Web3 cannot exist without MeMe coin, nor can it exist only with MeMe
Meme, Web3 cannot be without MeMe coin nor can it be only MeMe. Golden Finance, the largest MeMeCoin in the currency circle is Bitcoin.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
OKX Web3 Wallet has specially planned the "Security Special Issue" column to provide special answers to different types of on-chain security issues. Through the most real cases happening around users, in collaboration with experts or institutions in the security field, dual sharing and answers are conducted from different perspectives, so as to sort out and summarize the rules of safe transactions from the shallow to the deep, aiming to strengthen user security education while helping users learn to protect their private keys and wallet asset security from themselves.
Playing MEME is a big adventure
Rug Pull (withdrawal from the pool), Pixiu plate, smashing through, being clamped...many traps are ahead
I have always been a brave adventurer, until my knee was hit by an "arrow"
This issue is the 02nd security special issue. We specially invite CertiK, a well-known security organization in the industry, and the OKX Web3 team to share common MEME on-chain transaction security risks and prevention measures from the perspective of practical guidelines. We hope it can be helpful to MEME users.

CertiK Security Team:CertiK was founded by two professors from Yale University and Columbia University. It uses the most advanced formal verification technology, AI audit technology and manual audits by security experts to ensure the security of blockchain protocols and smart contracts by scanning and monitoring them. To date, CertiK has been recognized by more than 4,000 corporate customers, has discovered nearly 70,000 code vulnerabilities, and protected more than $400 billion in digital assets from loss.
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team:Hello everyone, I am very happy to share this. The OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team is mainly responsible for the security capacity building of the OKX Web3 Wallet, providing multiple protection services such as product security, user security, and transaction security. While protecting the security of user wallets 24/7, it also contributes to maintaining the security ecosystem of the entire blockchain.
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team:There are many types of risk cases of this type. We have selected several classic cases that users have encountered when trading MEME:
Case 1: Pixiu Plate
User A saw a hot discussion on a certain MEME on Twitter, and found the token address in the tweet comments of the MEME. After checking the transaction data of the MEME, he found that it performed well, so he bought it. As the price of the MEME continued to rise, User A wanted to sell and lock in profits, but he was unable to sell it. After investigation by our team, we found that the MEME token was a Pixiu disk, and the user's address could not be sold because it was blacklisted.
Case 2: Malicious Rug Pull
User B often speaks and participates in activities in a Telegram community, and is added as a friend in the address book by many group members. One day, a group member privately chatted with user B and recommended a MEME project to him, saying that the project was very popular and had great potential, and then immediately provided the address of the MEME token. User B was a little tempted, so he checked on a data analysis tool and found that the MEME token liquidity LP had been destroyed and no whales held positions. Therefore, he thought that the MEME project was more reliable and purchased it. But on the next day, user B suddenly found that the liquidity of the MEME project had been exhausted. After investigation by our team, we found that the token was a malicious Rug Pull token, which had a backdoor logic that could issue a large number of tokens.
There are endless cases of risks happening to MEME users. We hope that through the following conversation, we can provide users with some safety reference guides. This does not constitute any investment advice, but is only for everyone to learn and communicate.
CertiK Security Team:MEME risks are divided into two categories: one is the on-chain risk scenario, and the other is the general risk, which has nothing to do with blockchain technology.
Before introducing the specific on-chain risk scenarios, let’s first introduce the general risks, which mainly include five categories: extremely low coin issuance costs, easy manipulation of token prices, highly centralized projects, large investor trading wear and tear, and Rugpull scams.
1. The cost of issuing coins is extremely low
Generally speaking, the amount of technical development for launching MEME projects is extremely low or even non-existent, so that one-click coin issuing tools such as PandaTool have emerged. It is precisely because of the extremely low development cost that the cost for internal personnel and early investors of the project to obtain tokens is extremely low. In addition, the MEME project itself has no actual fundamentals. Once the market is no longer "FOMO" (Fear of Missing Out), these extremely low-cost tokens will be quickly sold, causing subsequent investors to bear huge losses.
2. The price of tokens is easily manipulated
The price of MEME is easily manipulated. On the one hand, due to its lack of substantial technical support, intrinsic value, and low issuance threshold, anyone can easily create and issue MEME, which makes the market full of a large number of highly speculative currencies.
At the same time, MEME usually relies on social media and network popularity to drive its price, and these factors are extremely vulnerable to manipulation by large or organized groups. These speculators can manipulate prices by buying or selling in large quantities, as well as creating false information and market noise, causing drastic price fluctuations, attracting more retail investors to chase ups and downs, thereby further exacerbating the possibility of price manipulation.
3. Highly centralized projects
MEME projects usually lack a decentralized governance mechanism, and decision-making power is concentrated in the hands of a few developers and core teams, making project direction and management susceptible to personal interests, increasing investor risks. On the basis of centralized decision-making power, various centralized risks may also arise, such as centralized control of token contracts and programs, centralized token holdings, and centralized liquidity control.
4. Large wear and tear on investor transactions
MEME transaction wear and tear is large, first attributed to its poor liquidity. Due to the relatively small number of participants in the market who buy and sell MEME and insufficient trading volume, the bid-ask spread (i.e., the gap between the buying price and the selling price) is large, which increases transaction costs. In addition, MEME coins with poor liquidity are prone to drastic price fluctuations in large transactions, further increasing transaction risks and costs. Investors often need to bear higher slippage and greater price impact when buying or selling, resulting in inefficient transactions and rising transaction costs.
The second is attributed to the "transaction tax" mechanism. In order to incentivize investors to hold or maintain project funds, many MEME projects usually charge a certain percentage of transaction taxes on each transaction. These taxes are usually used to repurchase tokens, reward holders, or support project development. However, this transaction tax increases transaction costs and makes frequent transactions more expensive. Traders need to pay additional taxes every time they buy or sell, which aggravates transaction wear and tear and further reduces liquidity. Investors must bear higher fees and risks when trading MEME.
5. Rugpull scam
MEME is easily targeted by the Rugpull scam because of its high anonymity, lack of transparency and regulation. The following are several common Rugpull methods and their phenomena:
1) Liquidity Pull:
Method: The development team will create a liquidity pool on a decentralized exchange (DEX) and add tokens and mainstream cryptocurrencies (such as ETH, USDT, etc.) to the pool. After attracting enough investors, the development team will suddenly withdraw all liquidity, making the tokens untradable.
Phenomenon: Investors find that they cannot sell tokens, the token price quickly returns to zero, and the liquidity pool shows that there is almost no funds left.
2) Developer Dumping
Method: Project parties or early holders hold a large number of tokens. When market demand is hyped up, they will sell most or all of their tokens in a short period of time, causing prices to plummet.
Phenomenon: Huge sell orders appear in transaction records, token prices fall sharply, market confidence collapses, and trading volume decreases rapidly.
3) Fake Projects:
Method: Criminals will create a fake MEME coin project, fabricate false visions and roadmaps, and attract investors through social media and celebrity endorsements. Once enough funds are raised, they will close the project and run away with the money.
Phenomenon: Project websites and social media accounts suddenly disappear, the development team cannot be contacted, and the value of tokens in investors' accounts depreciates rapidly.
4) Contract Exploits:
Method: The development team deliberately leaves backdoors or loopholes in the smart contract, allowing them to manipulate the contract under certain conditions and steal investors' funds.
Phenomenon: Token transactions are abnormal or suddenly stopped, investors cannot transfer or sell tokens, and the contract address shows that a large amount of funds have been transferred to unknown accounts.
5) Fake Forks:
Method: Claiming to upgrade or fork the original tokens, requiring holders to exchange old tokens for new tokens, in fact, is to collect and possess these old tokens.
Phenomenon: The old tokens lose value, the so-called new tokens cannot be traded on any exchange, and the project team loses contact.
Next, we will introduce the common on-chain risks when users conduct MEME transactions on the EVM public chain & Solana network. In order to facilitate users to more directly compare the differences in risk types, we share them in the form of a table.
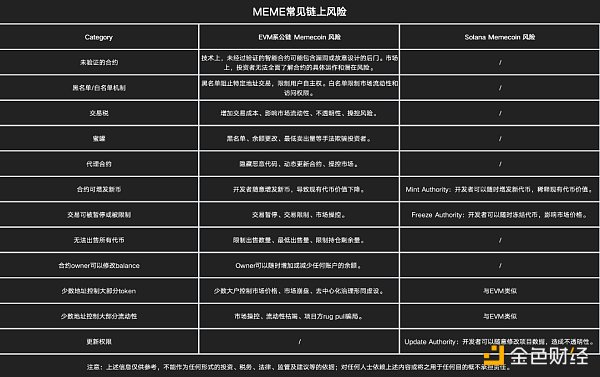
Image source: CertiK Security Team
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team:EVM-based public chains and Solana are the preferred networks for users to conduct MEME transactions. There are differences in the types of on-chain risks between the two, which is related to factors such as the different token issuance mechanisms of the two.
First, EVM is a public chain. Since the EVM public chain tokens have a high degree of freedom in issuance and the token content is implemented by developers, there are two common chain risks for MEME transactions on the EVM public chain:
(I) MEME with malicious logic
When the market is hot, there will be various malicious tokens forged as popular MEME. This type of malicious token usually has good transaction data, which leads users to misjudge and trade malicious tokens, thereby causing losses. There are currently two common malicious tokens:
1. Pixiu disk: refers to tokens that can only be bought but not sold. This type of malicious token usually sets a 100% tax rate or special transfer restriction logic, which prevents users from selling tokens.
2. Malicious rug pull tokens: refers to tokens with hidden issuance logic. This type of malicious token exhausts token liquidity by hiding the issuance logic and then issuing additional tokens.
(II) Project Party Evil
Currently, project party evil also mainly includes two types: privileged function evil and direct market crash.
1) Privileged function evil: The project party issues additional tokens to crash the market through privileged functions, such as mint function.
2) Direct market crash: The project party directly uses the tokens it holds to crash the market.
Second, Solana chain. It is worth noting that the Solana network issues tokens through fixed official channels. Therefore, when conducting MEME transactions on the Solana chain, the common on-chain risks mainly come from the project party's evil.
(I) Privileged functions
The project party uses privileged functions, such as the mint function, to issue additional tokens to dump the market; or freeze user addresses through freezing instructions, thereby achieving a similar purpose as the Pixiu market, preventing users from selling.
(II) Direct dumping
The project party directly uses the tokens held to dump the market. It is worth reminding that some malicious MEME project parties will evade the review of concentrated token holdings by distributing the tokens they hold.
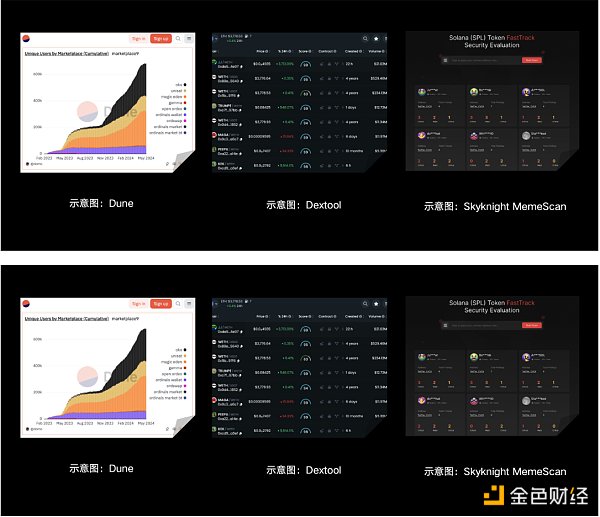
CertiK Security Team:This does not constitute any investment advice. It is just an introduction to some of the tools we personally use. It cannot 100% help users filter risks. It only provides a reference for users to initially judge whether a MEME has a high risk.
1) dune.com: A data analysis platform that can customize queries to analyze and monitor the on-chain data of tokens. It is relatively flexible, but relatively complex to use and requires a certain learning cost.
2) Dextools.io: A token information integration platform that can view some basic information of tokens, such as market value, liquidity, number of holders, token distribution, etc., and can also perform some simple security risk screening.
3) Skyknight MemeScan: A new platform launched by CertiK that provides a solution for evaluating the security status of MEME. The platform provides instant insights and on-chain behavior analysis, including contract minting analysis, transaction control detection, ownership concentration analysis, liquidity control assessment, etc.
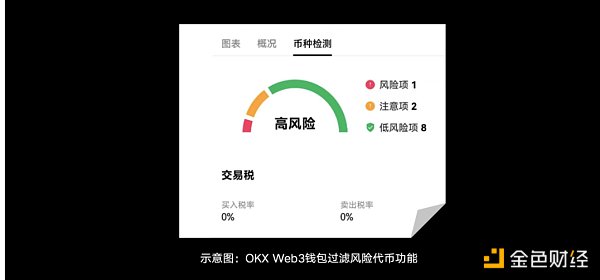
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team:There is no way and method to filter risks 100%, but from the perspective of token security and project health, we provide users with several dimensions that can initially filter out highly risky MEME items. It should be noted that users cannot judge the security of a project based solely on the following dimensions.
1) Smart contract security: You can use auxiliary tools to verify whether there are security issues at the source code level. These tools can check whether there is malicious logic in the project code and identify security vulnerabilities in the code itself. In addition, it is necessary to evaluate the permission control of the contract to ensure that the contract owner's permissions are not too large to prevent him from arbitrarily issuing or destroying tokens.
2) Token allocation and holding distribution: Check the distribution of token holders through the blockchain browser and avoid participating in projects with too concentrated token holdings, as these projects are vulnerable to manipulation and have a high risk of rugpull
3) Liquidity and trading activities: Observe the trading volume and price fluctuations of the token. Low trading volume and high volatility may mean that the project is unstable or there is a risk of manipulation.
4) Community and development team activities: Whether the project team is open and transparent, including the background, experience and social media activities of team members.
Currently, the OKX Web3 wallet also provides users with the ability to filter risky tokens, filtering out tokens that may cause damage to users from multiple levels such as code security and transaction security. While providing token information in various dimensions, it also protects users' MEME safe trading experience.
CertiK Security Team:First, Launchpad platforms and DEXs must have strong technical support to cope with the transaction response speed and transaction scale of MEME projects. In addition, liquidity is also a crucial link, and relevant platforms need to monitor any events that may affect liquidity security. Finally, regarding the compliance risks of MEME, the platform must understand and implement relevant regulatory policies and requirements to reduce possible legal risks.
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team:Next, we will introduce the current limitations or risks of the Launchpad platform and DEX respectively.
For the Launchpad platform, there are three main points:
First, the quality of projects launched on the platform is uneven. Although some Launchpad platforms will conduct reviews and due diligence, they may still fail to fully identify high-risk or low-quality projects.
Second, fund management risk. Launchpad platforms usually centrally manage a large amount of user funds. If these funds are not managed properly or are misappropriated maliciously, they may lead to user fund losses. In addition, the platform may lack sufficient safeguards to protect the safety of user funds.
Third, market manipulation. Project parties or large capital players may manipulate prices after the launch of Launchpad, causing drastic market fluctuations and affecting retail investors.
For DEX, there are relatively more limitations.
First, insufficient liquidity. Newly listed MEMEs usually have poor liquidity on DEX, which can easily lead to large transaction slippage and drastic price fluctuations.
Second, smart contract vulnerabilities. DEX relies on smart contracts for transactions. If there are vulnerabilities in these contracts, they may be exploited by hackers, causing financial losses.
Third, high transaction fees, especially on networks such as Ethereum, where transaction fees (gas fees) can be very high, affecting the cost-effectiveness of small traders.
Fourth, malicious project parties. Anyone can deploy tokens and list DEX transactions. Some project parties may deliberately leave backdoor functions in the contract, allowing the project party to arbitrarily manipulate the token balance or prevent users from selling tokens.
Fifth, user experience issues. The operation of DEX is relatively complicated for ordinary users, involving wallet connection, gas fee settings, etc. For entry-level users, the experience may not be as good as that of centralized exchanges (CEX).
CertiK Security Team:Telegram bots can significantly lower the threshold for trading and automate some steps in trading, making it easier for non-professionals to trade cryptocurrencies. However, special attention must be paid to the specific security risks of these bots. It is recommended to conduct a comprehensive security due diligence on any third-party dApp that interacts with the wallet to ensure its security.
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team:The application of Telegram bots in the field of cryptocurrency shows great potential for intent-based interaction. This trend is expected to promote the future development of decentralized exchanges (DEX) by optimizing user experience, enhancing transaction convenience and security, expanding the financial services ecosystem, and technological innovation.
1. Improve user experience
Simplify operations: Telegram bots use natural language processing to enable users to trade using simple chat commands, simplifying complex operation processes.
Automatic trading: Users can set automatic trading rules, such as stop loss and take profit points, to reduce the risk and time cost of manual operations.
2. Enhanced decentralized trading
Seamless integration: The robot is integrated with the decentralized exchange (DEX) through the API interface, hiding the complex trading operations and reducing the user's learning cost.
Real-time operation: The robot can monitor market dynamics in real time and notify users instantly, enabling them to make trading decisions quickly and execute transactions.
3. Improve security
Smart contracts: The robot uses smart contracts to ensure the transparency and security of transactions, reducing the possibility of human intervention and fraud.
Decentralization: Although the robot may be centralized, the actual transaction is carried out in a decentralized environment, which improves the security and transparency of the transaction.
4. Expanding the Ecosystem
Multi-functional platform: Telegram robots are not limited to transactions, but can also be extended to financial services such as asset management, lending, and staking, providing a one-stop financial solution.
Enhancing community interaction: Through the Telegram platform, robots can promote user communication and community building, and increase user participation.
5. Technology and market driven
Innovation driven: Advances in artificial intelligence and blockchain technology will make robot applications more and more intelligent and efficient, and promote the emergence of more decentralized applications and services.
Market acceptance: Users' growing demand for simplified and automated services is driving more DEXs to adopt robot services to enhance their competitiveness.
CertiK Security Team:With the development of the cryptocurrency market, Telegram BOT robots have become more and more common in transactions and information acquisition. However, these high-frequency tools also bring significant security risks, and users should pay special attention to the following aspects when using them.
First, many Telegram BOT robots have not been audited or their codes are public, and may contain malicious code or vulnerabilities. These malicious BOTs may steal users' private keys, identity information, or other sensitive data. In addition, malicious BOTs may disguise themselves as legitimate services and induce users to enter their private keys or mnemonics through phishing attacks, thereby stealing funds. Therefore, users should make sure to only use officially recommended or verified BOTs and avoid clicking on unknown links or entering sensitive information.
Secondly, some BOTs may require too many permissions, such as access to the user's contacts, files or other private information. When using, permissions should be granted with caution to ensure that the BOT only obtains the minimum permissions required for its normal operation. At the same time, the communication between the BOT and the Telegram server may be intercepted by a man-in-the-middle attack, resulting in data leakage or tampering. Users should ensure that they use BOTs with encrypted communication and check the implementation of their secure communication protocols.
Third, many Telegram BOTs provide automated trading functions, but if there are loopholes in the trading logic of these BOTs, it may cause serious financial losses. Users should conduct sufficient testing before using such functions and monitor trading behavior to prevent abnormal situations. In addition, BOT developers may collect and store a large amount of user data. Once this data is leaked or abused, user privacy will be seriously threatened. Users should choose BOTs with good reputation and privacy policies, and regularly check their privacy protection measures.
Finally, over-reliance on certain BOTs for transactions or asset management may result in users being unable to operate normally when BOT services are interrupted or shut down. Therefore, users should avoid over-reliance on a single BOT and prepare backup plans. By understanding and preventing these risks, users can use Telegram BOT robots more safely and protect their assets and privacy.
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team: BOT robots like TG not only provide convenient services, but also bring great risks. Next, we will give an example.
First, the risk of centralized custody of private keys. Most Telegram robots need to host users' private keys in order to actively sign and send transactions. This means that users' private keys are stored on third-party servers, increasing the risk of theft or abuse.
Second, phishing risks. Phishing links sent by Telegram robots may induce users to click on them, resulting in the theft of account information or private keys. In addition, artificial inducement in the chat window (such as fake customer service) may deceive users' mnemonics or other sensitive information.
Third, Trojan risk. Some robots may infect users' devices by sending malware (Trojans) or malicious SDKs, endangering the security of the entire system.
In short, users need to be cautious when using various BOT robots, do not click on unfamiliar links at will, and do not disclose their private keys.
CertiK Security Team: First, for any dApp that interacts with their wallet, including trading platforms and Telegram bots, users should conduct security due diligence. Choosing a dApp that has undergone security audits can reduce the risk of being attacked during operation and ensure the security of your private keys and identity information. Currently, CertiK helps users reduce risks by providing dApp penetration testing services.
Secondly, MEME transactions are highly dependent on the response speed and frequency of transactions, so it is crucial to choose a stable platform with reasonable transaction fees. When trading, try to choose platforms that are safe, stable, fast and have low transaction fees to get a better trading experience. For example, the MemeScan platform launched by CertiK mentioned above can provide instant security status information, including on-chain behavior analysis of MEME. For example, contracts can issue new coins, transactions can be suspended or restricted, a few addresses control most of the tokens, and a few addresses control most of the liquidity. I hope it can provide some help for users to trade safely.
OKX Web3 Wallet Security Team: Considering security, users need to know safe operations and risk prevention when conducting MEME transactions to ensure the correctness and security of transactions.
First, choose the right trading platform. Users should choose a reputable and highly secure cryptocurrency exchange, and try to avoid using unverified or unknown trading platforms, which may face the risk of asset theft. For on-chain transactions, confirm the official website of the project party and the correctness of the contract.
Second, enable a more secure authentication method. For greater security, users can enable two-factor authentication on all trading platforms and wallets, using Google Authenticator or other security applications. Try to avoid SMS verification, as it is vulnerable to SIM card swap attacks.
Third, use a highly secure wallet. Users should try to use verified wallets for transactions, and ensure that the mnemonics or private keys are securely backed up and stored in a safe place to avoid electronic backups. Without backing up the private key or mnemonics, assets will not be restored when the device is lost or damaged.
Fourth, prevent phishing. Users need to always verify the URL used for transactions to ensure that it is an official link. When you encounter a problem, make sure you contact the official customer service, ignore private messages in Telegram, Discord and other groups, never click on unknown links, sign signatures whose contents you do not know, and display private keys.
Fifth, a secure network environment. Users should operate under a trusted operating system and try not to use public wireless networks.
Finally, thank you for reading the 02nd issue of the OKX Web3 Wallet "Security Special Issue". We are currently preparing for the 03rd issue, which will not only include real cases, risk identification, but also security operation tips. Stay tuned!
This article is for reference only and is not intended to provide (i) investment advice or investment recommendations; (ii) an offer or solicitation to buy, sell or hold digital assets; or (iii) financial, accounting, legal or tax advice. Holding digital assets (including stablecoins and NFTs) involves high risks and may fluctuate significantly or even become valueless. You should carefully consider whether trading or holding digital assets is suitable for you based on your financial situation. Please be responsible for understanding and complying with local applicable laws and regulations.
Meme, Web3 cannot be without MeMe coin nor can it be only MeMe. Golden Finance, the largest MeMeCoin in the currency circle is Bitcoin.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceThis year’s Meme track has been a key sector in the crypto market and major public chain ecosystems. At the beginning of the year, many Meme tokens with astonishing growth emerged in the Solana ecosystem, and the daily trading volume of these tokens once reached tens of billions of dollars.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceOn June 3, Solana founder Anatoly and Ethereum Foundation researcher Justin mentioned the issue of economic security in a debate. Toly believed that economic security was a meme, which triggered subsequent discussions among many bilateral KOLs.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceMeme, the evolution of MEME coin Golden Finance, only this kind of simplicity and purity can create a classic.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceMEME plays a vital role in Web3 culture
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceAfter a period of market movement, the market will have a concentrated MEME season. This is because there is a lot of money in the market at this time and FOMO is high. Still want to find new opportunities to get rich.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance Coinlive
Coinlive A total of 37 major exploits were monitored, with a total loss of approximately $405 million

 Cointelegraph
CointelegraphThe ‘Ethereum is a security’ debate has been going on for a while now. With the move to proof of ...
 Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist