Author: Glassnode, Marcin Miłosierny; Translator: Tao Zhu, Golden Finance
Summary:
Monthly Overview: In April, despite high trading volumes at the beginning of the month and large ETF inflows, Bitcoin remained under consolidation pressure, with prices ranging between $60,000 and $66,700, mainly due to short-term holders selling. At the same time, Ethereum's ecosystem has sparked a heated debate over changes in staking rules, highlighting concerns about its future as a scalable platform and monetary asset.
Market Momentum: Currently, Glassnode's composite momentum index suggests that the market is cooling down. Several key indicators have entered a downward trend phase, indicating reduced demand and slowing positive momentum.
Indicator Focus:Miner Revenue Momentum uses the proportion of miner fee revenue to assess block space demand and highlights key inflection points via a 2-year rolling Z-score. High Z-scores indicate increased network activity and congestion, while low Z-scores indicate reduced demand and a potential market cooling.
Investor behavior in digital asset markets in April 2024 appears to be driven by two main emotions: anticipation for Bitcoin’s fourth halving and disappointment with the ensuing lackluster price action. While halvings have historically proven to be long-term bullish events, in the short term they tend to trigger a sell-off news reaction in the market.
For example, while Bitcoin supply reductions have long-term bullish implications, similar events in 2016 and 2020 also led to immediate market corrections. This year, macroeconomic uncertainty and geopolitical tensions have compounded the impact, causing the price of Bitcoin to fall by 16.09% in the weeks following the halving.
Similarly, Ethereum has also experienced significant volatility, with its price falling by 17.80%, in part due to ongoing uncertainty related to the United States. Watch for approval of an Ethereum ETF and debate within the community over proposed staking policy changes.
This reaction exemplifies the sensitivity of the broader market to major anticipated events, with traders often taking profits leading to a short-term sell-off. In our extensive coverage of the halving and its expected impact, we correctly anticipated that such a sell-off would occur.
In this issue of Financial Bridge, we explore the ongoing impact of the United States. Spot ETFs significantly supported trading volumes in April, even amid a broader market correction. We will also provide an update on factors that may affect Ethereum’s monetary characteristics and its technical suitability for the DeFi space.
Monthly Market Overview
Bitcoin continued its strong performance in the first few weeks of April, supported by a surge in spot trading and on-chain trading volumes. Following a peak in mid-March when spot trading volumes reached approximately $14.1 billion, the Bitcoin price consolidated between $64,000 and $73,000. This price level was primarily driven by US spot ETFs, which have become a significant force in the market, introducing a large amount of new demand and helping to maintain price levels above historical highs.
Daily spot trading volumes, while reduced from the peak in mid-March to approximately $7 billion per day, still reflect the strength of the 2020-2021 bull run. The strong trading volume highlights the continued optimism in the market, characterized by a net buy bias in the cumulative volume delta (CVD). The indicator measures the net amount of buying versus selling, highlighting the continued speculative interest and the prevailing bullish sentiment among traders.
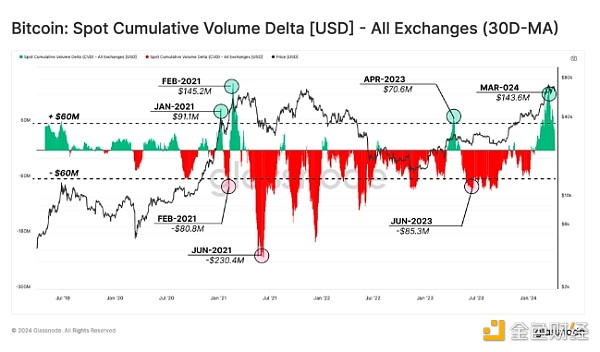
In addition, trading flows (both inflows and outflows) were very high, averaging $8.19 billion per day, significantly exceeding the peak levels observed during the previous bull run. While Binance still has a sizable market share (37.5%) in spot trading, its dominance has declined from higher levels seen in previous years, suggesting that market activity is expanding across platforms. In mid-April, Bitcoin underwent its fourth halving event, reducing daily supply inflation by 50% and annual issuance to 0.85%. The reduction reinforced Bitcoin’s hard currency status and marked the first time Bitcoin surpassed gold in terms of issuance scarcity.
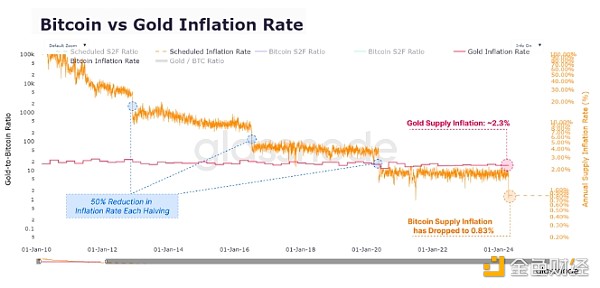
At the same time, the reduction in issuance did not have a significant impact on market dynamics, as newly mined tokens accounted for only a small proportion compared to global trading volume. Spot and derivatives trading volumes continued to dominate the market, with new supply accounting for less than 0.1% of total capital flows.
On the other hand, Bitcoin reached new milestones in several important metrics. The fundamentals of the network show significant trends across a variety of metrics. The network hashrate has reached an all-time high as miners invest in efficient hardware and optimize operating costs, ensuring that the reduction in issuance does not impact the security budget. This investment shows that the subsidy reduction is not an obstacle for miners.
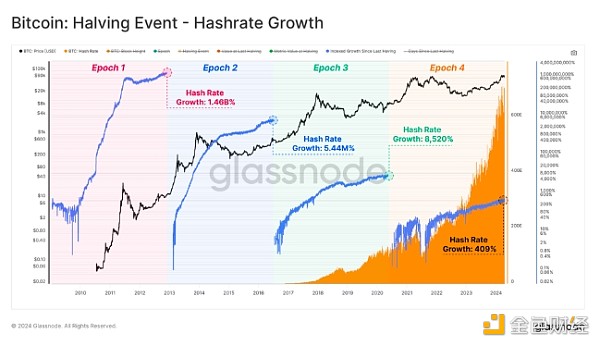
While the growth rate of network statistics has declined due to the expansion of the ecosystem, the absolute values of these metrics have hit new highs. In particular, over the past four years, as much as $106 trillion in value has been transferred and settled through the Bitcoin network. This impressive figure highlights Bitcoin’s ability to maintain its position as the primary settlement network regardless of volatility and periodic pullbacks.
Dealing with Market Corrections
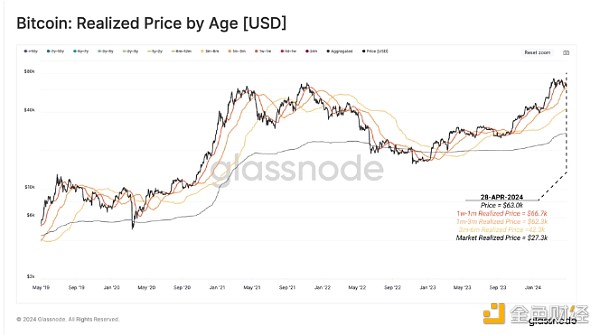
In the last week of April, Bitcoin markets entered a consolidation phase following the halving event. Following the March peak of $73,000, prices ranged between $60,000 and $66,700. During this period, sell-side pressure intensified as short-term holders (STHs), particularly those who purchased BTC in the past 1-6 months, dominated market losses.
Despite the increased selling pressure, the Net Unrealized Profit and Loss (NUPL) indicator suggests that the market is still in the “excitement” phase of the bull run. However, the indicator has also shown a meaningful cooling since the correction began. Selling pressure from STHs that have realized significant losses becomes a key indicator of local market lows.
We can observe that the cost basis of STHs that bought BTC in the past 1 week to 1 month is a key indicator of market sentiment. Their realized losses tend to peak near local market bottoms, which suggests that exhaustion of sellers in this group often signals an impending reversal.
Ethereum Development and Controversy
In April, the Ethereum ecosystem found itself at the center of a heated debate surrounding changes to the network’s staking policy. New innovations such as liquidity staking, re-staking, and liquidity re-staking protocols have greatly increased the demand for staking on Ethereum, leading to unprecedented growth in staking participation.Currently, over 31.4 million ETH (about 26% of the total supply) has been staked, driven primarily by re-staking protocols such as EigenLayer and liquidity re-staking providers. These developments have brought additional yield opportunities, creating incentives that extend beyond the original proof-of-stake vision.
Proposals to cap annual issuance to slow the expansion of staking pools have been met with strong resistance from the community. Supporters argue that such measures are necessary to preserve Ethereum’s monetary role and prevent derivative tokens from gaining too much influence on the network. Opponents, however, see these limits as a barrier to innovation and argue that no change is needed. These debates will continue as stakeholders work to balance Ethereum’s monetary policy with the growing demands of decentralized finance.
At the same time, there remain concerns that the rapid growth of staking could undermine Ethereum’s functionality as a monetary asset and shift governance power toward derivative projects that issue staking tokens. The future of Ethereum’s staking landscape remains uncertain as the community needs to perform this delicate balancing act to protect network scalability and its functionality as a store of value.
Market Momentum – Update and Key Insights from the On-Chain Momentum Framework
Tracking market momentum during bull markets requires detailed analysis of key on-chain data to capture underlying trends and changes in market behavior. Glassnode’s exploratory framework offers a potential approach to this dilemma by focusing on four main categories:
On-Chain Activity:This metric uses network activity and adoption rates to identify periods of growth and expansion in the user base. Increases in network activity often correlate with rising market momentum.
Market Profitability:By assessing the unrealized profits held by investors, this metric identifies periods when market participants are earning gains, which can indicate a healthy and upward-trending market.
Spending Behavior:This category identifies periods when there is enough demand to absorb profit-taking by existing holders. High demand during these periods indicates continued positive momentum.
Wealth Distribution:By examining the transfer of wealth between long-term holders and new market entrants, this indicator provides insights into market cycles and potential turning points.
By combining these indicators into a composite index, analysts can more fully assess the strength and direction of market momentum. This approach allows traders to make informed decisions based on a granular understanding of the market's current state and potential future moves.
Currently, less than 4 of the 8 conditions for strong momentum are met, suggesting a market cooling-off period.
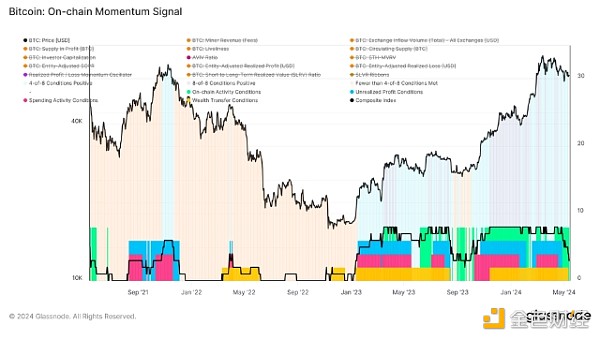
After the Bitcoin halving event in April 2024, several key indicators have changed significantly compared to previous trends, reflecting a possible short-term shift in market dynamics:
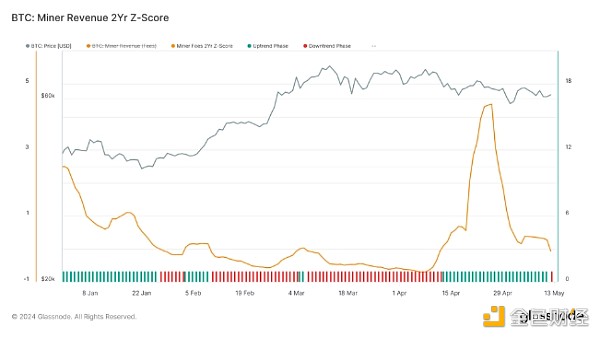
Miner Revenue 2-Year Z-Score:After the halving, miner revenue surged significantly as competition for block space increased, especially for transactions involving runes. Although this growth has slowed slightly, revenue levels are still above historical norms. However, Recently, the 2-year Z-score of miner revenue entered a downward trend phase for the first time in a month, indicating a reduction in demand for block space.
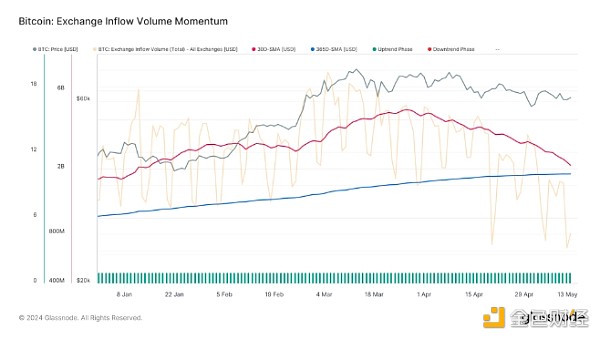
Exchange Inflows: Exchange inflows initially remained above the annual average, peaking in late March, and have since entered a sustained downward trend. This shift suggests that the positive momentum of capital inflows into the market is slowing down and may reverse soon, indicating that buying pressure is cooling down.
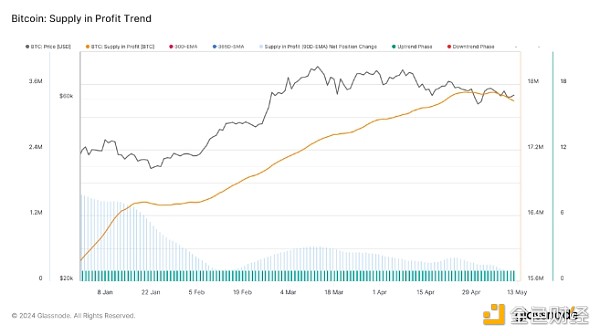
Profit Supply Trend: While still showing a positive trend, the profit supply has started to show signs of a reversal, both in absolute terms and at the 90-day EMA. While still in an uptrend, the indicator suggests that fewer holders are in profit, which could affect market sentiment.
MVRV Momentum: The overall market value to realized value (MVRV) momentum remains above its annual average, indicating that, on average, holdings are still valued above their cost basis. However, the short-term holder MVRV has reversed and is now trending down, which suggests that those who recently entered the market are starting to see profits take off, which could increase selling pressure.
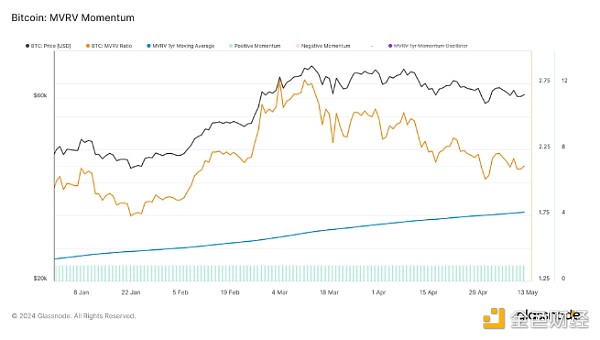
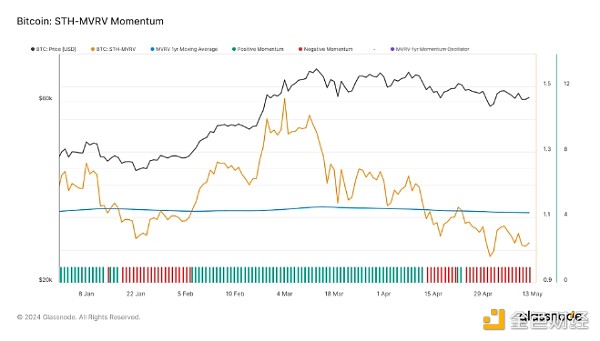
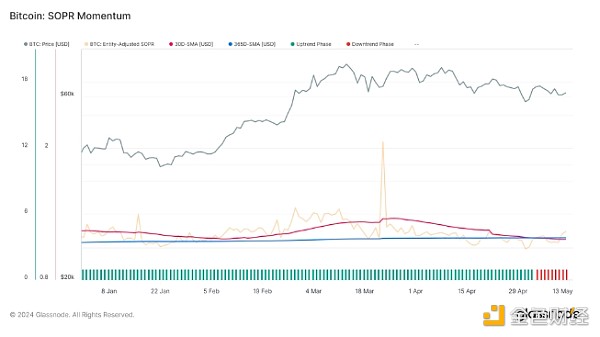
SOPR Momentum: Expenditure Output Profit Ratio (SOPR) Momentum is also trending downward, with the monthly average recently falling below the yearly average. This trend is not yet strong, but suggests that profitability of trading tokens is decreasing, which could lead to more cautious spending behavior among traders.
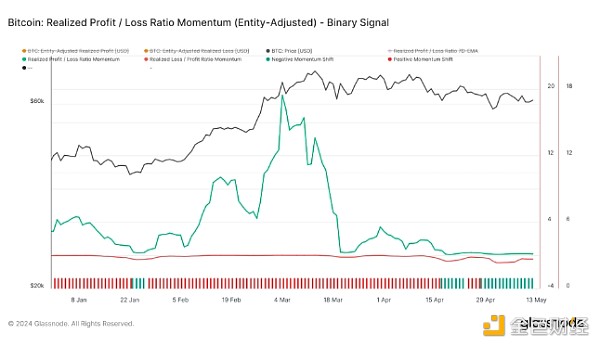
Conclusion and Actionable Insights for Momentum Traders
Current market indicators suggest that Bitcoin is going through a consolidation and potential correction phase. Given that key indicators such as exchange inflows, SOPR momentum, and short-term holder MVRV suggest a slowdown in positive momentum and increasing selling pressure, traders should remain cautious. The change in miner revenue and cooling SOPR momentum further suggest that demand for Bitcoin at higher price levels may be waning.
It is critical for momentum traders to closely monitor these downward trends. The potential for a reversal in indicators such as SOPR and profit feed could provide strategic entry points if signs of recovery or stabilization emerge. However, mounting realized losses highlight the need to remain vigilant against potential panic selling.
Indicator Focus – Miner Revenue Momentum
In our analysis of market momentum trends, we highlighted Miner Revenue Momentum. This metric measures blockspace demand using the proportion of revenue miners earn from fees. Fee pressure increases when users show a higher urgency and are willing to pay higher fees to be included in the next block. By applying a 2-year rolling Z-score to this data, we can normalize the dataset across cycles and spot inflection points, such as rising fees during a bear market waning or falling fees after a cycle peak.
By examining miner revenue momentum, analysts can gauge the intensity of network activity and its impact on miner behavior. High Z-scores indicate above-average miner revenue, often coinciding with rising transaction fees and increased network congestion. Conversely, falling Z-scores indicate a decreasing demand for blockspace, which could indicate a cooling market or reduced trading activity.
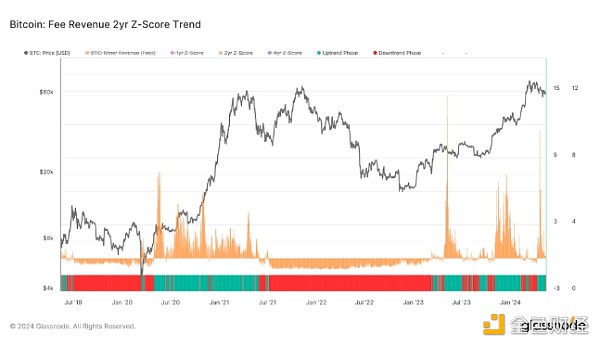
Look for Trends:Increasing miner revenues typically correspond to bullish market phases, as high demand for block space typically reflects increased transaction activity and network utilization. Conversely, declining miner revenue momentum can indicate waning interest and potential market consolidation.
Historical Examples:In the days following the April 2024 halving, miner revenue momentum spiked significantly amid intense competition for block space. Similar spikes have been observed during previous halvings and major network events, an indicator of strong market activity. The current downward trend of the Z score marks a turnaround from this peak, suggesting that speculative enthusiasm may be easing.
Indicator changes: Miner fee income percentage, miner fee Z score functional area income, miner capitulation risk.
 Edmund
Edmund



















