Author: Aimen Noor, CoinTelegraph; Compiler: Deng Tong, Golden Finance
1. Interpretation of Ethereum Burn Address
The Ethereum burn address is a unique element in the Ethereum blockchain that is specifically designed to permanently delete Ethereum from circulation.
The Ethereum burn address is represented by the address 0x00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000. The basic concept behind the burn address is the intentional destruction of tokens.
A key feature of a burn address is that there is no corresponding private key. Since private keys are required to control a cryptocurrency wallet, this deliberate omission ensures that any Ethereum (ETH) sent to the burn address is irretrievably lost. There is no mechanism to recover or reuse these burned tokens.
Ethereum burn addresses play a key role in managing the overall supply of ETH. By reducing the circulating supply, burning tokens creates potential deflationary pressure and affects the value dynamics of cryptocurrencies. This process helps maintain the health and long-term stability of the Ethereum network.
How Ethereum burn addresses work
Ethereum burn addresses work similarly to regular addresses, but lack private keys, making any tokens sent there inaccessible and permanently removed from circulation.
The mechanism of an Ethereum burn address is deceptively simple. It functions similarly to any other Ethereum address, but without an associated private key. When ETH or compatible ERC-20 tokens are sent to this address, they essentially enter a digital void, leaving the circulating supply forever.
The lack of a private key is key to the functionality of a burn address. In the world of cryptocurrency, private keys grant control over a wallet and its assets. Without a private key linked to the burn address, any tokens transferred there will be permanently inaccessible, ensuring the irreversibility of the burning process.
To "burn" ETH, a user or smart contract initiates a transaction and specifies the burn address (0x00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000) as the recipient. Once the transaction is confirmed on the Ethereum blockchain, the transferred ETH is effectively removed from circulation, thereby achieving the purpose of reducing supply.
Three, the economic impact of ETH burning
ETH burning creates deflationary pressure, which has the potential to increase the value of ETH and help stabilize transaction fees.
The ETH burning mechanism has a significant economic impact on the Ethereum ecosystem. Burning will permanently remove ETH from circulation, thereby introducing deflationary pressure. If the burn rate exceeds the rate at which new ETH is issued (through mining or staking rewards), the overall supply of ETH will decrease over time. Based on the principles of supply and demand, this potential scarcity can have a positive impact on the price of ETH.
Another economic impact lies in how ETH burning affects transaction fees. With the implementation of EIP-1559, a portion of each Ethereum transaction fee will be burned. This mechanism helps stabilize gas fees (transaction costs) and makes it more predictable for users. In addition, the reduction in ETH supply caused by burning may incentivize validators to prioritize transactions with higher fees, which may help with faster confirmation.
However, it is worth noting that the long-term economic consequences of burning ETH are still subject to market forces and the continuous development of the Ethereum network. The deflationary nature of burning may make ETH a more attractive means of storing value, while others warn that this is just one factor in a complex economic system. Ultimately, the interaction between ETH burning, network usage, and broader market dynamics will shape its overall economic impact.
IV. Example of ETH destruction mechanism
Ethereum utilizes ETH destruction mechanisms, including the basic fee destruction of EIP-1559 and the buyback and destruction of specific projects.
Multiple mechanisms within the Ethereum ecosystem facilitate the burning of ETH. One of the most important is the base fee burning introduced by EIP-1559. This upgrade fundamentally changes Ethereum's fee structure, requiring a portion of each transaction fee (the base fee) to be permanently burned. This mechanism has a continuous deflationary effect on the supply of ETH.
In addition to EIP-1559, individual projects built on Ethereum can implement their own destruction mechanisms. For example, some tokens adopt a buyback and burn model, where the project uses revenue to buy back its tokens from the market and then sends them to a burn address. This can help regulate the token supply and potentially support its price.
Some blockchain projects also utilize Proof of Burn (PoB) as an alternative consensus mechanism, where network participants burn tokens to gain the right to create new blocks. It involves sending tokens to an unusable address, often called a "black hole" address. In addition, some projects may burn tokens to introduce scarcity or implement a deflationary token economic model.
V. How to view the burned address
To view the Ethereum burning address, use a blockchain browser such as Etherscan and search for the address. This will display its balance and history of burned tokens.
Etherscan is widely considered the go-to browser for the Ethereum network. To get started, simply open your favorite web browser and navigate to the Etherscan website. Once there, find the search bar, which is usually prominently displayed near the top or center of the page. Carefully enter the burn address (0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000) into the search bar and initiate a search.
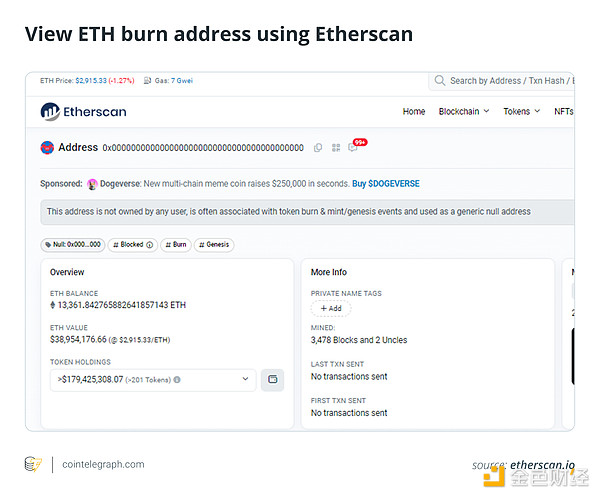
Etherscan will display a page dedicated to the burn address. On this page, you can view your ETH balance, which is always zero, since no ETH can reside in a burn address. It also shows a list of all transactions that sent ETH or compatible tokens to that address for burn.
Some browsers may offer additional tabs or sections, such as a token tracker (showing historical data about burned tokens) or even an analytics chart that visualizes burn activity over a selected time period.
Six, potential future developments related to ETH burn
ETH burns may increase deflationary pressure on supply, enhance the predictability of fee markets, and promote innovative projects that incorporate unique burn mechanisms.
The ETH burn mechanism may drive some exciting developments within the Ethereum ecosystem. One key area is the potential for increased deflationary pressure. If the rate of ETH burns continues to exceed the rate of ETH issuance (through mining or staking rewards), the overall supply of ETH will continue to decrease. This increasing scarcity may further enhance the value proposition of ETH, especially as the network becomes more widely adopted.
Another potential development is related to the evolution of the Ethereum fee market. The base fee burn mechanism introduced by EIP-1559 already helps improve the predictability of transaction costs. Future adjustments or upgrades may further optimize fee dynamics, perhaps including additional burn components or modifications to how the base fee is determined.
In addition, innovative projects and protocols may also incorporate unique ETH burn mechanisms in their token economic models. These may range from changes in buyback and burn models to novel use cases in decentralized finance protocols or non-fungible tokens. As the Ethereum ecosystem matures, the potential applications of ETH burns may expand.
 Dante
Dante
 Dante
Dante WenJun
WenJun JinseFinance
JinseFinance Xu Lin
Xu Lin Huang Bo
Huang Bo Alex
Alex Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph