Author: Darius Devėnas, DappRadar; Compiler: Felix, PANews
The blockchain industry is flooded with promises of quick and easy money. It is crucial to identify which projects are safe and which are doomed to fail after 3 months. This article introduces eight checks to help traders avoid effective scams.
1. Start with the basics
To verify the legitimacy of a token, you can start with the most accessible ways. For example, Google searches and Twitter, including researching the token and its team, checking for any dangers or warning signs, and looking for reliable sources of information such as official websites, news articles, and verified social media accounts.
Checking social media red flags
A verified X (Twitter) account can often help prove the legitimacy of this project. Also, participate in discussions about the token to get a sense of the community’s perspectives and opinions.
Be careful of projects that have a large number of followers on social media but very low engagement. Automated comments from fake accounts should also be a red flag. If all the comments are “this is a great project” and “Moon is coming soon”, beware.
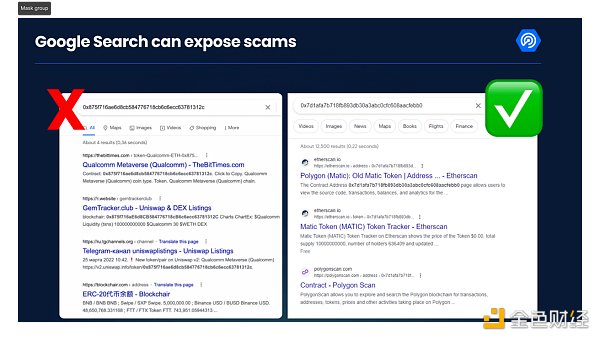
Check the Token Address in a Google Search
If you search the internet and can’t find a clear homepage, “whitepaper”, or obvious purpose for the token, it’s likely a scam. When searching for a token address, it’s imperative to easily find a block explorer link, an official website, and a whitepaper. If not, take that as a red flag.
Also, be aware that Google ads are often a free zone for scam sites. Never click on ads at the top of Google search results. Always make sure you are visiting the official website and avoid clicking on Wallet Drainers (note: malicious scripts for crypto wallets that transfer assets to attackers) or other hacking software.
2.Verify the code onEtherscan
Visit the block explorer of the chain of your choice and see if the source code is verified. For example, on Ethereum's block explorer Etherscan, it looks like the picture below. The code in the picture below is not verified, which should be an obvious warning sign. If the code is not verified, you may have encountered a scam.
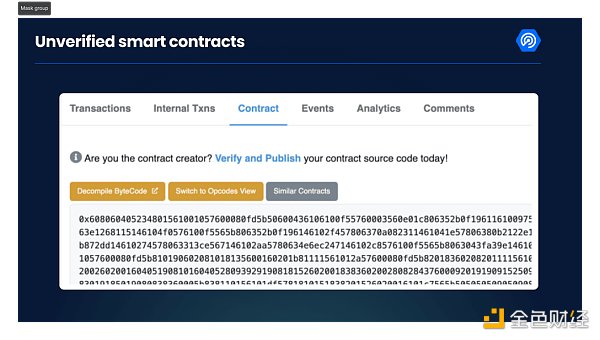
Why don't scammers just verify their code?
Because once the source code of a contract is public, everyone can know the intention behind the contract. Or a ridiculous token system, or a way for the developer to steal all your tokens. But does this mean that every unverified contract is a scam? Not necessarily, but it is a very serious red flag.
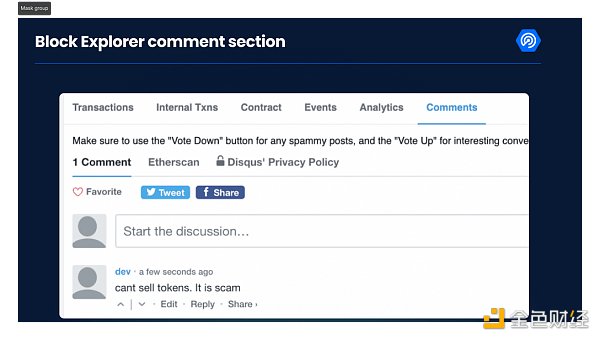
3.CheckEtherscanComments
This part is very simple, and there is usually a comments section on each block explorer. Most of the time there are no comments, but if a project is a scam you may find a bunch of angry people in the comments section. So be sure to click through. If someone says it's a scam, there is a 99% chance that it is a scam. If you are a victim of this project, please leave a comment as well.
4.CheckDappRadarBlacklist
You can compare the token blacklist compiled by DappRadar on Github, if the token address appears on the list, it is a scam.
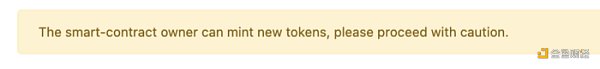
5. Check Token Details in Token Index
If you can’t find the token on CoinGecko or DappRadar’s Token Index (or similar token price trackers), then the token is likely a scam. If you see a warning like the one below, proceed with caution:
All legitimate tokens share their information with token index websites for verification. However, platforms like CoinMarketCap and Coingecko require certain specific conditions to be met. Therefore, not all tokens (regardless of legit or not) are automatically listed on this token index platform.
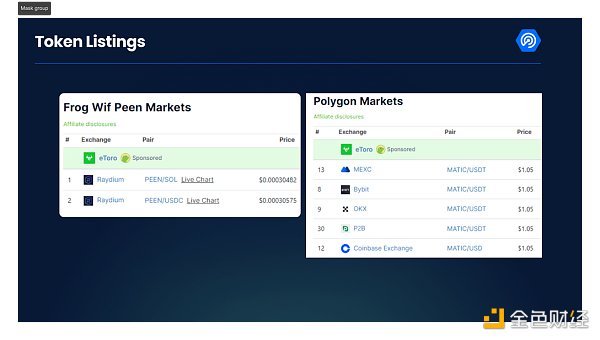
6. Check how many exchanges list the token
If the token is only traded on a few decentralized exchanges (DEX), it may be a scam. Listing on a centralized exchange requires KYC and additional trust, and the larger the exchange, the better the reputation of the listed token.
But not all tokens listed only on DEX are scams. Some projects do not require high trading volume, and some projects are only available to Web3 users rather than token traders.
However, tokens listed only on DEX are a riskier investment, and you are more likely to encounter a scam. The left side of the picture below is a token that is only used on DEX, while the right side is a token that can be used on multiple CEXs.
7. Check Liquidity in Token Balance Pools
Before investing in a token, you may want to check the overall demand and availability of liquidity. It is very easy to check the liquidity of a token on platforms like Uniswap V2 or other DEXs.
Liquidity refers to the amount of cryptocurrency or tokens locked in a smart contract that allows users to buy and sell assets through a (decentralized) exchange. If liquidity is below $100,000 or dropping rapidly, you may have encountered a scam.
When you use a DEX, always check for basic other on-chain activity, including:
If any of these look unusual, do a little more research.
8.Use third-party analysis tools
Here are some token analysis tools:
Smell Test: Automated audit of tokens. The lower the score out of 100, the more likely it is a scam.
Honeypot: A honeypot is a smart contract that has been deliberately inserted with an obvious programming flaw. When an attacker exploits the flaw, another hidden piece of code is activated to strike back at the attacker. Whether you are an intended crypto hacker or not, honeypots should be avoided.
DEXtools: Records real-time token prices and will help you assess the true value of tokens in real time.
Scammers are always there, both on the blockchain and in the real world. Following these suggestions should help you avoid fake tokens designed to defraud funds.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance












