Author: Garlam, Crypto KOL; Translation: 0xjs@黄金财经
Foreword
Bitcoin, as a pioneer in secure decentralized value exchange, has long been a bastion of reliability in the expanding blockchain ecosystem, however, its static nature has limited the development of the asset class compared to more general networks such as Ethereum. The Bitcoin Rune Protocol was launched in April 2024 and is expected to open up new areas for creating homogeneous tokens in the Bitcoin space.
Origins of Bitcoin Rune
Rune is the brainchild of Casey Rodarmor, the innovator behind the famous Bitcoin Ordinals protocol, with a vision to increase the efficiency and accessibility of token creation on the Bitcoin network. Rodarmor’s previous success with Bitcoin Ordinals, a non-fungible token protocol, laid the foundation for the development of Bitcoin Rune. Rune aims to simplify token economics and minimize operational complexity.
Understanding Bitcoin Rune
Bitcoin Rune represents a fungible asset built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain via the Rune protocol. Unlike its predecessor, Bitcoin Rune utilizes the Bitcoin-based UTXO model, allowing multiple tokens to reside in a single UTXO. This simple design enhances the user experience and eliminates the need for off-chain data storage or proprietary tokens, making Runes a native and efficient asset class in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Main Features and Use Cases
Bitcoin Runes inherit a wide range of potential applications, reflecting the versatility of ERC-20 tokens on Ethereum. From meme coins to DeFi, Runes provide a flexible platform for token-based projects. Notably, their compatibility with the Bitcoin mainnet and Lightning Network opens new avenues for microtransactions and scalable financial services, heralding a transformative era for Bitcoin-based DeFi solutions.
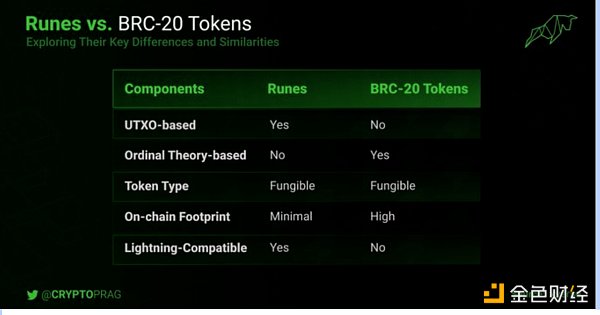
Bitcoin Runes vs. BRC-20 Tokens
While both Bitcoin Runes and BRC-20 tokens are homogenous assets on the Bitcoin network, there are some differences between them. Runes has Lightning Network compatibility and simplified data processing, reducing network pressure and enhancing scalability. In addition, Runes eliminates the need for a Taproot-enabled wallet, provides seamless integration with existing Bitcoin infrastructure, and enhances user accessibility.
Protecting and Managing Bitcoin Runes
Given the experimental nature of Bitcoin Runes, careful management of Bitcoin Runes is critical for participants.
Secure storage solutions, such as Ledger-compatible wallets such as Xverse and Leather, can provide strong protection against online threats while facilitating seamless interaction with the Runes protocol.
In addition, the use of trusted platforms such as Magic Eden and OKX ensures safe and efficient rune transactions in the emerging market.
Pre-Runes Projects: The Prologue of the Rune Era
Before the official launch of Bitcoin Runes, multiple Pre-Rune projects paved the way for the emergence of the Rune ecosystem.
These projects, including RSIC (Runestone Inscription Consortium), Rune Pups, and Prometheans, provide early insights into the potential of fungible tokens on the Bitcoin network.
By holding NFTs or BRC-20s from these pre-Rune projects, participants are positioning themselves at the forefront of the Rune revolution, which is expected to transition to a new era of Bitcoin tokenization.
Major Rune Collections
SATOSHI•NAKAMOTO: The First Major Meme on Rune•
RSIC: A well-known former Rune project, RSIC distributed 21,000 Runes to the OG Ordinals community, demonstrating a strong community base and strategic partnerships•
PUPS (Pups World Peace): As the mascot of the Rune industry, PUPS embodies the vibrant and uninhibited spirit of the community.
Runestone: Runestone is an open-source, transparent, volunteer and decentralized initiative to reward people for participating in the first year of the Ordinals protocol. Prometheans: CyberKongz's Pre-Rune series, symbolizing the ascension achieved through innovation and experimentation. And more
Bitcoin L2
Bitcoin Layer 2 is a specialized protocol built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain designed to enhance its scalability and functionality, solving many of the frictions users experience when trading Bitcoin-related tokens. These solutions, including popular frameworks such as Lightning Network, Rootstock, Stacks, and Liquid Network, address the inherent limitations of Bitcoin's slow transaction speed and low throughput by processing transactions off-chain. This not only speeds up transactions and reduces costs, but also introduces advanced features such as smart contract functionality and improved privacy. Bitcoin L2 leverages the security of the underlying Bitcoin network while significantly expanding its practicality and efficiency, making Bitcoin more competitive with other high-performance blockchains.

Rune Bridges and Tools
Bridges:
• MultiBit ($MUBI): Facilitates the seamless and secure exchange of BRC20 and ERC20 tokens, simplifies the transfer process, improves liquidity, reduces transaction costs, and makes it easier for users and developers to interact with DApps across both blockchains.
XLink (from ALEX Labs): is another tool that allows smooth transfers between L2 and the RUNES ecosystem, thereby expanding the liquidity of digital assets across different blockchain platforms.
• RunesBridge : supports the Runes protocol by connecting BRC-20 standard token holders within the Bitcoin ecosystem to various EVM compatible networks such as Ethereum, Polygon, and BNB Chain.
• Tools such as btctoolpro and rune mine : further support the ecosystem by providing basic services for token management and analysis.
Taken together, all of these tools and innovations will reduce the friction required to trade runes and even BRC-20
Tools:
Wallets: Xverse, OKX BTC Wallet, Unisat
Market Cap: https://runesmarketcap.com/
Markets: Unisat Rune Market https://unisat.io/runes/market; OKX Rune Market: https://www.okx.com/web3/marketplace/runes; Magic Eden Rune Market https://magiceden.io/runes
Mint & Etch: https://runesmarketcap.com/
Markets: Unisat Rune Market https://unisat.io/runes/market; OKX Rune Market: https://www.okx.com/web3/marketplace/runes; Magic Eden Rune Market https://magiceden.io/runes
Mint & Etch: href="https://luminex.io/runes/mint">https://luminex.io/runes/mint
https://unisat.io/runes/inscribe
https://www.okx.com/web3/marketplace/runes
TOP 10 RUNE GOODS
0. UNCOMMON•GOODS
1. Z•Z•Z•Z•Z•FEHU•Z•Z•Z•Z•Z
2. DECENTRALIZED
4. THE•RUNIX•TOKEN
5. DOG•DOG•DOG•DOG
6. SATOSHI•NAKAMOTO
7. MEME•ECONOMICS
8. RSIC•GENESIS•RUNE
9. LOBO•THE•WOLF•PUP
Bitcoin DeFi
A host of innovative protocols are ushering in a transformative era of financial innovation that could lead to the Bitcoin DeFi summer. As Bitcoin decentralized finance expands, Runes facilitates the creation and management of tokens directly on the Bitcoin blockchain, enhancing the utility and versatility of the network. The Bad Thing Bitcoin wasn’t really built for DeFi, so there are a lot of limitations. Trying to find arbitrage opportunities and researching Bitcoin DeFi is like looking at all these very expensive watches. The architecture is beautiful, but there are a lot of crazy inefficiencies, which really highlights the inefficiencies of the early blockchain era. 1. UTXO Complexity In Bitcoin, transactions are recorded differently than in traditional bank accounts. Instead of keeping balances in a single account, Bitcoin's ledger uses UTXOs. Each UTXO represents a bitcoin that can be spent. When someone sends you bitcoin, you receive it in the form of a UTXO. Each UTXO is uniquely identifiable and shows how much bitcoin was output from the previous transaction. To spend bitcoin, your wallet software selects the UTXOs associated with your wallet address as inputs to a new transaction. The sum of these inputs covers the amount you want to send. The transaction then creates new UTXOs as outputs, which are assigned to the recipient's address and returned to the sender as change if necessary.
Limitations of the UTXO Model
Scalability issues: Each transaction may involve multiple UTXOs as inputs and outputs. This can make transactions complex and large in size, especially when wallets contain many small UTXOs (often called "dust"). Larger transactions require more block space, leading to scalability issues as the network grows.
Increase in transaction fees: Bitcoin's transaction fees are calculated per byte of data in the transaction. Transactions involving many UTXOs are larger in size and therefore more expensive. This can become significant in times of severe network congestion.
Management complexity: Effectively managing UTXO requires complex wallet software that can choose which UTXOs to spend in a way that minimizes fees and preserves privacy. This complexity can be a barrier for both wallet developers and users.
Limited smart contract capabilities: Compared to account-based models such as Ethereum, the UTXO model inherently supports less complex smart contracts. This limits the type of decentralized applications that can be built directly on the Bitcoin blockchain without additional layers or sidechains.
2. Transaction speed: This is a nightmare for any trading shop trying to take advantage of any opportunity.
3. The threshold is high: Now everything in the BTC ecosystem is very complex, from bridges, wallets, markets, etc.
 Edmund
Edmund




