Interpretation of Vitalik’s latest article
ETH, interpretation of Vitalik’s latest article Golden Finance, the soul of Ethereum and the essence of the crypto world remain.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
Source: Aiying Payment Compliance
From the data of Token Terminal, we can see that in the past four years, the monthly stablecoin transfer volume has increased tenfold, from $100 billion per month to $1 trillion. On June 20, 2024, the total transaction volume of the entire cryptocurrency market was $74.391 billion, and stablecoins accounted for 60.13% of it, about $44.71 billion. Among them, USDT (Tether) is the most used, with a market value of $112.24 billion, accounting for 69.5% of the total value of all stablecoins. On June 20, USDT's transaction volume reached $34.84 billion, accounting for 46.85% of the total transaction volume on that day. 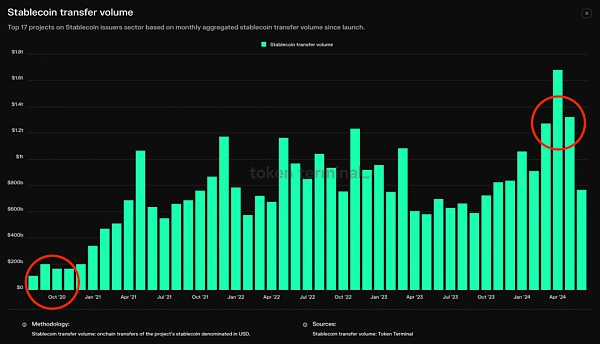
Stablecoins, as an important existence in the cryptocurrency market, are basically defined as cryptocurrencies that are linked to legal currencies or other assets to achieve stable value. The Bank of International Settlements defines stablecoins as "cryptocurrencies whose value is pegged to fiat currencies or other assets." This design aims to enable stablecoins to maintain a stable value relative to a specific asset or basket of assets to which they are pegged, thereby achieving a stable value storage and exchange medium. This mechanism is very similar to the gold standard, but because it is issued on the blockchain, it also has the characteristics of decentralization, peer-to-peer transactions, no need for central bank clearing, and immutability of crypto assets.
Aiying's report will delve into the definition of stablecoins and their main models, analyze the current market landscape and competitive situation, and focus on the operating principles, advantages and disadvantages of fiat currency collateral, crypto asset collateral, and algorithmic stablecoins, as well as the performance of different types of stablecoins in the market and future development prospects.
Stablecoins are literally cryptocurrencies with stable value. The Bank of International Settlements defines stablecoins as cryptocurrencies whose value is linked to legal currency or other assets. By extension, the main purpose of establishing stablecoins is to maintain a stable value relative to a specific asset or a basket of assets to which they are linked, so as to achieve a stable value storage and exchange medium, which is actually very similar to the gold standard. Since it is issued on the blockchain, it also has the decentralized, peer-to-peer, no need for central bank clearing, and non-tamperable characteristics of encrypted assets.
The main difference between the value stability of stablecoins and the pursuit of the stability of the value of legal currency by traditional central banks is that stablecoins pursue exchange rate parity relative to legal currency, while the value of legal currency pursues the stability of purchasing power across periods. In more popular terms, stablecoins essentially hope to anchor the legal currency system to achieve the stability of the value of tokens.
For stablecoins, if you want to ensure the anchoring of the legal currency system, according to the endorsement of the underlying assets, it is divided into two categories: collateral and uncollateralized, and from the issuance, it is divided into centralized and decentralized. For value stability, using real-world valuable assets as collateral and then issuing stablecoins to achieve anchoring with legal currency is the easiest and relatively safe way to achieve it. A higher collateral rate means sufficient solvency. According to the classification of collateral, it is further refined into legal currency collateral, crypto asset collateral, and other supporting asset collateral.
Specifically, there are the following subdivisions:
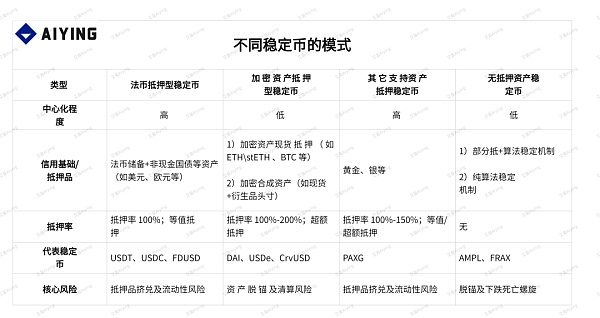
As can be seen from the above table, in terms of the basic operating model, the value stability of stablecoins mainly depends on collateral assets or algorithmic regulation to stabilize the price of stablecoins in a controllable legal currency exchange range. The key is not the fluctuation of the currency price, but how to reasonably correct this fluctuation so that it can operate in a stable range.
From the perspective of anchoring price, in addition to PAXG and other stablecoins anchored to gold prices, 99% of stablecoins are 1:1 anchored to the US dollar. There are also stablecoins anchored to other legal currencies, such as EURT anchored to the euro, with a market value of 38 million US dollars, and GYEN anchored to the Japanese yen, with a current market value of only 14 million US dollars; IDRT anchored to the Indonesian rupiah, with a market value of 11 million US dollars. The overall market value is very small.
The current proportion of stablecoins anchored to the US dollar is maintained at around 99.3%, and the rest are mainly composed of euros, Australian dollars, British pounds, Canadian dollars, Hong Kong dollars, and RMB.
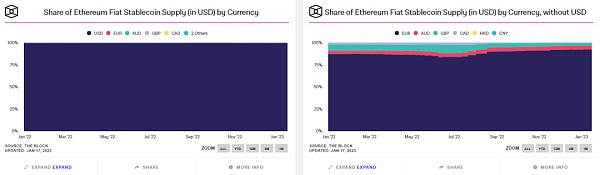
Market share of stablecoins anchored to fiat currencies Source: The Block
The issuance of stablecoins is closely related to the market. From the monitoring data, we can see that the issuance volume has continued to grow overall, but it has fallen back during the last round of bull-to-bear period (March 2022). It is currently in the marginal issuance upward stage, which also indicates the current bull market.
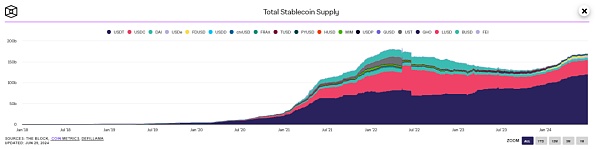
Chart 3: Historical issuance of stablecoins (Source: The Block)
According to the latest data from coingecko, as of May 4, USDT currently has a market share of 70.5% in the stablecoin market, followed by USDC 21.3%, DAI 3.39%, FDUSD 2.5%, and FRAX 0.41%.
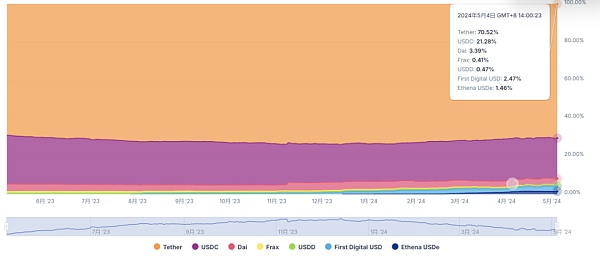
Chart 4: Market share of stablecoins Source: coingecko
In addition, from the perspective of market value, the current market value of all stablecoins is more than 160 billion US dollars, among which USDT is far ahead and has stable growth. The current market value exceeds 110 billion US dollars. The market value of USDC has risen steadily to more than 33 billion US dollars, but there is still a gap compared with USDT. Other stablecoins have remained basically stable.
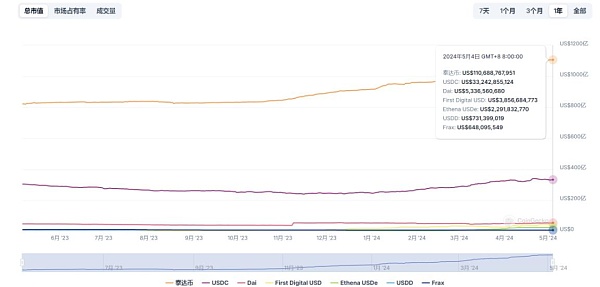
Chart 5: Market value of mainstream stablecoins Source: Coingecko
From the current top ten mainstream stablecoins, centralized US dollar-collateralized stablecoins are mainly composed of USDT\USDC\FDUSD, etc., with a broad collateral rate basically greater than 100%; DAI is a decentralized crypto-asset-collateralized stablecoin; USDe is a synthetic dollar, and the collateral is crypto assets; FRAX is an algorithmic stablecoin, and PAXG is a gold-collateralized stablecoin.
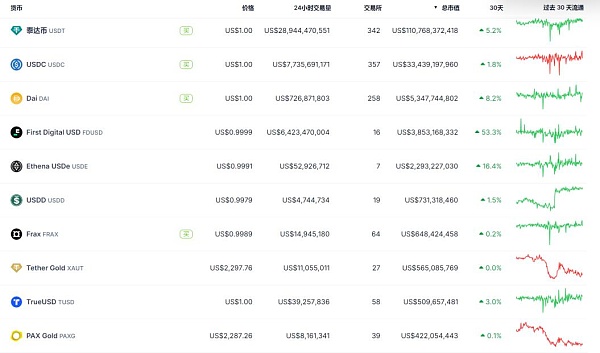
Chart 6: Market value of mainstream stablecoinsSource: Coingecko
From the changes in the coin holding addresses of the two, it can be clearly seen that the plunge in the coin holding addresses of the two is due to the decoupling from the US dollar. On March 11, 2023, USDC was affected by the SVB crash and was once decoupled from the US dollar. It fell to around 0.88, causing the coin holding address to decline rapidly. Although it subsequently recovered the lost ground, the coin holding address was once again pulled away by USDT.
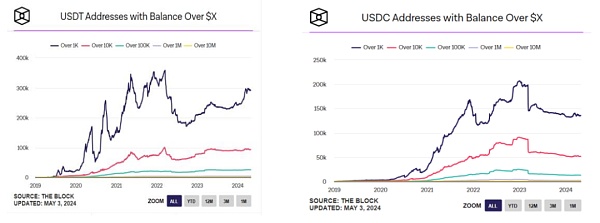
Chart 7: Changes in USDT vs USDC holding addressesSource: The Block
As can be seen from the above figure, after the depegging incident, the addresses of USDC have been reduced from more than 1,000 US dollars to more than 10 million US dollars. It has dropped by about 30% from the peak, while USDT has steadily increased.
Continuing from the above analysis, the current mainstream stablecoins are mainly distinguished by the type of collateral assets and the degree of centralization of issuance. Generally speaking, those collateralized by fiat currencies are mostly issued in a centralized manner and currently occupy the mainstream of the market; those collateralized by crypto assets or algorithmic stablecoins are mostly issued in a decentralized manner, and each track has its leader. Each stablecoin design framework has its advantages and disadvantages.
1) The main operating principle of USDT
Basic introduction:
In 2014, Tether, a subsidiary of iFinex, created the stablecoin USDT. At the same time, the company also owns the cryptocurrency exchange Bitfinex, which is registered in the British Virgin Islands and headquartered in Hong Kong. Tether is headquartered in Singapore. The current CEO is Paolo Ardoino (the company's former CTO), an Italian who mainly developed trading systems for hedge funds in the early days. He joined Bitfinex as an executive in 2014 and joined Tether in 2017. He currently owns 20% of Tether's shares.
Issuance and circulation:
It is mainly divided into five steps. The first step is that the user deposits US dollars into Tether's bank account; the second step is that Tether creates a corresponding Tether account for the user and mints USDT of corresponding value in his account; the third step is the transaction circulation between accounts; the fourth step is the redemption stage. If the user redeems US dollars, the USDT must be handed over to Tether. The fifth step is that Tether destroys the USDT of corresponding value and returns the US dollars to the user's bank account.
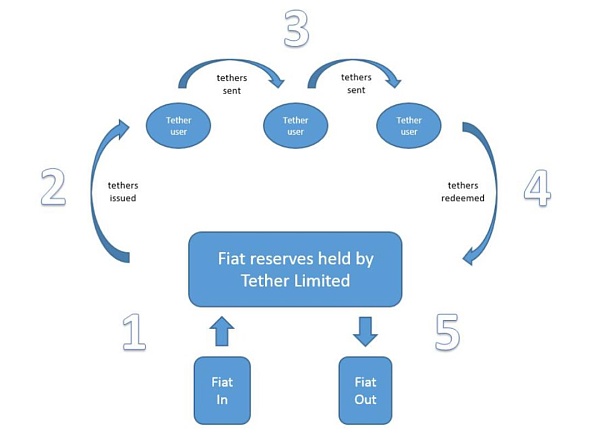
Chart 8: The whole process of USDT issuance, trading, circulation and recycling Source: Tether Company White Paper
Technical Implementation:
Tether issues USDT To realize the above process, it is necessary to embed blockchain technology. The overall technical architecture is not complicated and is mainly divided into three layers.
The first layer is the blockchain main network, which was mainly the Bitcoin blockchain in the early days and has now expanded to more than 200 public chains. The USDT transaction book is embedded in the blockchain through the Omni layer protocol.
The second layer is the Omni Layer Protocol, which mainly serves the Bitcoin blockchain and is used to mint, trade and store USDT. After 2019, USDT minting has gradually shifted to Tron and Ethereum, mainly using the TRC-20 and ERC-20 protocols.
The third layer is Tether, which is mainly responsible for the issuance and management and audit of mortgage assets.
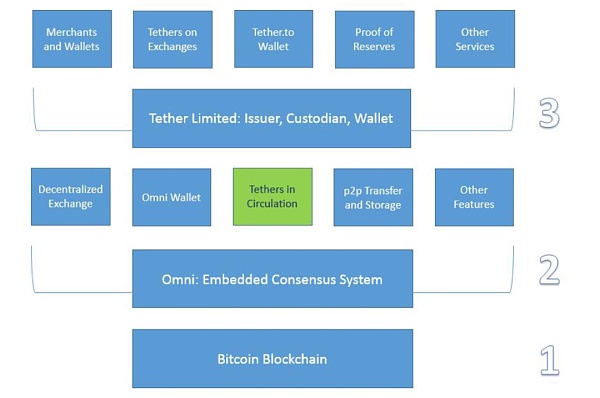
Figure 9: USDT technical implementation architecture (taking the Bitcoin network as an example) Source: Tether Company White Paper
In the above-mentioned issuance and technical implementation, the most fundamental is the Proof of Reserves mechanism operated by Tether. Specifically, as long as one USDT is minted, the corresponding Tether company must increase its reserves by $1. In other words, for every USDT it issues and mints, the corresponding collateral must increase by $1 to ensure 100% equal collateral.
Asset (collateral) reserves:
The total asset reserves are currently over 110 billion US dollars, which is consistent with its current market value. From the perspective of asset reserve categories; cash and cash equivalents account for 83%, and others account for 17%.
In terms of subdivision, among cash and cash equivalents, short-term US Treasury bonds account for the highest proportion of about 80%, followed by overnight reverse repurchase agreements at nearly 12%, and the rest are composed of money market funds, cash and bank deposits, regular repurchase agreements, and non-US Treasury bonds. Among other asset categories, they are mainly composed of Bitcoin, high-grade corporate bonds, precious metals, and mortgages, among which Bitcoin and mortgages account for a large proportion.
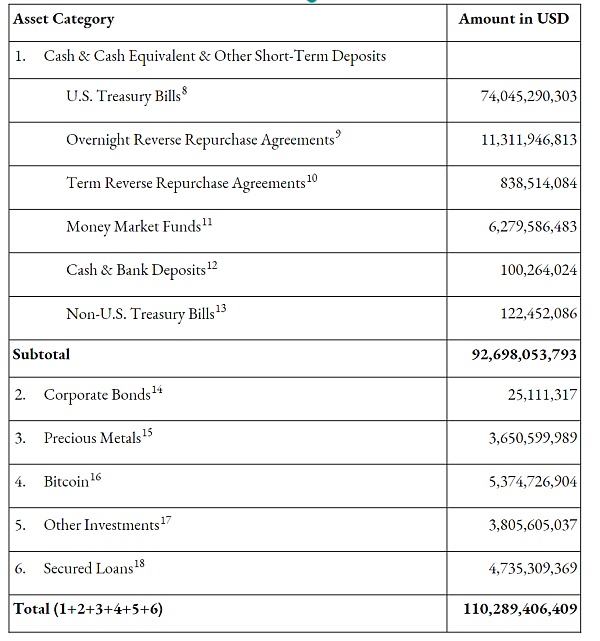
Chart 10: Composition of Tether's asset reserves (data as of the first quarter of 2024) Source: Tether official website
In addition, it can be seen from the audit reports of the past three years that Tether has kept up with the external macroeconomic environment in terms of asset reserves. The proportion of short-term U.S. Treasury bonds and money market funds has continued to expand, while corporate bonds, cash and bank deposits have been reduced. In addition, due to the different maturities of its assets, this is the most likely situation to lead to shorting USDT. According to the data revealed in the audit report, the Treasury bonds and term repurchase agreements currently held by it are all ultra-short-term, less than 90 days. The only longer ones are corporate bonds and non-U.S. Treasury bonds, with maturities of 150 days and 250 days or less.
The allocation of these reserve assets indirectly increases the returns on its asset operations, while also further reducing its risk factor. The security of assets is further improved, especially the shortening of maturity, which helps prevent short selling due to maturity mismatch.
Profit model:
Cost side: Very few technical and operation and maintenance personnel, with extremely low marginal costs
Revenue side: Service fee after KYC registration (US$150/person), deposit and withdrawal fees (about 0.1%), interest income (such as 4-5% income from short-term treasury bonds, but its cost is 0, and there are other loan interest income), custody fees (fees for some institutions to hold custody in Tether. In the first quarter of 2024, Tether announced that its net profit in the first quarter was US$4.5 billion, a record high, but its number of employees was only about 100. Goldman Sachs and Morgan, which have the same profit, have more than 50,000 employees. The efficiency of making money is very rare.
2) The main operating principle of USDC
Similar to USDT, USDC The main issuance, circulation and technical implementation of USDC are similar. 1USDC is pegged to 1 US dollar. It is a stable currency created by Coinbase and Circle in 2018. It is later than USDT, but there are some differences in the specific operational details:
Higher transparency of asset reserves: Compared with USDT's quarterly disclosure of asset reserves, USDC discloses its assets monthly. The asset reserves are audited by a third-party auditing agency every year. In the early days, it was mainly Grant Thornton, and it was changed to Deloitte in 2023. As of March 2024, the information disclosed was that USDC in circulation was US$32.2 billion, and Circle's equivalent assets were approximately US$32.2 billion. Basically the same.
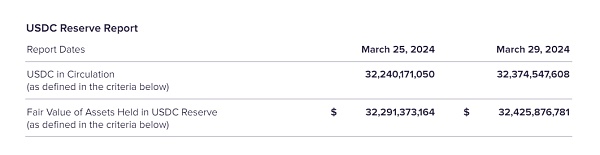
Chart 11: The entire process of USDT issuance, trading, circulation and recovery
The asset reserves are mostly short-term treasury bonds and cash, with shorter maturities and higher liquidity than USDT: Compared with USDT, which only discloses the overall maturity of treasury bonds, USDC will announce the maturity dates of its main treasury bond assets. According to the data disclosed in March, the maturity is within 3 months, and the latest is the short-term debt due in June, with an overall scale of US$11.4 billion; in addition, it is mainly repurchase agreements and cash reserves, totaling US$28.2 billion. In addition, there is US$4.2 billion in cash, all of which are placed in the CRF (Circle reserve Fund) registered by BlackRock in the SEC. Overall, it is similar About 95% of its assets are under the supervision of the SEC. In addition, due to the higher cash ratio of its assets, the liquidity at the redemption level is also higher than that of USDT.
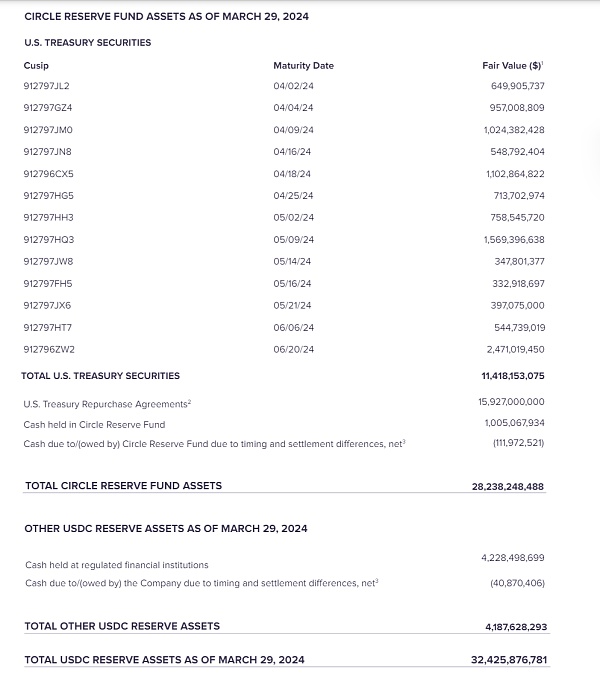
Chart 12: USDC reserve assets (as of March 2024) Source: Circle official website
The creation of USDC was carried out under the US regulatory framework, and its legal status is higher: Circle is registered as a money service business institution under the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network of the US Treasury Department, and is also carried out in accordance with the laws of various states on money transmission business. It is regulated as a prepayment method as a whole. Compared with USDT, USDC's reserve assets are independent. Assuming that Circle goes bankrupt, these reserve assets will be protected according to the New York Banking Law and the Federal Bankruptcy Law.
USDC is not directly exchanged with individuals. For USDT above $100,000, you can directly exchange it with Tether as long as you pay the registration fee, but Circle operates according to customer levels. Only its partners or Class A users (exchanges, financial institutions) are eligible to exchange with Circle. Individual ordinary users (Class B) need to go through third-party channels (such as coinbase). In addition, USDC and USDT are basically the same in terms of profit sources, but because USDC assets are mainly short-term treasury bonds and cash, the risk exposure is lower than USDT, so the yield is relatively low.
3) The main operating principle of FDUSD
After the New York State Department of Financial Services ordered the cryptocurrency company Paxos to stop issuing new BUSD, the world's largest exchange Binance also stopped supporting BUSD products on December 15, 2023, and announced that it would automatically convert BUSD balances into FDUSD. Since then, the market value of FDUSD has been rising all the way, occupying the third place in the fiat-collateralized stablecoin market.
Basic introduction:
FDUSD is a stablecoin anchored to the US dollar launched by FD121 (First Digital Labs) in June 23. The parent company, First Digital Trust, is a qualified custody and trust company in Hong Kong, mainly engaged in digital asset-related businesses. It was established by Legacy Trust in 2017 and officially separated in 2019 to become a completely independent public trust company. Legacy Trust is a well-established public trust company established in 1992.
Operation mode:
FDUSD is basically the same as USDT\USDC in terms of its operation mode. Users deposit US dollars, and the issuer casts the corresponding amount of FDUSD. Similarly, if US dollars are withdrawn, the corresponding amount of FDUSD will be destroyed. The auditor of FDUSD is Prescient Assurance (an accounting firm located in New York, one of the top 20 global security testing and auditing organizations certified by CREST), and the contract auditor is Paidun.
Asset disclosure and reserve status:
Similar to USDC, FDUSD also discloses its assets on a monthly basis. Its reserve assets are mainly managed by a public trust company in Hong Kong. It does not disclose the specific names of the financial institutions where the reserve assets are located, but it is clear that these financial institutions are all rated A-2 by Standard & Poor's. As of March 2024, the issued and circulated FDUSD is US$2.5 billion, and the corresponding reserve assets are also US$2.5 billion. In terms of reserve asset classification, short-term treasury bonds are US$1.86 billion, with the latest maturity date being May 21, fixed deposits are US$265 million, with a term of 1 month last night, and other cash assets are US$170 million. Overall, they are all ultra-short-term assets with very high liquidity and instant repayment effects.
4) Summary of the Fiat-collateralized Stablecoin Track
If you review the top three fiat-collateralized stablecoins, USDT, USDC, and FDUSD, you can clearly see
three different paths to success. A brief summary is as follows:
USDT: 1) The biggest advantage is the first-mover advantage, but its rise is mainly due to the support of exchanges and the outbreak of the market. At the beginning of the wild era of cryptocurrency, from the early Bitcoin blockchain to the later Ethereum ecosystem, USDT was a well-deserved pioneer and also accurately guessed the market explosion. Looking back at its currency holding addresses and market value, although it was established in 2014, it really started to rise in 2017. In addition to the bull market that year, USDT began to issue super-new shares, which was criticized by the market for manipulating the price of Bitcoin. However, in hindsight, this is a reversal of cause and effect. What is easily overlooked is that China closed down virtual currency that year, and more importantly, USDT was launched on the top three exchanges at the same time that year. 2) Suffering from risk events, but responding promptly and appropriately, quickly regaining market confidence. Bitfinex, an affiliated company of Tether, was once considered a company by the outside world. It was attacked by hackers and fined by the US government from 2014 to 2016. Tether was cut off from international wire transfers by Wells Fargo and Taiwan Bank, and even decoupled from the US dollar. Tether's main response was to quickly disclose its asset reserves, including its excess reserves and undistributed profits, to restore market confidence through the health of its financial situation. Regardless of whether its information was falsified, it did respond to market concerns very effectively. Through first-mover advantage and several market public relations, USDT has formed a strong consumption habit for consumers. It is still the most preferred stablecoin for deposits and withdrawals, including the trading pairs covering the most exchanges.
USDC: 1) Rising at the time of the USDT crisis, transparent, regulated, and more liquid asset reserves have won the favor of customers. If we look back at the rise of USDC, the surge in its currency holding addresses usually corresponds to the decline in USDT holdings, which is usually when USDT has risk events, especially because it was the only stablecoin trading pair of the compliant exchange Coinbase in the early days. This regulatory blessing brought great benefits to the early expansion of the USDC market and was also its main competitiveness in impacting the top spot of USDT. 2) Due to compliance, Defi protocols prefer USDC, and liquidity mining has enabled USDC to quickly increase in volume and gain more advantages on the chain. After Maker introduced the regulated stablecoin USDC in 2020, USDC became the first choice for major Defi protocols. Currently, the three major Defi protocols MakerDAO, Compound and Aave are the main supporters of USDC. In addition to the benefits of regulation, more importantly, as the collateral of Defi protocols, USDC has lower volatility than USDT. USDC's victory can be summarized as a victory of compliance. However, it is worth noting that since USDC is a compliant collateral, in August 2023, Circle froze the USDC of Tornado Cash (money laundering charges) in accordance with the instructions of the U.S. Treasury Department, which also planted the seeds of disagreement on whether decentralized Defi protocols should rely too much on centralized stablecoins.
FDUSD: 1) The support of top exchanges and implicit regulatory compliance have become one of the main reasons for the rise of FDUSD. Binance, the top 1 cryptocurrency exchange, decided to abandon BUSD in 2023 and switched to supporting FDUSD as the only designated stablecoin for its Launchpad and Launchpool liquidity mining in July of that year. Thanks to the huge profits from Binance mining and new listings, the overall market value of FDUSD has grown rapidly and has quickly grown into the top three fiat-collateralized stablecoins in the market. Binance's support can be said to be the most direct factor in the rise of FDUSD. More importantly, the market is not short of legally regulated stablecoins (USDC). Binance's choice is more concerned with the regulatory environment in Hong Kong and the attitude of the United States towards Binance. As a result, FDUSD, which was born in Hong Kong, has become the best choice. 2) Scenario-based and wealth effects determine its growth rate and upper limit. Assuming that FDUSD is adopted by exchanges, it will be difficult to rise without a suitable application scenario. After listing on Binance, FDUSD has become the only mining cryptocurrency on Launchpool and Launchpad (the other is BNB). Since its launch, the average annual mining income through FDUSD mining is close to 70%, which is a relatively high income for short-term mining users. This alone has rapidly increased the usage rate of FDUSD.
In general, for stablecoins that are only collateralized by fiat currencies, their success is inseparable from several important factors:
Whether it is launched under the regulatory framework is conducive to gaining user trust in the early stage. For example, USDC, FDUSD, etc. are all like this.
It is the audit, security and transparency advantages of proof of reserves. (For example, TUSD will start real-time auditing in 2023, including using chainlink to ensure the security of coinage, making this old stablecoin shine again; the rise of USDC is also due to this factor).
It is the support and extensive cooperation of exchanges that determine the lower limit of development. From USDT to USDC and FDUSD, the rise is inseparable from the support of exchanges. Only with the huge liquidity support of these exchanges can stablecoins achieve a smooth start.
Application scenarios and wealth effects determine the speed and upper limit of development. Typical examples include FDUSD, USDC, and PYUSD (parasitic on the Paypal wallet) launched by PayPal. The key to their rapid development is that they have formed a strong wealth effect or more convenient services in a certain segmented scenario, thereby increasing the user adoption rate.
Due to the huge volatility of crypto assets, their credit basis is weaker than that of risk-free assets in US dollars (government bonds, US dollar deposits), so they are generally over-collateralized. However, synthetic dollars through derivative hedging models can also achieve a collateralization rate close to 100%; but due to the crypto assets used, they usually have decentralized characteristics.
1) The main operating principle of DAI
Basic introduction:
DAI is currently the leader of decentralized stablecoins, Maker DAO, which was officially issued and managed in 2017. MakerDAO is a decentralized finance (DeFi) project headquartered in San Francisco, USA, and its founder is Rune Christensen. Project investors include A16z, Paradigm, Polychain Capital and other well-known investment institutions in the crypto industry. In the early days, it was mainly operated by the Maker Foundation. Currently, its community manages (holds MRK tokens) stablecoins through a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO).
Main operating mechanism:
DAI is also 1:1 anchored to the US dollar as a whole. The Maker protocol launched the collateralized DAI in 2017, mainly allowing users to mint DAI by staking ETH; in 2019, it launched multi-collateral DAI, accepting collateral other than ETH. In addition to changes in collateral, DAI deposit interest was introduced to support stablecoin interest. In addition, the collateral bond warehouse was renamed the vault, and the stablecoin generated by a single collateral was renamed SAI.
The creation process is as follows.
Step 1Create a vault through the Oasis Borrow portal or community-created interfaces such as Instadapp, Zerion, MyEtherWallet, and lock in a specific type and amount of collateral to generate Dai (Maker Protocol currently also supports RWA assets as collateral, such as real estate mortgages and accounts receivable).
Step 2Initiate and confirm transactions through crypto wallets, and generate DAI (equivalent to collateral lending) at the same time.
Step 3If you want to redeem the collateral, the user needs to repay the corresponding amount of DAI (equivalent to repaying the debt) and pay a stability fee (equivalent to risk compensation, or it can be regarded as a risk parameter to adjust supply and demand and maintain the 1:1 peg between DAI and the US dollar. In a bull market, the stability fee can be as high as 15% or more). Step 4, the Maker Protocol will automatically destroy the DAI and return the collateral assets to the user.
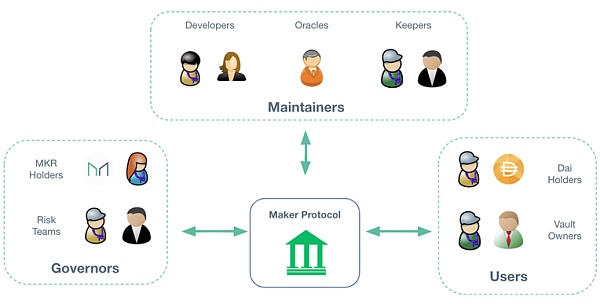
Chart 13: Maker Protocol ParticipantsSource: Maker Official Website
DAI's price stabilization mechanism. Compared with the stablecoins collateralized by fiat currencies, its pledged assets have risk-free characteristics and high liquidity, which are hard anchors, and the price range can be quickly stabilized through reserve assets. For decentralized stablecoins collateralized by crypto assets, the volatility and transactions of the crypto market itself will lead to the price difference of the anchor, so a price stabilization mechanism needs to be set to stabilize it. It is mainly through interest rate adjustment and liquidation. The interest rate mainly involves the stabilization rate and the DAI deposit rate (DSR). The stabilization rate is based on the risk factor of continuous peg to the US dollar, which is equivalent to the loan interest; the DSR is equivalent to obtaining the basic yield or deposit rate of DAI. This stability logic is similar to traditional bank lending. Assuming that the loan income (stability fee income) is lower than the DSR income (interest expenses on deposited DAI), the protocol as a whole will have bad debts. To make up for the bad debts, it is necessary to issue additional MRK (governance tokens), and the bearer will be passed on to the MKR holder. This mechanism also ensures that everyone is fair and reasonable when voting for the stability fee.
DAI's liquidation mechanism. Just like traditional credit, if the value of the collateral drops significantly and the assets are insufficient to cover the liabilities, the bank will face forced recovery. DAI also sets up the same mechanism, using a Dutch auction (price ladder decreases, bid is the transaction), and the main auction startup mode is determined by the ratio of the collateral value to the debt (liquidation rate), and the vaults created by different users have different liquidation rates. For example, if the collateral is ETH, the pledge rate is 75%, and the market price is 3000U, then the user can get a maximum of 2250U of DAI. For insurance purposes, the user only took 2000U of DAI. At this time, the collateral asset coverage ratio is 1.5, and the use exposure is 66.7%. Generally, when facing liquidation, the exposure utilization ratio is greater than the pledge rate, that is, when ETH falls to 2666U, it faces liquidation risk. DAI's anchored stability protocol. It is difficult to understand literally. If expressed in traditional financial terms, it is a currency swap agreement. The simple operation is the exchange of DAI and stablecoin assets such as USDC. In other words, if a user deposits 1USDC, 1DAI can also be minted at a 1:1 exchange rate. In addition, through the stablecoin swap, the protocol converts the USDC and other legal stablecoins in the reserve pool into US dollars for investment in short-term US bonds, further increasing its returns, feeding back its DSR returns, and attracting users.
DAI's profit analysis. Mainly through stability fee income (loan interest), analogous to the funding rate of USDT deposit and withdrawal. Liquidation penalty income; stablecoin swap transaction fees of anchoring modules; and investment income of pledged RWA. The protocol revenue in 2023 is US$96 million.
2) The main operating principle of USDe
Basic introduction:
USDe is a decentralized on-chain stablecoin created by Ethena Labs. Its early concept was proposed by Arthur Hayes, a famous KOL in the currency circle. At the same time, the project has also received investment from Arthur Hayes, the founder of BitMEX, and his family fund. In addition, it also includes the support of a number of giant funds such as Deribit, Bybit, OKX, Gemini, etc. After going online on February 19, 2024, the supply has skyrocketed and has entered the top five in the stablecoin supply industry, second only to FDUSD.
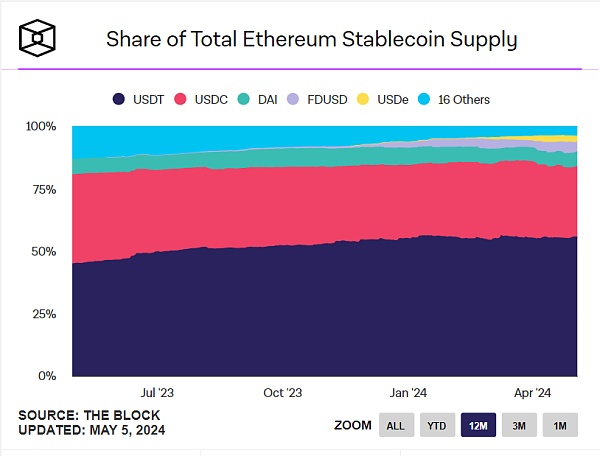
Chart 14: Top five stablecoin supply (as of May 2024) Source: The Block
How USDe works: Application of neutral hedging strategy in cryptocurrency
Ethena Labs' USDe is a synthetic dollar protocol. In cryptocurrency, the so-called synthetic dollar protocol is to achieve a stable peg between the issued stablecoin and the US dollar through a series of crypto derivatives.
In specific operations, USDe uses a delta neutral strategy. Traditionally, Delta = option price change / underlying asset price change, then Delta neutrality generally refers to the value of the investment portfolio in finance. It is not affected by small price changes of assets, which is generally called delta neutrality (delta is 0).
Ethena's neutral strategy operates as follows. The user mints 1USDe of Ethena stablecoin, and ENA will also deposit 1 USD worth of ETH on the derivatives exchange, and establish a perpetual contract to short 1ETHUSD. If ETH falls 10 times, the contract will earn a profit of 9ETH, and ENA's total position will be 10 ETH. Since the price has also fallen 10 times, it is equivalent to the total value of its holdings not changing; the same is true for price increases. This ensures the stability of minted stablecoins. If the user chooses to redeem USDe, ENA will quickly close the short contract. The collateral of USDe is actually spot ETH and the corresponding short order. Under bull market conditions, it is basically 100% fully collateralized. If ENA tokens are included, the broad collateral rate exceeds 120%.
The secret of USDe's rapid rise: a Ponzi-like mechanism, but more than just a Ponzi, it is essentially a term arbitrage financial product.
First of all, for users who mint USDe, they can quickly stake it in Ethena after the minting is completed to obtain the staking income. Compared with other stablecoins such as USDT, you can't enjoy dividends at all. In traditional finance, in other words, any currency issuance will collect seigniorage, and the existing USDT does not share at all. USDe directly takes out the staking income. This alone is enough to attract large institutions to participate. After all, when MakerDAO achieved a yield of 8%, the market had already taken off directly, not to mention that the income of sUSDe (staking USDe certificate) once exceeded 30%.
Secondly, for $ENA, it is the platform governance currency of the project party. While the project party pledges USDe to obtain basic income, it also gives ENA token rewards. At the same time, conversely, if you hold ENA, you can also participate in staking, which will also increase the reward for staking USDe accordingly.
Fundamentally speaking, USDe has built a stablecoin architecture based entirely on ETH as the underlying asset. Its core anchor is to maintain the value stability of the collateral through derivative futures contracts, which is used as a key model. At the same time, in order to attract users, the constructed investment portfolio returns are returned to users who mint stablecoins, so that users can not only enjoy the stability of the stablecoin price, but also enjoy the dividends of the seigniorage; at the same time, the platform currency ENA is issued. Not only can you get ENA by staking USDe, but also, in reverse, you can increase the income of your staking stablecoins. It has Ponzi properties, but it is not a simple Ponzi, because its core profit model is a term arbitrage. As an individual, you can actually use this method. ENA only pools everyone's funds to make a larger profit collection.
USDe's profit model:
USDe's minting itself requires users' stETH, and at the same time cooperates to do short orders for perpetual contracts. There are two parts of income here, one is the staking income of stETH (APY3%-4%), and the other is the funding rate for eating short orders. The funding rate mechanism of perpetual contracts is relatively simple. In order to equalize the contract and spot prices as much as possible, when the market has more long orders than short orders, the longs pay the shorts funding fees; conversely, the shorts pay the longs. In a bull market, the funding rate for longs is generally relatively high (APY25%), otherwise it will be difficult to attract counterparties. This part is the biggest profit of the project. It is worth noting that the project party deposited stETH not on a general CEX, but on custodial platforms such as Cobo and CEFFU to prevent misappropriation or CEX crashes.
USDe core risk:
USDe is a crypto-asset collateral stablecoin. Its most basic model is futures-spot arbitrage. The value of the collateral is actually spot ETH and the corresponding short orders. Under bull market conditions, it is basically 100% fully collateralized, not to mention the circulating market value of ENA itself, which means that there is no risk of thunderstorms at this stage. However, there is an exception that ETH's LST collateral (stETH) is decoupled from ETH itself. The most recent precedent is that when 3AC thunderstorms, stETH was once decoupled by nearly 8%. The biggest risk is the scale limit. If the proportion of short positions in a single exchange is too large, it is likely to face the problem of no counterparty, which will lead to a decline in funding rate income. Judging from the current market situation, the upper limit of safe casting is about 10 billion US dollars. The second is the sustainability of the pledge yield, which is an obvious problem without going into details. There is also the custody model of ENA, which theoretically also has the risk of evil, or even bankruptcy, which will trigger a series of leveraged liquidations. The last and biggest risk is the risk of the project party, who may run away with the money.
3) Summary of the Crypto-asset Collateralized Stablecoin Track
Compared with the stablecoins collateralized by fiat currencies, the crypto-asset collateralized stablecoins do not actually rely on scenarios and centralized exchanges. Whether it is DAI or USDe, their paths to success are highly consistent, with wealth effects and transparent management. Both DAI and USDe were born in the bull market and grew rapidly. Thanks to the growth of the bull market, the lending agreement derived from DAI has given retail investors the opportunity to leverage and gain higher returns. At the same time, compared with the stablecoins collateralized by fiat currencies, the crypto-asset collateralized stablecoins basically have basic deposit returns. As an anchor to attract customers, they can be regarded as interest-bearing assets. The wealth effect brought by high returns is the main reason why crypto-collateralized stablecoins can gain a foothold and spiral upward. Compared with USDT and USDC, if you simply hold them, you cannot enjoy interest-bearing dividends. At the same time, the asset may depreciate due to changes in the US dollar exchange rate or inflation.
The last peak of algorithmic stablecoins was UST, an algorithmic stablecoin created by LUNA, which eventually collapsed due to its Ponzi mechanism. So far, no popular algorithmic stablecoins have appeared in the market, and projects such as FRAX are not very popular at present. Algorithmic stablecoins have two modes: single-token and multi-token. The former is the main mode of early stablecoins, such as AMPL, ESD, etc. The latter is mainly FRAX (hybrid algorithmic stablecoin). The biggest flaw of a single-token pure algorithmic stablecoin is that unless it is designed as a Ponzi model (high yield), it is almost impossible to form a good scenario in terms of growth, and due to the extreme volatility of the crypto market, it is difficult to encourage users to have confidence in the algorithm itself. On this basis, FRAX has developed a model of hybrid algorithmic stablecoins.
FRAX has designed a relatively complex hybrid stablecoin with a collateral + algorithmic model. The collateral is mainly USDC and FXS (project governance token). Its core foothold is based on arbitrage trading.
The main operating logic is:
When the protocol was first launched, it took 1USDC to mint 1 FRAX. As the market demand for FRAX increased, the USDC pledge rate dropped accordingly. If it was adjusted to 90%, it would only take 0.9USDC to mint 1FRAX, and burn 0.1 FXS tokens. If redeemed, the return would be 0.9USDC and 0.1 FXS. This model must be stable, and it essentially relies on arbitrage trading. If FRAX is less than 1 US dollar, arbitrage trading will buy FRAX, then redeem USDC and FXS, and simultaneously sell FXS for profit. As the demand for FRAX in arbitrage trading increases, the exchange rate can be restored. And vice versa. In the latest second version, the project introduced the algorithmic market controller (AMO). The main progress is that under the premise of FRAX 1:1 anchoring to the US dollar, the collateral of the protocol is placed in other Defi protocols to earn revenue.
Main profit model: the cost of minting and destroying stablecoins, the income in various Defi protocols under the AMO mechanism; FRAX lending. In addition, you can also use pledged ETH and other assets to stake nodes and obtain income. The current total market value exceeds US$600 million. Core bottleneck: Whether compared with stablecoins such as USDC/USDT and DAI, even if FRAX has improved security through semi-staking, its upper limit is currently limited due to scenario restrictions (arbitrage within the ecosystem). This is also the main bottleneck of stablecoins, how to expand its application scenarios in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Whether it is fiat currency collateral, cryptocurrency collateral or uncollateralized stablecoins, the degree of decentralization, capital efficiency, and price stability of stablecoins have their own advantages and disadvantages and the key to their development.
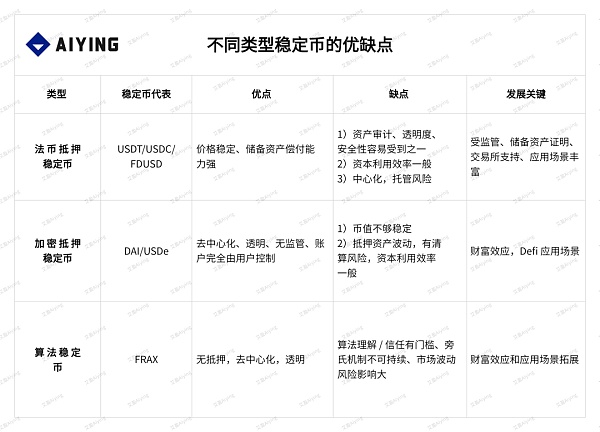
Through the inventory of the stablecoin track, we can see that whether it is fiat currency collateral, crypto collateral, or algorithmic stablecoin. Their common feature is the support of application scenarios. Either they have sufficient convenience and credit endorsement, or the use of their stablecoins in the scenario can earn benefits for users. The rise of USDC proves the importance of regulated endorsement, the rise of FDUSD proves the importance of scenarios brought by exchange drainage, and the rapid outbreak of USDe has once again practiced that the only most powerful driving force for cryptocurrency projects is always the wealth effect.
Based on the above summary and analysis, if a stablecoin project wants to find market recognition. Under the existing market structure, its path is relatively clear.
1) If it is a fiat currency collateralized stablecoin. The two necessary conditions for success are the trust foundation of compliance supervision and the scenario blessing brought by the drainage of exchanges/payment institutions. Both are indispensable.
2) Crypto collateral and calculation stability. The necessary conditions for success are: one is the basic rate of return/high rate of return, which can solve the user's demand for efficient turnover of crypto assets; the other is the continuously expanding Defi/payment application scenarios. If the above two points are met, a stablecoin project will initially have the possibility of success. In addition, the project party will always need to seek trade-offs and balances in the three aspects of capital efficiency, value stability, and decentralization.
For Hong Kong, put aside the peg to the US dollar. The remaining pegs are the Hong Kong dollar and the offshore RMB. In addition to the rigidity of supervision, purely from the perspective of the minting of stablecoins, there is almost no difficulty in reality, but the more difficult is the application scenario problem after minting (or the circulation problem), if it cannot be used for large-scale real physical world payments or cross-border remittances. Just in the crypto world itself, even if there are large exchanges cooperating with it, there are also major obstacles, after all, the credit and circulation of the US dollar are stronger. From a regulatory perspective, the Hong Kong stablecoin regulatory framework will be launched sooner or later, especially after the Hong Kong virtual asset photography takes effect in 2023, the regulatory trend of stablecoins will be relatively clear. If the Hong Kong dollar is used as the legal tender pegged to it, the application can be expanded in the following aspects:
1) Introduce the interest-bearing effect of crypto assets into legal tender pledge. That is, the assets pledged by the Hong Kong dollar will be distributed to users through the income of the pledged assets, so as to gain the early trust of users.
2) Hong Kong dollar stable currency payment. Expand it into a payment tool rather than a simple transaction medium, including cross-border trade settled in Hong Kong dollars. In addition, since the Hong Kong dollar and the US dollar are linked at a fixed exchange rate, if it is not a financial product/payment tool with income, its necessity and attractiveness are almost rare. In addition to the Hong Kong dollar, Hong Kong also has more than 10 trillion offshore RMB and RMB assets (including offshore RMB bonds), of which offshore deposits are nearly 1.5 trillion, mainly concentrated in Hong Kong, Singapore and other places. In fact, offshore RMB stablecoins are not new, such as TCHN launched by Tron, CNHT launched by Tether, CNHC issued by CNHC Group (the project owner was arrested in the mainland in 2023, but not because of the stablecoin project), etc. The main reasons why it has not grown yet are, on the one hand, the uncertainty of Hong Kong's regulatory framework, and on the other hand, the lack of a suitable entry point. For offshore RMB, the key points are as follows:
1) Offshore RMB is not subject to domestic foreign exchange controls, but the identity of the asset holder is still an obstacle.
From the perspective of the People's Bank of China, the most important thing is the legal status of the RMB. If only the stable currency is pegged to the offshore RMB, on the one hand, it is conducive to the internationalization of the RMB, and more importantly, it is conducive to the activation of the huge offshore RMB assets. The biggest bottleneck at present is that most of the holders of offshore RMB are from mainland China,
which still poses considerable difficulties and obstacles in actual operation.
2) There is institutional endorsement from banks such as Bank of China (Hong Kong). Bank of China (Hong Kong) is the clearing bank for offshore RMB. If
an offshore stable currency is issued, and the subsequent clearing and custody are bound to Bank of China (Hong Kong), then its core trust foundation can be solved.
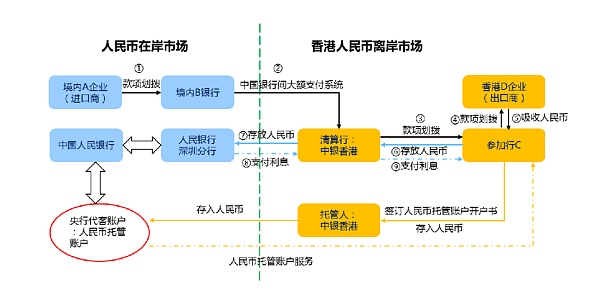
Chart 15: Onshore and offshore RMB flows under cross-border trade
3) Expanding payment and procurement scenarios under cross-border trade will be the core scenario application of offshore RMB.
Currently, offshore RMB CNH mainly comes from cross-border trade, procurement, and payment, and then forms a retention in Hong Kong/Singapore, especially in the Belt and Road countries. Because from the perspective of global offshore US dollars, most countries are very short of US dollars, and many countries' local currencies are unstable, so trade with China will be deposited in the form of RMB. Through the offshore RMB stablecoin/USDC trading pair, the channel for RMB to exchange for US dollars in the Belt and Road countries will be greatly improved. In addition, for payments under trade, we can cooperate with cross-border payment institutions to explore payment scenarios for e-commerce, games, and commodity transactions.
4) We can try to build a unique income model for offshore RMB. In addition to the traditional minting and redemption fees, the key is how to give back to users' income expectations. You can also try to mix RMB collateral with US dollar asset collateral to achieve exchange rate neutrality, achieve higher stability, and obtain two-way short-term asset financial management income, which can then be used as the basic income of stablecoins. In addition, it is also possible to consider the securitization and on-chain issuance of high-grade credit subject physical assets (RWA) abroad as another anchoring direction for stablecoin income (refer to DAI), including the foreign exchange derivatives market of offshore RMB. In addition, offshore bonds of up to 300 billion yuan per year can also be issued in a tokenized manner.
On the whole, the biggest difficulty for both Hong Kong dollar stablecoins and offshore RMB is not in issuance, but in the design of application scenarios. From the perspective of future trend development, offshore RMB has a wider application space and scenarios than Hong Kong dollars. If it is strongly anchored to the RMB and regulated under the Hong Kong framework, it will not directly conflict with the legal tender status of the RMB, but it will be beneficial in that it can expand the convenience of offshore RMB payments (no need to open a bank account, payment anytime, anywhere), while enriching the global issuance of domestic RMB assets and greatly expanding the global flow of domestic RMB assets. This has a certain policy space and acceptance in the current cycle of stricter foreign exchange controls and economic downturn.
ETH, interpretation of Vitalik’s latest article Golden Finance, the soul of Ethereum and the essence of the crypto world remain.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceMembers of the crypto community on X are abuzz with speculation about Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin's recent deposit of $330K worth of crypto into Railgun's privacy protocol.
 Kikyo
KikyoVitalik transferred 100 ETH to the privacy protocol RAILGUN, and then tweeted again to like RAILGUN, saying that privacy is normal and Railgun uses a privacy pool protocol, which makes it more difficult for bad actors to join the pool without compromising user privacy.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceVitalik has joined forces with four co-authors to unveil in a research paper that introduces a technological marvel known as "privacy pools," designed to address one of the most pressing issues in the blockchain sphere.
 Catherine
CatherineThe new update includes “The Scourge” which would help to solve MEV issues.
 Beincrypto
BeincryptoWhat a decade of essays – covering everything from Soulbound tokens to superrational DAOs – says about Ethereum and crypto.
 Coindesk
CoindeskThe inventor of Ethereum Vitalik Buterin and his father Dmitry “Dima” Buterin talked about the crypto market, volatility, and speculators. ...
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistCompared with PoW, PoS is a better blockchain security mechanism.
 链向资讯
链向资讯Compared with PoW, PoS is a better blockchain security mechanism.
 Ftftx
FtftxThe small southeast European nation is beginning to sift through the murky waters of blockchain regulation by granting the Ethereum co-founder citizenship.
 Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph