the US manufacturing industry. We will resist China's theft of US intellectual property and demand that China stop its cyber espionage against US companies." "The Democratic Party will work with its allies to mobilize more than half of the world's economies to confront China and negotiate from the strongest position possible." "Democrats' attitude toward China will be guided by the national interests of the United States and the interests of its allies, and will use the openness of American society, the vitality of the economy, and the strength of its alliances to shape international norms that reflect our values." "We believe that Europe is our natural partner in competing with China."
At the beginning of the outbreak of Sino-US trade frictions in 2018, we made three major judgments: "Sino-US trade frictions are long-term and increasingly severe", "This is containment under the banner of trade protectionism", and "Our best response is to promote a new round of reform and opening up with greater determination and courage, and to remain firm. In this regard, we must remain sober, calm and strategically focused."
Faced with strategic containment from the United States, China's best response is to do its best, promote reform and opening up with greater determination and greater strength, and go all out to fight for the economy. The macroeconomic policies of a big country are based on China and serve the domestic economy and employment. As long as the stock market is booming, the real estate market stops falling and stabilizes, the economy recovers, employment improves, people's income grows, and entrepreneurs actively invest, the world will continue to flow into China to support China's economic development. In time, the results will be clear.
 Weatherly
Weatherly










