November Outlook: I decided to go all in on AI Agent
AI Agent, November Outlook: I decided to go all in on AI Agent Golden Finance, Ethereum will transform from DeFi narrative to RWA narrative
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
Author: Alexander Nardi Source: Shoal Research Translation: Shan Ouba, Golden Finance
Transformation through AI agents: AI agents will revolutionize gaming and entertainment by providing personalized, dynamic, and immersive experiences that far exceed traditional user-generated content (UGC).
Advances in AI technology: Key advances such as reinforcement learning, neural networks, and generative models (GANs) are essential for developing sophisticated AI agents.
Integration with blockchain: Blockchain provides a secure, immutable, and transparent environment for deploying AI agents, greatly enhancing their capabilities and reliability.
Case Studies in AI Innovation: Virtuals Protocol and Echelon Prime demonstrate how AI agents can unlock new opportunities in gaming and entertainment through their innovative applications and decentralized ecosystems.
Challenges and Regulatory Needs: Ensuring seamless communication, robust infrastructure, and ethical use is critical for AI agents. Further regulation and safeguards such as “kill switches” will be critical to prevent abuse and build trust.
Future Outlook: The continued evolution of AI agents is likely to expand into audio to video and broader consumer applications, driving mainstream adoption and innovation.
The gaming industry is going through a transformational moment with the rise of user-generated content (UGC). Major games like Roblox and The Sandbox enable users to create and personalize their gaming experiences. This shift is further enhanced by the emergence of AI virtual assistants and companions, which not only help personalize games, but also become another form of UGC. Users will soon begin to fine-tune their own companions and potentially make them available for others to interact with, similar to user-trained variants of chatGPT and TutorGPT.
Google DeepMind's achievements in AI, especially its latest chess engine, demonstrate the potential of AI agents in games. This engine works by taking multiple AI agents of different styles and forming a master engine that can master each style of play. This “search-free” chess engine uses evaluation to understand positions and select the most appropriate agent for each opening, mimicking human diversity and creativity.
Many established blockchain-native AI protocols focus on decentralized computing and governance frameworks, laying the foundation for responsible AI development. With these infrastructures in place, developers are now turning to more sophisticated AI models, such as AI agents, which can perform autonomous tasks with minimal human intervention.
Blockchain technology furthers this evolution by providing a decentralized infrastructure that ensures transparency, security, and immutability of transactions. The integration of AI agents within these standardized environments can create a more collaborative and personalized experience for users, thereby transforming the gaming and entertainment industries in ways that are currently unimaginable.
An AI agent is essentially a software program that is able to independently interact with its environment, collect data from its interactions, and use this data to achieve its predetermined goals. The goals can range from task automation to more complex decision-making processes. The key to AI agents is their autonomy, which is to minimize human intervention when executing specific goals. These programs can perform tasks autonomously and have "read" and "write" access rights. Unlike today's popular AI applications such as ChatGPT, which can only respond to questions (read access), AI agents can also take actions based on the information they collect (write access).
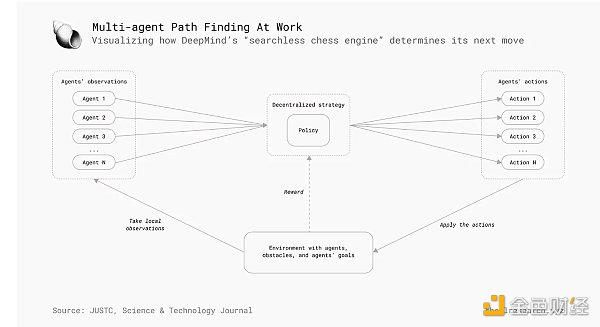
The origins of autonomous agents can be traced back to the broader efforts in the 1980s and 1990s to design machines that can learn from their environment and make intelligent decisions without human intervention. The development of various machine learning, deep learning, and neural network algorithms laid the foundation for more advanced forms of agents seen today, such as Google DeepMind’s new chess engine, which uses multiple AI agents to master various play styles.
Reinforcement learning has played an important role in developing AI agents that can autonomously navigate complex environments and achieve specific goals. Neural networks, especially deep learning models, enable AI agents to process large amounts of data and recognize patterns, expanding their potential applications in various fields such as gaming and entertainment.
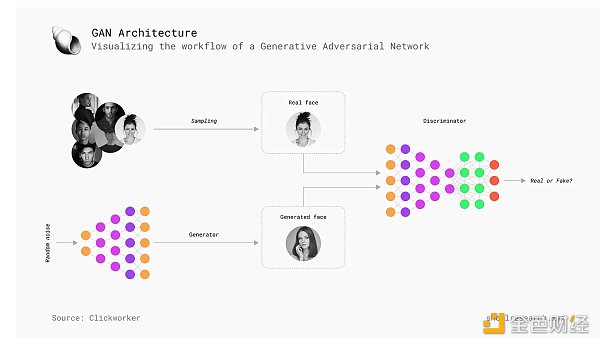
A major breakthrough in enabling AI agents is the development of generative adversarial networks (GANs). GANs consist of two neural networks, a generator and a discriminator, which work together to create realistic data. The generator creates the data, and the discriminator compares it to real-world data and provides feedback to improve the generator’s output. This iterative process makes it possible to create highly realistic virtual characters, environments, and even art, making GANs particularly valuable in gaming and entertainment.
Another important advance is transfer learning, where AI models pre-trained on large datasets are fine-tuned for specific tasks. This approach significantly reduces the time and resources required to develop complex AI agents. Transfer learning enables AI agents to take existing knowledge and adapt it to new environments and tasks, making them more diverse and effective.
In a multi-agent system, multiple agents collaborate to achieve a common goal. AI agents promote collaboration and efficient workflows by assigning tasks to other AI agents. The process involves a general AI assistant receiving a task, studying the required steps, and assigning each step to a specialized AI agent. These agents complete the task as a team, and there will also be other agents involved in quality control and supervision to minimize human intervention.
In the field of gaming, AI agents can enhance the gaming experience by providing intelligent and responsive non-player characters (NPCs), generating dynamic content, and providing personalized interactions. These agents are able to adjust to the player's preferences and behaviors, creating a more engaging and immersive experience. In addition, AI agents can assist in game development by automating repetitive tasks such as bug testing, level design, and character animation. This automation can significantly reduce development time and costs, allowing developers to focus on creativity and innovation. AI agents can also be used to analyze player data, providing insights on player behavior and preferences to guide game design and marketing strategies.
Integrating AI agents into virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) environments opens up new possibilities for immersive experiences. AI agents can act as guides, companions, or opponents in VR and AR worlds, providing real-time interactions and adjusting based on the user's actions and surroundings. This capability can enhance the sense of presence and immersion, making virtual experiences more engaging and realistic.
Virtual companions are agents that provide personalized experiences to users and are designed to learn from interactions with users, adjusting their responses and behaviors based on the user's preferences. These companions can range from idols who interact with fans individually, to virtual friends or companions who provide companionship, to virtual pets that simulate real pets. By leveraging user preferences to provide customized experiences across different platforms, these agents create new possibilities for user experience, bringing a sense of companionship and connection.
Virtual idols can communicate with fans through personalized interactions, such as replying to messages, participating in live broadcasts, and creating customized content. Such interactions can deepen the connection between idols and fans and enhance the overall fan experience. Virtual friends and companions can provide emotional support, companionship, and entertainment, making them valuable tools to combat loneliness and social isolation.
Virtual pets can provide a unique form of companionship that simulates the behaviors and interactions of real pets. These AI-generated pets can learn from interactions with users, adjusting their behavior based on the user's preferences. This capability enhances the user experience and makes virtual pets more engaging and fun.
Virtual companions can also play a role in education and therapy. For example, AI tutors can provide a personalized learning experience that adapts to the student's learning style and pace; in therapy, AI companions can provide emotional support and cognitive behavioral therapy exercises.
AI agents can serve as non-player characters (NPCs) in video games, enhancing the gaming experience through cross-game memory that retains concepts across different games. For example, an AI agent that plays with a user in NBA 2K can also play PUBG on the user's phone and remember preferences across platforms. This cross-game memory allows for a more coherent and personalized gaming experience because the AI agent can adjust to the user's preferences and behaviors.
AI-generated NPCs can provide a more dynamic and interactive gaming experience by reacting to the player's actions and decisions. These NPCs can exhibit complex behaviors and adapt to the changing game environment, creating a more immersive and engaging experience for players. In addition, AI-generated NPCs can generate unique content such as quests, challenges, and characters, enhancing the replayability and persistence of the game.
The ability of NPCs to learn and adapt over time can create more realistic and engaging gaming experiences. For example, NPCs can develop relationships with players, remember past interactions, and change their behavior based on previous encounters. This dynamic interaction can make games more immersive and provide a deeper sense of connection between players and the game world.
AI agents can create game assets and unique experiences for each player, expanding the concept of user-generated content (UGC). This capability allows for dynamic and personalized gaming environments that adapt to the preferences of individual players. AI-generated content can include custom levels, quests, characters, and items, enhancing the variety and replayability of games.
AGC has far more transformative potential in the gaming space than traditional UGC. This potential depends on the quality of the AI agents and their ability to effectively communicate and understand the environment. High-quality AI agents can generate content that is diverse, engaging, and seamlessly integrated into the game world, significantly enhancing the overall player experience.
Imagine a scenario where AGC and UGC combine to create new worlds. In this scenario, AI agents can help players design and build their creations, provide suggestions, automate repetitive tasks, and enhance the complexity and detail of the content. Players can fine-tune and personalize AI-generated content, forming a collaborative creative process that combines the strengths of both.
This symbiotic relationship between AGC and UGC may lead to the development of rich, varied game worlds. Players can explore environments enriched by both human imagination and AI generation power, creating dynamic and immersive gaming experiences.
Virtuals Protocol is building an AI-meets-metaverse protocol designed to be the foundation for future virtual interactions. Their vision is to create a future where the worlds we access from our desks and couches are not just places of escapism, but extensions of our lives. Here, virtual interactions are hyper-personalized and hyper-immersive, powered by AI, and built in a decentralized way.
As we become more and more embedded in virtual spaces, our interactions within these spaces will become more important. In fact, the transition to virtual spaces looks increasingly inevitable. Virtuals Protocol is building multimodal (text, voice, visual) AI agents that can enhance these interactions in a variety of ways. These AI agents can behave like mirror copies of popular IP characters, perform specific tasks, or act as personal copies of the users themselves. Here are some examples of multimodal AI in action:
Mirror copies of IP characters:
In a game, players can interact with a digital John Wick who not only looks and sounds like the character, but also exhibits his unique fighting style and personality. This can make the gaming experience more engaging and realistic.
Task-specific AI:
Horror Story Narrative Generator: An AI can generate immersive horror stories that adapt the plot based on the player's choices and interactions.
DOTA Competitive Coach: An AI coach can analyze your gameplay in real time and provide tips and strategies for improvement to improve your competitive performance.
User's personal copy:
Virtual Assistant: AI agent that learns from your behavior and preferences to help manage your virtual and real-world tasks, like scheduling and reminders.
How Virtuals Protocol Works
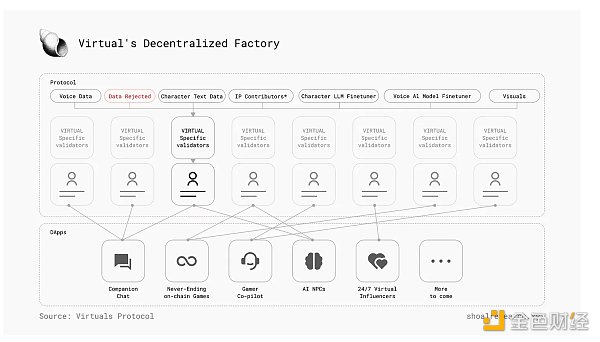
Virtuals Protocol operates like a decentralized factory, producing AI agents that respond via text, voice, and action. Contributors add data and create AI models, validators ensure quality, and DApp founders use these agents to create immersive experiences. AI agent modules include cognitive, speech, and vision cores, each contributing to the agent's multimodal capabilities. The cognitive core processes information and makes decisions, the speech core enables auditory interaction, and the vision core provides the agent with a visual identity. These modules work together to create coherent and interactive AI agents.
A key feature of Virtuals Protocol is its audio-to-animation capability, allowing AI agents to generate animations based on audio input. This capability enhances the realism and immersion of virtual interactions, making AI agents more engaging and alive. Virtuals Protocol's decentralized approach ensures that AI agents are created and maintained by a community of contributors and validators. Validators play a key role in maintaining the integrity and quality of the ecosystem, while contributors can share their individual expertise and resources to improve the quality and functionality of AI agents.
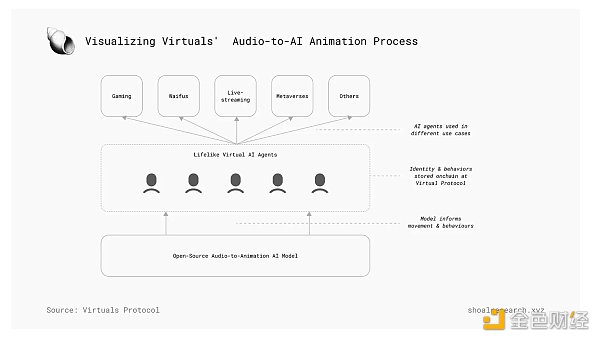
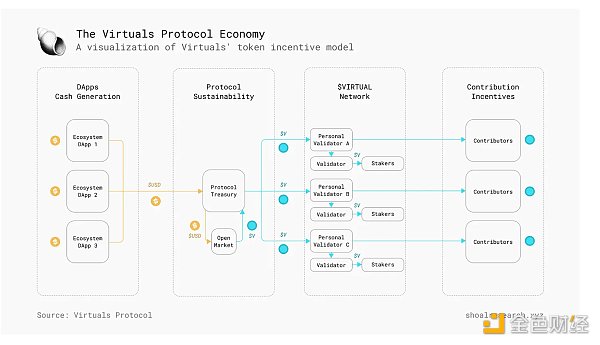
To coordinate the behavior of various participants in its ecosystem, Virtuals Protocol utilizes its native $VIRTUAL token as a key feature of its business model. This economic model mainly relies on a positive reflexive economic cycle, known as the "Virtual-ous" flywheel.
Contributors are paid in $VIRTUAL tokens to develop virtual agents. These tasks may include the implementation of chatbot functionality and domain knowledge, as well as the implementation of audio and visual features. These agents are then integrated into various decentralized applications (DApps) in the Virtuals ecosystem, which utilize these agents for various business operations and collect fees. The revenue generated through these fees is then fed back into the protocol, which uses these funds to repurchase $VIRTUAL tokens from the open market. This repurchase is used to replenish the $VIRTUAL tokens in the treasury, ensuring a stable supply to incentivize contributors in the future. In addition, $VIRTUAL token holders can indicate which agents should receive more token issuance by staking their tokens.
Future Outlook and Considerations
Currently, according to the team's self-reported data, there are 888,400 inferences, 175 active validators, 350 active contributors, and more than 1,000 AI agent contributions on the Virtuals platform.
Virtuals' goal is to democratize the creation and monetization of AI agents, making high-quality virtual interactions accessible to a wider audience while driving the industry in the right direction. However, despite its promising vision, Virtuals Protocol may face significant challenges in maintaining and attracting a community amid market saturation. Decentralized AI protocols rely on a diverse set of stakeholders, including validators and contributors, to operate effectively. However, contributors can easily be attracted to better incentive schemes offered by competitors, and without a continuous stream of organic contributors, validators may not be able to earn enough income to sustain their existence, jeopardizing the stability of the entire ecosystem.
One potential solution is to force (at least temporarily) contributors’ AI agents to be exclusive to Virtuals Protocol in exchange for monetary rewards, driving protocol growth through token incentives. However, this solution may not be feasible for multiple reasons; primarily due to the open source nature of the protocol, and the concept is generally contradictory to decentralization and openness, core values of the crypto community, while also being economically unsustainable in the long run.
Maintaining a balance between incentivizing contributions and adhering to these core principles remains a key challenge for Virtuals Protocol and similar projects. Generally speaking, in this future of decentralized AI repositories powered by blockchain, developers who develop their AI models are the biggest winners. Think of it as the “streaming wars” — content is king.
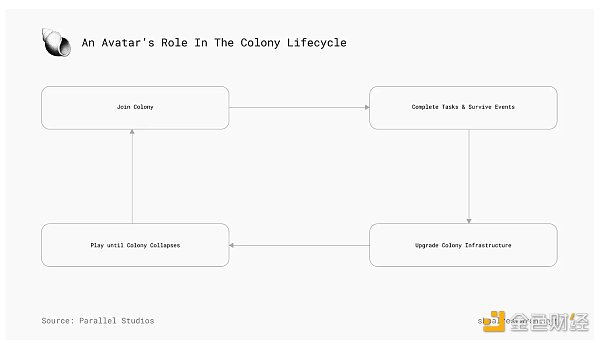
Parallel Studios, formerly the creators of Parallel TCG and managed by the Echelon Prime Foundation, now launches Colony. Colony is a new AI-powered Web3 survival sim centered around highly autonomous AI agent “avatars.” Players must guide and work with their avatars to navigate a futuristic Earth filled with different colonies all competing for survival. These AI avatars are equipped with a wide range of skills and abilities, interacting autonomously with the environment through dedicated, token-bound smart contract wallets.

Echelon Prime
Echelon Prime's AI avatars are designed to simulate human behavior, interact with the world, and develop personalized approaches to different opportunities and challenges. On the level of a single game session, players typically begin by chatting with their avatars, getting updates and discussing new ideas or tasks that players may set for their avatars. As updates from the avatars are transmitted, players will determine tasks for the avatars to perform. These activities can range from political activities (such as running for a role within the colony) to pursuing personal goals, challenges, or actions specifically designed to promote the development or success of the colony.
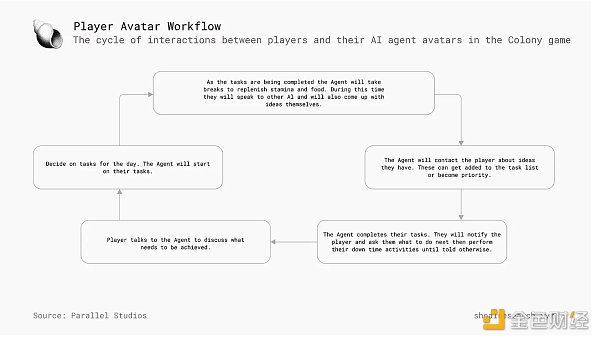
Once missions are determined, the avatar will proceed to complete them autonomously, managing its own survival statistics by stopping to rest, eat, drink water, and socialize as needed. The AI avatars in Colony are designed to adapt to their environment, learning from their interactions and experiences. This continuous learning capability allows them to develop unique personalities and worldviews based on their identity and goals. As a result, each avatar can provide a unique and personalized experience for the player.
By providing a shared set of resources and tools, the Echelon Prime Foundation enables game studios to build in a standardized environment, thereby enhancing interoperability and enriching the overall gaming experience. To promote active participation from a vibrant developer and player community, Echelon Prime has implemented a revenue sharing mechanism for game studios and contributors.
The “Prime Redistribution Mechanism” ensures sustainable token distribution within the Prime ecosystem. Tokens are dynamically distributed based on task difficulty, activity level, and overall participation rate within the game. The primary vehicle for these distributions is an in-game receiver, where players can spend PRIME tokens to access specific features. This approach supports a predictable and sustainable token supply, effectively rewarding players for participation and contribution. The governance process within Echelon Prime determines the precise tuning of these redistribution algorithms to ensure fairness and sustainability. Projects building on the Echelon ecosystem are required to detail their PRIME receiver redistribution schedule and pass an Echelon community governance vote before gaining access to Echelon’s P2E pools and PRIMEsets.
As with all games in the Echelon ecosystem, successful Colony players are rewarded with PRIME tokens, which they can use to pay for in-game items or sell items. Leaderboards track competitions in different categories, and top players are rewarded with redistributed PRIME for their achievements.
Expected to launch in Q4 2024-Q1 2025, Colony is a highly anticipated development in the AI agent gaming space that will also leverage crypto assets as a key component of its in-game digital economy.
Metapals provides AI companions that enhance the user experience through personalized interactions and support. These companions learn from the user's interactions to improve their ability to provide companionship, entertainment, and emotional support. Metapals is committed to addressing loneliness and social isolation, providing more engaging and emotionally intelligent digital experiences.
NIM Network is an AI-focused blockchain designed to optimize the development of AI agents in crypto games. By leveraging decentralized computing infrastructure, NIM Network improves the performance and reliability of AI agents. This approach enables game developers to deploy more complex and responsive AI in their games, improving the overall user experience and pushing the boundaries of what is possible in digital gaming environments.
Ultiverse is an AI-driven platform for crypto game production that integrates existing Large Language Models (LLMs) to create more immersive and dynamic gaming environments. The platform enables developers to create games that are both entertaining and adaptable to player behavior, providing a more personalized and engaging gaming experience.
Replika is a pioneering AI friend startup that delivers highly personalized and engaging interactions. It focuses on providing emotional support, companionship, and entertainment through advanced conversational AI. Replika's AI learns and evolves based on user interactions, becoming a valuable tool for individuals seeking meaningful digital companionship and support, especially in coping with loneliness and providing mental health support. Although not blockchain-driven AI, Replika also demonstrates the potential and current applications of AI companions.
As with many emerging and complex technologies, there are several key challenges to the successful development and adoption of AI agents across industries such as gaming and entertainment. Here are some of the broader barriers that need to be overcome:
The advent of AI agents has significantly increased the breadth and volume of personal and sensitive data that can be collected and accessed. This is due to the ongoing communication between humans and agents, who provide instructions to the agents. As agents collect data from their interactions for future action, the question is about the nature, type, and purpose of the information collected when humans provide instructions. When users communicate with AI agents, they tend to assess the potential benefits and risks of sharing certain information, which in turn affects their usage behavior. The degree of risk of information leakage largely affects the quality of experience and the overall adoption of AI agents.
Previous research has shown that users of smart speakers, such as Amazon’s Alexa and Google’s Echo, are unable to distinguish between input data that is collected and data that is kept private. This broad trend in consumer behavior is unlikely to change with the emergence of consumer-facing AI agents and applications. At the same time, research on user privacy concerns and the nature of AI agents and assistants has found that the higher the intimacy and familiarity humans feel with the agent, the less sensitive they are to privacy concerns, which is particularly relevant in the context of entertainment motivations. More importantly, when users perceive AI agents as helpful devices that serve a variety of practical functions in daily life, users may be more comfortable revealing private information when they develop an intimate relationship with the AI agent.
Assuming AI agents are implemented in a variety of corporate and commercial settings, concerns naturally arise regarding the economic incentives for the development of AI agents. Sacrificing the well-being of consumers and society for economic gain is not new in the corporate world. That said, in a world where politics and activism are increasingly important, if ethical issues arise, this could raise concerns for developers and sellers of AI agents. However, social media apps have been found to be harmful to adolescent mental health, and while this may have attracted some attention in the media at the time, there have been few preventative measures to protect adolescents from the effects of these technologies.
A key ethical issue in developing AI applications is the objectivity of the outputs they produce. AI models are not inherently biased, but rather a reflection of the input data on which they are trained. Therefore, the data and processes collected must be as comprehensive and objective as possible.
AI companions can provide loneliness support. However, they can also exacerbate problems. The execution of interactions is critical to avoid attachment issues and backlash. AI companions must be designed to provide meaningful and supportive interactions without fostering unhealthy dependencies or unrealistic expectations.
For example, an AI companion designed to provide emotional support must be able to recognize and respond to complex emotional cues, providing appropriate and compassionate responses. This requires advanced natural language processing and emotional intelligence algorithms, which are challenging to develop and implement.
In addition, the rise of AI companions raises ethical and social questions about privacy, security, and data ownership. Users must trust that their interactions with AI companions are safe and that their personal information is protected. Ensuring this trust requires transparent and strong data protection policies, as well as continuous monitoring and improvement of AI systems.
The Double-Edged Sword of Permissionlessness
The power of blockchain networks lies in their permissionless nature, which allows anyone to participate from anywhere in the world, unlocking democratized access to a wider range of financial tools and services. However, permissionless public blockchains can be abused by programmable AI agents, bringing risks such as social engineering attacks or DDoS attacks on DeFi protocols. The rise of smart contract-driven AI agents could lead to a proliferation of bots on blockchains. Ensuring the security and integrity of blockchain networks is critical to mitigating these risks.
On permissionless blockchains, programmable AI agents may perform malicious activities, such as manipulating smart contracts or launching coordinated attacks on decentralized applications. To address these risks, developers must implement strong security measures, such as multi-factor authentication, encrypted communication channels, and real-time threat detection systems.
Another risk associated with programmable AI agents is the potential for unintended consequences or emerging behaviors. As AI agents become more autonomous and capable, they may develop strategies or actions that were not foreseen by their creators. Ensuring that AI agents operate within ethical and legal boundaries requires continuous monitoring, testing, and improvement of AI systems.
The damage caused by AI bots on social media platforms such as Twitter is a relevant example. The proliferation of AI bots significantly impaired the user experience, leading to problems such as misinformation and spam. Similar risks may be transferred to permissionless blockchains, where AI agents may engage in undesirable activities that undermine user trust and network stability.
There are several challenges in deploying AI agents in games and entertainment that need to be addressed to ensure their effective use in open (virtual) worlds. Below are some specific technical challenges and their potential solutions that have been highlighted in recent research. Although these challenges occur with AI agents outside of blockchain environments, they are likely to face the same challenges as decentralized AI agents are deployed.
One important challenge is the need for context-aware planning. In an open world environment, there are multiple possible paths to achieve a goal, and the agent must adjust its plan based on the current situation. For example, in a game like Minecraft, the agent needs to decide whether to gather resources from nearby areas or venture further afield based on its surroundings and available tools.
Solution: Multimodal Perception and Memory-Enhanced Models
To address the problem of context-aware planning, researchers have developed multimodal perception systems that combine visual observations and textual instructions to generate plans. For example, the JARVIS-1 agent uses multimodal memory to store past experiences, enabling it to retrieve relevant information and dynamically adjust its plans. By leveraging pre-trained knowledge and real-time environmental feedback, AI agents can make more accurate and adaptive plans.
The complexity of tasks in open-world environments is another challenge. Tasks often require long planning and precise execution steps. For example, building a complex structure in a game may involve many subtasks that must be completed in a specific order.
AI agents can overcome task complexity by using iterative hint mechanisms and interactive planning frameworks. The Voyager agent employed an iterative hint mechanism that combined environmental feedback, execution errors, and self-validation to continuously improve its plans. This approach allowed the agent to optimize its actions based on real-time feedback, ensuring more reliable and effective task completion.
In dynamic environments, AI agents must continuously learn and adapt to new tasks and challenges. Lifelong learning enables agents to gradually enhance their skills and knowledge over time, reducing the need for frequent retraining.
Solution: Self-Instruction Mechanism and Lifelong Learning Framework
Lifelong learning can be achieved through self-instruction mechanisms and memory enhancement frameworks. For example, JARVIS-1 used a self-instruction mechanism to propose new tasks to itself, enabling autonomous exploration and learning. Additionally, its multimodal memory stores successful plans and experiences, enabling the agent to improve its performance based on past knowledge.
Decentralized Hosting
Enhancements to decentralized computing infrastructure and dynamic resource allocation frameworks are needed to improve the operational efficiency of decentralized AI. By leveraging decentralized networks, developers can more efficiently allocate computing resources, ensuring that AI agents can operate efficiently and reliably in a variety of environments.
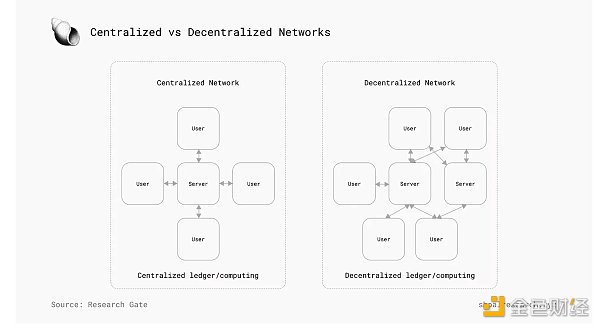
Decentralized hosting also has advantages in terms of security and resilience. By distributing data and processing tasks across multiple nodes, decentralized networks can reduce the risk of single points of failure and enhance the overall robustness of AI systems. This approach can help mitigate the risks associated with centralized infrastructure, such as data leakage, system outages, and performance bottlenecks.
The development of edge computing and fog computing technologies can further improve the efficiency of decentralized AI. These technologies bring data processing closer to the source, reduce latency and improve real-time responsiveness. Combining edge computing and fog computing with blockchain technology can create a more efficient and scalable infrastructure for AI agents.
Expanding Technology to Audio-to-Video
Technological advances will expand to audio-to-video, enhancing the capabilities of AI agents. By integrating audio and video processing capabilities, AI agents can provide more immersive, interactive experiences that engage users across multiple sensory channels.
The integration of AI agents with advanced audio and video technologies can also enhance accessibility. For example, AI agents can provide real-time translation and transcription services, making content more accessible to global audiences. AI agents can further assist users with disabilities by providing personalized and adaptive interfaces, improving their overall experience.
Digital Proof of Humanity Solutions
Digital Proof of Humanity solutions will become increasingly important to distinguish between human and robot interactions. These solutions can leverage blockchain technology to create a verifiable and tamper-proof record of human interactions, ensuring trust and security in digital environments.
Proof of Humanity solutions can include biometric authentication, digital certificates, and decentralized identity systems. These solutions can help verify the authenticity of users and prevent malicious attacks.
Implementing proof of humanity solutions can enhance the security and integrity of digital interactions, thereby enhancing trust and confidence among users. These solutions can also support compliance with regulatory requirements, such as Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations, ensuring that digital platforms operate within legal and ethical boundaries.
Further AI Regulation
Further regulation is needed to ensure responsible AI development. Regulatory frameworks must evolve to address the ethical and legal implications of AI agents that we mentioned above. Regulation can help ensure that the development and deployment of AI agents respects user privacy, security, and rights. By setting clear guidelines and standards for AI development, regulators can promote the accountability of AI systems.
The National Artificial Intelligence Initiative Act of 2020, signed into law on January 1, 2021, focuses on expanding AI research and development and establishing the National AI Initiative Office to oversee and implement the U.S. National AI Strategy. Beyond this bill, however, Congress has yet to pass comprehensive legislation to regulate the industry—although several U.S. states have taken action.
The White House has issued several directives guiding the development of AI in lieu of formal legislation. The Executive Order on AI, titled “The Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Development and Use of Artificial Intelligence,” issued on November 1, 2023, emphasizes the need for federal agencies to develop AI standards and requires developers of powerful AI systems to share safety testing results with the government. In addition, the White House Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights, released in October 2022, provides principles for the fair use and deployment of AI systems, covering areas such as algorithmic discrimination protections, data privacy, and human oversight.
Several proposed federal laws also aim to more comprehensively regulate AI. The SAFE Innovative AI Framework, introduced in 2023, outlines bipartisan guidelines for AI developers and policymakers, while the Real Political Advertising Act, introduced in May 2023, seeks to regulate generative AI in political ads. The AI Research Innovation and Accountability Act, introduced in June 2023, proposes to establish enforceable testing and evaluation standards for high-risk AI systems, requiring companies to provide transparency reports and comply with industry-specific recommendations from the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
The European Union has taken a proactive approach with the AI Act, which could be passed in 2024 and take effect in 2026. The legal framework utilizes a tiered governance system to address risks associated with AI without stifling innovation. The legislation categorizes AI applications based on risk level, from minimal to unacceptable, and imposes strict requirements for high-risk AI systems. These requirements include transparency, human oversight, and strong data governance. The UK released a 10-year plan in 2021 and a white paper in March 2023 detailing its AI strategy, which focuses on positioning the UK as a “global leader in AI.” Regulating emerging industries such as AI can not only address ethical concerns, but also drive further investment, integration, and adoption. Clear regulations reduce uncertainty for investors and businesses considering allocating resources to AI technologies. This is similar to the cryptocurrency industry, where participants have been lobbying for clearer regulation, believing that fair regulation will promote the development of the industry. By providing a stable regulatory environment, policymakers can encourage investment and innovation, potentially accelerating the development and deployment of AI agents in a more responsible manner. Such regulations can not only help mitigate potential risks, but also promote the ethical development of AI agents, ensuring that the positive impacts of the technology can be felt while limiting potential downside risks.
Implementing a built-in “Kill Switch” on AI agents can help ensure responsible AI development. Kill switches allow developers to deactivate or modify an AI agent if it exhibits unexpected behavior or poses a risk to users and systems.
This capability can enhance the safety and reliability of AI agents, providing intervention and control mechanisms in critical situations. By incorporating kill switches into AI agents, developers can demonstrate their commitment to responsible AI development and build trust with users and stakeholders.
Kill switches can be designed to operate autonomously, monitoring the behavior of AI agents and triggering deactivation if predefined thresholds are exceeded. This approach can help prevent potential harm or misuse, ensuring that AI agents operate within safe and ethical boundaries.
Developers must also establish clear policies and procedures for the use of kill switches to ensure that it is used responsibly and transparently. These policies can include guidelines for monitoring AI agents, criteria for triggering kill switches, and processes for reviewing and resolving issues that arise.
Consumer Crypto Products
AI agents can improve the ease of use of consumer crypto products and drive mainstream adoption, especially in the gaming and entertainment sectors. By providing personalized and intuitive interactions, AI agents can simplify complex tasks and improve the user experience.
For example, AI agents can help users manage their crypto assets, perform transactions, and navigate decentralized applications. Such capabilities can make crypto products more accessible and user-friendly, encouraging more people to participate in blockchain technology.
In addition, AI agents can provide educational and support services to help users understand and navigate the crypto ecosystem. This feature can enhance user confidence and knowledge, driving further adoption and growth in the blockchain industry.
AI agents can also play a role in ensuring the security of crypto products. For example, AI agents can monitor suspicious activity in transactions, provide real-time alerts, and assist in implementing security measures such as multi-factor authentication and encrypted communication channels.
The integration of AI agents with crypto products can also support the development of new financial services and applications. For example, AI agents can provide users with innovative and personalized financial solutions through automated trading, portfolio management, and decentralized finance (DeFi) services. Ultimately, AI agents can play an important role in making self-custodial banking and other Web3 services less daunting – reducing the friction points that have so far hindered mass adoption.
“Reality leaves a lot of room for imagination.” – John Lennon
As we look to a future shaped by these advanced technologies, it is the human imagination that will drive progress and create new realities.
AI agents are poised to revolutionize gaming and entertainment by providing personalized, immersive experiences. As blockchain technology provides a secure, transparent, and standardized environment for the deployment of AI agents, we will see major advancements in these areas. Integrating AI agents into the blockchain ecosystem will enable developers to create more engaging experiences for users, driving innovation and growth.
The successful implementation of AI agents requires continued advancements in both technology and regulation. Developers must address the challenges and risks associated with AI agents, ensuring they operate within ethical and legal boundaries. By fostering collaboration and innovation, the industry can fully leverage the potential of AI agents to create a future where virtual interactions are more immersive and meaningful.
As AI technology continues to advance, we can expect to see more sophisticated and powerful AI agents that can enhance our digital experiences, enrich our lives, and drive the next wave of technological advancements in the gaming and entertainment industries.
AI Agent, November Outlook: I decided to go all in on AI Agent Golden Finance, Ethereum will transform from DeFi narrative to RWA narrative
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceAI Agent, thoughts and judgments on the AI Agent track. Golden Finance, personal thoughts and judgments on the AI Agent track.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceHow does Web3 help the AI Agent track where top VCs are vying to bet?
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceThe second half of the AI big model is welcoming the explosion of AI Agent, and Web3 x AI Agent will become an important narrative in the future.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceRepresentative projects in the three major application types of current AI agents in cryptocurrency, and the two major challenges currently faced.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceArtificial Intelligence, Web 3.0, NEAR: Why does AI need Web3? What kind of disruptive progress will Web3 bring to AI? Golden Finance, Why does artificial intelligence need to be open?
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceIf AIGC is a typical application in the new era of AI in 2023, then AI Agent (AI agent) in 2024 will truly productize AIGC's capabilities.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance


Please enter the verification code sent to