This report is jointly produced by Beosin, Elven, and Footprint Analytics. The authors of this chapter are Mario and Donny from the Beosin research team


*Due to limited space, this article only shows the report Regarding the security situation, we will release regulatory policies and other content in the future.
Foreword
This research report is sponsored byBlockchain Security Initiated by the alliance and co-created by alliance members Beosin, Web3 Xiaolu, and Elven, it aims to comprehensively explore the global blockchain security situation in 2023 and key regulatory policies in the encryption industry. Through analysis and assessment of the current status of global blockchain security, the report will reveal current security challenges and threats and provide solutions and best practices. At the same time, the report will also examine the positions and policy orientations of governments and regulatory agencies in various countries on the regulation of the encryption industry to help readers understand the dynamic changes and possible impacts of the regulatory environment.
Through this report, readers will be able to more comprehensively understand the dynamic evolution of the Web3 blockchain security situation and the core points of regulatory policies. This will help readers assess and respond to the security challenges faced by the blockchain field and promote the sustainable development of the industry while complying with regulatory requirements. In addition, readers can also obtain helpful suggestions from the report on security measures, compliance requirements and industry development directions to help them make informed decisions and actions in this emerging field. Blockchain security and supervision are key issues for the development of the Web3 era. Through in-depth research and discussion, we can better understand and respond to these challenges and promote the security and sustainable development of blockchain technology.
1. Overview of Web3 Blockchain Security Situation in 2023< /h2>

Data Blockchain Security Audit Company Beosin's EagleEye platform monitors thatthe total losses in the Web3 field due to hacker attacks, phishing scams, and project parties' Rug Pulls in 2023 reached US$2.02 billion. There were 191 attack incidents, with a total loss of approximately US$1.397 billion; 267 project Rug Pull incidents, with a total loss of approximately US$388 million; and phishing scams, with a total loss of approximately US$238 million.
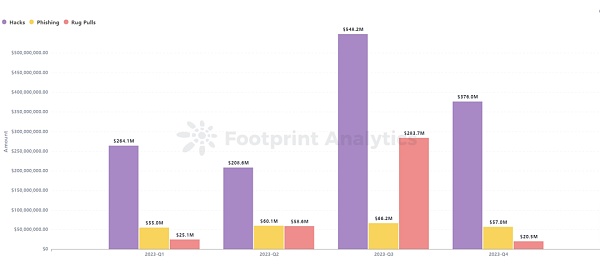
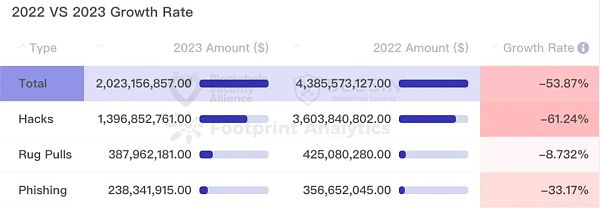
In 2023, Hacking attacks, phishing scams and project party Rug Pull incidents have all dropped significantly compared with 2022, with the total amount falling by 53.9%. Among them, hacker attacks have seen the largest decline, from US$3.6 billion in 2022 to US$1.397 billion in 2023, a drop of approximately 61.2%. Phishing scam losses were down 33.2% from 2022, and rug pull losses were down 8.8% from 2022.
A total of losses occurred in 2023 There were 4 attacks with losses in the range of US$10 million to US$100 million, and 17 attacks with losses ranging from US$10 million to US$100 million. The total loss of the top 10 largest security incidents is approximately US$1 billion, accounting for 71.5% of the total annual attack costs.
The types of projects attacked in 2023 are more extensive than in 2022, including DeFi, CEX, DEX, public chains, cross-chain bridges, wallets, payment platforms, and gambling platforms , crypto brokers, infrastructure, password managers, development tools, MEV bots, TG bots and many more types. DeFi is the project type with the highest frequency of attacks and the highest amount of losses. 130 DeFi attacks caused a total loss of approximately US$408 million.
In 2023, the types of public chain attacks will be more frequent, and there will be many security incidents involving theft on multiple chains. Ethereum is still the public chain with the highest amount of losses. 71 attacks on Ethereum caused losses of US$766 million, accounting for 54.9% of the total losses for the year.
From the perspective of attack methods, 30 private key leaks caused a total loss of approximately US$627 million, accounting for 44.9% of the total losses, making it the attack method that caused the most losses. Contract vulnerability exploitation is the most frequent attack method. Of the 191 attacks, 99 came from contract vulnerability exploitation, accounting for 51.8%.
Approximately $295 million in stolen funds were recovered throughout the year, accounting for approximately 21.1%, a significant increase from 2022. Approximately $330 million in stolen funds were transferred to mixers throughout the year, accounting for 23.6% of the total stolen funds.
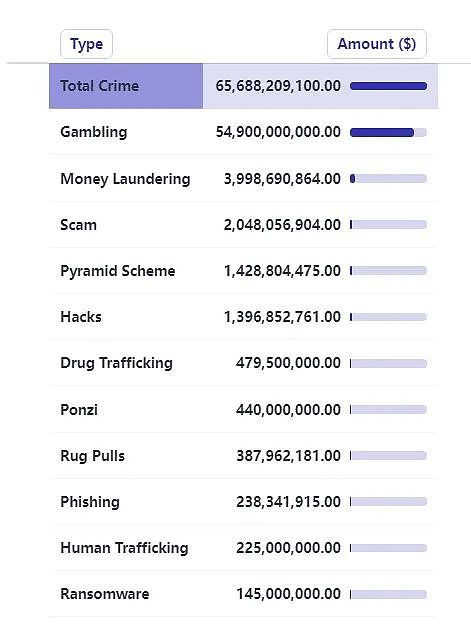
Unlike the significant decrease in on-chain hacking attacks, phishing scams, and project Rug Pull amounts, criminal data in the off-chain encryption field will increase significantly in 2023. In 2023, the amount of crime in the global encryption industry reached a staggering $65.688 billion, an increase of approximately 377% from $13.76 billion in 2022. The top three types of crimes involving amounts of money are online gambling, money laundering and fraud.
2. Top ten security incidents in Web3 ecosystem in 2023
A total of 2023 There were 4 attacks with losses exceeding 100 million USD: Mixin Network (USD 200 million), Euler Finance (USD 197 million), Poloniex (USD 126 million), and HTX & Heco Bridge (USD 110 million). The total loss of the top 10 largest security incidents was approximately US$1 billion, accounting for 71.5% of the total annual attack incidents.
No.1 Mixin Network
Amount of loss: US$200 million
Attack method: Cloud service provider database attack
In the early morning of September 23, the Mixin Network cloud service provider database was attacked by hackers, resulting in the loss of some assets of the main network. Lost, involving approximately US$200 million. On September 25, the founder of Mixin publicly explained the incident in a live broadcast, saying that the damaged assets were mainly Bitcoin core assets, and assets such as BOX and XIN were not seriously stolen. The specific attack situation It cannot be disclosed yet.
No.2 Euler Finance
< strong>Amount of loss: US$197 million
Attack method: Contract vulnerability - Business logic issue
< /p>
On March 13, the DeFi lending protocol Euler Finance was attacked, resulting in a loss of approximately US$197 million. The root cause of the attack was that the contract did not properly check the number of tokens actually held by the user and the health of the user's ledger after the donation. All stolen funds in this incident have been returned by the attacker.
No.3 Poloniex
Amount of loss: US$126 million
Attack method: Private key leak/APT attack
On November 10, Justin Sun Addresses related to its subsidiary exchange Poloniex continued to transfer large amounts of assets and were suspected of being stolen. Immediately afterwards, Justin Sun and Poloniex issued announcements on social platforms confirming the theft. According to Beosin Trace tracking statistics used by the Beosin security team, the total stolen assets of Poloniex are approximately US$126 million.
No.4 HTX & Heco Bridge
Amount of loss: US$110 million< /p>
Attack method: Private key leak
On November 22, Justin Sun’s exchange HTX and cross-chain bridge Heco Bridge were hacked, with a total loss of 110 million US dollars, of which Heco Bridge lost US$86.6 million and HTX lost approximately US$23.4 million.
No.5 Curve/ Vyper
Amount of loss: US$73 million
< /h3>
Attack method: Contract vulnerability - Reentrancy
In the early morning of July 31, the Ethereum programming language Vyper tweeted that Vyper 0.2.15 , 0.2.16 and 0.3.0 versions have reentrancy lock vulnerabilities, and the native ETH can adjust the callback during transfer, resulting in these LP pools in the ETH group being vulnerable to reentrancy attacks. Then Curve’s official Twitter posted that many stablecoin pools using Vyper 0.2.15 (alETH/msETH/pETH) were attacked due to a failure in the reentry lock. The loss in this incident was approximately US$73 million.
No.6 CoinEx
Amount of loss: 70 million US dollars
< strong>Attack method: Private key leak/APT attack
On September 12, the encryption exchange CoinEX issued a statement stating that the risk control system detected the emergence of a hot wallet used to temporarily store platform trading assets. A special team has been set up to deal with the suspicious large-amount withdrawal activities immediately. This incident mainly involves token assets such as ETH, TRON, and Polygon, and the stolen amount is approximately US$70 million.
No.7 Atomic Wallet
< strong>Amount of loss: 67 million US dollars
Attack method: Private key leakage/APT attack
Beosin's EagleEye security risk monitoring, early warning and blocking platform monitoring showed that Atomic Wallet was attacked in early June. According to statistics from the Beosin team, based on the known victim report information on the chain, the damage caused by this attack was at least approximately 67 million US dollars.
No.8 Alphapo
Amount of loss: 60 million US dollars
Attack method: Private key leak/APT attack
On July 23, the hot wallet of cryptocurrency payment service provider Alphapo was stolen, resulting in a total loss of US$60 million. The incident was attributed to the North Korean hacker group Lazarus.
No.9 KyberSwap
Amount of loss: 54.7 million US dollars
< p>
Attack method: Contract vulnerability - Business logic issueOn November 22, the DEX project KyberSwap was attacked, causing a total of approximately 54.7 million dollar loss. Kyber Network stated that this hacking attack is one of the most complex attacks in DeFi history, and the attacker needs to perform a series of precise on-chain operations to exploit the vulnerability.
No.10 Stake.com
Amount of loss: 4130 ;Ten thousand dollars
Attack method: Private key leak/APT attack
On September 4, the encrypted gambling platform Stake.com encountered a hacker attack. After the attack, Stake.com stated that unauthorized transactions occurred in its hot wallets on ETH and BSC, and that it is investigating and will resume deposits and withdrawals as soon as the wallet is fully re-secured. The incident was attributed to the North Korean hacker group Lazarus.
3. Types of attacked projects
and 2022 Compared with 2023, the types of projects attacked are more extensive, and the amount of losses is no longer concentrated on certain project types. In addition to common types such as DeFi, CEX, DEX, public chains, cross-chain bridges, and wallets, hacker attacks in 2023 will also appear on payment platforms, gambling platforms, crypto brokers, infrastructure, password managers, development tools, and MEV robots , TG robot and other project types.
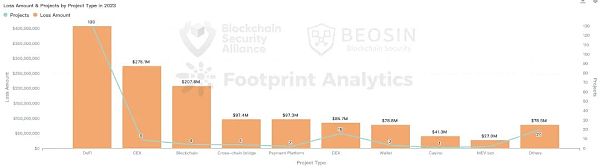
191 attacks in 2023 In the incident,DeFi projects accounted for 130 times (about 68%), making it the type of project that has been attacked the most. The total loss from DeFi attacks is approximately US$408 million, accounting for 29.2% of all losses, and is also the type of project with the largest loss.
The second largest loss was CEX (centralized exchange), with nine attacks causing a total loss of US$275 million. In addition, 16 attacks occurred in the DEX (decentralized exchange) type, resulting in a total loss of approximately $85.68 million. Taken together, exchange types will experience frequent security incidents in 2023, and exchange security is the second biggest challenge after DeFi security.
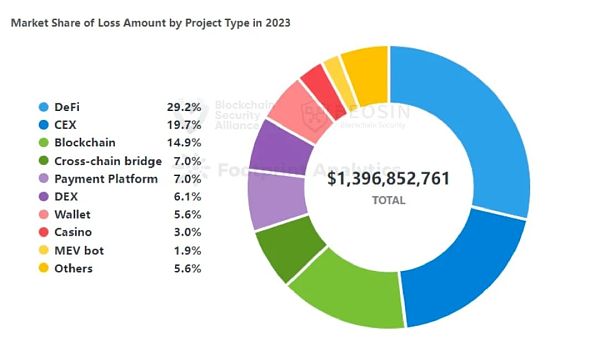
Loss amount ranking In third place is the public chain, with losses of approximately US$208 million, mainly due to the US$200 million theft of Mixin Network.
In 2023, cross-chain bridge losses ranked fourth, accounting for approximately 7% of all losses. In 2022, 12 cross-chain bridge security incidents caused a total loss of approximately US$1.89 billion, accounting for 52.5% of the total loss that year. Significant reduction in cross-chain bridge security incidents in 2023.
Ranked 5th is the encrypted payment platform. Two security incidents (Alphapo and CoinsPaid) resulted in a total loss of approximately US$97.3 million. Behind the scenes of these two incidents The hackers all pointed to the North Korean APT organization Lazarus.
4. Loss amount of each chain
Compared with 2022, the types of public chains where attacks occurred in 2023 are also more extensive, mainly due to the fact that multiple CEX private key leaks occurred in 2023, causing losses on multiple chains. The top five in terms of loss amount are Ethereum, Mixin, HECO, BNB Chain, and TRON; the top five in terms of number of attack events are BNB Chain, Ethereum, Arbitrum, Polygon, Optimism, and Avalanche (tied for fifth place) ).
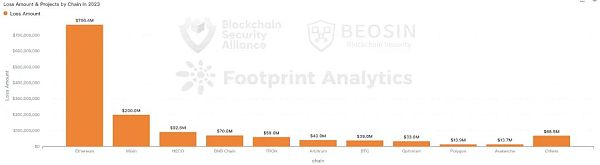
And 2022 Same as last year, Ethereum is still the public chain with the highest amount of losses. 71 attacks on Ethereum caused $766 million in losses, accounting for 54.9% of the total losses for the year.
Mixin chain losses ranked second, with losses from a single security incident reaching $200 million. In third place was HECO, with losses of approximately $92.6 million.
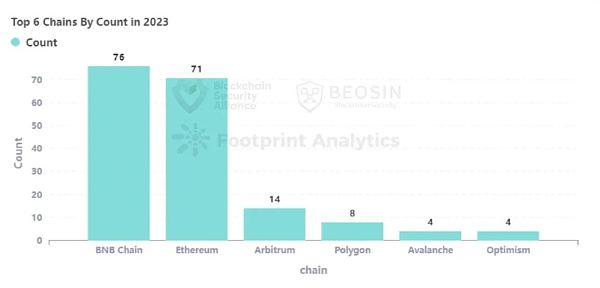
Attacks on BNB Chain It reached 76 times, accounting for 39.8% of the total number of attack events, which is the highest number of attack events among all chain platforms. The total loss on BNB Chain is approximately US$70.81 million, with the vast majority of events (88%) concentrated below US$1 million.
5. Analysis of attack techniques
And 2022 Compared with 2023, the attack methods are more diverse, especially a variety of Web2 attack methods have been added, including:Database attacks, supply chain attacks, third-party service provider attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, DNS attacks, front-end attacks, etc.
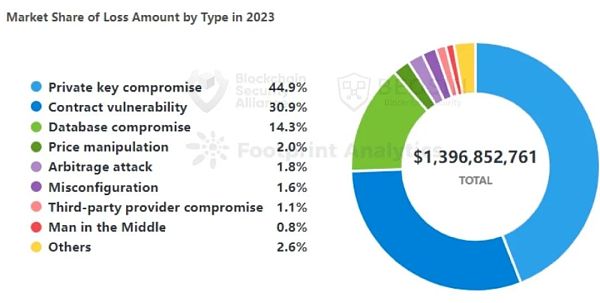
2023 , 30 private key leak incidents caused a total loss of US$627 million, accounting for 44.9% of the total loss, and was the attack method that caused the most losses. Private key leaks that caused large losses include: Poloniex (USD 126 million), HTX & Heco Bridge (USD 110 million), CoinEx (USD 70 million), Atomic Wallet (USD 67 million), Alphapo (USD 60 million) Dollar). Most of these incidents are related to the North Korean APT group Lazarus.
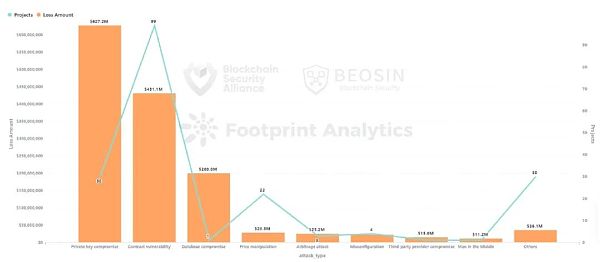
Contract vulnerability Exploitation is the most frequent attack method. Among the 191 attacks, 99 came from the exploitation of contract vulnerabilities, accounting for 51.8%. The total loss caused by contract loopholes was US$430 million, ranking second in terms of loss amount.
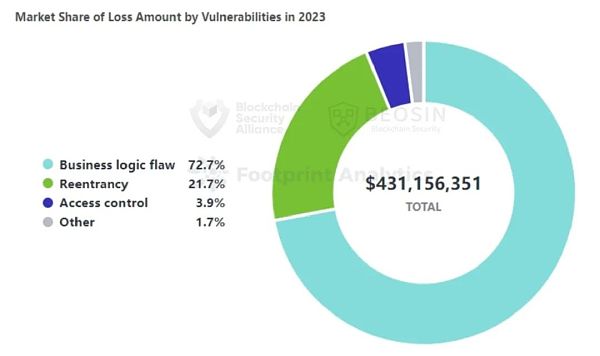
According to the breakdown of vulnerabilities, the ones that occur most frequently and cause the most losses are business logic vulnerabilities. About 72.7% of the losses in contract vulnerability incidents come from business logic vulnerabilities. Total losses were approximately US$313 million. The contract vulnerability with the second largest loss is reentrancy, with 13 reentrancy vulnerabilities causing losses of approximately US$93.47 million.
6. Analysis of typical case attack techniques
6.1 Euler Finance Security Incident
Event Summary
March 13, on the Ethereum chain Euler Finance, a lending project, was attacked by flash loans, causing losses of US$197 million.
On March 16, the Euler Foundation offered a reward of US$1 million for information that would help arrest the hacker and return the stolen funds.
On March 17, Euler Labs CEO Michael Bentley tweeted that Euler "has always been a security-conscious project." From May 2021 to September 2022, Euler Finance received 10 audits from 6 blockchain security companies including Halborn, Solidified, ZK Labs, Certora, Sherlock and Omnisica.
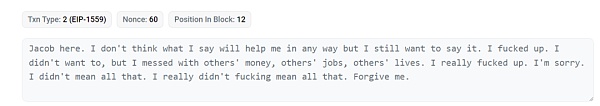
From March 18 to April 4, the attackers began to return funds one after another. During this period, the attacker apologized through a message on the chain, saying that he had "disrupted other people's money, other people's work, and other people's lives" and asked for everyone's forgiveness.
April 4, Euler Labs said on Twitter that after successful negotiations, the attackers had returned all stolen funds.
Vulnerability Analysis
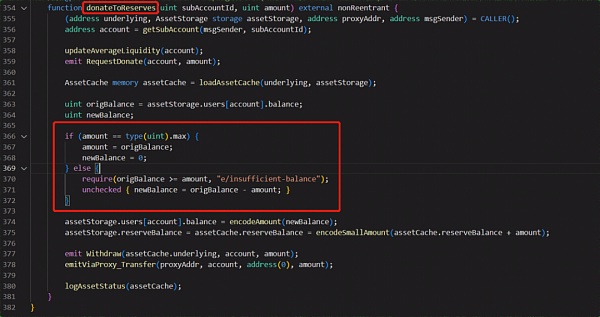
In this attack, the donateToReserves function of the Etoken contract did not correctly check the number of tokens actually held by the user and the user’s ledger after donation. health status. The attacker exploited this vulnerability and donated 100 million eDAI, but in fact the attacker only pledged 30 million DAI.
Because after the donation, the health status of the user's ledger meets the liquidation conditions, the loan contract is triggered to be liquidated. During the liquidation process, eDAI and dDAI will be transferred to the liquidation contract. However, because the amount of bad debt is very large, the liquidation contract will apply the maximum discount for liquidation. After the liquidation, the liquidation contract has 310.93M eDAI and 259.31M dDAI.
At this time, the health of the user's ledger has been restored and the user can withdraw funds. The amount that can be withdrawn is the difference between eDAI and dDAI. But there is actually only 38.9 million DAI in the pool, so users can only withdraw this amount.
6.2 Vyper/Curve Security Incident
Event Summary
On July 31, the Ethereum programming language Vyper was released According to the tweet, Vyper versions 0.2.15, 0.2.16 and 0.3.0 have reentrancy lock vulnerabilities. Curve stated that multiple stablecoin pools using Vyper 0.2.15 (CRV/alETH/msETH/pETH) were attacked, with total losses reaching US$73 million. Afterwards, approximately US$52.3 million has been returned by hackers. .
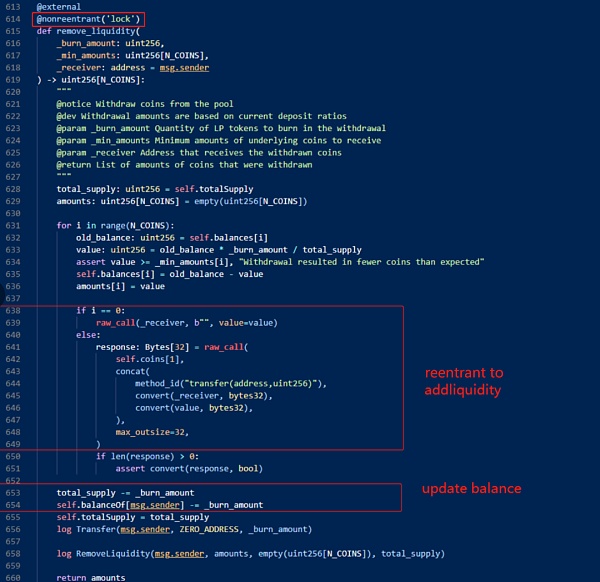
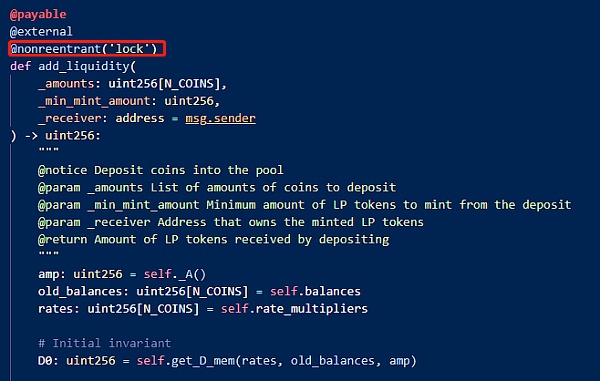
Vulnerability Analysis< /strong>
This attack is mainly caused by the failure of the anti-reentrancy lock of Vyper 0.2.15. The attacker removes liquidity by reentrancy when calling the remove_liquidity function of the relevant liquidity pool. The add_liquidity function adds liquidity. Since the balance is updated before re-entering the add_liquidity function, an error occurs in the price calculation.
7. Reverse Analysis and review of typical money laundering incidents
7.1 Atomic Wallet wallet theft case< /strong>
According to Beosin’s EagleEye security risk monitoring, warning and blocking platform, Atomic Wallet was attacked in early June this year. According to statistics from the Beosin team, based on the known victim reporting information on the chain, the damage caused by this attack was at least approximately US$67 million.
According to the analysis of the Beosin team, the chain involved in this theft incident so far includes a total of 21 chains including BTC, ETH, and TRX. The stolen funds were mainly concentrated on the Ethereum chain. Among them:
The Ethereum chain has found that the stolen funds are 16,262 ETH worth of virtual currency, about 30 million US dollars.
Tron Chain Tron Chain’s known stolen funds are 251335387.3208 TRX worth of virtual currency, about 17 million US dollars.
BTC chain BTC chain’s known stolen funds are 420.882 BTC worth of virtual currency, equivalent to 12.6 million US dollars.
BSC Chain BSC Chain’s known stolen funds are 40.206266 BNB worth of virtual currency.
Remaining chain Ten thousand US dollars
We use the example of money laundering on the Ethereum chain
In the hacker's operation of stolen money, Ethereum was There are two main ways to attack the chain:
Use Avalanche to launder cross-chain money after dispersing through contracts
According to the analysis of the Beosin team, hackers will first remove all the money in the wallet. The valuable currency is uniformly exchanged for the main currency of the public chain, and then collected through two contracts.
The contract address will package ETH into WETH through two layers of transfer, then transfer WETH to the contract used to disperse ETH, and transfer it to Avalanche's wallet address for Cross Bridge through up to 5 layers of transfer. Cross-chain operations are performed in Avalanche. This cross-chain operation does not use contracts and belongs to Avalanche's internal accounting transaction type.
The Ethereum link diagram is as follows:

Aggregation Agreement 1:
0xe07e2153542eb4b768b4d73081143c90d25f1d58 involved a total of 3357.0201 ETH
After switching to WETH, transfer it to the contract 0x3c3ed2597b140f31241281523952e936037cbed3
The detailed map of the stolen goods sale route is as follows:
< img src="https://img.jinse.cn/7055101_image3.png">
aggregation agreement 2: 0x7417b428f597648d1472945ff434c395cca73245 involved a total of 3009.8874 ETH
< /p>
The hacker switched to WETH and transferred it to the contract 0x20deb1f8e842fb42e7af4c1e8e6ebfa9d6fde5a0
The detailed map of the stolen goods sale route is as follows:
Two aggregation contracts were confirmed by agreeing on the source of the handling fee, and some were not Transaction behavior address hiding. The handling fee path is as follows:

In addition , on the Ethereum chain, hackers also laundered money through various cross-chain bridge protocols and exchanges. The current amount involved in this part is 9896 ETH, and this part will be collected through multiple collection addresses.
During the entire incident, there were many channels for hackers to launder money, mainly through various exchange accounts, but also directly into cross-chain bridge contracts. For analysis of fund flows on other chains, click here: A wallet theft involving at least US$60 million , BeosinKYT takes you through hackers’ money laundering routines
Other anti-money laundering case analysis:
< strong>1 Stake.com was attacked and lost US$40 million. Beosin KYT/AML helps you track the flow of stolen funds
2 Beosin KYT analyzes the capital flow behind the JPEX crisis. How can users analyze on-chain data to improve asset security?
3 Following the attack on Poly Network, Beosin KYT/AML will help you track the flow of stolen funds. Unlock more tricks of hackers
4 A $31.6 million Rug Pull? Beosin KYT helps you track capital movements and teaches you how to spot high-yield scam traps!
8. Fund flow analysis of stolen assets
Of the funds stolen throughout 2023, approximately US$723 million remains at hacker addresses (including cases of cross-chain transfers and dispersion to multiple addresses), accounting for 51.8% of total stolen funds. Compared with last year, this year hackers are more likely to use multiple cross-chains to launder money and spread the stolen funds to many addresses. The increase in addresses and the complexity of money laundering paths will undoubtedly make investigations more difficult for project parties and regulatory agencies.
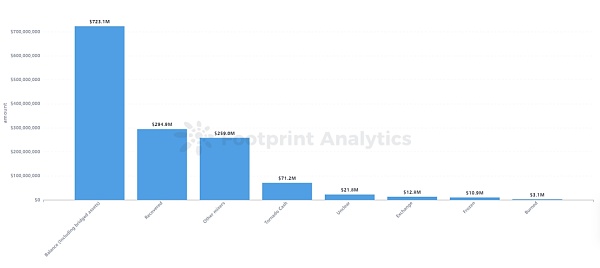
About 295 million U.S. dollars The stolen funds were recovered, accounting for approximately 21.1%. In 2022, only 8% of funds were recovered. The recovery of stolen funds in 2023 is significantly better than in 2022, with most coming from on-chain negotiated returns.
Approximately $330 million of stolen funds were transferred to mixers throughout the year (approximately $71.16 million was transferred to Tornado Cash, and another $259 million was transferred to other mixing platforms), accounting for 23.6% of total stolen funds. This proportion is significantly lower than last year's 38.7%. Since the U.S. OFAC sanctioned Tornado Cash in August 2022, the amount of stolen funds transferred into Tornado Cash has dropped significantly, and has been replaced by an increase in the use of other currency mixing platforms, such as Sinbad, FixedFloat, etc. In November 2023, the US OFAC added Sinbad to the sanctions list, calling it "the main money laundering tool of North Korea's Lazarus organization."
In addition, a small amount of stolen funds (USD 12.79 million) were transferred to the exchange, and a small amount of stolen funds (USD 10.9 million) were frozen.
9. Project audit situation analysis
Among the 191 attack incidents, the project parties of 79 incidents have not been audited, and the project parties of 101 incidents have been audited. The proportion of audited project parties this year is slightly higher than last year (the proportion of audited/unaudited projects last year was roughly the same).

79 no Among the audited projects, contract vulnerability incidents accounted for 47 cases (59.5%). This suggests that projects without audits are more susceptible to potential security risks. In comparison, contract vulnerability incidents accounted for 51 (50.5%) of the 101 audited projects. This shows that auditing can improve project security to a certain extent.
However, due to the lack of complete regulatory standards in the Web3 market, the audit quality is uneven, and the final results are far from expected. In order to effectively ensure the security of assets, it is recommended that the project must find a professional security company to conduct an audit before going online. Beosin, as a world-leading blockchain security company, is committed to the safe development of the Web3 ecosystem. It has audited more than 3,000 smart contracts and public chain mainnets, including PancakeSwap, Ronin Network, OKCSwap, etc. Beosin, as a trustworthy blockchain security company, can provide project parties with excellent security audit services.
10. Rug Pull Analysis
2023 In 2020, Beosin's EagleEye platform monitored a total of 267 Web3 ecological Rug Pull incidents, with a total amount involved of approximately US$388 million, a decrease of approximately 8.7% compared to 2022.
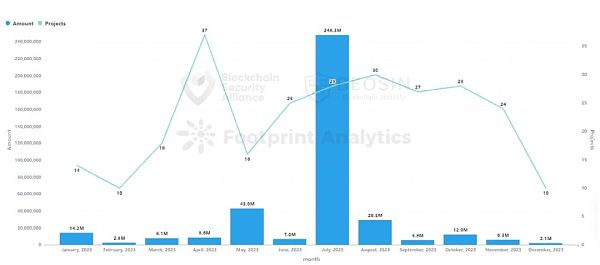
In terms of amount, 267 Among the Rug Pull incidents, 233 (87%) incidents were worth less than US$1 million, which is roughly the same proportion as in 2022. There are 4 projects involving more than 10 million US dollars, including Multichain (US$210 million), Fintoch (US$31.6 million), BALD (US$23 million), and PEPE (US$15.5 million).
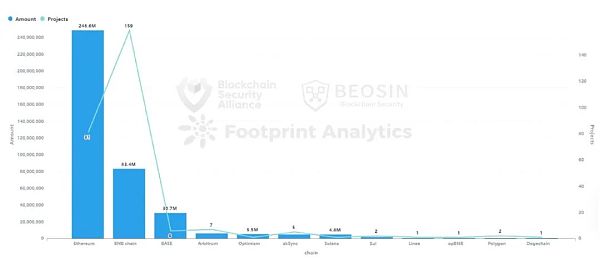
The Rug Pull projects on BNB Chain and Ethereum accounted for 92.3% of the total number, 159 and 81 respectively. A small number of Rug Pull events have also occurred in other public chains, including: Arbitrum, BASE, Sui, zkSync, etc.
11. 2023 Global Encryption Industry Crime Data
In 2023, the amount of crime in the global encryption industry reached a staggering US$65.688 billion, compared with The $13.76 billion in 2022 is up about 377%. While the amount of on-chain hacking attacks has dropped significantly, crime cases in other areas of cryptocurrency have increased significantly. The largest increase was in online gambling, which reached US$54.9 billion. The following are money laundering (about 4 billion U.S. dollars), fraud (about 2.05 billion U.S. dollars), pyramid schemes (about 1.43 billion U.S. dollars), and hacking attacks (about 1.39 billion U.S. dollars).

With the global encryption regulatory system With the improvement of cryptocurrency and the in-depth crackdown on cryptocurrency crimes, in 2023, police around the world uncovered a number of major cases involving hundreds of millions of dollars. The following is a review of some typical cases:
No.1 In July 2023, the Hubei police in China cracked the country's "first virtual currency case", involving 400 billion yuan (approximately $54.9 billion). More than 50,000 people were involved in this online gambling case. The server was located outside China. The principal culprit Qiu Moumou and others have been sent for trial in accordance with the law.
No.2 In August 2023, the Singaporean authorities investigated the largest money laundering case in history, with the amount involved reaching S$2.8 billion. The money laundering method was mainly through virtual currency.
No.3 In March 2023, the Jiangsu police in China launched a public prosecution against Ubank’s “coin speculation” scam, involving a pyramid scheme transaction volume of more than 10 billion yuan (approximately US$1.4 billion).
No.4 In December 2023, according to a statement from the U.S. Attorney’s Office for the Eastern District of New York, the co-founder of the virtual currency exchange Bitzlato pleaded guilty to US$700 million in money laundering charges.
No.5 In July 2023, the Brazilian Federal Police busted two drug trafficking criminal gangs, transferring a total of more than 417 million U.S. dollars and providing money laundering services through encrypted assets.
No.6 In February 2023, according to an indictment in Oregon, the founder of Forsage was indicted in connection with a $340 million DeFi Ponzi scheme.
No.7 In November 2023, the police in Himachal Pradesh, India, arrested 18 people in a $300 million cryptocurrency fraud case.
No.8 In August 2023, Israeli police accused businessman Moshe Hogeg and his partners of defrauding investors of $290 million in cryptocurrency.
No.9 In June 2023, the Thai police uncovered a suspected cryptocurrency fraud case, with the amount involved possibly exceeding 10 billion baht (approximately US$288 million).
No.10 In October 2023, JPEX, a virtual asset trading platform in Hong Kong, was suspected of fraud. The police arrested a total of 66 people, involving an amount of approximately HK$1.6 billion (approximately US$205 million).
2023 is the year of a surge in cryptocurrency crimes. The frequent occurrence of fraud and pyramid schemes also means that the probability of ordinary users suffering asset losses has greatly increased. Therefore, it is urgent to strengthen regulation of the cryptocurrency industry. We can see that global regulatory agencies have made a lot of efforts to regulate cryptocurrency this year, but there is still a long way to go before a complete, safe, and positively developing ecosystem.
12. Summary of Web3 Blockchain Security Situation in 2023
In 2023, on-chain hacking activities, phishing scams, and project party Rug Pull incidents have all dropped significantly compared with 2022. The amount of hacker attack losses has dropped by 61.3%, and the most costly attack method has also changed from last year's contract vulnerability exploitation to this year's private key leakage. The main reasons for this change include:
1. After last year’s rampant hacker activities, the entire Web3 ecosystem has paid more attention to security this year, and everyone from project parties to security companies have made improvements in all aspects. Efforts,such as real-time on-chain monitoring, paying more attention to security audits, and actively learning from past contract vulnerability exploitation incidents. This makes it harder than last year to steal funds through contract loopholes.
2. The strengthening of global supervision and the improvement of anti-money laundering technology. It can be seen that 21.1% of stolen funds were recovered in 2023, which is significantly better than in 2022. As currency mixing platforms such as Tornado Cash and Sinbad are sanctioned by the United States, hackers’ money laundering paths are becoming more complicated. At the same time, we have also seen news about hackers being arrested by local police, which has a certain deterrent effect on hackers.
3. The impact of the crypto bear market at the beginning of the year. The expected return for hackers to steal assets from Web3 projects has declined, thus weakening hacker activity. This has also led to hackers no longer being limited to attacking DeFi, cross-chain bridges, exchanges, etc., but turning to payment platforms, gambling platforms, crypto brokers, infrastructure, password managers, development tools, MEV robots, TG robots, etc. type.
What is different from the significant decrease in hacker activities on the chain is the significant increase in more covert criminal activities off the chain, such as online gambling, money laundering, pyramid schemes, etc. Due to the anonymity of cryptocurrencies, various criminal activities are more inclined to use cryptocurrencies for transactions. However, it would be one-sided to attribute the increase in virtual currency crime cases solely to the anonymity and lack of supervision of cryptocurrencies. The fundamental reason still lies in the increase in global criminal activities, and virtual currencies provide a relatively hidden and difficult-to-track funding channel for these criminal activities. In 2023, the global economic growth slowed down significantly and the political environment faced many unstable factors, which to a certain extent contributed to the surge in global criminal activities. Under such economic expectations, global criminal activities are expected to remain at a high level in 2024, which poses a severe test to global law enforcement agencies and regulatory authorities.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance





























