Source: Beosin
Reference source: Top Centralized Exchange Hacks: Lessons Learned from History
In recent years, centralized exchanges (CEXs) like Mt. Gox and WazirX have suffered major losses from external hacks, while others like FTX have collapsed due to internal fund misuse. Even industry giants Binance and Coinbase face existential threats from the world's most powerful financial regulators.
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) can effectively defend against the three major threats - hacks, fraud, and overregulation - that have plagued CEXs. Of course, there are other threats besides "hacks." For example, the downfall of FTX involved its executives' mismanagement and misuse of customer funds, which is less feasible on DEXs because the inherent structure of DEXs promotes transparency and user control.
This article explores the biggest breaches in the history of top centralized exchange hacks, from infamous intrusions to systemic vulnerabilities, the cryptocurrency world has experienced turmoil. Here, we review the top 10 worst centralized exchange hacks.
10. Bithumb Hack: Repeated Hacks
Founded in 2014, Bithumb quickly became a cornerstone of the South Korean cryptocurrency market, with over 8 million registered users and over $1 trillion in trading volume. Despite its prominence, Bithumb has been repeatedly hacked.
Starting in 2017, Bithumb suffered multiple breaches:
February 2017: Hackers stole $7 million.
June 2018: Employee personal data was used to steal nearly $32 million in cryptocurrency.
March 2019: Bithumb announced it had been hacked again, suspending deposits and withdrawals after losing around $20 million in EOS and XRP.
June 2019: Bithumb was attacked again, and hackers stole $30 million worth of digital tokens.
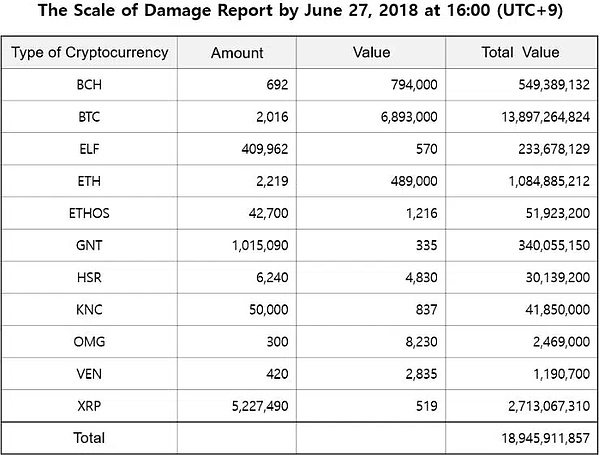 Bithumb reported stolen assets during the June 2018 hack
Bithumb reported stolen assets during the June 2018 hack
In response to the repeated violations, the Ministry of Science and Technology (MIC) launched a thorough investigation, and the main findings included:
Inadequate network isolation.
Poor monitoring system that failed to distinguish between normal and suspicious activities.
Inadequate management of encryption keys and passwords.
9. WazirX Crypto Hack
More than $473 million worth of crypto was lost to hacks and fraud in 108 incidents in 2024. WazirX alone accounted for 86.4% of the total amount of crypto lost to hacks in July.
Indian CEX WazirX announced plans to reverse all transactions after freezing withdrawals on July 18, 2024. On that day, WazirX suffered a major wallet vulnerability attack, resulting in the unauthorized transfer of more than $230 million in crypto assets. The attack targeted WazirX's multi-signature wallet on Ethereum.
Over $100 million in Shiba Inu (SHIB), 20 million MATIC tokens ($11 million), 640 billion PEPE tokens ($7.5 million), 5.7 million USDT, and 135 million GALA tokens ($3.5 million) were stolen.
Despite advanced security measures such as hardware wallets and address whitelisting, WazirX suffered a sophisticated attack.
8. Binance Hack: A Grim Reminder of Crypto Vulnerabilities
In 2019, Binance, the world’s leading cryptocurrency exchange, suffered a major centralized exchange hack. On May 7, malicious attackers used phishing and viruses to attack Binance’s security systems and steal users’ two-factor authentication codes and API keys.
8. Binance Hack: A Grim Reminder of Crypto Vulnerabilities
In 2019, Binance, the world’s leading cryptocurrency exchange, suffered a major centralized exchange hack. On May 7, malicious attackers used phishing and viruses to attack Binance’s security systems and steal users’ two-factor authentication codes and API keys.
The breach allowed them to steal 7,074 Bitcoins from the exchange’s hot wallet in a single transaction, worth more than $40 million at the time.
Following the incident, Binance CEO Changpeng Zhao announced the creation of the Secure Asset Fund for Users (SAFU) to protect users’ funds in extreme cases. Despite these measures, Binance faced another major security challenge in October 2022. Hackers used the cross-chain bridge BSC Token Hub to illegally generate and steal 2 million BNB tokens, equivalent to approximately $570 million.
7. KuCoin: Suffered a Hollywood-style heist
In September 2020, KuCoin suffered a Hollywood-style heist that ranks among the top centralized exchange hacks. The hackers first launched a cunning attack to steal Bitcoin and Ethereum into a mysterious wallet. The conspiracy became more complex as the digital thieves gained access to the vault by stealing the private keys of KuCoin’s hot wallets.
The next day, the crypto community was already on edge when KuCoin CEO Johnny Lyu addressed the world in a live stream. The KuCoin team responded quickly, moving the remaining funds to a new hot wallet, closing the stolen wallet, and temporarily freezing all customer transactions to mitigate further risk.
Further investigation revealed that the stolen funds involved a variety of cryptocurrencies including BTC, ETH, LTC, XRP, totaling approximately $281 million. Despite the heavy losses, the proactive measures taken by KuCoin recovered approximately $204 million of the stolen funds within a few weeks.
Even more intriguingly, KuCoin worked with international law enforcement to attribute the cyberattack to a suspected North Korean hacking group.
6. BitGrail: An Inside Job
Italian cryptocurrency exchange BitGrail is embroiled in controversy after €120 million ($146.55 million) was stolen from its platform. Italian police have accused Firano, also known as “FF,” of either participating in the hack or negligently failing to strengthen security measures after the initial discovery of the breach.
The series of events resulted in the loss of funds for approximately 230,000 users, and Firano faces charges including computer fraud, fraudulent bankruptcy, and money laundering, in one of the largest financial breaches in Italian history.
In the aftermath, the Italian bankruptcy court took decisive action and declared Firano and BitGrail bankrupt. The court also ordered Firano to return as much of the stolen assets as possible to its customers.
In addition, the court approved the seizure of Firano’s assets, including more than $1 million in personal items and millions in cryptocurrency in BitGrail accounts. The court found that a software flaw in the BitGrail platform led to multiple improper withdrawal requests.
In CEXs like BitGrail, control of all assets and security measures is centralized, making them an attractive target for hackers.
5. Poloniex: A Tale of Two Hacks
Poloniex has suffered two serious security breaches.
In March 2014, hackers exploited a software vulnerability to steal 97 Bitcoins, or 12.3% of the exchange’s Bitcoin holdings at the time. Despite the setback, Poloniex managed to rebound and fully compensated affected users.
Fast forward to November 2023, the exchange was hacked again, this time on a much more serious scale. The attackers, suspected to be the North Korea-linked Lazarus group, stole private keys and stole approximately $126 million from Poloniex’s hot wallets.
The modus operandi included the use of social engineering and malware to obtain critical private keys. After the hack, the hackers adopted complex strategies, including sending different tokens to specific addresses and using decentralized exchanges to launder the money, which made it difficult to track and recover.
4. Bitstamp theft
The cybercriminals targeted Bitstamp's system administrator Luka Kodric, who unknowingly downloaded a malicious file, compromising the exchange's security. The malware, hidden in a harmless document, activated a script that infected Bitstamp's servers, giving the hackers access to the critical wallet.dat file and passwords.
Bitstamp acted quickly after becoming aware of the breach, establishing an emergency response team and alerting the entire company. Despite these measures, the hackers were able to steal 18,866 bitcoins from the hot wallet, resulting in a loss of approximately $5 million at the time of the hack.
Afterwards, Bitstamp made a massive overhaul of its trading platform, choosing to rebuild it from the ground up rather than patch it. They migrated their infrastructure to Amazon’s secure cloud servers in Europe, implemented multi-signature wallet access, and hired Xapo for cold wallet management.
3. Bitfinex theft
In August 2016, Bitfinex suffered a cyberattack. Hackers exploited a vulnerability in the exchange’s multi-signature security system, which was supported by BitGo. They manipulated security protocols and illegally withdrew 120,000 bitcoins from Bitfinex’s hot wallet.
After the hack, Bitfinex was transparent about its financial losses. The losses were spread across user accounts, with each account losing 36%. To mitigate the losses, Bitfinex issued BFX tokens to affected users, redeemable for U.S. dollars or iFinex Inc. shares, to facilitate a gradual recovery.
2. The Coincheck Heist
In late January 2018, Coincheck, a well-known Japanese cryptocurrency exchange, suffered one of the worst centralized exchange hacks in history. Hackers hacked into the exchange's hot wallet and stole 523 million NEM tokens, worth about $534 million at the time.
Despite previous lessons from other hacks, Coincheck still stored a large amount of assets in hot wallets and lacked adequate multi-signature protection. After the attack, the exchange immediately stopped all deposits and withdrawals to stop the flow of stolen funds.
The cryptocurrency community quickly rallied to prevent the stolen assets from being liquidated. Exchanges such as ShapeShift banned trading of the stolen NEM coins and marked related addresses to prevent further trading. Despite these efforts, full recovery of funds has not been feasible.
1. Mt. Gox: A hack that will never be forgotten
The Mt. Gox hack remains arguably the most infamous and high-profile cryptocurrency theft, primarily due to its size and timing. This major incident is a classic example of a top centralized exchange hack.
In 2011, Mt. Gox, then the world’s largest Bitcoin exchange, suffered its first major security breach, resulting in the loss of 25,000 Bitcoins. Things got worse in 2014, culminating in a catastrophic theft of approximately 850,000 Bitcoins.
The hack was huge, affecting the price of Bitcoin and the trust of the global cryptocurrency community. “I lost almost everything. It has forever changed my perspective on digital currency security,” one forum user shared, highlighting the profound personal and financial impact of the hack.
Precautions for Exchange Security
Exchange security issues have become a focus of the entire cryptocurrency industry in recent years, especially after some major security incidents and internal problems led to the closure of exchanges or loss of funds. To improve security, exchanges can take a variety of measures.
For example, keeping most assets in offline cold wallets and only storing a small amount of funds in networked hot wallets to cope with daily trading needs can significantly reduce the risk of hackers successfully stealing large amounts of funds. On the other hand, by requiring multiple key holders to sign transactions, multi-signatures can prevent the loss of funds due to the leakage of a single key.
By hiring a professional blockchain security company, exchanges can conduct a comprehensive security audit of their systems to identify and patch potential vulnerabilities. For example, the audit of smart contracts can prevent the loss of funds due to vulnerabilities.
Real-time monitoring and threat detection: Implementing real-time network monitoring can quickly identify abnormal activities and take corresponding measures to prevent attacks.Through strict KYC and KYT measures, exchanges can prevent illegal funds from entering the platform and reduce the risk of money laundering activities. And cooperate with professional security companies to conduct regular systematic security assessments and penetration tests to help exchanges prevent and respond to potential network threats.
 Cheng Yuan
Cheng Yuan







