Source: web3 Chinese
Today, the BTC Layer2 project BEVM officially announced that it has completed the seed round and part of the Series A financing of tens of millions of US dollars, with a post-investment valuation of US$200 million, becoming The shining star on the BTC Layer2 track. Since the beginning of 2024, BTC Layer2 has become the biggest hot spot in the encryption market. Various BTC Layer2 projects have also emerged first, and the Bitcoin second-layer solutions selected by each project are also different. Today we use an article to explain the differences between various BTC L2 solutions on the market.
There are various BTC L2 solutions currently on the market that are diverse and complex. From the perspective of technical implementation, it can be roughly divided into five categories: Bitcoin side chain, UTXO + client verification, Taproot Consensus, multi-signature + EVM, and Roullp. We will analyze the advantages and disadvantages of these five types of Bitcoin L2 solutions from three major perspectives: Bitcoin’s nativeness, degree of decentralization, and degree of implementation.
Why does it need to be analyzed from the three perspectives of Bitcoin’s nativeness, degree of decentralization, and degree of implementation?
First: without making any changes to the Bitcoin code, but directly using the mature and time-proven Bitcoin native technology to build BTC L2, which can not only minimize the Risks and elimination of uncertainty, the native nature of Bitcoin and compliance with the original purpose of Bitcoin, basically determine whether it can be recognized by the mainstream Bitcoin community, which has far-reaching significance for the launch and development of the BTC L2 project.
Second: Decentralization is the spiritual core of the blockchain. In the Bitcoin community where decentralization is the core culture, whether a BTC L2 is decentralized enough almost determines the life or death of the project. The decentralization of BTC L2 is directly reflected in the security of BTC management and entry and exit expenses. A BTC L2 that cannot safely manage BTC in a decentralized manner will simply not be able to gain the support and trust of BTC users. Therefore, decentralization is a core proposition that all BTC L2 must face.
Third: BTC L2 has been developed for 6-7 years. Many solutions sound sexy, but the actual implementation situation is very cruel. From the earliest Stack, RSK, and then After RGB has been proposed for four years, including the release of the white paper, there is no more sound to BitVM. The implementation situation is basically the most direct way to test the solution. Therefore, the implementation of various BTC L2s should be one of the important indicators for us to measure the pros and cons.
1. Bitcoin side chain:
Bitcoin side chain means that it can be independent of Bitcoin Existing expansion blockchains, such as Stack and RSK, are all Bitcoin sidechain solutions. Bitcoin side chains generally use multi-signature or Hash Lock methods to manage Bitcoin. At the same time, BTC is mapped on the second-layer blockchain, so that BTC has the ability to expand complex scenarios on the second layer.
1. Bitcoin nativeness:
The Bitcoin side chain solution can be simply understood as multi-signature+ VM blockchain, and these Bitcoin side chains can exist independently of Bitcoin, so Bitcoin is less native, and therefore, it is difficult to gain support from the Bitcoin community.
2. Degree of decentralization:
Since Bitcoin side chains generally use multi-signature and Hash lock and other solutions to achieve Bitcoin management. Therefore, the degree of decentralization is generally poor, and the security of assets completely relies on multi-signature.
3. Level of implementation:
The Bitcoin side chain solution has been around for many years, but whether it is Stack Neither RSK nor RSK has achieved great results in ecological development. The core reason is that if the decentralization of the chain and the security of assets are not resolved, it will be difficult to gain the trust of users and funds.
2. UTXO+client verification
UTXO+client verification refers to the method based on the Bitcoin UTXO account model. This type of expansion plan is generally based on Bitcoin UTXO to do ledger calculations under the Bitcoin chain. At the same time, client verification is used to ensure the authenticity of the ledger, thus having both the native nature of Bitcoin and the It can achieve the goal of ensuring the security of the second-layer ledger shared Bitcoin ledger. The UTXO + client verification solution sounds sexy, but the reality is cruel and extremely difficult to implement. Because, in the minimalist Bitcoin UTXO account model, which does not originally support complex operations, the "extra tasks" of ensuring the security of the second-layer ledger are abruptly inserted. Whether this model is feasible remains to be verified. Typical representatives of this type of projects are: RGB and BitVM
1. Bitcoin nativeness:
UTXO+ Client-side verification focuses on the nativeness of Bitcoin and is entirely based on UTXO. However, due to too much emphasis on nativeness, it is extremely difficult to implement and seems to have gone to the other extreme. It was originally intended to be a Bitcoin expansion plan, but it turned out to be more and more complicated. Moreover, the essence of client-side verification is to hand over the security verification problem to the user, returning to the most primitive and least efficient single verification mode. There is often too much emphasis on nativeness, and feasibility and practicality may be ignored.
2. Degree of decentralization:
Due to the solution based on the UTXO model, although it seems to be relying on The Bitcoin blockchain ensures the trustworthiness of the second layer, but in essence, it still adopts the off-chain method of client verification. Although the client can be sufficiently dispersed and decentralized, this point-to-point verification model, It is not a decentralization that relies on network consensus, but a distributed verification that relies on a dispersed number of clients. This mode often relies on the client's own verification capabilities. If some clients do not know enough about the verification mode, or there are problems with the verification method, they are likely to face problems such as asset loss and double spending of assets. It is difficult to say that it is a truly feasible decentralized solution.
3. Level of implementation:
It has been 4 years since RGB was proposed, and BitVM has been proposed for one year , however, are still in the white paper or theoretical stage, there is still no testable version of RGB directly, and BitVM has made no clear progress since the release of the white paper. Some projects that claimed to be built based on RGB and BitVM have also ceased operations or found another way out. It can be seen that the expansion plan of UTXO+ client verification still faces huge uncertainty.
3. Taproot Consensus
Taproot Consensus is built based on the three native technologies of Bitcoin The second-layer solution is a solution that has gradually matured since Bitcoin’s Taproot upgrade in 2021. The essence of Taproot Consensus is Schnorr Signature+MAST Contract+Bitcoin Light Node Network.
Schnorr Signature allows Bitcoin multi-signature addresses to be expanded to 1,000, realizing the decentralization of multi-signature addresses; MAST Contract implements coding of multi-signature management, without relying on people to sign. Instead, it relies on code-driven; Bitcoin Light Node Network realizes multi-signature driven by Bitcoin light node network consensus, fully realizing decentralized Bitcoin cross-chain and management.
Taproot Consensus is a solution proposed and implemented by the BEVM team. BEVM is also a typical use case of Taproot Consensus.
1. Bitcoin nativeness:
Taproot Consensus is completely built based on the three native technologies of Bitcoin It does not introduce or add any other technology outside of Bitcoin. It is a comprehensive solution for Bitcoin’s 2021 Taproot upgrade and many of Bitcoin’s core technologies. Therefore, Taproot Consensus is extremely native and highly implementable. After all, whether it is Schnorr Signature, MAST Contract, or Bitcoin Light Node Network, they are mature technologies that have been verified for many years in the history of Bitcoin. Including, the core behind Ordinals relies on MAST Contract.
It is worth mentioning that since the nodes of the Bitcoin second-layer network based on Taproot Consensus are all Bitcoin light nodes, the second-layer network cannot exist independently of Bitcoin. , and has an inseparable dependence on Bitcoin.
2. Degree of decentralization:
The core of Taproot Consensus is to solve the decentralization of Bitcoin The issue of access and spending is the core proposition of all Bitcoin L2. Taproot Consensus can realize completely decentralized Bitcoin management through the BFT consensus network composed of 1000+ Bitcoin light nodes, thus solving the problem of introducing BTC into the second-layer network in a trustless manner, and ultimately achieving the expansion of Bitcoin.
3. Implementation level:
Taproot Consensus Bitcoin second-layer solution has been proposed since 2021. It will actually be put into practice in July 2023. The BEVM pioneer network built on Taproot Consensus has been running stably for 8 months, processing 6 million transactions, with 100,000+ users on the chain, 30+ ecological projects, and the BEVM main network based on Taproot Consensus. It has been launched on the mainnet recently. Therefore, Taproot Consensus is currently a highly implemented second-layer Bitcoin solution.
4. Multi-signature + EVM
Multi-signature + EVM is currently used by many BTC L2 The solution, whether it is an MPC multi-signature solution, a threshold signature solution, or a Hash Lock, DLC and other solutions, is essentially a multi-signature + EVM solution. Users transfer BTC to a multi-signature address and then generate new BTC on the EVM chain, thus making BTC activities compatible with the capabilities of EVM smart contracts.
This type of scheme is the simplest to implement, and the technical threshold is also very low. However, in essence, this type of scheme is still a Bitcoin side chain scheme, but in the implementation method It is simpler and more crude than side chain. Typical projects of this type are Melin Chain, etc.
1. Bitcoin nativeness:
Solutions such as multi-signature + EVM are not native. Word. The essence is to store Bitcoin in a multi-signature address and map a new BTC asset on the second layer to run on the second layer. Moreover, the second-layer blockchain can exist completely independent of Bitcoin.
2. Degree of decentralization:
The essence of multi-signature is to trust multi-signers and multi-signatures Mechanism, not trust network consensus. Therefore, the asset security of the multi-signature + EVM Bitcoin second-layer solution completely relies on the multi-signature person or private key holder designated by the project party. There isn’t much decentralized consensus.
3. Implementation level:
The solution of multi-signature + EVM is very easy to implement, one A multi-signature wallet + an EVM-compatible blockchain is not a very complicated technical problem, and there are many open source versions. Therefore, the startup cost is the lowest. Therefore, a large number of so-called Bitcoin second-layer solutions visible on the market adopt Such plans. However, this type of scheme very much tests the management capabilities of multi-signers. After all, the security of assets relies on these multi-signers.
5. Roullp
Both ZK-Roullp and OP-Roullp are originally Ethereum L2 solution, however, many entrepreneurs borrow roullp to Bitcoin L2 solution. But is running roullp on Bitcoin really feasible? Ethereum essentially supports smart contract verification. Ethereum can also verify the second-layer roullp ledger information. Therefore, the second layer of Ethereum roullp can share the security of Ethereum. However, Bitcoin does not support any form of roullp verification. of.
. This is equivalent to going around in a circle. Bitcoin only saves the roullp ledger itself. However, without verification, the verification is still left to the client, or the DA layer built by the BTC L2 project party. Then, the security of the BTC L2 project itself is became the key to all problems. Typical representatives of this type of projects are: B2 and Bison.
1. Bitcoin nativeness:
The Roullp solution essentially comes from the second-layer solution of Ethereum. The essence of Roullp is about how the second-layer ledger can be trusted. It has nothing to do with Bitcoin in essence. The Bitcoin blockchain only plays a role of storing evidence but not verifying it. Therefore, Roullp is less native and has difficulty gaining support from core Bitcoin users.
2. Degree of decentralization:
The decentralization of BTC L2 is mainly from two aspects. First, The first aspect involves the decentralization of asset management and the decentralization of the second-layer ledger. The Roullp solution generally uses a multi-signature solution for Bitcoin asset management on the first layer, and a sequencer solution for the second layer. Currently, most of Ethereum's sequencers are centralized and are the L2 project's own nodes. to run the sequencer. At present, most BTC L2 with roullp as the core solution still does not solve these two aspects of decentralization issues.
3. Implementation level:
Since the Roullp solution is mature in the Ethereum ecosystem, it is The second layer of Bitcoin is not complicated to implement, and many chains use a multi-signature method to implement Bitcoin management. Therefore, the overall implementation is not difficult. At present, the user scale and TVL of BTC L2 projects such as B2 have begun to take shape. However, projects of this type still need to accept two major challenges from the market. The first is the issue of Bitcoin asset management and the credibility of the second-layer ledger.
Summary:
Analysis from the three dimensions of Bitcoin’s nativeness, degree of decentralization and degree of implementation , the five major BTC L2 solutions each have their own advantages and disadvantages.
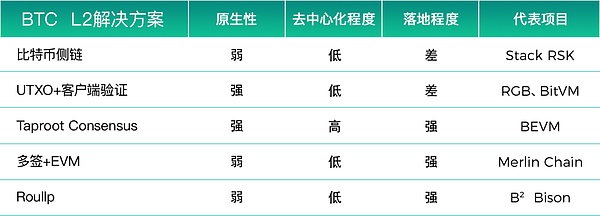
Bitcoin sidechain solution for many years The development results in the past have also verified that it is almost difficult to obtain the support and recognition of mainstream Bitcoin users; in terms of entrepreneurial difficulty, multi-signature + EVM is the easiest solution to copy, and the core test is the market and marketing capabilities of the project party. However, In the long term, due to the low degree of decentralization, it is difficult to obtain the support and trust of large Bitcoin funds in the long term, and the sustainability of project development remains to be seen.
From the perspective of the native nature of Bitcoin, the UTXO+ client verification mode is the most native and purest. However, the technical implementation is too complex, and in the short and medium term, it is extremely difficult to implement; the Roullp solution, It directly borrows the solution and rhetoric of Ethereum L2. Although it does not solve the fundamental problem of BTC L2, the cost of brand communication is low. If long-term development is to be achieved, the problem of decentralization still needs to be solved.
Taproot Consensus solution, since it directly uses Bitcoin native technology to build a decentralized BTC L2 solution, therefore, both in terms of Bitcoin nativeness and degree of decentralization, including In terms of the current level of implementation, Taproot Consensus is the most noteworthy BTC L2 solution at the moment.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance







