Source: Chain Tea House
1. Project Introduction
EtherFi is an innovative project focusing on Ethereum staking and liquidity re-staking in the field of decentralized finance (DeFi). By providing a non-custodial staking solution, EtherFi enables users to earn staking income while maintaining asset liquidity, thus solving the problem of fund lock-up in traditional staking.

EtherFi is built on a series of core principles designed to ensure the integrity and decentralization of the Ethereum ecosystem. These principles include decentralization, sustainability and ethical operations, and community focus. EtherFi introduces a complex system involving multiple stakeholders such as stakers, node operators, and node services, divided into three strategic stages: delegated staking, liquidity pools, and node services. Through its innovative design, EtherFi enables stakers to retain control of their keys, which is particularly prominent in the DeFi space.
In addition, EtherFi has introduced a Liquid Staking Token (LST), namely EETH, which marks EtherFi’s commitment to liquidity and flexibility.
2. How it works
2.1 Phase 1: Delegated Staking
In this stage, the pledger can delegate staking in units of 32 ETH, which can be achieved through the following steps:
Node Operator Bids: Node operators submit bids to indicate they are eligible for allocation of validator nodes.
Staking and Auction Mechanism: Stakers deposit 32 ETH into EtherFi’s deposit contract, triggering the auction mechanism and assigning node operators to run validators.
Generate NFTs and Insurance Mechanism: This process mints two NFTs (T-NFT and B-NFT), representing ownership of the withdrawal vault. B-NFTs are unique and provide an insurance mechanism in case of problems with the validator.
Key Management and Validator Launch: Stakers encrypt the validator key and submit it as an on-chain transaction, and node operators use the decrypted key to launch the validator.
Exit Commands and Fund Recovery: Stakers or node operators can issue an exit command to transfer the staked ETH to the withdrawal vault and destroy the NFTs to get their ETH back (minus fees).
2.2 Phase 2: Liquidity Pools and eETH
This phase provides opportunities for stakers with less than 32 ETH or those who do not want to directly monitor the validation nodes to participate:
Liquidity Pools and Asset Mixing: Liquidity pools contain ETH and T-NFTs, with ETH accounting for a small proportion of the pool.
Minting and destroying eETH: When stakers deposit ETH into the pool, the pool mints eETH tokens and transfers them to the depositor. Stakers holding T-NFTs can also deposit them into the pool and mint an equivalent amount of eETH.
Conversion of eETH and ETH: Stakers holding eETH can convert it into ETH at a 1:1 ratio if there is sufficient liquidity.
2.3 Phase 3: Node Services
This is a prospective phase of the protocol, which includes many undecided technical decisions:
NFT and Node Services: Leverage NFTs to create a programmable staking infrastructure layer to create economic incentives for node operators and stakers.
Registration and management of node services: Nodes can be registered to provide additional services, which requires the joint consent of node operators, B-NFT holders, and EtherFi.
3. Core Mechanism
3.1 Delegated Staking and Non-custodial Control
EtherFi allows stakers to maintain full control of their Ethereum keys, which is a key feature that distinguishes it from other staking protocols. In EtherFi, stakers do not just send their ETH to the protocol, but through a special mechanism that ensures that they still control their assets throughout the process.
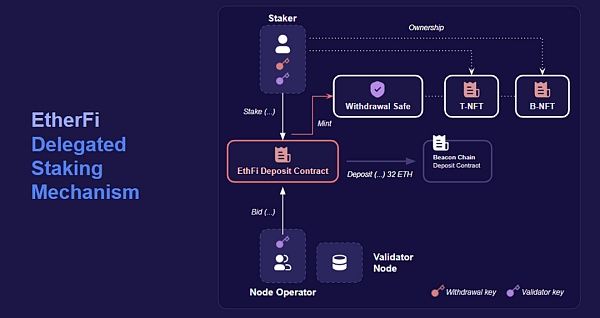
3.1.1 Delegated Staking
In EtherFi, delegated staking allows stakers to stake their Ethereum to the network to support the operation and security of Ethereum, but unlike traditional staking methods, stakers do not need to deliver ETH to centralized node operators or staking pools. Instead, they delegate node operators to run validators through EtherFi's protocol while maintaining control of their assets. This approach reduces dependence on centralized entities and enhances decentralization and security.
3.1.2 Non-custodial control
Non-custodial control is another key feature of EtherFi, which ensures that stakers always control their crypto assets. In the EtherFi protocol, stakers' ETH will never leave their wallets or be transferred outside of protocol control. This is achieved through the use of smart contracts and encryption technology, where stakers generate and hold their own private keys, and smart contracts securely handle staking operations without the need to transfer control.
3.2 NFT and Validator Management
In the EtherFi protocol, the combination of NFT (non-fungible token) and validator management is one of its core innovations. This mechanism greatly improves the flexibility and operability of Ethereum staking. By using NFT as a direct management tool for validators, EtherFi provides stakers with a transparent, verifiable and decentralized management method.

3.2.1 NFTization of Validators
In EtherFi, the creation of each validator is accompanied by the minting of a unique NFT. This NFT not only represents the ownership of the funds staked on the validator, but also contains all the key data required to manage and run the validator.
NFT Content:
Validator Information: Including the node on which the validator runs, the physical location, the node operator, and detailed information on the node service.
Management Rights: NFT holders have control over the validator, including but not limited to the ability to start, stop, or reconfigure the validator.
Pledged ETH Information: Each NFT is bound to a certain amount of ETH, usually 32 ETH, which is the standard pledge amount required to start an Ethereum validator.
3.2.2 Decentralization of Validator Management
Through NFT, EtherFi allows stakers to manage their validators in a very flexible and decentralized way. This approach reduces the trust issues common in traditional staking services, and stakers do not have to transfer their ETH to a third party.
Operation process:
Minting NFT: When a staker decides to start a validator through EtherFi, the system automatically mints an NFT.
Trading and transfer of NFT: NFT can be freely traded on the market, allowing validator management rights to be transferred from one staker to another without actually moving the ETH bound to the NFT.
Dynamic management of validators: NFT holders can directly manage validators through smart contracts, such as changing node operators or adjusting validator configurations, all of which are performed through the NFTs held.
3.2.3 Extended Uses of NFTs
EtherFi’s NFTs are more than just a management tool; they also serve as the foundation for a sophisticated permissions and management framework.
Functionality and Security:
Verification and Transparency: NFTs provide a complete record of validator operations, increasing transparency and traceability of operations.
Enhanced Security Measures: NFTs can be used with smart contracts, such as implementing an automatic stop strategy for validators to address potential security threats.
Integration of Other Services: Other decentralized services can be integrated into NFTs, such as automatic re-staking, yield optimization strategies, etc.
Through this innovative combination of NFT and validator management, EtherFi provides a more secure, flexible, and user-friendly staking solution, greatly enhancing users’ control over their staked assets, while also bringing new possibilities to the Ethereum ecosystem.
3.3 Decentralized Validator Technology (DVT)
In the EtherFi platform, Distributed Validator Technology (DVT) is a key innovative technology designed to improve the validator management and operation of Ethereum. DVT allows multiple independent operators to jointly manage a validator, which not only increases the decentralization of the network, but also improves security and reliability.

The following is a detailed introduction to DVT in EtherFi:
3.3.1 Core Concepts of DVT
In the traditional Ethereum staking model, a validator is usually managed by a single node operator. This model may introduce centralization risks in some cases. For example, if the node operator is unreliable or attacked, it may affect the performance and security of the validator.
DVT disperses the risk of single point failure by allowing multiple independent entities to jointly manage a single validator. This approach has several key advantages:
Enhanced security: Since there is no longer a single entity to control the validator, the risk of being attacked or abused is reduced.
Improved decentralization: The participation of multiple managers further decentralizes the network, which is in line with the core principles of the Ethereum ecosystem.
3.3.2 How DVT works
Key splitting: In DVT, the key that controls the validator is split into multiple fragments, and each entity involved in management holds a part. Only when most or all of the fragments are combined can the validator be operated.
Consensus mechanism: Consensus is required between managers to perform key operations, such as updates, withdrawals, or other key configuration changes to the validator.
Contracts and agreements: There are usually clear contracts and agreements between DVT participants to regulate everyone's responsibilities and rights, ensuring the fairness and transparency of the entire system.
3.3.3 Implementation and challenges of DVT
The implementation of DVT faces some technical and operational challenges, mainly including:
Technical complexity: The implementation of key splitting and consensus mechanisms requires a high degree of technical ability and precise execution.
Coordination and Cooperation: Coordination and cooperation among multiple independent entities may be difficult, especially in the face of network consensus or emergency situations.
Legal and Compliance: Legal and regulatory requirements in different jurisdictions may have an impact on the implementation of DVT, especially regarding the protection of funds and data.
4. ETHFI Token
The EtherFi Token (ETHFI) is the native token of the EtherFi platform, with multiple uses, designed to support the platform's decentralized staking and node running activities.

The following is a detailed introduction to the ETHFI token:
4.1 Token Functions and Uses
Payment of protocol fees: ETHFI tokens are used to pay various protocol fees incurred when trading and operating on the EtherFi platform.
Incentivize stakers and node operators: Through ETHFI tokens, the platform rewards users who participate in staking and running nodes, encouraging them to contribute to the security and stability of the network.
Governance voting: Users holding ETHFI tokens can participate in the platform's governance decisions and vote on key protocol updates and changes.
4.2 Token Allocation and Release
Total Supply: The total supply of ETHFI is 1 billion. The current circulation is 115,200,000 ETHFI, accounting for 11.52% of the total.
Public Sales and Private Sales: EtherFi conducted several rounds of private and public sales, attracting participation from top funds such as Arrington XRP Capital and Consensys.
Initial Exchange Offering (IEO): The ETHFI token conducted an IEO on Binance Launchpool, with 2% of the supply allocated to this event.
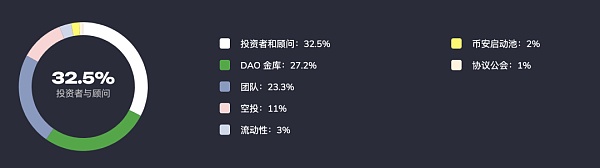
The distribution of tokens is: Investors and Advisors: 32.5%, DAO Treasury: 27.2%, Team: 23.3%, Funding: 11%, Liquidity: 3%, Binance Launch Pool: 2%, Protocol Guild: 1%
Token Release
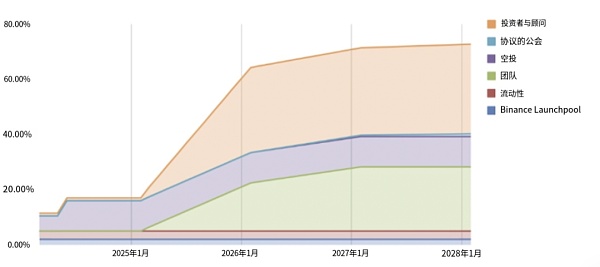
4.3 Security and Stability
4.4 Governance and Future Planning
DAO Governance: ETHFI token holders can participate in a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) and influence the direction of the platform through voting.
Technical Development: EtherFi plans to continue to advance technological innovation, including expanding its decentralized validator technology (DVT) and improving the openness and permission model of smart contracts.
4.5 ETHFI Airdrop

Airdrop Overview: In Season 1, those who minted EtherFan NFTs (at a price of 0.01 ETH) received an airdrop of 430 ETHFI tokens, which were worth approximately $36,000 at the time. In addition, those who staked EETH on EtherFi received additional token allocations. Season 2 has begun and once again announced an airdrop to community members participating in Liquid.
Liquid Platform: Liquid is an automated DeFi strategy vault that allows users to easily participate in the DeFi ecosystem using their EETH. Users simply deposit EETH, WEETH, or WETH, and the vault will allocate these assets across a variety of DeFi positions.
Ranking and Loyalty Points: StakeRank is an 8-tier system that allows users to advance one tier for every 100 hours of ETH staked, with each tier having a progressively increasing rate of loyalty points. Stake balances need to exceed 0.1 EETH to continue to rank up.
Other Incentives: Those who participated in Season 1 will start at Level 2 in Season 2. EtherFan NFT holders will automatically be promoted to Level 3.
Quarterly Transitions: In order to fairly treat participants in Seasons 1 and 2, everyone's loyalty point accumulation rate will be increased by 10 times. While this dilutes old points, they will still be calculated based on the following conditions.
4.6 ETHFI Token Performance Analysis
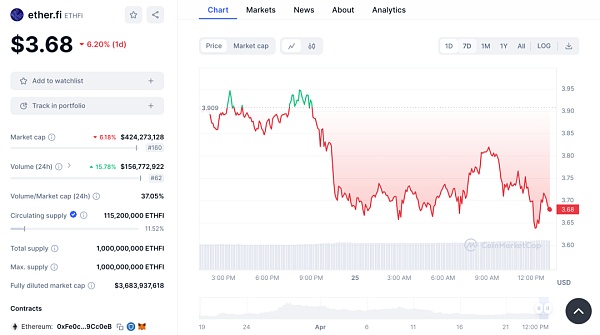
As of now, the price of the ETHFI token is $3.68, down 6.20% in a day.
Market Capitalization: With a market capitalization of $424 million, it ranks 160th among all cryptocurrencies. This shows that it has a relatively small but significant share of the crypto market.
24-hour trading volume: The trading volume has increased, rising by 15.78% to about $157 million. This could indicate increased market activity, rising trading interest, or greater price volatility.
24-hour Volume/Market Cap Ratio: This ratio is relatively high at 37.05%, indicating that the coin has had fairly active trading activity relative to its market cap over the past 24 hours.
5. Team/Partners/Financing
5.1 Team
The EtherFi team consists of many professionals in the fields of blockchain and decentralized finance

Mike Silagadze (Founder and CEO): Mike has been investing in crypto since 2010 and previously founded Top Hat. He holds a BA from the University of Waterloo.
Chuck Morris (Vice President, Chief Engineer): Chuck has built and led engineering teams for over a decade. He holds an MS in Computer Science from the University of Chicago.
Rok Kopp (Director of Customer Success): Rok holds a BA from the University of Notre Dame and has over a decade of startup sales and marketing experience.
5.2 Partners
EtherFi has established partnerships with many parties, such as:
Kiln: Provides infrastructure services for Ethereum, such as node operation or staking solutions
DSRV: A company that provides blockchain infrastructure support, including node services and other technical support.
Chainnodes: A blockchain service provider focusing on node operation and management.
Obol: A company focusing on distributed trust protocols or decentralized technologies related to blockchain.
5.3 Financing
EtherFi has achieved significant growth through multiple rounds of financing.
Initially, the company completed a $5.3 million round of financing, co-led by North Island Ventures, Chapter One and Node Capital, with participation from well-known figures such as BitMex founder Arthur Hayes (coindesk).

Since then, EtherFi has successfully raised $23 million in a Series A round led by Bullish Capital and CoinFund, with participation from other investors such as OKX ( coindesk ). This capital injection has greatly boosted EtherFi's operations, enabling it to expand its services and enhance its platform. The Series A round significantly increased the company's capital base from $103 million to $1.66 billion, marking a significant increase in its financial and operational scale ( coindesk ). These developments highlight EtherFi's solid position in the decentralized finance (DeFi) space and its continued appeal to investors looking for opportunities in the blockchain and cryptocurrency space.
6. Project Evaluation Analysis
6.1 Track Analysis
The EtherFi project belongs to the staking and liquidity staking in the field of decentralized finance (DeFi). This track focuses on providing decentralized staking services, especially services that allow Ethereum holders to earn income by staking ETH without losing liquidity. Its feature is to enable users to stake their ETH to the Ethereum network to support the network operation and obtain staking rewards, while issuing corresponding tokens to maintain the liquidity of the staked assets.
EtherFi is mainly aimed at cryptocurrency holders who want to earn income from their holdings through the staking mechanism without losing liquidity. By providing non-custodial liquid staking solutions, EtherFi attracts individual and institutional investors interested in decentralized and scalable financial solutions.
Similar projects to EtherFi include:
Lido Finance provides liquidity solutions for ETH2.0 staking.
Rocket Pool is another decentralized Ethereum staking network that allows users to stake with smaller amounts of ETH.
Stakewise provides a decentralized Ethereum staking service through which users can earn staking income.
Ankr Staking provides a liquidity staking service where users can stake their crypto assets and earn income.
Marinade Finance is a platform that provides similar services for the Solana blockchain.
6.2 Project Advantages
High Total Locked Value (TVL): Having a TVL of $300 million means that EtherFi is strongly recognized by the market and has a large amount of funds locked in the platform. High TVL usually indicates that a project has an active user base, strong capital attraction and stable liquidity.
Low Token Inflation Rate: Maintaining a low inflation rate (0.46%) in the first year after the TGE (token issuance) helps maintain the stability of the token price, which is an attractive factor for early investors and token holders because it reduces the risk of dilution.
Low FDV/Initial Market Cap Ratio: The ratio of fully diluted market cap (FDV) to initial market cap is 11.52%, which indicates that the increase in market cap is controllable even if all tokens enter the market circulation. The low FDV/market cap ratio may reassure new investors because it implies that the upper limit of future token price fluctuations is reasonable.
Growth Marketing and PR Performance: Strong market growth strategy and PR activities indicate that EtherFi has performed well in expanding market influence and increasing brand awareness.
Experienced Team: An experienced team usually means that the project has better execution and a higher probability of success, because team members may have accumulated valuable experience and resources in related fields before.
Security Audit: Security audits performed by top companies increase the credibility of the project and provide users with a safe staking and trading environment, which is particularly important in the DeFi field.
Top Funding Support: The support of top funds not only provides the necessary financial resources, but also brings networks and expertise, which is particularly important for startups.
6.3 Project Disadvantages
1. Weak Marketing Infrastructure and SEO Performance:
Inadequate marketing infrastructure and search engine optimization (SEO) may result in low visibility of the project on the Internet, making it difficult to attract new users or keep existing users active. This may affect the overall growth and brand building of the project. To improve this, EtherFi may need to invest in marketing teams and technologies, conduct targeted marketing campaigns, and optimize its online content to improve search engine rankings.
2. The token inflation rate in the second year after the TGE is quite high:
High inflation rates may lead to dilution of token value, which will have an adverse impact on long-term holders. High inflation may also undermine investor confidence in the project, especially if the inflation is not justified by substantial project progress or revenue growth. EtherFi needs to clearly communicate the reasons for inflation and management strategies to ensure that the community understands and supports its token policy.
3. Lack of transparency in token economics:
If investors and users cannot easily access information about token pricing, distribution, and vesting conditions, it may have a negative impact on the trust and attractiveness of the project. Transparency is a key factor in building investor and community trust. Lack of transparency may lead to insufficient investment decisions and reduced market participation. EtherFi can enhance transparency and credibility by providing a detailed token economic white paper, regular updates, and public Q&A.
In response to these shortcomings, the EtherFi team may need to make some strategic adjustments, including strengthening its marketing and PR activities, re-evaluating its token economic model to better manage inflation, and improving the overall transparency of the project to ensure long-term sustainable development and community support.
7. Conclusion
Looking forward, EtherFi has several potential development directions:
Technology and product iteration: With the development of blockchain and DeFi technology, EtherFi needs to continuously update and optimize its products to remain competitive. This includes improving its liquidity re-pledge protocol and adding more integrations with other DeFi projects and protocols.
Enhance marketing and user education: In order to expand its user base and market share, EtherFi needs to strengthen its marketing strategy and increase brand awareness and project visibility. At the same time, the project should increase education for users to help them understand the project's advantages and operating methods.
Addressing regulatory challenges: With the increase in DeFi regulation around the world, EtherFi may need to adapt to changes in relevant regulations to ensure the compliance of its operations.
Cooperation and ecosystem expansion: Through cooperation with other DeFi projects and traditional financial institutions, EtherFi can further expand its ecosystem, increase the inflow of users and funds, and improve the market adaptability and attractiveness of its products.
In summary, despite the challenges, EtherFi has the potential to achieve long-term success in the DeFi field and become a leader in staking services with its innovative solutions and strong team background. Through continuous technological innovation and market strategy adjustments, EtherFi is expected to occupy an important position in the future blockchain staking market.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance





















