Article author: Siddhant Kejriwal
Article compilation: Block unicorn
At the beginning of the article, let’s first introduce bits The advantages and disadvantages of the second-layer Bitcoin network so that everyone can better judge the second-layer Bitcoin project.
Advantages
Enhanced scalability: Second The layer solution significantly increases transaction throughput beyond the capabilities of the Bitcoin base layer.
Lower transaction fees: By processing transactions outside the main chain, second-layer networks can significantly reduce transaction costs.
Smart contract functionality: Platforms like Stack and Rootstock introduce smart contracts and DApps, expanding the utility of Bitcoin.
Improved privacy protection: Certain second-layer solutions provide enhanced privacy features for transactions that are not available on Bitcoin's mainnet.
Disadvantages
User complexity: second-layer ecosystem Systems introduce an additional layer of complexity for end users that can hinder adoption.
Security relies on the base layer: While leveraging Bitcoin's security, second-layer solutions may face unique vulnerabilities that do not exist on the mainnet.
Liquidity fragmentation: Liquidity may be fragmented across different second-layer solutions, exacerbating the complexity of trading and other financial activities.
Developer learning curve: The need to understand new protocols, languages, and environments can slow down development and innovation within the ecosystem.
Introduction
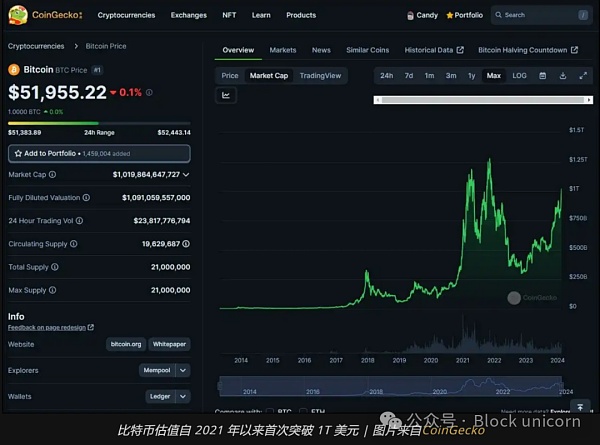
In the crypto space, the Bitcoin network Unique in value, security and decentralization. As of February 2024, this pioneering blockchain has a market value of over a trillion dollars, proving its enduring appeal and robustness.
Bitcoin, often hailed as "digital gold," is the cornerstone of the crypto space and the most sought-after asset. It is appreciated for its properties as a store of value and an “inflation hedge.” Its unparalleled status makes Bitcoin the world’s most-held crypto-asset, a clear indication of its profound impact on investors and the trust it commands.
Bitcoin's widespread adoption has laid the foundation for the success of the Lightning Network, an innovative second-layer solution designed to enable faster and more efficient payments on top of the Bitcoin network.
While the Lightning Network marks a major leap forward, solving some of the scalability issues that have long plagued Bitcoin, it also raises questions about its users and developers A realization among readers: The potential of the Bitcoin network is far from being fully realized. This growing sentiment has paved the way for groundbreaking projects seeking to unlock new capabilities in this ancient blockchain.
One of these transformative developments is Bitcoin Ordinals, which greatly expands the range of possibilities on the Bitcoin network. The Ordinals project showcased Bitcoin’s versatility beyond peer-to-peer payments, igniting a renaissance among developers by enabling unique digital artifacts to be inscribed directly onto Bitcoin’s blocks. Inspired by the secure and immutable nature of the Bitcoin blockchain, these developers are now exploring and building complex smart contracts and second-layer execution environments, promising to further enrich the ecosystem.
This analysis delves into Bitcoin’s burgeoning second-layer innovation beyond what the Lightning Network offers. It aims to shed light on the cutting-edge solutions emerging in the Bitcoin ecosystem. This article highlights how developers can leverage the network's unparalleled security and trust to build smarter, more capable apps. As we embark on this exploration, we'll reveal the groundbreaking efforts that enhanced Bitcoin's utility and solidified its status as a cornerstone of the crypto world.
SegWit and Taproot – Upgrading Bitcoin
Bitcoin’s evolution has been characterized by continued innovation and adaptation, with two landmark upgrades, Segregated Witness (SegWit) and Taproot, playing key roles in its ongoing revolution. These upgrades address some of the most pressing challenges facing the network and set the stage for new development and expansion within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
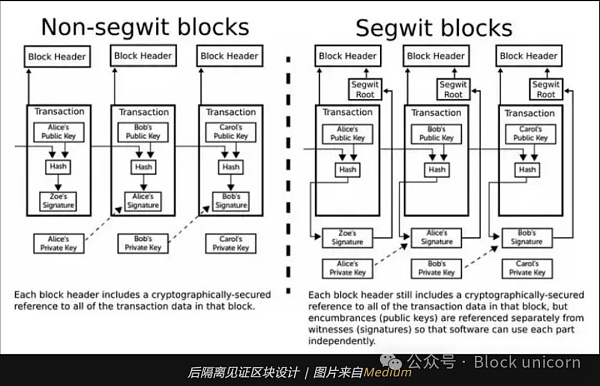
SegWit (Segregated Witness): Improve memory efficiency
SegWit is a groundbreaking upgrade implemented in 2017 to address Bitcoin’s scalability challenges:
Increase block capacity: By separating (or "isolating") digital signatures (i.e. "witnesses") from transaction data, SegWit effectively reduces the size of transactions, allowing more transactions to fit into a single block , without increasing the block size limit. Under optimal conditions, SegWit enables Bitcoin blocks to theoretically support transactions of up to 4 MB.
Solves the problem of transaction tampering: SegWit solves an important security issue, which is to allow transactions in the Issues with modifying transaction details before blockchain confirmation. This improvement improves security and enables the development of second-layer solutions like the Lightning Network, increasing transaction speed and efficiency.
Taproot: Making Bitcoin Smarter
Although SegWit is enhanced Bitcoin’s scalability and security foundation was laid, but the Taproot upgrade, activated in November 2021, brings additional improvements focused on privacy, efficiency, and smart contract functionality:
Schnar Signature: Replacing the ECDSA signature scheme, Schnar Signature allows multiple signatures to be aggregated into one. This merger simplifies and solidifies complex Bitcoin transactions, making them indistinguishable from simple transactions on the blockchain.
Enhanced Privacy and Efficiency: By making multi-signature transactions look the same as regular transactions, Taproot enhances It improves user privacy and optimizes space on the blockchain, resulting in higher transaction throughput and lower fees.
Smart contract function: Taproot facilitates the deployment of more complex and efficient intelligence on the Bitcoin network contracts that enable developers to create innovative applications that leverage Bitcoin’s security and decentralization.
SegWit and Taproot upgrades are more than just technical improvements, they are transformative milestones that significantly expand Bit The currency’s capabilities transcend its original purpose as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system. These upgrades set the stage for the thriving Bitcoin second layer ecosystem that we will explore next.
Bitcoin Ecosystem
Lightning Network is first An important Bitcoin scalability solution that introduces Bitcoin micropayments. It increases the capacity of the Bitcoin network by creating a second layer of payment channels to handle large volumes of off-chain transactions and settle final states on-chain.
While the Lightning Network further enhances Bitcoin’s usefulness as a store of value by making it easier to exchange value on a daily basis, SegWit and Taproot enable the network to go far beyond Capabilities well beyond this initial purpose. The latest Bitcoin scalability solutions take advantage of a property of Bitcoin that has remained largely untapped all these years – its value as the most secure and decentralized distributed ledger.
After the Taproot upgrade, the Bitcoin second layer solution improves the efficiency of Bitcoin and expands the dynamics of its capabilities by introducing the following features:
Programmability:
Scalability: A key innovation in the Bitcoin ecosystem is the creation of a high-throughput network through modular blocks Chain design to improve the scalability of the Bitcoin network, in which the Bitcoin mainnet ensures the finality of applications and transactions executed on the second layer.
NFT: In addition to ordinals, networks built on the Bitcoin network are creating non-fungible token standards and building an NFT ecosystem.
Synthetic Bitcoin: Layer 2 solutions are creating trust-minimized two-way pegs with the Bitcoin mainnet to issue their synthetic versions on Layer 2 , and implement DeFi on Bitcoin.
The evolution of Bitcoin and Ethereum reflects a shared vision for enhanced scalability, security, and efficiency, despite their different technical approaches.
Ethereum’s transition to Ethereum 2.0 and its Rollup-centric roadmap highlights the strategic focus on optimizing the mainnet to become the second A secure and decentralized foundation for layer scaling solutions. Key upgrades, such as Danksharding, are designed to enhance the Ethereum network’s ability to support Rollups, increase throughput, and reduce transaction costs while maintaining the network’s decentralized ethos.
The Bitcoin ecosystem is undergoing a similar evolution, with the emergence of second-layer solutions with smart contract capabilities like Stacks and Liquid Network. These innovations leverage Bitcoin's unparalleled security and decentralization to build efficient virtual machines and application layers that sit on top of the Bitcoin blockchain. Just like Ethereum’s Rollup leverages the strengths of the mainnet to provide scalable solutions, Bitcoin’s second-layer projects leverage the properties of the core blockchain to extend its utility beyond simple transactions.
This trend toward building on the solid foundation of Bitcoin reflects Ethereum’s strategy and underscores the blockchain space’s move toward second-layer solutions. A broad trend, these solutions enhance functionality without sacrificing decentralization and security principles.
The following sections explore the leading scalability solutions in the Bitcoin network,specifically Rootstock, Stacks, and Liquid Network.
Rootstock (RSK)
Rootstock (RSK, the token is RIF) represents a significant advancement in integrating smart contract functionality with the security and broad acceptance of the Bitcoin network. As a sidechain pegged bi-directionally to Bitcoin, RSK enables the deployment of decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts without compromising Bitcoin’s core principles.
This analysis will explore the key features and components of the RSK network, highlighting its unique position in the blockchain ecosystem.
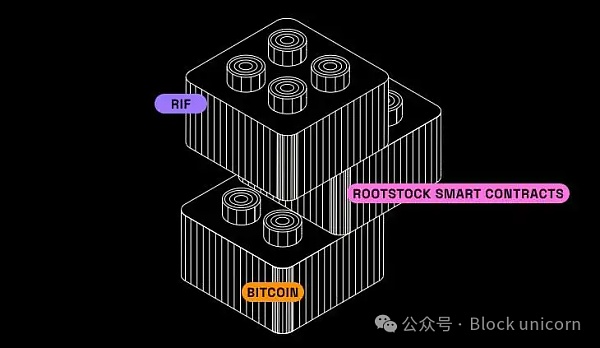
Two-way peg to Bitcoin and RBTC
RSK uses a native cryptocurrency called RBTC, with Bitcoin Bitcoin (BTC) is linked one to one. This peg mechanism is implemented through a bridge, ensuring safe and seamless conversion between BTC and RBTC. Users can also deploy smart contracts and use DApps on the RSK network.
Merge mining with Bitcoin
RSK's The security model leverages Bitcoin’s existing mining infrastructure through merged mining. This method allows Bitcoin miners to mine Bitcoin and RSK blocks simultaneously, using the same computational effort. Merged mining enhances the security of RSK without requiring additional energy consumption and is consistent with Bitcoin’s Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. Miners receive the majority of RSK network transaction fees from the RSK blocks they mine.
RSK Virtual Machine (RVM)
RVM and Ethernet It is fully compatible with Ethereum’s virtual machine (EVM), allowing the execution of Ethereum-designed smart contracts on the RSK network. This compatibility enables developers to deploy their existing Ethereum DApps on RSK, leveraging Bitcoin’s security while benefiting from Ethereum’s smart contract capabilities. RVM handles smart contracts and runs DApps, promoting a rich decentralized application ecosystem.
Decentralized alliance and security measures
The alliance goes further Enhanced security and functionality of RSK. A set of semi-trusted third parties is crucial in managing bidirectional anchoring and providing additional functionality such as oracle messaging and transaction acceleration. This setup contributes to the security of the network.
Scalability Solutions and RIF Services
For To solve the scalability issue, RSK combines off-chain trading solutions and integrates with the Rootstock Infrastructure Framework (RIF) to provide a series of services to enhance user experience and scalability. These services include RIF Storage, RIF Identity and RIF Payments, supporting a variety of applications and use cases in the RSK ecosystem.
Rootstock Ecosystem and DApp
RSK Ecosystem Hosting It hosts a variety of decentralized applications, including Sovryn, a comprehensive DeFi protocol; Money on Chain, which offers crypto-collateralized stablecoins and decentralized staking; Liquality, a cross-chain wallet with built-in exchange capabilities; and Tropykus, a platform for emerging Market-tailored lending agreements with flexible repayment options.
In summary, RSK seamlessly integrates the ultimateness and liquidity of Bitcoin with the versatility and adaptability of Ethereum smart contracts for decentralized applications. The program creates a unique and powerful platform. By leveraging merged mining, two-way pegging with Bitcoin, and compatibility with the EVM, RSK not only enhances the capabilities of the Bitcoin network, but also opens up new avenues for developers and users seeking to interact with the broader blockchain ecosystem. new ways.
Stacks Network
Stacks Network is built on Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions on the blockchain, designed to extend the functionality of Bitcoin by introducing smart contracts and DApps, while leveraging Bitcoin’s unparalleled security and finality.
Here is a comprehensive breakdown of the Stacks network and its features:
Transfer Proof (PoX) consensus protocol
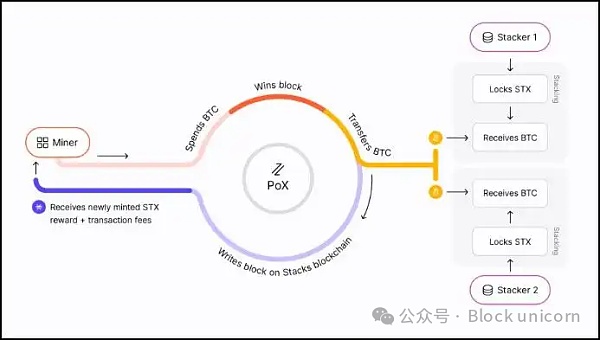
Stacks innovates through its proof-of-transfer consensus mechanism, connecting Stacks and the Bitcoin blockchain. This unique protocol allows for the creation of new Stacks (STX) blocks, with miners earning STX tokens for their efforts. At the same time, STX holders (called “stackers”) can earn Bitcoin by participating in the network’s consensus, thus promoting a symbiotic relationship between the two ecosystems.
Satoshi Hard Fork
Satoshi Nakamoto Named after Bitcoin's anonymous creator, the hard fork represents a major upgrade designed to increase transaction speeds, improve block generation through a tenure-based system, and incorporate Stacks microblock hashes into Bitcoin zones block to enhance the security of Stacks transactions. The upgrade addresses the Micro Extractable Value (MEV) issue and introduces sBTC, a trustless synthetic representation of Bitcoin on Stacks that maintains a 1:1 peg to BTC.
Clarity Smart Contract
Stacks uses the Clarity language for intelligence Contract development emphasizes security and predictability. Clarity is designed to prevent common mistakes and vulnerabilities in smart contract development, making it ideal for developers looking to build on a secure platform.
STX Token

Stacks network’s native token STX plays a key role in the operation of the network, including transaction fees and stacks award. STX’s token economics are closely tied to Bitcoin’s, affecting miners’ commitment to the network.
Stacks Ecosystem
Stacks Ecosystem is vibrant and Diversity, including Bitcoin NFTs, Bitcoin Naming System (BNS), and various DApps such as Boom, Arkadiko, StackingDAO, and Arcane. These applications span DeFi, Yield, Stacks, and NFT platforms, demonstrating the versatility and potential for growth within the Stacks network.
Stacks differentiates itself from other Layer 2 solutions by recording its entire transaction history on the Bitcoin blockchain, claiming the same security and immutability as Bitcoin. Additionally, Stacks is exploring integrating rolling upgrades to enhance scalability and functionality.
In summary, Stacks is a testament to the evolving landscape of blockchain technology, in which the fundamental principles of Bitcoin are expanded to create a more versatile and flexible ecosystem. system. Through its innovative consensus mechanism, smart contract capabilities and ongoing development work, Stacks aims to unleash Bitcoin’s full potential as a platform for decentralized applications and financial instruments.
Liquid Network
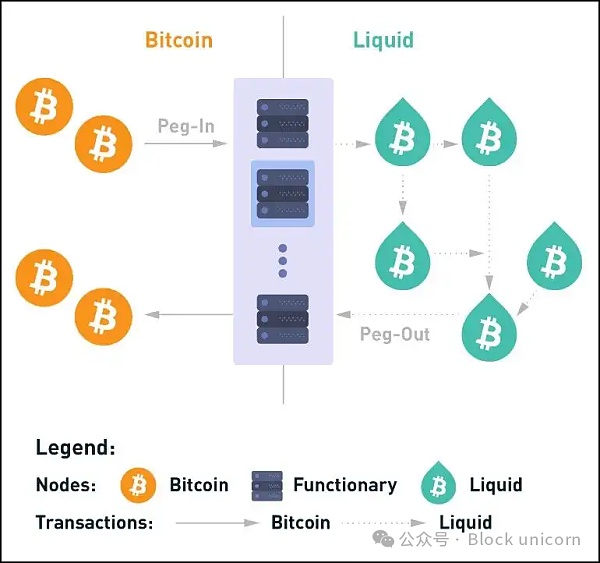
Liquid Network is a Layer 2 solution The program aims to enhance the Bitcoin ecosystem by providing faster, more confidential transactions and enabling the issuance of digital assets. The network operates as a sidechain for Bitcoin and is built on the Elements open source platform, which is based on the Bitcoin codebase. Elements facilitates the creation of independent blockchains or sidechains that can be connected to other Layer 1s and provide features such as confidential transactions, federated two-way pegs, asset issuance, and Schnorr signatures.
Main features and operations of Liquid Network sidechains
Liquid Network supports the seamless transfer of Bitcoin between the Bitcoin network and Liquid Network via a two-way peg, allowing Liquid Network Bitcoin (L-BTC) to be minted on the Liquid Network sidechain. This process is facilitated by a consortium called the Liquid Network Alliance, which consists of large exchanges, financial institutions, and Bitcoin-centric companies around the world, ensuring that there is no single point of failure due to its decentralized nature.
Participant roles in Liquid Network:
District Block Signer: Responsible for generating blocks every minute and ensuring the security and consistency of the Liquid blockchain through a federated consensus model. This model requires a super majority to make decisions, enhancing the security and reliability of the network.
Guardian: This role involves managing the Bitcoin held by the alliance, overseeing the peg-in and peg-out processes between Bitcoin and Liquid Network, and ensuring The integrity of funds moving across the network.
Asset Issuance and Confidential Transactions
Liquid Network has the ability to issue assets and is one of the first to tokenize fiat currencies and Bitcoin. Foreign cryptocurrencies, digital collectibles, and more open up many possibilities. These issued assets are assigned unique identifiers and their transaction details can be kept confidential, providing privacy protection for users on the network.
Benefits and Use Cases
The network is designed to Improve Bitcoin transaction speed and confidentiality. With block times of just one minute and transactions reaching final confirmation quickly, Liquid Network is particularly beneficial for traders and institutions that require fast, private transactions. Issuing digital assets, including stablecoins and security tokens, on the Liquid Network further broadens the scope of Bitcoin’s utility.
Liquid Network introduces features such as confidential transactions and asset issuance without compromising Bitcoin's security premise, allowing a variety of applications, from financial instruments to games assets. A degree of decentralization is ensured through the operation of the Liquid Network Alliance, with alliance members playing a key role in maintaining the integrity and functionality of the network.
Essentially, Liquid Network leverages Bitcoin's robust security model to provide enhanced functionality for digital asset issuance and trading, solving the main problems of Bitcoin in the cryptocurrency ecosystem. specific needs that cannot be met by the chain.
Other Emerging Bitcoin Layer 2 Solutions
While Rootstock, Stacks, Lightning Network, and Liquid are among the most widespread Bitcoin-centric innovations in the ecosystem, many other projects are building numerous scaling solutions, trusted bridges, and innovative Bitcoin layers. Let's list some of the more notable ones:
Babylon
" >Babylon aims to extend Bitcoin to secure a proof-of-stake (PoS) economy. It introduced the Bitcoin Proof-of-Stake protocol, allowing Bitcoin holders to earn income from their idle Bitcoins without having to trust a third party, bridge, or pin their Bitcoins to another chain. This is achieved through a trustless, self-hosted mechanism that gives them the right to validate the PoS chain and earn rewards.
Key features of the Babylon method include:
Trustless Stake Mining: Bitcoin holders can lock their Bitcoins in a self-custodial manner, gaining the right to verify the PoS chain and earn rewards, emphasizing an ecosystem that does not require third-party trust .
Security against PoS attacks: The protocol is designed to provide complete security against PoS attack to ensure the security of mortgage assets.
Quick unlocking and scalable re-staking: these features are designed to provide Bitcoin stakers Maximum liquidity and yield, allowing them to enjoy the benefits of staking without significant downsides.
Ecosystem partnerships: Babylon’s ecosystem includes partnerships with various blockchain projects Partnership designed to enhance Bitcoin’s utility and security in the decentralized economy.
Interlay
Interlay focuses on integrating Bitcoin with decentralized finance (DeFi) on multiple blockchains, providing a comprehensive platform for trading, lending, borrowing, and creating leveraged positions using BTC. The project launches iBTC, a trustless representation of Bitcoin in DeFi, secured by a decentralized network and an insurance mechanism, fitting the description provided.
Key aspects of Interlay include:
Modular approach : Interlay is designed as a modular, programmable layer between Bitcoin and the multi-chain ecosystem, providing novel decentralized use cases for BTC.
Control of private keys: Users maintain control of their private keys when participating in DeFi activities, emphasizing security and user sovereignty.
iBTC: This mechanism allows users to securely lock their BTC, mint iBTC at a 1:1 ratio, and participate in DeFi on various blockchains Activity. iBTC can be exchanged for native BTC on Bitcoin, ensuring trustless interaction.
Security and trustworthiness: Built on cutting-edge, peer-reviewed research and audited by leading companies in blockchain security, Interlay is designed to Providing a high level of security and trustworthiness to its users.
Decentralized governance: Interlay is governed by the community through voting rights of governance (INTR) tokens, allowing stakeholders to participate in decision-making.
Mintlayer
Mintlayer is a software designed to enhance Token interoperability and efficient energy-based blockchain solutions that enable asset transactions and system functions aim to change the status quo of DeFi. It is built on Bitcoin and aims to solve the limitations of current blockchains by providing the following features:
Legalized tokenization: Supports compliant tokenization of assets such as equity and real estate, supports complex token economic models, and does not require native chain tokens as GAS.
Decentralized exchange: improve scalability and security through a unique consensus mechanism, promote Decentralized exchange.
Cost efficiency and throughput: reduce transaction costs and increase throughput through transaction batching and Lightning Network quantity.
Bitcoin compatibility: maintain compatibility with Bitcoin and achieve two-way pegs and cross-region Blockchain transfer.
Enhanced Privacy: Provides enhanced privacy through UTXO structure and optional "Confidential Transaction" mode Privacy features.
Mintlayer's innovative approach aims to leverage Bitcoin's infrastructure to create a more inclusive, efficient and secure DeFi ecosystem to achieve wider financial market applications.
Threshold Network
Threshold Network uses threshold cryptography to protect digital assets and enhance the sovereignty of users on public blockchains. Threshold Network’s key features and functions include:
tBTC: the decentralization of Bitcoin in DeFi A centralized bridge that allows users to deposit and redeem BTC without an intermediary, promoting seamless integration of Bitcoin into the DeFi ecosystem.
TACo plugin: Provides end-to-end decentralized encryption for DApps, managed through independent thresholds Access to node group encrypted data ensures privacy and security.
DAO governance model: The network operates using the DAO governance model, enabling T token holders to Participation in the decision-making process reflects a community-driven approach to network governance.
Security and decentralization: Threshold uses threshold cryptography to distribute operations among independent parties time, enhance security, reduce trust assumptions, and ensure privacy on public blockchains.
The network aims to provide a secure, private and decentralized infrastructure for digital assets, supporting a strong governance Framework that empowers users and token holders.
Drivechain
Drivechain proposes a solution through BIPs 300 and 301 ways to enable Bitcoin to interact with sidechains, enabling new features and applications without compromising the security of the main blockchain. Key points of Drivechain include:
Peer-to-peer Bitcoin sidechain: Drivechain allows for cross-platform integration between Bitcoin and Create, delete and transfer BTC between sidechains, enabling users to opt-in to new features or trade-offs.
Permissionless innovation: It emphasizes that anyone can create new blockchain projects and Allow Bitcoin to adopt any beneficial features of other cryptocurrencies and promote the formation of an innovative environment.
Zero-risk solution: Drivechain is proposed as a zero-risk solution, if needed Easily recover, solving Bitcoin’s major challenges such as scalability and flexibility.
BIPs 300 and 301: These Bitcoin improvement proposals detail the technical mechanisms behind the operation of Drivechain , including "computing power hosting" and "blind merge mining" to promote interaction between side chains.
Drivechain's approach to empowering Bitcoin through sidechains is intended to provide a platform for the development of new applications and features within the Bitcoin ecosystem. A scalable, flexible and secure framework.
Are the second layer networks of Bitcoin and Ethereum equivalent?
Many of the Bitcoin second-layer networks we have discussed share a common proposition—inheriting Bitcoin’s security, finality, and Decentralization. So let’s dive into this statement and critically analyze it, comparing it to prominent second layer architectures on Ethereum.
Ethereum’s second-layer solution and validator interaction
In Ethereum's second-layer solutions, such as optimistic rollups and zk-rollups, validators on the Ethereum network play a key role in ensuring the security and integrity of second-layer transactions. These solutions involve the following mechanisms:
Optimistic Rollup requires validators to challenge fraud during the dispute period Transactions are assumed to be valid unless there is evidence to the contrary.
zk-Rollups uses zero-knowledge proofs, allowing the verifier to verify the data without looking at the complete data. Verify the correctness of transactions, ensuring privacy and scalability while maintaining security.
This model means that Ethereum second-layer solutions directly leverage the security mechanisms of the Ethereum mainnet, including its validators , to ensure the integrity of second-layer transactions. Validators are provided with the necessary data (or proofs, in the case of zk-rollup) to reconstruct the second-layer state and validate transactions, which makes the second-layer security closely tied to the Ethereum mainnet.
Interaction between Bitcoin second-layer solutions and validators
After Taproot, Bitcoin has enhanced its ability to conduct more complex transactions and smart contracts by improving efficiency and privacy. However, Bitcoin’s consensus mechanism and its approach to second-layer solutions, such as using the Stacks protocol, Rootstock (RSK), or Liquid Network, will not essentially change the ability of Bitcoin validators to directly verify second-layer block data. character of.
Bitcoin validators continue to secure the network by validating and confirming transactions in Bitcoin blocks without directly participating in the execution or verification of second-layer transactions. Layer 2 solutions on Bitcoin therefore rely on their own security and consensus mechanisms, although often anchored to the finality and security of the Bitcoin blockchain.
Impact
This difference in operation means , while Ethereum’s second-layer solutions can inherit security directly from the Ethereum mainnet through active validator verification, Bitcoin’s second-layer network may not inherit Bitcoin’s security in the same direct way. They benefit from the finality of transactions resolved by Bitcoin on the mainnet, but rely on their own security protocols for verification within the second layer.
Therefore, Bitcoin's second-layer network may face challenges if the second-layer security mechanism is compromised without direct intervention by Bitcoin validators. Malicious transactions may achieve finality. This requires strong layer 2 specific security measures and may introduce different trust assumptions than Ethereum layer 2 solutions.
However, this does not necessarily weaken the security of Bitcoin's second layer solutions; rather, it highlights the design and Importance of implementation. This also highlights the need for users to understand the specific trust assumptions and security guarantees of any second-layer solution they use, whether on Bitcoin or Ethereum.
Challenges of the Bitcoin Layer 2 Ecosystem
The Bitcoin Layer 2 (L2) ecosystem is at a critical stage of development and faces a series of challenges spanning technical, economic and regulatory domains. Addressing these challenges is critical to fostering growth, adoption, and innovation in this space. Here’s a comprehensive look at nine key barriers, including relevant examples and supporting data:
1. Technical Limitations: Layer 2 Solutions with Ethereum Unlike Bitcoin's second-layer solutions like Stacks and RSK, where validators actively participate in validating second-layer transactions, they rely on independent security mechanisms. This divergence requires a strong independent security model, potentially limiting the possibility of directly inheriting security from the Bitcoin blockchain.
2. Ethereum-centered DeFi: Ethereum’s dominance in the DeFi field is due to the active developers and a large number of DApps. For example, data from DeFi Llama shows that Ethereum’s DeFi platform has billions of dollars of value locked, highlighting Bitcoin’s challenges in attracting similar participation based on DeFi.
3. Launch new liquidity: New Bitcoin second-layer platforms must provide compelling reasons to attract liquidity from the established ecosystem System transfer. Initiatives like liquidity mining on Ethereum have shown that incentives can attract large amounts of capital; a similar strategy may be needed for Bitcoin’s second layer.
4. Developer learning curve: Developers must deal with the complexity of Bitcoin-specific programming languages (e.g., Stacks’ Clarity) and unique consensus mechanisms, which May slow down development and innovation.
5. Interoperability and integration: Like encapsulated tokens such as WBTC on Ethereum, the ability of assets to flow freely between chains highlights interoperability importance. Bitcoin layer 2 solutions must develop or integrate cross-chain communication protocols to facilitate similar functionality.
6. User adoption and experience: The success of platforms like Uniswap demonstrates the value of user-friendly design in attracting non-technical users into the DeFi space. Bitcoin layer 2 solutions must prioritize simplifying user interactions to enhance adoption.
7. Regulatory and security issues: As the global regulatory framework continues to evolve, Bitcoin second-layer projects must remain flexible to comply with diverse legal requirements , while ensuring the highest level of security to prevent hacker attacks and exploitation.
8. Network effects and ecosystem development: Developing a thriving ecosystem is not just about attracting developers and users, it is also about building a community and promoting partners relation. Ethereum’s annual Devcon is a great example of how community participation drives growth in the ecosystem.
9. Scalability and throughput: It is critical to ensure that Bitcoin’s second layer can handle high transaction volumes without degrading performance. Solutions like zk-Rollup on Ethereum demonstrate the potential to increase throughput while maintaining security, a model that Bitcoin’s second layer can learn from.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, including technological innovation, strategic incentives, regulatory navigation and community building. The evolution of Bitcoin’s second-layer ecosystem depends on its ability to adapt and overcome these obstacles, thereby unlocking new possibilities beyond Bitcoin’s original design as a digital currency. As the blockchain space continues to mature, the solutions developed to address these challenges will shape not only the future of Bitcoin’s second layer, but also the broader landscape of decentralized finance and blockchain technology.
Is Bitcoin still considered a commodity?
SEC (U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission) accepting Bitcoin as a commodity and distinguishing it from a security is an important milestone for Bitcoin The regulatory environment brings clarity. This classification is primarily based on the characteristics of Bitcoin as a decentralized digital currency that is primarily designed to serve as a store of value and medium of exchange, without the involvement of a central issuer or the promise of returns, which is typical of securities.
The emergence of second-layer solutions supporting smart contracts on the Bitcoin network brings it closer to the functionality of Ethereum. Therefore, is it possible that Bitcoin’s classification could be challenged? Let’s analyze this idea:
No change to Bitcoin Core consensus
The second-layer solutions discussed above operate on Bitcoin without changing its underlying consensus mechanism. Bitcoin’s primary function as a peer-to-peer transaction network and the role of miners in securing the network remain unchanged.
The architectural separation between Bitcoin and its second layer ensures that the innovation and complexity introduced by the second layer does not affect Bitcoin's consensus.
Regulatory perspective of functions and classifications
From From a regulatory perspective, the classification of an asset as a commodity or security generally depends on its issuance, the expectation of profiting from the efforts of others, and the degree of dispersion. The addition of second-layer functionality does not necessarily imply an expectation of profit or the involvement of a centralized party responsible for the assets, which are important considerations in the classification of securities.
Precedent for other commodities
Revolving around traditional commodities such as The evolution of products and services such as gold or oil adds a dimension of utility or financialization but does not change the basic classification of the underlying commodity. Similarly, the development of second-layer solutions on Bitcoin can be seen as analogies to these enhancements, extending utility but not changing the core characteristics of the commodity.
In summary, although second-layer developments on the Bitcoin network enhance its utility and bring its functionality closer to Ethereum, they do not fundamentally violates the classification of Bitcoin as a commodity. The core principles and functionality of the Bitcoin network remain focused on its role as a digital store of value and medium of exchange, with second-layer solutions acting as complementary enhancements to its fundamental nature, rather than modifying it.
Ending Thoughts
As the Bitcoin ecosystem embraces With new developments, it finds itself at a fascinating crossroads, getting closer to Ethereum in terms of functionality and innovation. While Bitcoin remains unrivaled as a store of value, its technology framework has traditionally lagged behind Ethereum in supporting the complex infrastructure required for DeFi.
On the contrary, although Ethereum is not widely recognized in terms of value storage properties, it dominates the DeFi field and hosts the vast majority of activities and innovations. . This disagreement highlights the unique advantages and trade-offs between the two leading cryptocurrencies. Therefore, the value orientation of each cryptocurrency depends on what investors and users prioritize: the unparalleled security and store of value provided by Bitcoin, or the dynamic and extensive DeFi ecosystem enabled by Ethereum.
As both ecosystems continue to evolve, the interplay between these fundamental characteristics will continue to shape the future of the digital asset space.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance







