Author: Cara (X account @Cara6289) and XiG (X account @SHXiGi) of ZAN Team
On May 15, 2024, Sonne Finance was attacked on the Optimism chain, with losses of up to $20 million.
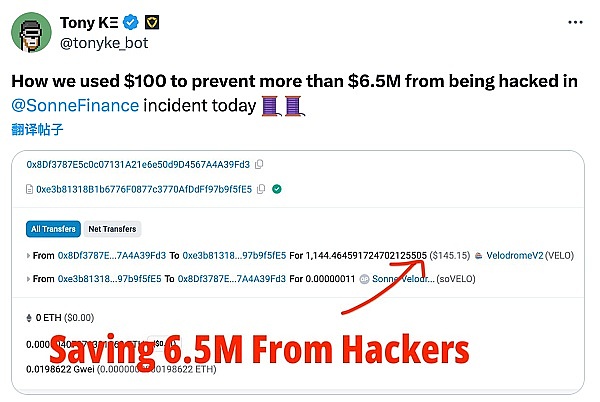
After the attack, @tonyke_bot user on X tweeted that he used about $100 to protect the remaining approximately $6.5 million in Sonne Finance's token collateral pool (also known as market, similar to cToken in Compound).
(https://twitter.com/tonyke_bot/status/1790547461611860182)
After discovering the attack, the Sonne Finance project quickly suspended all markets on Optimism and stated that the markets on Base are safe.
(https://twitter.com/SonneFinance/status/1790535383005966554)

Attack Summary
Sonne Finance is a decentralized lending protocol on Optimism that forks Compound V2, providing financial services for individuals, institutions, and protocols. The Sonne Finance protocol aggregates users' token assets to form a lending liquidity pool, providing users with a bank-like lending business. Like Compound, protocol participants can pledge their tokens to Sonne Finance's lending liquidity pool and obtain soToken (same as cToken). SoToken is an interest-bearing asset certificate. It will generate certain income as the block progresses, and will also receive SONNE token incentives. Participants can also borrow other tokens from the Sonne lending asset pool with their soTokens. For example, participants can pledge a certain amount of USDC to obtain soUSDC certificates, and then borrow WETH for further circulation. The mortgage lending in the Sonne Finance protocol can be a many-to-many asset relationship. During the mortgage lending process, the protocol will automatically calculate the health factor of the participant's address. When the health factor is lower than 1, the collateral of the address will be supported for liquidation, and the liquidator can also receive a certain amount of liquidation rewards.
The relationship between the number of underlying tokens deposited by users and the number of soTokens minted is mainly related to a variable called exchangeRate, which can be roughly used to indicate how much underlying tokens each soToken is worth. The calculation formula for exchangeRate is as follows:
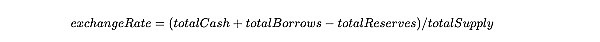
In the above formula, totalCash refers to the number of underlying tokens held by soToken, totalBorrows refers to the number of underlying tokens borrowed in a certain market, totalReserves refers to the total reserve amount (including the interest paid by the borrower), and totalSupply refers to the number of soTokens minted.
When redeeming, users can specify the number of underlying tokens they want to redeemAmount to calculate the number of soTokens that need to be destroyed, redeemTokens. The calculation method is roughly "redeemTokens = redeemAmount / exchangeRat". Note that there is no processing for precision loss here.
The essence of this attack is that when the market (soToken) was created, the attacker performed the first mortgage casting operation, minting a small number of soTokens with a small amount of underlying tokens, resulting in the value of "totalSupply" of soToken being too small. The attacker then took advantage of the vulnerability of Solidity contract precision loss, and sent the underlying token directly to the soToken contract (no soToken will be minted, which means that "totalSupply" remains unchanged and "totalCash" increases), instead of depositing the underlying token by mortgage + casting. This operation makes the "totalCash" variable in the contract larger, but "totalSupply" remains unchanged, which causes the exchangeRate to increase. In the end, when the attacker redeemed the underlying token, the soToken he needed to destroy was less than the soToken minted during the mortgage. The attacker used the soToken he earned to borrow the underlying tokens WETH and USDC from other soTokens (such as soWETH and soUSDC), and ultimately made a profit of up to 20 million US dollars.
Key addresses involved in the attack
Attack preparation transaction:
https://optimistic.etherscan.io/tx/0x45c0ccfd3ca1b4a937feebcb0f5a166c409c9e403070808835d41da40732db96
Attack profit transaction:
https://optimistic.etherscan.io/tx/0x9312ae377d7ebdf3c7c3a86f80514878deb5df51aad38b6191d55db53e42b7f0
Attack EOA Related address:
0x5d0d99e9886581ff8fcb01f35804317f5ed80bbb
0xae4a7cde7c99fb98b0d5fa414aa40f0300531f43
Attacker (contract) related address:
0xa78aefd483ce3919c0ad55c8a2e5c97cbac1caf8
0x02fa2625825917e9b1f8346a465de1bbc150c5b9
underlying token (VELO Token Vulnerable contract (soVELO, similar to Compound’s cToken):
0xe3b81318b1b6776f0877c3770afddff97b9f5fe5
X on @tonyke_bot User rescue transaction:
https://optimistic.etherscan.io/tx/0x816f9e289d8b9dee9a94086c200c0470c6456603c967f82ab559a5931fd181c2
Attack process analysis
Previous situation
Sonne Finance project recently passed a plan to add VELO market to Sonne Finance The proposal was made by the ETH/ETH multi-signature wallet (https://optimistic.etherscan.io/tx/0x18ebeb958b50579ce76528ed812025949dfcff8c2673eb0c8bc78b12ba6377b7). These five transactions are used to create the VELO market (soVELO contract) and set some key configurations of the market, such as setting the interest rate model, setting the price oracle, setting the collateral factor, etc. After the VELO market is created, users can deposit VELO tokens to mint soVELO tokens, which can be used to borrow other soTokens.
Attack Preparation
The attack preparation phase is mainly that after the two-day lock-up period of the proposal ends, the attacker creates the VELO market (soVELO contract) according to the information in the Sonne Finance project proposal, sets key configurations, and mints soVELO tokens by pledging VELO tokens into the soVELO contract. At the same time, the attacker also increases the exchangeRate by directly sending the VELO tokens he holds to the soVELO contract to prepare for subsequent attack profits.
The specific steps are as follows:
After the two-day lock-up period ends, the attacker first packages the operations of the first four transactions arranged in the proposal into one transaction (transaction 0x45c0cc) to create the VELO market (soVELO contract) and set key configurations. When the VELO market is initialized, the exchangeRate is set to "200,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000".
The attacker calls the "mint" function of the soVELO contract to deposit VELO tokens and mint soVELO tokens. The attacker specifies "mintAmount" as "400,000,001" (the number of VELO tokens). From the function "exchangeRateStoredInternal", it can be seen that since the "_totalSuppl" of the soVELO token is 0 at this time, the exchangeRate is the value set in step 1. According to the formula "mintTokens = actualMintAmount / exchangeRate", the number of soVELO tokens that should be minted at this time is 2. In short, in this step, the attacker deposits a value of "400,000,001" of VELO tokens into the soVELO contract, and the attacker obtains a value of 2 soVELO tokens.
soVELO.mint:

The attacker sent VELO tokens with a value of "2,552,964,259,704,265,837,526" to the soVELO contract by directly sending VELO tokens to the soVELO contract. At this time, the number of VELO tokens held by the soVELO contract increased, but because no new soVELO tokens were minted, the totalSupply remained unchanged, which means that the exchangeRate calculated according to the exchangeRate calculation formula will increase.
The attacker transferred the soVELO tokens he held multiple times, and finally transferred them to another attack EOA 0xae4a.
Attack Profit
The attack profit phase mainly involves the attacker executing the fifth transaction of the proposal, and borrowing VELO tokens through flash loans and sending them directly to the soVELO contract to further increase the exchangeRate. Then the attacker used the soVELO tokens with a value of 2 in his hand to borrow WETH, USDC and other underlying tokens from other soToken (such as soWETH, soUSDC, etc.) contracts, which became the attacker's profit. Then the attacker redeemed his underlying token from the soVELO contract. Due to the increase in exchangeRate and the loss of precision when calculating the soVELO tokens that needed to be destroyed for redemption, the attacker finally redeemed almost all of the VELO tokens previously deposited using only soVELO tokens with a value of 1. It can be understood that the attacker used the extra soVELO tokens with a value of 1 to earn WETH, USDC and other underlying tokens by borrowing from other soTokens. The attacker used the same method to repeat the attack many times and finally made a huge profit.
The specific steps are as follows:
The attacker executed the fifth transaction in the proposal and set the loan factor specified in the proposal.
The attacker flash-loans VELO tokens with a value of "35,469,150,965,253,049,864,450,449" from the VolatileV2 AMM - USDC/VELO pool, which triggers the attacker's hook function. In the hook function, the attacker continues to perform the attack operation.
The attacker sends the VELO tokens he holds to the soVELO contract to further increase the exchangeRate. Currently, there are a total of VELO tokens with a value of "35,471,703,929,512,754,530,287,976" in the soVELO contract (the sum of the VELO tokens transferred by the attacker three times).
The attacker creates a new contract 0xa16388a6210545b27f669d5189648c1722300b8b. In the constructor, the attacker transfers the two soVELO tokens to the newly created contract 0xa163 (hereinafter referred to as attacker 0xa163).
The attacker 0xa163 borrows WETH with the soVELO tokens he holds from soWETH, with a value of "265,842,857,910,985,546,929".
The attacker 0xa163 calls soVELO’s “redeemUnderlying” function and specifies the value of VELO tokens to be redeemed as “35,471,603,929,512,754,530,287,976” (almost all the VELO tokens that the attacker has previously transferred or pledged into the soVELO contract). At this time, the formula “redeemTokens = redeemAmountIn / exchangeRate” is needed to calculate the number of soVELO tokens that need to be destroyed for redemption.
From the " exchangeRateStoredInternal " function, we can see that since _totalSupply is 2 instead of 0 at this time, we need to calculate the value of exchangeRate. Through the formula " exchangeRate = (totalCash + totalBorrows - totalReserves) / totalSupply ", we can see that the current exchangeRate is " 17,735,851,964,756,377,265,143,988,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 ", which is much larger than the set initial exchangeRate of " 200,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,00 ".
The value of "redeemTokens" calculated based on the new exchangeRate is "1.99". Due to the rounding down feature of Solidity, the value of "redeemTokens" is finally 1. This means that the attacker 0xa163 used the soVELO token with a value of 1 to redeem almost all the VELO tokens previously deposited. At the same time, the attacker 0xa163 also earned "265,842,857,910,985,546,929" of WETH borrowed from soWETH.
soVELO.redeemUnderlying:

soVELO.exchangeRateStoredInternal:

The attacker 0xa163 transferred all the borrowed WETH and redeemed VELO tokens to the upper-level attacker, and then self-destructed.
The attacker calls soWETH's "liquidateBorrow" function to liquidate part of the assets borrowed by the newly created contract 0xa163, in order to get back the locked soVELO token with a value of 1. Currently, the attacker only holds a soVELO token with a value of 1.
The attacker calls soVELO's "mint" function to once again pledge soVELO tokens, in order to collect enough soVELO tokens with a value of 2, and then execute steps 3-8 again to profit from other undeylying tokens.
The attacker executes step 9 several times to pay off the flash loan and leave with a profit.
How $100 can leverage $6.5 million
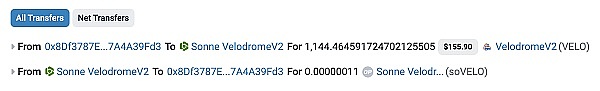
After the attack, @tonyke_bot on X minted 0.00000011 soVELO by mortgaging 1144 VELO tokens to the soVELO contract in transaction 0x0a284cd. This operation prevented the attacker from further attacking because the transaction changed the size of totalSupply in soVELO and the number of VELO tokens held, totalCash. The increase in totalSupply has a greater impact on the calculation of exchangeRate than the increase in totalCash, so the exchangeRate becomes smaller, which makes it impossible for the attacker to use the loss of precision to earn soVELO when attacking, and the attack can no longer be carried out.
Fund Tracking
The attacker transferred the funds shortly after grabbing the illegal proceeds. Most of the funds were transferred to the following 4 addresses. Some were to change addresses to continue the attack, and some were to launder money:
0x4ab93fc50b82d4dc457db85888dfdae28d29b98d
The attacker transferred 198 WETH to the address, and then the address used the same attack method to obtain illegal proceeds in the following transactions:

After the attack, the address transferred the illegal income to 0x5d0d99e9886581ff8fcb01f35804317f5ed80bbb.
0x5d0d99e9886581ff8fcb01f35804317f5ed80bbb
The attacker transferred 724277 USDC and 2353 VELO to the address and exchanged USDC for Ether. Then, part of the funds were immediately transferred to the Stargate cross-chain bridge, and most of the remaining illegal funds remained in this address:
0xbd18100a168321701955e348f03d0df4f517c13b
The attacker transferred 33 WETH to this address and used peel chain The money laundering link is as follows:
0xbd18100a168321701955e348f03d0df4f517c13b -> 0x7e97b74252b6df53caf386fb4c54d4fb59cb6928 -> 0xc521bde5e53f537ff208970152b75a003093c2b4 -> 0x9f09ec563222fe52712dc413d0b7b66cb5c7c795.
0x4fac0651bcc837bf889f6a7d79c1908419fe1770
The attacker transferred 563 WETH to this address, and then transferred it to 0x1915F77A116dcE7E9b8F4C4E43CDF81e2aCf9C68. There is no further action at present.
The attacker's money laundering methods are relatively professional, and the methods show a trend of diversity. Therefore, for us Web3 participants, we must continuously improve our anti-money laundering capabilities in terms of security, and improve the security of Defi projects through relevant blockchain transaction security products such as KYT and AML.
Security Recommendations
Precision loss needs attention. Security issues caused by precision loss are endless, especially in Defi projects, where precision loss often leads to serious financial losses. It is recommended that project owners and security auditors carefully review the code with precision loss in the project, and do a good job of testing to avoid this vulnerability as much as possible.
It is recommended that the creation and initial mortgage casting of markets such as cToken in Compound be performed by privileged users to avoid being operated by attackers and thus manipulate the exchange rate.
When there are key variables in the contract that depend on the value of "this.balance" or "token.balanceOf()", it is necessary to carefully consider the conditions for changing the key variable, such as whether it is allowed to change the value of the variable directly by transferring the native currency or token to the contract, or whether the value of the variable can only be changed by calling a specific function.
 Cheng Yuan
Cheng Yuan
 Cheng Yuan
Cheng Yuan Cheng Yuan
Cheng Yuan Others
Others Others
Others Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph