Author: Revc, Golden Finance
Babylon platform announced that its Bitcoin staking mainnet has been officially launched. In the first phase, the platform set a staking cap of 1,000 Bitcoins, and this cap has been fully reached. According to platform data, more than 12,700 users have participated in staking, with a total staking value of more than 1,000 Bitcoins.
What is Babylon
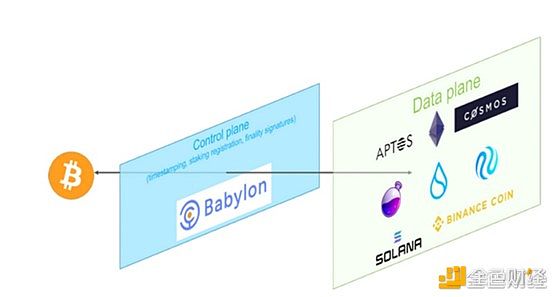
Babylonis a protocol designed to use the security of Bitcoin to provide security for otherPoSchains.Babylon can provide secure, cross-chain-free, and custody-free native staking solutions for PoS chains including BTC layer2, and promote cross-chain interoperability. It is often compared to Eigenlayer of the Ethereum ecosystem.
Babylon's core working principle
Remote staking: Using Bitcoin's UTXO model and script system to achieve staking, forfeiture and rewards for Bitcoin.
Timestamp server: By recording events of the PoS chain on the Bitcoin blockchain, it provides an unalterable timestamp for these events.
Three-layer architecture: Bitcoin is the bottom layer, Babylon is the middle layer, and the PoS chain is the upper layer. Babylon is responsible for recording the checkpoints of the PoS chain on Bitcoin.
BabylonAdvantages
Enhance the security of the PoS chain: Utilize the security of Bitcoin to improve the anti-attack ability of the PoS chain.
Shorten the pledge cycle: Through the timestamp mechanism of Bitcoin, shorten the pledge cycle of the PoS chain.
Promote cross-chain interoperability: Enable seamless communication and data sharing between different blockchains.
Bring new vitality to the Bitcoin ecosystem: Activate dormant Bitcoin and bring new application scenarios to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
BTCFiEcosystem Overview
At present, the Bitcoin ecosystem has entered the stage of large-scale infrastructure, and all parties are rushing to the BTCFi track. After all, the track has assets worth nearly 1.5 trillion US dollars to be activated. The following is an inventory of the top BTCFi projects:
BounceBit
BounceBit combines CeFi and DeFi to provide Bitcoin with a more flexible way to earn income. Through liquidity custody and re-staking, users can earn income on multiple chains.
Core functions:
CeFi+DeFi combination: Deposit Bitcoin in the CeFi platform and participate in the DeFi protocol at the same time to obtain double income.
Liquidity Custody: Provides liquidity custody services so that users can redeem assets at any time.
Re-staking: Allows users to re-stake staked Bitcoin to other protocols to obtain more returns.
Technical Design: BounceBit ensures the security of cross-chain assets and reduces the risk of hacker attacks through multiple security mechanisms such as validator consensus, Mainnet Digital's custody services, and Ceffu's MirrorX technology.
Solv Protocol
Solv Protocol has created a full-chain yield Bitcoin asset SolvBTC, bringing Bitcoin's liquidity to various DeFi protocols.
Core Functions:
SolvBTC: A derivative asset representing staked Bitcoin that can be used on multiple chains.
Decentralized asset management: Ensure asset security through smart contracts and multi-signatures.
Cross-chain interoperability: Support the use of SolvBTC on multiple blockchains.
Technical design: Concentrate various liquidity resources and investment opportunities on one platform, and users can automate their investments by setting up trading strategy Vaults.
Yala
YalaAims to build a multi-chain stablecoin ecosystem that leverages Bitcoin's liquidity.
Core functions:
Multi-chain stablecoins: Provide Bitcoin-based stablecoins that can be used on multiple chains.
DeFi ecosystem: Provide DeFi services such as lending and staking.
Modular architecture: Flexible and scalable, supporting custom modules.
Currently, the parties have adopted a centralized approach in terms of security solutions, namely CeFi and multi-signature, in an attempt to maximize the activation of the value flow on the Bitcoin chain, because although the on-chain verification methods such as UTXO are decentralized to ensure security, it is difficult to stimulate the flow of value due to the lack of a complete smart contract system on Bitcoin, and on-chain verification is mostly used in the re-pledge track.
Thinking about the Bitcoin re-pledge track
Back to the re-pledge track itself where Babylon is located, first of all, the blockchain mainly shares security consensus in a modular way. The modular blockchain provides infrastructure for other blockchains by "renting" the security, decentralization and value consensus of high-quality public chains such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, thereby improving the performance and efficiency of the blockchain. At present, there are mainly three types of solutions:
Ethereum-based solutions:
Advantages: High security, strong legitimacy, and direct use of Ethereum ecological resources.
Disadvantages: The throughput and cost may be low, and it is not suitable for all types of application chains.
New DA layer solution (such as Celestia):
Advantages: Good performance, low cost, and aims to provide security and decentralization features comparable to Ethereum.
Disadvantages: Security and decentralization features still need time to be verified, lack of legitimacy, and may be rejected by the Ethereum community.
Proof of Stake (POS) shared security solution (such as Babylon, EigenLayer):
Advantages: Inherits the legitimacy and security of Bitcoin or Ethereum, provides more practical value for its assets, and has high flexibility.
Disadvantages: Relatively new, long-term performance still needs to be observed.
Babylon adopts the core concept of Proof of Stake (POS), which uses the asset value of Bitcoin or Ethereum to create a shared security service. The advantage is that it inherits legitimacy and security while providing more practical value for the main chain assets and providing higher flexibility. But this also triggered a series of thoughts:
In the Ethereum network, the security responsibility of general pledgers is greater than that of non-pledgers, because the pledged ETH participates in consensus maintenance, and the ETH in circulation is actually the beneficiary of network security, and they also pay the opportunity cost of staking. So from the perspective of shared security, the proof of stake sharing scheme is currently lower than the basic scheme of Ethereum, unless the assets of the proof of stake scheme are assets such as stETH, because stETH corresponds to the ETH involved in verification in the Ethereum network. Roughly speaking, the Ethereum network is secure, and other PoS networks using stETH staking are also safe.
Babylon's PoW+PoS solution does not have a perfect security sharing logic. First of all, the main personnel of the Bitcoin network's security maintenance system are miners. Although miners are also driven by the value of BTC tokens, Bitcoin holders pledged in the Babylon protocol do not directly and actively maintain the security of the Bitcoin network, nor do they directly transmit the security of the Bitcoin network to the Pos network connected to the Babylon network. Here we can think about whether the beneficiaries of security can also pass on security guarantees to others. That is to say, the security of the entirePoS network is lowly correlated with the Bitcoin network and strongly correlated with Bitcoin pledgers, so we have to think about whether shared security is shared at the asset level (more like a guarantee) or at the network level.
BTC pledgers or holders do not actively maintain the security of Bitcoin and PoS networks. From the design of the first phase of Babylon, the Bitcoin network is more like passively receiving data from the PoS network. In fact, the overall security depends more on the Babylon PoS network itself.
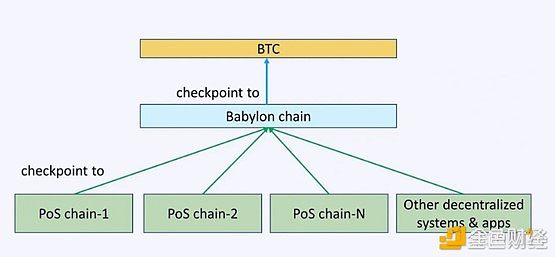
From a quantitative point of view, the 1,000 bitcoins in the first phase account for a very small share of the current circulation of bitcoins. Economically, the current PoS chain does not share the security of the Bitcoin network, and the security of shared assets and the security of the network where the shared assets are located are two concepts, which deserves further discussion.
In addition, technically, how does the timestamp of PoS coordinate with the timestamp of the Bitcoin network block? The block time of the Bitcoin network is at the minute level, and there is a certain uncertainty in the block time and transaction confirmation, while the finality of the transaction confirmation of the PoS network is at the second level, which immediately gives rise to a problem of block coordination between PoS and PoW.
Summary
The Bitcoin network is the most valuable decentralized network. Many BTCFi projects, including Babylon, have the potential to make the Bitcoin network the cornerstone of the entire crypto industry and bring new possibilities to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
In the process of development, in addition to focusing on the inheritance of decentralized attributes, the BTCFi project also needs to attach great importance to the security of protocols and smart contracts because of the huge amount of funds involved.
 Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist
 Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Beincrypto
Beincrypto Beincrypto
Beincrypto Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Coindesk
Coindesk Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph