Author: Marcel Deer, CoinTelegraph; Compiler: Baishui, Golden Finance
1. What is chain abstraction?
Chain abstraction is a concept that simplifies the user experience of blockchain technology and unifies transactions across multiple networks.
Web3 is still a distributed industry, resulting in a complex and technical user experience. This is an entry barrier for the mainstream public, who must create multiple crypto wallets, store mnemonics, and switch between blockchains to use various applications.
It's like going out for pizza, but going to a different restaurant for each meal - one place for dough, another for pepperoni, and another for mozzarella. Plus, you have to use a different currency for each. It won't be a pleasant experience.
Blockchain chain abstraction aims to solve this problem by hiding or "abstracting" the technology from users. This means that people don't know that they are using a blockchain or which blockchain they are using.
The idea is to remove technical details such as token bridging, gas fees, consensus mechanisms, and users' native tokens. Instead, it allows them to use Web3 with one wallet and one cryptocurrency. All the technical work happens behind the scenes.
Did you know? There are now over 1,000 different blockchains in existence, each with their own features and use cases. While they all use the core principles of cryptography and distributed ledger technology, many are independent projects. This has created a fragmented ecosystem that makes it difficult to transfer assets between networks.
How does chain abstraction work?
Chain abstraction in blockchain works by providing a single interface that enables users and developers to interact with multiple blockchains without having to manage the complexity of each individual chain.
Chain abstraction solutions are still in development, and many companies are working on the problem. At present, how this all works is not an exact science, but a multi-chain solution may allow users to seamlessly use Web3 from a single account.
It may look like this:
Users first create a zero-funded account by logging in with an email. No private keys or seed phrases need to be remembered.
Next, users can fund their accounts with a single "master" currency, which is used to pay for their Web3 activities. Users will then be able to find and use Web3 applications regardless of which blockchain it runs on. Any interaction will be forwarded and signed on the applicable network, and fees will be automatically paid. Currency bridging or swaps will be done out of the user's sight through smart contracts.
For example, you can collect NFTs minted on different blockchains without the need for separate wallets, exchanging cryptocurrencies, or storing recovery seed phrases.
Did you know? The idea of chain abstraction is not new. It draws inspiration from traditional software engineering. Developers have been using this concept to simplify complex systems for users for decades. In fact, end users don't need to know how things work internally - they need to achieve their end goals as simply as possible.
3. Benefits of Chain Abstraction
Both users and developers benefit from chain abstraction because it removes the complexity of using blockchains, allowing seamless multi-chain interoperability.
Here are the main benefits of chain abstraction:
Unified interface:Chain abstraction reduces fragmentation and complexity for users. It enables them to manage their assets and access decentralized applications (DApps) on different blockchains from a single interface, wallet, or platform.
No Learning Curve:Currently, Web3 has a huge learning curve where users need to understand wallet usage, private key storage, asset bridging, decentralized applications, etc. Chain abstraction gradually eliminates this difficulty, allowing people to use Web3 quickly and easily.
Simplified Transactions:It eliminates the manual processes currently required to use multiple blockchains. Users can seamlessly trade between multiple blockchains without the hassle of trading and bridging tokens. There is no need to understand the underlying Web3 technology to pay gas fees, utilize DApps, or manage assets across multiple chains.
Liquidity:As assets aggregate on different chains, chain abstraction can provide virtually unlimited liquidity across the ecosystem. Tokens can move freely and be pooled from multiple sources without friction. This makes it easier for traders and investors to access larger liquidity pools while helping to reduce market slippage and improve efficiency.
DApp Development:For developers, the complexity of building multiple blockchains can also be simplified. It becomes faster and easier to create applications that run across multiple chains without having to write separate code for each network.
Fourth, the application of chain abstraction
By improving transaction efficiency, access to DApps, and development processes, it can revolutionize the scalability of blockchains, including decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, games, NFTs, and software as a service (SaaS) industries.
Several projects are working to solve the chain abstraction problem:
Particle Network aims to unify all chains through a universal account. The company has raised $40 million in funding from multiple venture capitals and Alibaba Group to continue its development. Their goal is to make the use of Web3 simpler so that users only need to use one account for any chain.
Near is a smart contract platform that provides chain abstraction to solve these blockchain ecosystem problems. With one account, users can sign transactions on multiple blockchains, such as BNB Smart Chain and Ethereum. This includes multiple chain abstraction use cases such as minting NFT collections across multiple chains or operating DAO applications that accept proposals and votes through multiple chains.
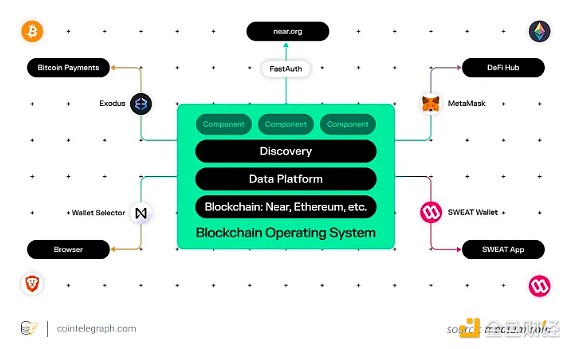
Xion enables developers to build consumer-ready platforms and remove the complexity of Web3. It claims to be the first wallet-less blockchain ready for mainstream adoption. Using a single account, users can manage their entire Web3 experience, from signing transactions to enjoying social media networks.
Did you know? Some popular DeFi platforms already use chain abstraction to help aggregate liquidity and provide users with an enhanced trading experience. Platforms such as ThorChain and AnySwap allow transactions to swap tokens between different blockchains without using a separate bridge or exchange.
V. Future Outlook of Chain Abstraction
Chain abstraction technology offers a promising future as it attempts to solve the biggest pain points in Web3 adoption. Currently, the industry needs to be more cohesive, and blockchain projects are often committed to trying and dominating the industry rather than building a user-friendly ecosystem.
As crypto infrastructure enters its second decade, long-term users are scattered with various wallets and keys. Although wallet providers are committed to providing multi-asset storage, bridging the asset gap between cross-chains and applications remains a problem. For the average mainstream consumer, Web3 is technically overwhelming, while Web2 is a smooth co-pilot in daily life.
To have a similar impact on the world, Web3 will need to rely heavily on chain abstraction. The process is technically complex because it needs to ensure seamless blockchain interoperability while maintaining the security of a large number of networks. This requires extensive cooperation from developers working on first- and second-layer projects.
Regulatory uncertainty may pose another problem, as it always does in such innovative areas. Ensuring compliance across jurisdictions and industries (especially finance) is another area that is expected to take years to fully master.
 Hui Xin
Hui Xin
 Hui Xin
Hui Xin Davin
Davin Aaron
Aaron YouQuan
YouQuan Hui Xin
Hui Xin Brian
Brian Davin
Davin YouQuan
YouQuan Brian
Brian Aaron
Aaron