Author: Bixin Ventures
Introduction
As an early holder and staunch supporter of BTC, Bixin Ventures has always been committed to the BTC ecosystem. We believe that BTC assets should play a greater role in excellent DeFi protocols on various chains and gain more benefits. Therefore, an efficient cross-chain bridge is necessary, so we invested in DLC.link early last year.
With the rise of inscription assets and the expansion of the Bitcoin data flow network, Bitcoin applications are increasing. Faced with its limited native smart contract functionality, Bixin Ventures views DLC.Link as an innovative solution. After the collapse of FTX, the market is in dire need of safe, decentralized alternatives to Bitcoin. DLC.Link is consistent with our vision and is committed to building a secure, trustless ecosystem and promoting the application of Bitcoin in various scenarios.
DLC.Link technology analysis
How to use DLC technology in Taproot upgrade Schnorr Signatures
Bitcoin’s Taproot upgrade introduced Schnorr signatures, a more secure alternative to ECDSA for creating and Verify key. Schnorr signatures have linear properties and can effectively verify multiple transactions at once by combining public keys and signatures [1]. The Discreet Logging Contract (DLC) takes full advantage of the Schnorr and PTLC technologies already implemented in Tarproot. Because these two technologies are already native features of the Bitcoin network, there is no need to rely on L2 or sidechains when using DLC. On the contrary, DLC technology is protected by the computing power of the entire Bitcoin network, making it more secure and reliable.
In scenarios where DLC technology is used for lending, we usually use Schnorr signatures to handle conditional results. In this process, both parties each generate a unique key, combine it with their respective long-term keys to form a "public key", and prepare signatures corresponding to each potential outcome in advance, such as repayment or liquidation. Next, a decentralized network of witnesses confirms real-world results through discreet log numbers, unlocking pre-prepared signatures to trigger contract execution on the blockchain [2]. This demonstrates the universality, flexibility and safety of DLC technology in practical applications.
How DLC technology secures Bitcoin on-chain without validators
The Discreet Log Contract (DLC) no longer requires external verifiers, but directly inherits the security of Bitcoin to ensure on-chain security [2]. In the DLC.Link architecture, the witness network is an innovative design. As witnesses of off-chain services, they actively monitor the blockchain through smart contracts and publicly announce DLC events in JSON format. After getting the corresponding result from the data source (a smart contract on another blockchain), the witness certifies and signs it. To enhance security, DLC.Link adopts 5-of-7 witness multi-signature, which reduces the risk of collusion between witnesses and one party to the contract. The DLC.Link management contract will randomly select untrustworthy witnesses from the whitelist [3]. The design also allows third parties and organizations to run witness nodes, thereby further promoting decentralization. The decentralized witness network avoids single points of failure and effectively facilitates DLC creation and signature requests. This comprehensive design not only protects the integrity, security and flexibility of Bitcoin transactions, but also proves that DLC.Link is the ideal infrastructure for integrating BTC with decentralized finance (DeFi).
How FROST signatures advance the security of DLC technology
DLC.Link also integrates FROST (Flexible Round-Optimized Schnorr Threshold Signatures) to improve security and simplify witness management. FROST's key re-sharing function gives the witness network dynamic management capabilities, allowing participants to quickly adjust without affecting the integrity of the service [4]. When setting up or changing witnesses, the system uses a collaborative approach to generate keys. The entire process creates both a shared key and an individual key for each Attestor. The flexibility of this key generation mechanism ensures that the witness network can be safely modified later without disrupting service.
When a blockchain event triggers the creation of a DLC contract, the coordinator among the witnesses broadcasts the create-dlc command, thereby generating a consensus-backed DLC announcement. Likewise, when it comes to closing a DLC, a blockchain event prompts the coordinator to arrange for the creation of a final witness of the DLC, where the signature of each witness ensures the security and verifiable closure of the contract. This advanced upgrade introduces the ability to dynamically adjust the witness network and significantly reduces computational complexity while maintaining strict security standards.
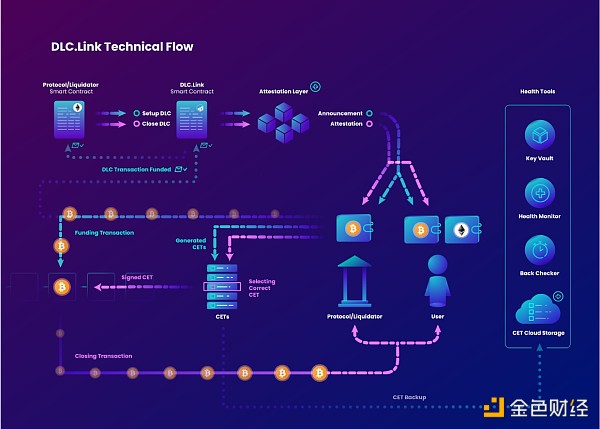
Figure 1. DLC.Link Technical Process
DLC.Link’s product introduction
dlcBTC
DlcBTC will launch in early 2024 and will be at the forefront of decentralized finance (DeFi), offering custody-free Bitcoin on the Ethereum network through discreet logging contracts (DLCs). Using dlcBTC, users can "self-encapsulate" their deposits, with the BTC locked by themselves and the locking mechanism protected by the authenticator. dlcBTC depositors do not send BTC to DLC.Link or any third party.
In this groundbreaking process, users use DLC to securely lock their Bitcoin into DLC.Link, creating and more Value of dlcBTC. DLC acts as a digital safe on the Bitcoin blockchain, establishing a pre-signed contract between the user and the protocol. Even more secure, key distribution adopts a 2-of-2 multi-signature UTXO mechanism, where one key is held by the user and the other key is intelligently distributed in a network of trusted prover nodes.
Cross-chain bridges have a bad reputation due to their many vulnerabilities. DLCs are a unique solution because it solves the problem of cross-chain communication without the security concerns of bridging. Unlike bridge assets such as wBTC, dlcBTC does not require an intermediary, instead choosing to protect the asset by the entire hash rate of the Bitcoin network. Set to launch in the first quarter of 2024, dlcBTC v1 will introduce features such as whitelist access, strict security measures, multi-functional trading pairs, and seamless integration with existing DeFi protocols, marking a major advancement in the decentralized finance space [ 5].
We believe that after Bitcoin, the most decentralized network is Ethereum. So with dlcBTC we are working to bring native BTC to DeFi on the Ethereum network without having to build another L2 or solution that is smaller, untested and more dangerous. Minted dlcBTC tokens are used as collateral in well-known DeFi platforms such as Curve and AAVE and enable users to actively participate in DeFi activities such as investing, lending, and hedging, etc.
DLC.Link is widely used in the Bitcoin ecosystem
DLC.Link is a transformative force within the broader Bitcoin ecosystem, offering a range of applications through its Discreet Log Contract (DLC). This innovation has special significance for all parties including credit trading desks, prime brokers, digital asset custodians, exchanges and OTC trading desks. This integration allows custodians to extend financial services to self-custodial Bitcoin customers, support custody and conditional instant transfers of local Bitcoin, and provide borrowing services to miners and other self-custodial Bitcoin customers.
DLC.Link’s role in decentralized finance (DeFi) is equally extensive and influential. Its integration facilitates the development of collateralized loans and stablecoins based on on-chain Bitcoin assets, providing advantages to lending protocols. In addition, DLC.Link can also be seamlessly extended to cross-chain protocols to enable the transfer of local Bitcoins between different blockchains. BRC-20 assets are currently hot, and DLC.Link can also accept them into cross-chain bridging [6]. In addition, it supports the trading and lending of inscribed assets in NFT markets (such as OpenSea) and other smart contract-based platforms, bringing new use cases to DeFi.
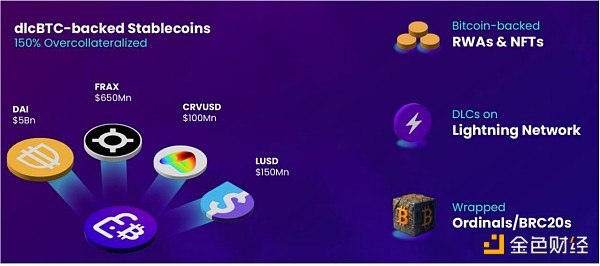
Figure 2. DLC.Link Extensive use cases
Conclusion
The reason why Bixin Ventures strategically invested in DLC.Link in the early seed round is that it hopes to integrate with decentralized finance (DeFi). ) to help solve challenges facing the Bitcoin ecosystem. DLC technology overcomes the limitations of Bitcoin's smart contracts, makes better use of Bitcoin's powerful security, and provides a safer solution. Schnorr Signatures in the recent Taproot upgrade enables DLC.Link to establish a witness network, and the integration of FROST further improves the dynamic management of witnesses. The launch of dlcBTC also responds to the growing demand for secure, decentralized self-wrapped Bitcoin. In addition, DLC.Link also implies huge potential in various other product application layers, including self-custody deposits in CeFi and cross-chain inscriptions in DeFi. Bixin Ventures strategically invested in DLC.Link, demonstrating its commitment to shaping decentralized finance (DeFi). We recognize DLC.Link’s innovative contributions to the crypto space and foresee it playing a key role in providing Bitcoin liquidity throughout the broader crypto ecosystem.
Reference
[1] Namcios. Why You Should Care About Taproot, The Next Major Bitcoin Upgrade. Bitcoin Magazine. Retrieved from https://bitcoinmagazine.com/technical/short-bitcoin-taproot-explainer
[ 2] Dryja, T. Discreet Log Contracts. Retrieved from https://adiabat.github.io/dlc.pdf
[3] DLC.Link. How DLCs Secure Bitcoin On Chain without Validators. Retrieved from https://www.dlc.link/blog/how-dlcs-secure-bitcoin-on-chain-without-validators
[4] Komlo, C., & Goldberg, I. FROST: Flexible Round-Optimized Schnorr Threshold Signatures. Retrieved from https://eprint.iacr.org/2020/852.pdf
< p style="text-align: left;">[5] DLC.Link. DLC.Link Introduces dlcBTC. Retrieved from https://www.dlc.link/blog/dlc-link-introduces-dlcbtc-a-game -changing-bitcoin-bridge-for-trustless-defi-operations
[6] DLC.Link. DLC.Link Docs Generic Use Cases. Retrieved from https: //docs.dlc.link/applications/generic-use-cases
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Huang Bo
Huang Bo JinseFinance
JinseFinance Joy
Joy JinseFinance
JinseFinance Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph