Abstract:
Fractal Bitcoin, launched on September 9, 2024, may represent another blind spot between the Eastern and Western crypto markets. Despite capturing a significant portion of Bitcoin’s hashrate within days of its launch, Fractal is still relatively unknown to many in the global crypto community. This study seeks to shed light on this innovative project that is rapidly gaining traction in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Key Points:
Ecosystem Integration: Fractal’s successful integration of key players in the Bitcoin ecosystem, including the BRC-20, Ordinals, and Runes communities, puts Fractal ahead of current Bitcoin trends.
Innovative Mining Approach: Fractal introduces a hybrid mining model that combines merged-mining and free-for-all mining. This model offers a new perspective on PoW, proving that PoW remains a robust approach to network security even as the industry tilts toward PoS.
Pilot Network for Bitcoin: Due to its compatibility with the Bitcoin mainnet, Fractal provides a real-world testing environment for developers, providing valuable user data and activity insights. The activation of OP_CAT on Fractal marks the beginning of many anticipated experiments, solidifying Fractal’s role as a testing ground for potential Bitcoin upgrades and innovations.
Strong User Base from Day One: Through its partnerships with OKX and UniSat, Fractal has successfully attracted Bitcoin’s most active users from day one. This early adoption helps Fractal avoid the “cold start” issues common to new platforms.
Grassroots and community-oriented: Fractal maintains a pragmatic, community-driven strategy that avoids excessive hype and institutional influence. This focus on organic growth and engagement is at its core.
1. Introduction
Fractal Bitcoin is the only Bitcoin scaling solution that uses the Bitcoin Core code itself to recursively scale to an infinite level, built on the world’s most secure and widely held blockchain.
To fully understand Fractal’s innovation, it’s important to understand the historical context of the Bitcoin scaling discussion. In 2017, the Segregated Witness (SegWit) soft fork was designed to increase Bitcoin’s block capacity, followed by the controversial Bitcoin Cash hard fork as an alternative scaling method. Since 2018, more and more attention has turned to second-layer solutions such as the Lightning Network. In this ongoing quest to expand Bitcoin’s scalability and functionality, Fractal stands out as a new approach that offers a unique perspective on these long-term challenges.
As a major milestone, Fractal’s mainnet was officially launched on September 9, 2024 at 00:00 UTC. The launch was a remarkable success, demonstrating the strong traction and technical robustness of the project. In just 24 hours of the mainnet launch, Fractal’s merged mining accounted for more than 40% of Bitcoin’s total hashrate, while free mining on Fractal accounted for 2% of Bitcoin’s hashrate. To put these numbers into context, Fractal’s free mining hashrate is more than three times the total hashrate of Bitcoin Cash (BCH). This rapid adoption by miners shows a high level of confidence in Fractal’s technology and its potential.
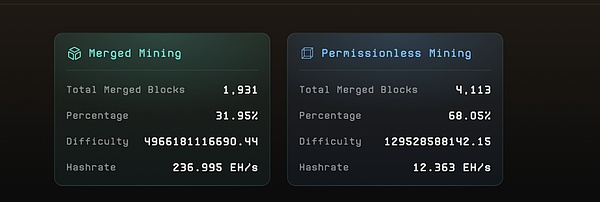
(snapshot taken at 10pm HKT on Sep 10, 2024)
The project has attracted participation from major players in the mining sector. Large mining pools such as F2Pool, Antpool and Spiderpool have already joined Fractal's mining ecosystem. In addition, there are other well-known mining pools ready to participate, which shows that the interest in the Fractal mining network is increasing and has the potential to expand further.
2. Core Concepts and Technologies
2.1 Native Bitcoin Extension
As a native extension of Bitcoin, Fractal's approach distinguishes it from other extension solutions. By leveraging Bitcoin's existing codebase and modifying block production parameters, Fractal maintains full compatibility with the Bitcoin mainnet, ensuring seamless integration with existing infrastructure. This approach achieves feature enhancements without affecting Bitcoin's core security model, striking a balance between innovation and maintaining Bitcoin's fundamental principles.
2.2 Technical Specifications
Fractal introduces several key technical innovations:
Block Time: Fractal achieves a 30-second block time, a significant improvement over Bitcoin's 10-minute block time. This faster block time enables faster transaction confirmation, greatly improving the user experience. In addition, it significantly increases the overall throughput of the network, potentially supporting a wider range of complex applications that require high transaction volumes.
Mining Mechanism: Fractal uses a unique hybrid mining approach. Two out of every three blocks are permissionless mining, and the other is merged-mined with Bitcoin. This innovative mechanism encourages decentralization by allowing individual miners to freely participate in two-thirds of block production. At the same time, it enhances security by leveraging Bitcoin's strong computing power through merged mining of every third block. This balanced approach aims to maintain network security and decentralization, and incentivize existing Bitcoin miners to support the Fractal network.
Scalability: Fractal's architecture theoretically supports unlimited layers of improvements. Each Fractal layer provides a 20x capacity increase relative to the Bitcoin mainnet. This means that the base layer provides 20x the capacity of Bitcoin, and the second layer will provide 400x the capacity. This exponential scalability model allows Fractal to address Bitcoin's throughput limitations while maintaining the security properties of the base layer.
Smart Contract Capabilities: By implementing the OP_CAT opcode, Fractal enables Turing-complete smart contracts on a Bitcoin-based platform. OP_CAT is a simple connect operation that, combined with other opcodes, enables complex smart contract logic. This capability opens up the possibility of advanced DeFi protocols, complex NFT mechanisms, and other decentralized applications that were previously limited to the Ethereum platform.
Parallel Execution: Fractal's architecture allows different applications to run their own instances, so that specific optimizations do not affect the entire network. For example, a gaming platform can run on a specially optimized Fractal layer for high-frequency, low-value transactions, while a DeFi protocol can leverage a separate layer with fine-tuned parameters for financial operations.
Compatibility: Fractal maintains 100% compatibility with Bitcoin standards such as BRC-20 and Ordinals. This ensures that existing Bitcoin tokens and NFTs can operate seamlessly. In addition, users can use the same address between the Bitcoin mainnet and Fractal, simplifying the user experience and reducing the risk of errors in address management.
Lorenzo, founder of UniSat and core contributor of Fractal, outlines his vision in response to community questions.
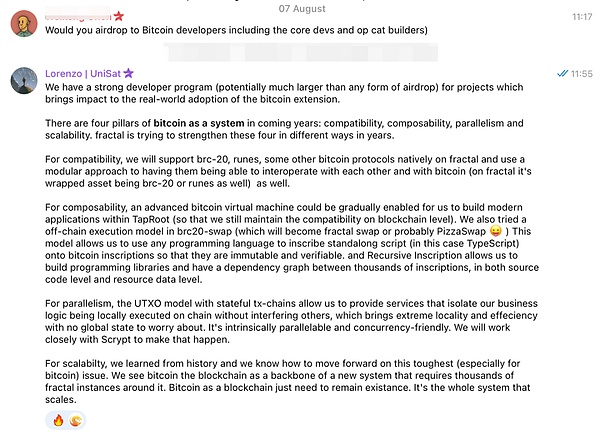
2.3 Unique User Experience
Unlike other Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions, the wallet address on Fractal is exactly the same as the mainnet address. This design provides Ethereum-like convenience, where users can access different layers by simply switching networks in UniSat or OKX wallets. Unlike other Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions that require a separate EVM wallet address, Fractal allows users to continue using Bitcoin mainnet addresses for Layer 2 activities. As of now, major wallets such as OKX Wallet and UniSat Wallet, which serve most active Bitcoin DeFi and collectibles users, fully support Fractal Bitcoin.
3. Fractal's Position in the Bitcoin Ecosystem
3.1 Comparison with Other Bitcoin Solutions
Fractal has entered a highly competitive market for Bitcoin scaling solutions. Here’s how it compares to some of the main alternatives:
EVM-compatible Layer 2: Several projects have attempted to create EVM-based second-layer solutions for Bitcoin. While these solutions are relatively easy to implement and launch, they face significant challenges in terms of acceptance within the Bitcoin community. The Bitcoin ecosystem, especially its core users and developers, often view these EVM-compatible solutions as “stitched together.” In contrast, Fractal takes a Bitcoin-native approach that aims to extend Bitcoin’s capabilities without introducing external architecture. This approach may be more in line with the philosophy of Bitcoin purists and may lead to better integration and adoption within the existing Bitcoin ecosystem.
Bitcoin Cash (BCH): Bitcoin Cash emerged as a hard fork of Bitcoin, designed to improve scalability through a larger block size. This approach led to divisions within the Bitcoin community and forced users to choose between two competing visions of Bitcoin. The BCH fork sparked many political debates that often overshadowed the technical discussions. In contrast, Fractal takes a fundamentally different approach. Rather than creating a separate chain or forcing users to make a choice, it embraces Bitcoin as the mainnet and seeks to natively scale it. Fractal's architecture allows for the creation of multiple instances that scale together, potentially providing unlimited scalability without sacrificing the security or decentralization of the base layer.
Lightning Network: The Lightning Network excels in fast, low-cost payments and high privacy, but its smart contract functionality is limited and it faces channel liquidity issues. In contrast, Fractal provides full smart contract support, does not require channel management, and provides a simpler user experience.
3.2 Market Strategy and Built-in User Base
Fractal stands out in the competitive Layer 2 space, relying not only on technological innovation, but also on strategic market approaches and a strong built-in user base to gain advantages. Backed by UniSat, a leading Bitcoin wallet with approximately 1 million weekly active users, Fractal is able to reach an already engaged audience.
Many UniSat users already hold assets such as BRC20 tokens and Runes in their wallets. These users naturally desire a cheaper, faster, and more feature-rich trading environment. Fractal is able to directly address this need, providing an improved trading experience while maintaining familiarity and compatibility with the Bitcoin ecosystem these users are accustomed to.
This built-in user base gives Fractal a significant advantage over other Layer 2 solutions and new blockchain platforms, which often face the "cold start" problem, i.e. the challenge of attracting an initial user base and building network effects from scratch. By leveraging UniSat's existing user base, Fractal may be able to bypass the barriers to early adoption.
In addition, Fractal's strategy on growth metrics also sets it apart from many other blockchain projects. While many Layer 2 solutions and new blockchains consider Total Value Locked (TVL) as a core metric, Fractal plans to use transaction volume as its North Star metric. This strategy aligns with its built-in user base, which is likely to naturally generate a large number of transactions as they interact with existing assets on a more efficient platform.
By focusing on transaction volume rather than TVL, Fractal is able to demonstrate real usage and adoption, which may be more attractive to users and investors in the long run. This strategy also makes Fractal stand out from many projects that compete on TVL numbers.
4. Ecosystem Building
Fractal's ecosystem development strategy is committed to decentralization and community-driven growth. This section outlines Fractal's strategy for building a strong and diverse ecosystem.
4.1 Decentralization Philosophy
At the core of Fractal’s ecosystem construction is a firm commitment to decentralization. This philosophy is reflected in several key aspects:
Diverse cross-chain bridge solutions: Unlike some Layer 2 solutions that rely on a single official bridge, Fractal encourages multiple cross-chain bridge methods between the mainnet and its network. This approach reduces the risk of single points of failure and promotes innovation in cross-chain interactions.
Open development environment: Fractal does not mandate specific development frameworks or methods, allowing developers to innovate freely within the ecosystem.
Community-driven governance: The direction of the ecosystem is primarily determined by community input and initiatives, rather than unilaterally by a central authority.
Distributed Infrastructure: Fractal promotes distributed infrastructure development and encourages multi-party participation in the construction of key components of the ecosystem.
4.2 Launching Users and Developers
Fractal has implemented a series of strategic plans to launch user and developer participation:
User Reward Program: After the mainnet launch, Fractal distributed 1 million FB tokens to more than 100,000 eligible addresses from OKX wallets and UniSat wallets. This move established a broad base of FB token holders and laid the foundation for increasing participation in Fractal activities.
OKX Wallet Partnership: The successful partnership with OKX Wallet demonstrates Fractal’s ability to work with major players in the cryptocurrency space, significantly expanding its potential user base.
Developer Incentives: Through various grant programs and developer resources, Fractal incentivizes developers to contribute to the growth of the ecosystem.
4.3 Grant Programs and Project Evaluation
Fractal’s grant program is designed to support and incentivize projects that contribute to the growth of the ecosystem and are aligned with the philosophy of decentralization:
Retrospective Model: Fractal adopts a retrospective funding approach, rewarding projects based on their actual impact rather than speculative promises. This model encourages high-quality work and substantial results.
Evaluation Criteria: Projects will be evaluated on their contribution to the ecosystem, technological innovation, alignment with Fractal’s decentralization principles, and potential for long-term impact.
Diverse Project Types: The grant program supports a wide range of projects from core infrastructure development to application layer innovation, ensuring a well-rounded ecosystem.
4.4 Highlighted Funded Projects
Through Fractal’s grant program, several key projects have been supported:
sCrypt: Enhances Fractal’s scripting capabilities to enable complex smart contracts on the Bitcoin network.
F2Pool: Serving as the primary mining pool, contributing to the security of Fractal and providing critical feedback on mining functionality.
Nubit: Developing a data availability (DA) layer to support scalable applications, including Ordinals and Layer 2 solutions.
DeTrading: Supporting cross-chain atomic swaps without central authorities or collateral, simplifying trustless trading on Fractal.
UniWorlds: Creating immersive environments on Fractal, developing community and gaming toolkits for building interoperable virtual worlds.
FractalEcosystem.io: A community-driven directory showcasing Fractal projects, enhancing transparency and discoverability of the ecosystem.
4.5 Future Outlook
Looking ahead, Fractal is poised for continued growth and innovation in the ecosystem:
Expanded Grant Program: The upcoming first quarter post-grant program (September 9 to October 9, 2024) will accelerate ecosystem development.
Community Engagement: Community bounties and the establishment of a community committee, planned for Q4 2024, will deepen community engagement in the direction of the ecosystem.
Potential Use Cases: Fractal’s architecture supports a wide range of future applications, including advanced DeFi protocols, enhanced NFT functionality, enterprise solutions, and decentralized identity systems.
Scalable Infrastructure: As the ecosystem grows, Fractal will continue to support scalable infrastructure development to accommodate growing network activity.
Cross-Chain Interoperability: Future development may focus on enhancing interoperability with other blockchain ecosystems, expanding Fractal’s impact and use.
5. Token Economics and Economic Model
Fractal has designed a comprehensive token economic model that aims to ensure long-term sustainability while maximizing value for the community and investors. This model incentivizes all participants in the ecosystem, from miners to developers, to work together to promote network growth and success.
5.1 Token Details
Name: FB (Fractal Bitcoin)
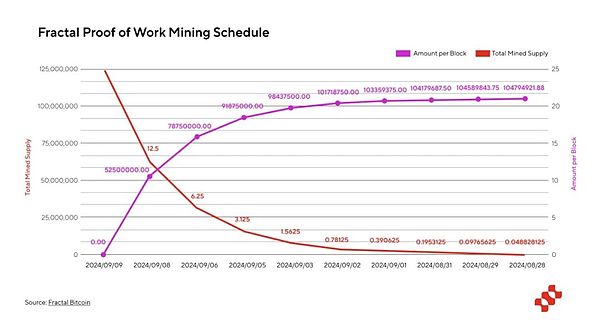
Maximum Supply: 210 million
Total Supply: 105,153,225.00000000
Circulating Supply: 1,213,225.00061300
Main Use: Transaction Fees (within the Fractal Ecosystem)
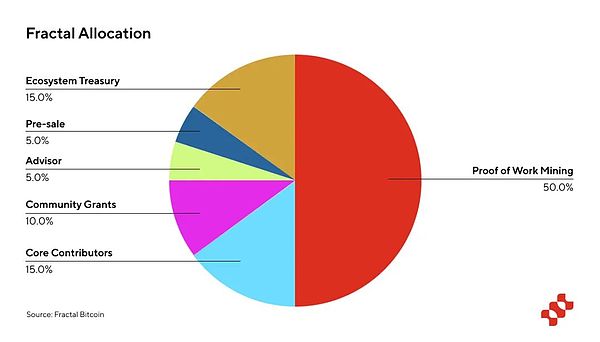
Ecosystem Reserve (15%): This portion is used to invest in the Fractal ecosystem, to support and fund projects that improve the ecosystem, and to fund continued core improvements of Fractal. Up to 10% of this pool can be used each year for 10 years.
Community Rewards (10%): Used to build partnerships and liquidity programs. These community-led initiatives are designed to increase network participation over time. Similar to the Ecosystem Reserve, this pool can be used up to 10% each year for 10 years.
Pre-Sale (5%): This portion is allocated to early investors to cover initial development and operating costs, as well as to conduct security audits. These tokens have a seven-month lockup period, after which they will be linearly released until the end of the twelve-month period.
Advisor Pool (5%): Reserved for current and future advisors who will provide strategic advice and support for Fractal's continued development. A maximum of 20% may be used each year during the year.
Core Contributors (15%): Allocated to those who build and maintain Fractal's core software. These tokens follow the same lockup and release schedule as the pre-sale tokens.
5.3 Release and Lock-up Periods
To ensure long-term commitment and align interests:
Pre-sale and Core Contributor Tokens have a seven-month lock-up period, followed by a linear release until the end of twelve months.
Ecosystem Reserve and Community Reward Tokens have a maximum release rate of 10% per year over 10 years.
Advisor Tokens have a maximum release rate of 20% per year over 5 years.
5.4 Transparency and OP_CAT Governance Voting Mechanism
For full transparency, Fractal has published the official addresses for each token allocation category, which can be tracked when the mainnet goes live. This transparency allows the community to monitor the distribution and use of tokens.
In addition, Fractal encourages all users to participate in the ongoing governance process and contribute to the project development. Proposals may include protocol upgrades, parameter adjustments, and allocation decisions for the ecosystem reserve or community reward funds. This participatory approach is designed to ensure that Fractal is responsive to community needs and adapts to changing market conditions.
The Fractal team plans to adopt an OP_CAT-based governance voting mechanism. This innovative approach will be the first application in the Bitcoin space. By enabling OP_CAT, Fractal token holders will vote on proposals directly within the Fractal ecosystem.
6. Team & Partners
6.1 Core Contributors
Fractal Bitcoin is built by an experienced team in the Bitcoin ecosystem:
UniSat: As a leading Bitcoin wallet with over 900,000 weekly active users, UniSat has extensive experience in cryptocurrency application interface design, implementation and support of Bitcoin standards such as BRC-20 and Ordinals, and secure management of high-value digital assets. Their participation adds credibility to the project and provides a large potential user base for early adoption.
Block Space Force: The co-founders have successfully built and scaled world-class projects such as Coinbase, CoinMarketCap, and Cobo. Their decades of experience in USD A9 exits and 100x investment projects, as well as developing the world’s most used blockchain applications, demonstrates their expertise in scaling blockchain projects from concept to mass adoption, navigating regulatory challenges in the cryptocurrency space, and managing investor relations.
6.2 Developer Platform Partnership
Fractal is backed by the Scrypt team, which is building a smart contract meta-protocol on Bitcoin using OP_CAT. This partnership could bring important synergies, including co-development of advanced smart contract standards, shared security audits, best practices, cross-platform promotion, and ecosystem building.
7. Challenges and Risks
While Fractal proposes innovative ways to extend Bitcoin’s functionality, it also faces challenges that potential investors and users need to consider:
Programmability is the main challenge facing Fractal. Since it is 100% compatible with the Bitcoin mainnet, Fractal is programmed in Bitcoin Script, which may hinder the growth of the ecosystem. To better understand this problem, according to Electric Capital's developer report, Bitcoin has 1,071 monthly active developers, while Ethereum has 7,864 monthly active developers. Bitcoin Script is not as well-known as popular languages such as Rust or Solidity, and is more challenging to use, which may lead to a small number of developers. Fractal's high coding threshold, coupled with the fact that its functionality may not be as good as other blockchains, may slow down the expansion of the ecosystem. Additionally, the relative immaturity of Bitcoin Script development tools, libraries, and frameworks compared to other blockchain environments could further hinder application development and deployment on Fractal.
Technical risks also pose a significant challenge. Modifying Bitcoin’s core parameters and implementing new features such as OP_CAT inherently carries the risk of introducing vulnerabilities or unintended consequences. Managing recursive extensions and multiple layers of complexity adds to the technical challenge.
Adoption risk is another significant challenge. Fractal could face resistance from Bitcoin maximalists who believe that any modification or extension to Bitcoin is unnecessary or potentially harmful. Convincing users and developers to switch to Fractal from established Layer 2 solutions or other blockchain platforms could be difficult, especially given the network effects of these incumbents. Additionally, despite Fractal’s compatibility, the Runes, Ordinals, and BRC-20 communities may be reluctant to adopt the same standards. These communities have already established their own ecosystems and may not see enough incentive to migrate or expand to a new platform, even if it offers better performance. Fractal will need to clearly articulate its value proposition and potentially offer significant incentives to drive early adoption among these user groups. The challenge will be not only in delivering a technical advantage, but also in overcoming the inertia of established communities and their existing investments in current platforms.
To address these challenges, particularly the programmability issue, Fractal will likely need to invest significantly in developer education, create robust development tooling, and potentially explore ways to make the development process more accessible without compromising its integration with Bitcoin Core.
8. Conclusion
Fractal Bitcoin represents a groundbreaking approach to extending Bitcoin functionality. As the only Bitcoin scaling solution that leverages the Bitcoin Core code itself to recursively scale to unlimited layers, Fractal offers a unique value proposition in the competitive market for Layer 2 solutions.
Fractal's key advantages include:
Native Bitcoin Integration: Fractal maintains full compatibility with the Bitcoin mainnet, enabling seamless integration with existing infrastructure while enhancing its functionality.
Technical Innovation: With a 30-second block time, a hybrid mining method, and support for OP_CAT, Fractal significantly improves transaction speeds and enables complex smart contracts on Bitcoin-based platforms.
Built-in User Base: Fractal has a significant advantage in overcoming the "cold start" problem. With the support of UniSat wallet, Fractal has a solid foundation of over 1 million weekly active users, and through the Fractal mainnet launch program, 100,000 active addresses hold FB tokens, which are the most engaged users in the Bitcoin ecosystem. In addition, the full integration of OKX wallet further expands Fractal's potential user base in the OKX ecosystem.
Strong Mining and Network Security: Obtain 30-40% of Bitcoin hashrate through joint mining and 1-2% of Bitcoin hashrate through free mining.
Ecosystem Development: Through strategic funding programs and community initiatives, Fractal is actively cultivating a diverse ecosystem covering DeFi, gaming, and core infrastructure development.
Unique User Experience: Fractal’s approach allows users to use the same address between Bitcoin mainnet and Fractal, providing an Ethereum-like network switching experience.
Team with a Long-Term Vision: Fractal’s core contributors have been building in the Bitcoin and crypto industry since 2013, which has helped the team adopt a longer-term industry perspective and bring Fractal to a wider audience.
However, Fractal also faces some significant challenges:
Programmability: Bitcoin Script may pose a barrier to developers more familiar with Solidity or Rust.
Technical Risks: There are inherent risks in modifying Bitcoin’s core parameters and implementing new features such as OP_CAT.
Adoption Barriers: Convincing users and developers to switch from established solutions to Fractal may be challenging.
Despite the challenges, Fractal’s innovative approach, strong support, and early mining adoption show great potential. The project’s success in attracting major mining pools and rapidly growing hashrate after launch are particularly encouraging signs.
As the ecosystem continues to grow, Fractal is positioning itself as an innovative Bitcoin application platform for a variety of sectors, potentially reshaping Bitcoin’s utility and adoption landscape. The planned implementation of an OP_CAT-based governance voting mechanism further demonstrates Fractal’s commitment to innovation within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
While the road ahead is filled with opportunities and challenges, Fractal Bitcoin represents a bold step forward in Bitcoin's scaling journey. Its success could profoundly impact the future of Bitcoin and the blockchain ecosystem. As with any emerging technology, potential investors and users should carefully weigh the project's potential against its risks and closely monitor its technological development, ecosystem growth, and market adoption.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance







