Source: Machine Heart
Large language models can also break through, OpenAI has once again proved its strength.
At midnight on September 13th, Beijing time, OpenAI officially released a series of new AI large models designed to specifically solve difficult problems. This is a major breakthrough. The new model can achieve complex reasoning, and a general model can solve more difficult problems than previous scientific, code, and mathematical models can do.

OpenAI said that the new model released today in ChatGPT and the large model API is the first model in the series, and it is only a preview version - o1-preview. In addition to o1, OpenAI also showed the evaluation of the next update currently under development.
The o1 model has created many historical records in one fell swoop.
First of all, o1 is the strawberry model that OpenAI has been "highly publicizing" from Sam Altman to scientists. It has real general reasoning ability. It has shown super strength in a series of difficult benchmark tests, which is a huge improvement over GPT-4o, raising the upper limit of large models from "unbearable" to excellent level. It can directly win the gold medal in the Mathematical Olympiad without special training, and even surpass human experts in the scientific question-and-answer session at the doctoral level.
Altman said that although o1's performance still has flaws, you will still be shocked when you use it for the first time.
Secondly, o1 has brought an upward curve to the scale expansion vs performance of large models. It reproduces the success of AlphaGo reinforcement learning in the field of large models - the more computing power is given, the more intelligence is output, until it surpasses the human level.
That is, from a methodological point of view, the o1 large model proves for the first time that language models can perform real reinforcement learning.
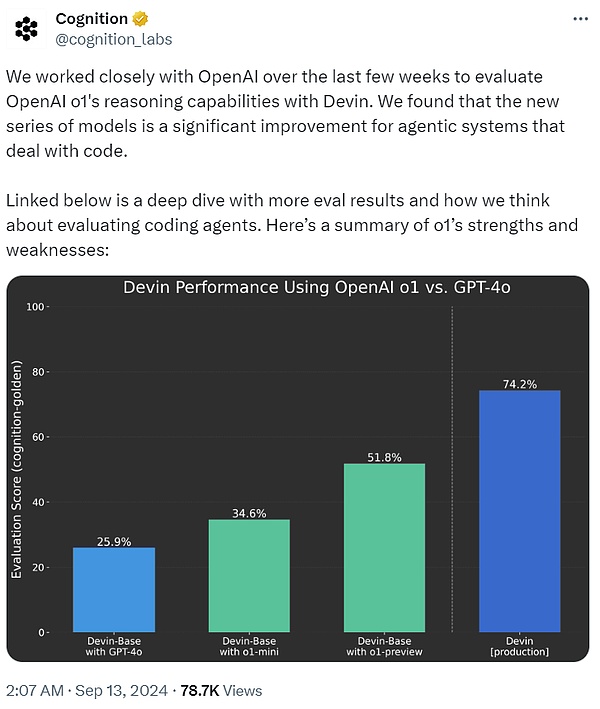
Cognition AI, which developed the first AI software engineer Devin, said that it has been working closely with OpenAI in the past few weeks to use Devin to evaluate the reasoning ability of o1. It was found that compared with GPT-4o, the o1 series of models is a major improvement for intelligent systems that process code.
Finally, in practice, after o1 went online, ChatGPT can now think carefully before answering questions instead of blurting out answers immediately. Just like the human brain's System 1 and System 2, ChatGPT has evolved from using only System 1 (fast, automatic, intuitive, and error-prone) to being able to use System 2 thinking (slow, deliberate, conscious, and reliable). This allows it to solve problems that were previously unsolvable.
From the user experience of ChatGPT today, this is a small step forward. Under simple prompts, users may not notice much difference, but if you ask some tricky math or code questions, the difference begins to become obvious. More importantly, the path for future development has begun to emerge.
In short, the bombshell dropped by OpenAI tonight has shocked the entire AI community, and they have expressed tql, sleeplessness, and have begun to study hard late at night. Next, let's take a look at the technical details of the OpenAI o1 large model.
OpenAI o1 Working Principle
In the technical blog "Learning to Reason with LLMs", OpenAI gave a detailed technical introduction to the o1 series of language models.
OpenAI o1 is a new language model trained by reinforcement learning to perform complex reasoning tasks. The characteristic is that o1 thinks before answering - it can generate a long internal chain of thinking before responding to the user.
That is, the model needs to spend more time thinking about the problem like humans before responding. Through training, they learn to improve their thinking process, try different strategies, and recognize their mistakes.
In OpenAI's tests, the subsequent updated models in this series performed similarly to doctoral students on challenging benchmark tasks such as physics, chemistry and biology. OpenAI also found that it performed well in mathematics and coding.
In the International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO) qualifying exam, GPT-4o only answered 13% of the questions correctly, while the o1 model answered 83% of the questions correctly.
The model's coding ability was also evaluated in the competition, ranking 89% in the Codeforces competition.
OpenAI said that as an early model, it does not yet have many practical functions of ChatGPT, such as browsing the web to obtain information and uploading files and pictures.
But for complex reasoning tasks, this is a major improvement and represents a new level of artificial intelligence capabilities. In view of this, OpenAI reset the counter to 1 and named the series of models OpenAI o1.
The point is that OpenAI's large-scale reinforcement learning algorithm teaches the model how to use its thought chain to think efficiently in a data-efficient training process. In other words, it is similar to the Scaling Law of reinforcement learning.
OpenAI found that with more reinforcement learning (calculated during training) and more thinking time (calculated during testing), the performance of o1 continues to improve. And the limitations of expanding this method are very different from those of large model pre-training, and OpenAI is still continuing to study.
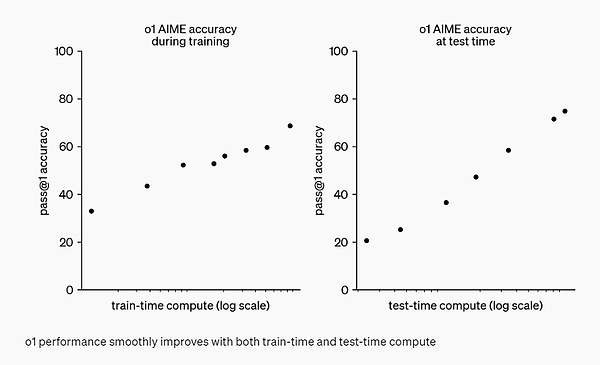
Evaluation
To highlight the improvement in reasoning performance relative to GPT-4o, OpenAI tested the o1 model on a series of different human exams and machine learning benchmarks. Experimental results show that o1 performs significantly better than GPT-4o in the vast majority of reasoning tasks.
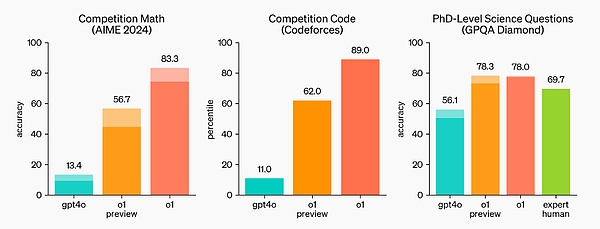
o1 has made significant improvements over GPT-4o on challenging reasoning benchmarks.
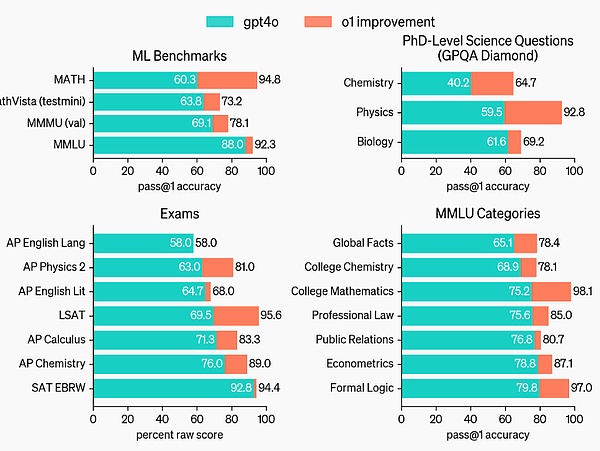
o1 improves over GPT-4o on a wide range of benchmarks, including 54/57 MMLU subcategories, 7 are shown for illustration.
O1 performs comparable to human experts on many inference-intensive benchmarks. Recent cutting-edge models perform so well on MATH and GSM8K that these benchmarks are no longer effective in distinguishing models. Therefore, OpenAI evaluated math performance on AIME, an exam designed to test the smartest high school math students in the United States.
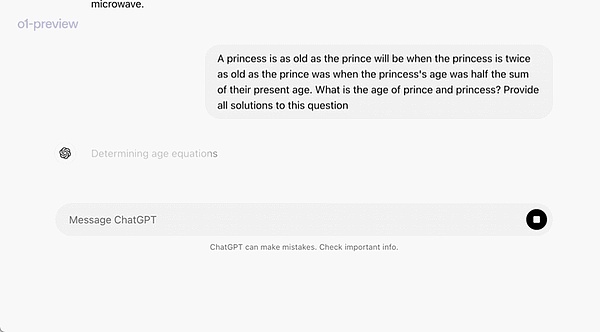
In an official demo, o1-preview solves a very difficult reasoning problem: When the princess is twice as old as the prince, the princess is the same age as the prince, and the princess' age is half of the sum of their current ages. How old are the prince and princess? Provide all solutions to this problem.
On the 2024 AIME exam, GPT-4o solved only 12% (1.8/15) of the questions on average, while o1 averaged 74% (11.1/15) when there was only one sample per question, 83% (12.5/15) when there was agreement between 64 samples, and 93% (13.9/15) when reranking 1,000 samples using the learned scoring function. 13.9 points can rank among the top 500 in the United States and is higher than the score line for the US Mathematical Olympiad.
OpenAI also evaluated o1 on the GPQA Diamond benchmark, a difficult intelligence benchmark that tests expertise in chemistry, physics, and biology. To compare the model with humans, OpenAI hired experts with PhDs to answer GPQA Diamond benchmark questions.
Experimental results show that: o1 surpasses the performance of human experts, becoming the first model to do so on this benchmark.
These results do not mean that o1 is more capable than a PhD in all aspects - just that the model is better at solving some problems that a PhD should solve. On several other ML benchmarks, o1 achieved new SOTA.
With visual perception enabled, o1 scored 78.2% on the MMMU benchmark, becoming the first model to be on par with human experts. o1 also outperformed GPT-4o on 54 of the 57 MMLU subcategories.
Chains of Thought (CoT)
Similar to how humans think for a long time before answering a difficult question, o1 uses chains of thoughts when trying to solve a problem. Through reinforcement learning, o1 learns to hone its chains of thoughts and improve the strategies it uses. o1 learns to recognize and correct mistakes, and can break down tricky steps into simpler ones. o1 also learned to try different approaches when the current one didn’t work. This process greatly improved the model’s reasoning ability.
Programming Skills
After initializing with o1 and further training its programming skills, OpenAI trained a very strong programming model (o1-ioi). The model scored 213 points on the 2024 International Olympiad in Informatics (IOI) competition, ranking in the top 49%. And the model participated in the competition under the same conditions as human contestants in the 2024 IOI: 10 hours to answer 6 difficult algorithmic questions, and each question was limited to 50 submissions.
For each question, the specially trained o1 model samples many candidate answers and submits 50 of them based on a test-time selection strategy. The selection criteria include performance on IOI public test cases, model-generated test cases, and a learned scoring function.
The research shows that this strategy is effective. Because if you just randomly submit an answer, the average score is only 156. This means that under the conditions of the competition, this strategy is worth at least 60 points.
OpenAI found that if the submission restrictions are relaxed, the model's performance can be greatly improved. If 10,000 answers are allowed per question, even without the test-time selection strategy mentioned above, the model can get 362.14 points - enough to win a gold medal.
Finally, OpenAI simulated a competitive programming competition hosted by Codeforces to demonstrate the model's coding skills. The evaluation used was very close to the competition rules, allowing 10 code submissions. GPT-4o has an Elo score of 808, which is in the top 11% of human competitors. The model far exceeds GPT-4o and o1 - its Elo score is 1807, outperforming 93% of competitors.
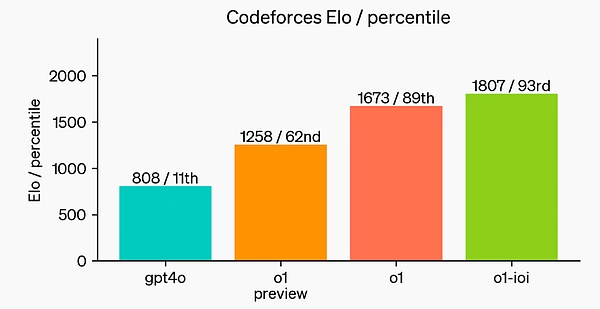
Further fine-tuning on programming competitions has increased o1's capabilities and ranked in the top 49% under the rules of the 2024 International Olympiad in Informatics (IOI).
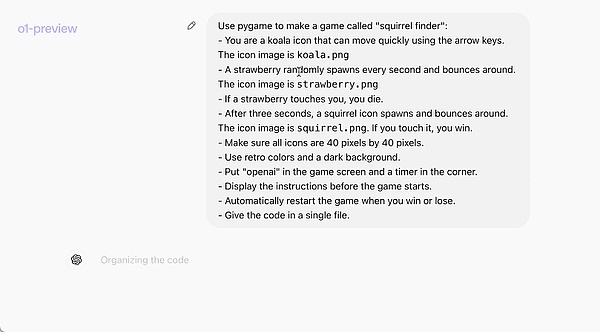
The following official example intuitively demonstrates o1-preview's programming capabilities: a prompt allows it to write a complete and runnable game.
Human Preference Evaluation
In addition to exams and academic benchmarks, OpenAI also evaluated human preferences for o1-preview and GPT-4o on challenging open prompts in more fields.
In this evaluation, human trainers anonymously responded to prompts from o1-preview and GPT-4o and voted for the responses they liked better. In categories with strong reasoning capabilities such as data analysis, programming, and mathematics, o1-preview is much more popular than GPT-4o. However, o1-preview is not popular on some natural language tasks, indicating that it is not suitable for all use cases.
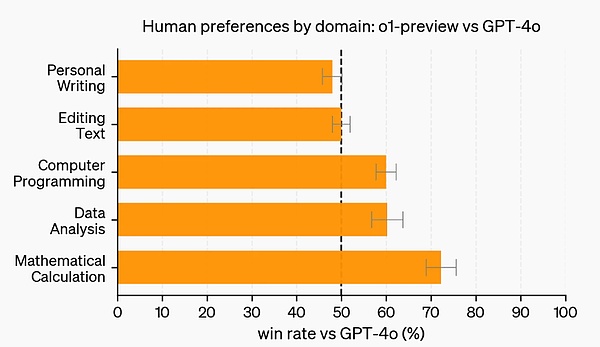
In areas that require stronger reasoning capabilities, people prefer o1-preview.
Safety
Chain of Thought (CoT) reasoning provides new ideas for safety and alignment. We found that incorporating model behavior policies into the thought chaining of reasoning models can teach human values and principles efficiently and robustly. By teaching models their own safety rules and how to reason about them in context, we found evidence that reasoning capabilities directly benefit model robustness: o1-preview achieved significant improvements on key jailbreak evaluations and the most stringent internal benchmarks used to evaluate model safety rejection bounds. We believe that using thought chaining can lead to significant advances in safety and alignment because 1) it enables observation of model thinking in a clear way, and 2) model reasoning about safety rules is more robust to out-of-distribution scenarios. To stress-test our improvements, we ran a battery of safety and red team tests based on our own safety readiness framework before deploying. We found that thought chaining reasoning helped improve capabilities throughout the evaluation process. Of particular note, we observed interesting instances of reward hacking.
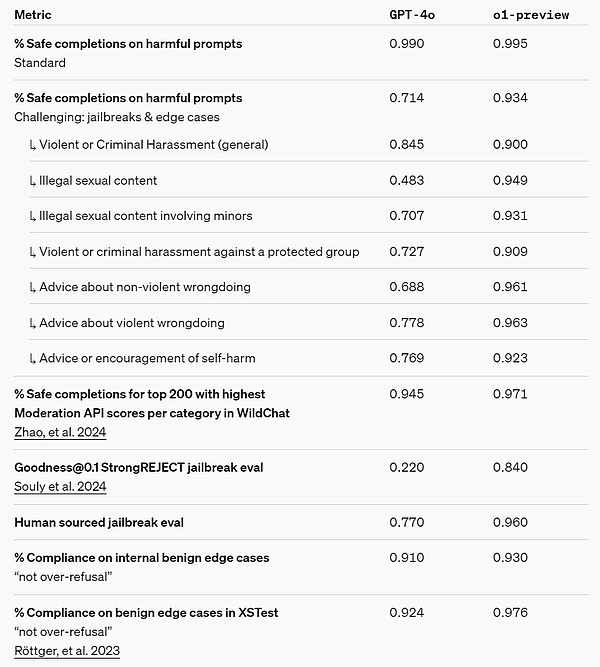
Safety Readiness Framework Link: https://openai.com/safety/
Hidden Thought Chain
OpenAI believes that hidden thought chain provides a unique opportunity for monitoring models. Assuming it is faithful and clear, hidden thought chain makes it possible to "read" the model's thoughts and understand its thought process. For example, people may want to monitor thought chain in the future to look for signs of manipulating users.
But to do this, the model must be able to freely express its thoughts in an unaltered form, so it cannot be trained on any policy compliance or user preference training in terms of thought chain. OpenAI also does not want users to directly see inconsistent thought chain.
Therefore, after weighing multiple factors such as user experience, competitive advantage, and the option of pursuing thought chain monitoring, OpenAI decided not to show the original thought chain to users. OpenAI admits that this decision has disadvantages, so it strives to partially compensate by teaching the model to reproduce any useful ideas in the thought chain in the answer. At the same time, for the o1 model series, OpenAI shows the thought chain summary generated by the model.
It can be said that o1 significantly improves the state of the art of AI reasoning. OpenAI plans to release improved versions of this model in the process of continuous iteration, and expects that these new reasoning capabilities will improve the ability to combine models with human values and principles. OpenAI believes that o1 and its subsequent products will unlock more new use cases for AI in science, programming, mathematics, and related fields.
OpenAI o1-mini
o1 is a series of models. This time OpenAI also released a mini version of OpenAI o1-mini. The company gave different definitions of preview and mini versions in a blog post: "To provide developers with more efficient solutions, we also released OpenAI o1-mini, a faster and cheaper reasoning model that is particularly good at programming." Overall, the cost of o1-mini is 80% lower than o1-preview.
Because large language models such as o1 are pre-trained on large text data sets, although they have extensive world knowledge, they may be costly and slow for practical applications.
In contrast, o1-mini is a smaller model that is optimized for STEM reasoning during pre-training. After training with the same high-computation reinforcement learning (RL) pipeline as o1, o1-mini achieves comparable performance on many useful reasoning tasks while significantly improving cost efficiency.
For example, in benchmarks that require intelligence and reasoning, o1-mini performs well compared to o1-preview and o1. But it performs poorly on tasks that require non-STEM factual knowledge.
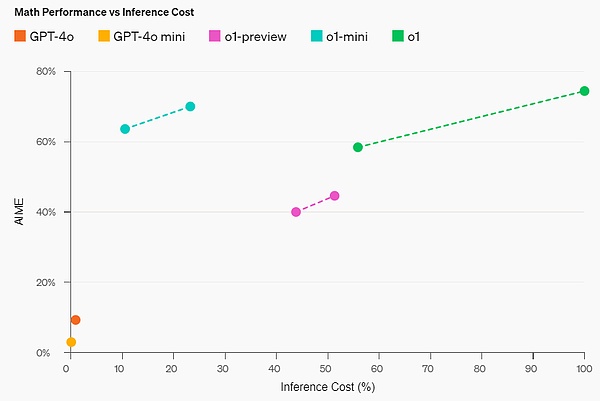
Math Skills: On the high school AIME math competition, o1-mini (70.0%) is comparable to o1 (74.4%), but much cheaper and better than o1-preview (44.6%). o1-mini scores (about 11/15 questions) in the top 500 high school students in the United States.
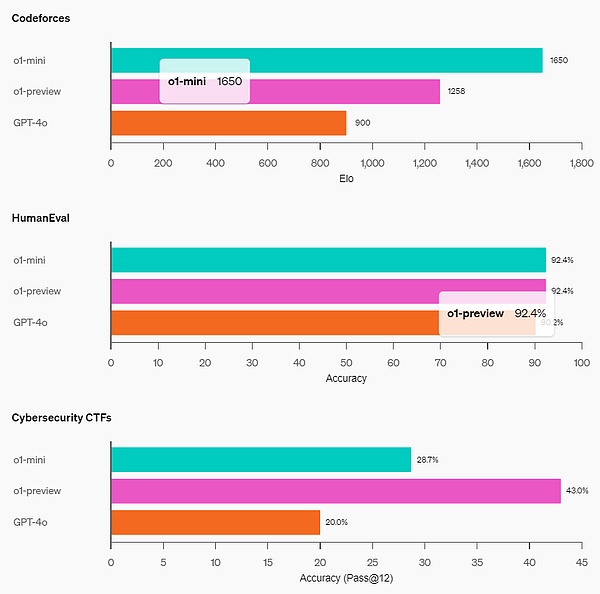
Coding Skills: On the Codeforces competition site, o1-mini's Elo score of 1650 is comparable to o1 (1673) and better than o1-preview (1258). o1-mini also performs well on the HumanEval coding benchmark and the high school cybersecurity capture the flag challenge (CTF).
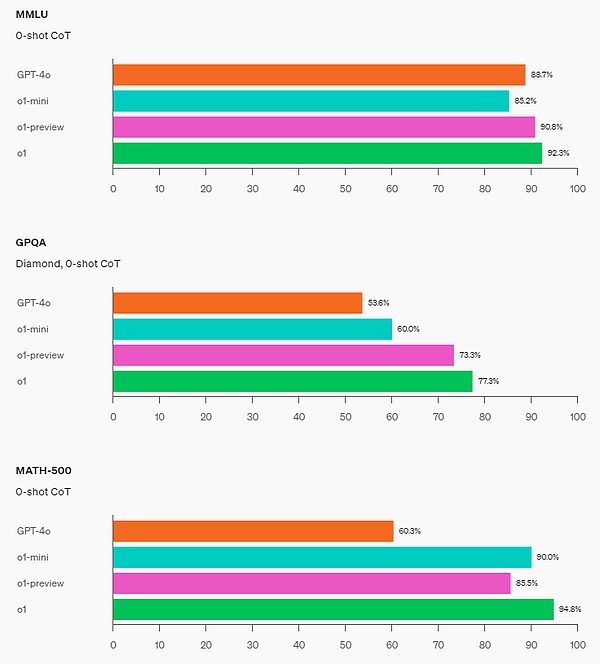
STEM: o1-mini outperforms GPT-4o on some academic benchmarks that require reasoning, such as GPQA (science) and MATH-500. o1-mini performs worse than GPT-4o on tasks such as MMLU, and lags behind o1-preview on the GPQA benchmark due to its lack of broad world knowledge.
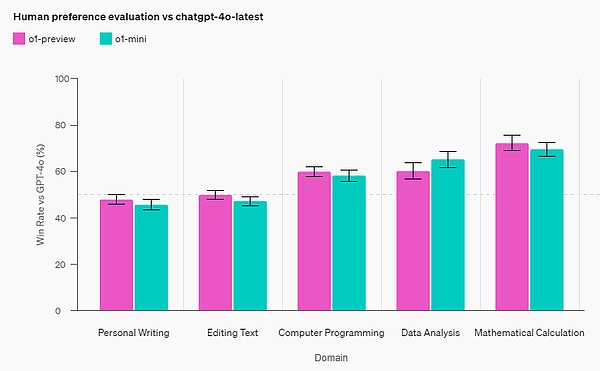
Human preference evaluation: OpenAI had human raters compare o1-mini and GPT-4o on challenging open-ended prompts in various fields. Similar to o1-preview, o1-mini is more popular than GPT-4o in reasoning-intensive fields, but not in language-centric fields.
In terms of speed, OpenAI compared the answers of GPT-4o, o1-mini, and o1-preview to a word reasoning question. The results showed that GPT-4o answered incorrectly, while o1-mini and o1-preview both answered correctly, and o1-mini came up with the answer about 3-5 times faster.

How to use OpenAI o1?
ChatGPT Plus and Team (individual paid and team editions) users can start using the o1 model in the company's chatbot product ChatGPT right now. You can manually choose to use o1-preview or o1-mini. However, user usage is limited.
Currently, each user can only send 30 messages per week to o1-preview and 50 messages to o1-mini.
Yes, very little! But OpenAI said it is working hard to increase the number of times users can use it and enable ChatGPT to automatically select the appropriate model for a given prompt word.
As for enterprise and education edition users, they will not be able to start using these two models until next week.
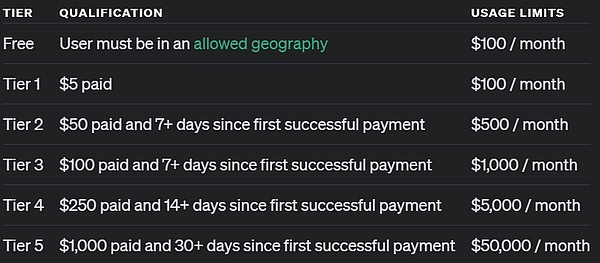
As for users accessing through the API, OpenAI said that developers who have reached level 5 API usage can start using these two models to develop application prototypes immediately, but they are also limited to 20 RPM. What is level 5 API usage? Simply put, it means that you have consumed more than $1,000 and have been a paying user for more than 1 month. Please see the figure below:
OpenAI said that API calls to these two models do not include functions such as function calls, streaming, and system support messages. Similarly, OpenAI said that it is working to increase these limits.
Future
OpenAI said that in the future, in addition to model updates, it will also add features such as web browsing, file and image uploads to make these models more useful.
"In addition to the new o1 series models, we plan to continue to develop and release our GPT series models."
References:
https://openai.com/index/introducing-openai-o1-preview/
https://openai.com/index/openai-o1-mini-advancing-cost-efficient-reasoning/
https://openai.com/index/learning-to-reason-with-llms/
https://x.com/sama/status/1834283100639297910
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance

























