Author: JackInabinet, Bankless Analyst; Translation: Golden Finance xiaozou
On February 19, EthenLabs opened its synthetic U.S. dollar stablecoin deposits to the public, becoming the virtual currency on CryptoTwitter A hot topic that everyone cares about.
With double-digit yields and the provision of points for upcoming airdrops, Ethena’s USDe stablecoin has rapidly expanded and has exceeded the supply of $770 million, becoming the sixth largest USD-pegged stablecoin!
While Ethena’s rise has been truly impressive, the project is not without its critics, who are skeptical of Ethena’s high yields and feel that it is designed in a way that makes it easier for the Terra/Luna ecosystem to Just as collapsed.
In this article, we will discuss what Ethena is and analyze the risks of the protocol to help you understand whether this opportunity is suitable for you and make an informed decision!
1. What is Ethena?
First of all, basis trading (basis trades) has a long history, both in the crypto market and in the traditional financial market. It is a trade between spot assets and futures instruments. Arbitrage of pricing differences.
The most common form of these transactions is to go long the spot asset and short the corresponding futures. Due to the need for leverage and the associated costs of holding the spot asset, futures instruments usually trade in contango (i.e., higher than the underlying price). ).
Crypto markets have also historically operated in contango trading, meaning that the price of perpetual futures contracts often exceeds the price of spot assets, resulting in an environment where net funding rates are positive. In this environment, longs pay shorts the ability to hold positions.
In this case, one can easily deploy lucrative delta neutral basis trades by holding spot crypto assets and hedging the notional value of their positions via perps, allowing the use of this strategy Insulate investors from cryptocurrency price fluctuations while enabling them to generate income from financing payments.
Ethena is essentially an open-end hedge fund that uses the above strategy to earn income and tokenizes its trading collateral into stablecoins!
Ethena uses liquidity staked ETH tokens as collateral and shorts an equal amount of ETH to create a delta 0 portfolio. This configuration ensures that the net value of Ethena’s holdings does not follow the underlying value of its assets. fluctuates with changes in , and at the same time can obtain income from ETH pledges and financing payments for its short positions.
There have been multiple protocols using similar strategies to Ethena before, but due to Relying on decentralized trading venues, previous iterations were difficult to scale. Ethereum circumvents this liquidity cap by leveraging centralized exchanges like Binance.
In order to protect users' collateral, Ethena utilizes an over-the-counter settlement (OES) solution, holding funds with a reputable third-party custodian, and only mapping account balances to CEX to provide trading margin, ensuring Funds are never deposited into a centralized exchange.
Since staked ETH can be perfectly hedged with short positions of equal notional value, USDe can be minted at a 1:1 collateralization ratio, making Ethena as capital efficient as USD asset-backed stablecoins such as USDC and USDT ), while also avoiding reliance on obtaining assets from traditional financial markets, where asset issuers are subject to the regulations of the real world.
While Ethena’s current model only uses staked ETH as collateral, the protocol may further use BTC as collateral to achieve greater scale, but doing so may dilute USDe’s earnings because BTC Collateral does not generate staking returns.
2. Ethena is the most What's the worst case scenario?
In the crypto world, there is no financial reward without corresponding risk. Ethena Opportunity participants should not expect any other answers.
Although the generous financing interest rate plus staking income will definitely bring an attractive APY annual rate of return, it is not without risks...
In addition to the standards expected by DeFi users In addition to crypto risks, Ethena also has some atypical risk factors that have triggered alarms and comparisons with the Terra/Luna algorithm UST stablecoin.
(1) Collateral decoupling risk
Ethena’s main risk is the mixed use of LST collateral and ordinary Ethereum short positions. While this optimization of ETH basis trading helps the protocol maximize its ability to sustain returns, it increases risk!
If Ethena’s LST collateral were decoupled from ETH, Ethena’s ETH shorts would be unable to capture the volatility, causing the protocol to suffer paper losses.
While LST typically trades close to its peg, we have witnessed multiple decoupling scenarios for these tokens, such as Lido during the mid-year 3AC (Three Arrows Capital) black swan liquidation event in 2022 The price of stETH is greatly discounted, approaching 8%!
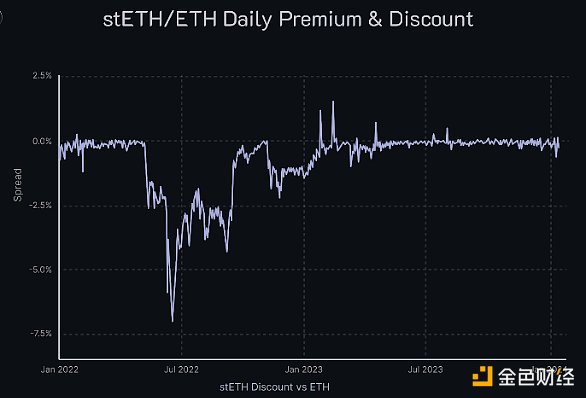
April 2023 The Shapella upgrade enables Ethereum staking withdrawals, which makes the 3AC liquidation likely to create the most widespread decoupling we have seen in blue-chip LST, but the fact remains that any future decoupling event will impose Ethena’s margin requirements (which must The amount of funds deployed to exchanges to maintain their hedging exposure and avoid liquidation of their positions) creates pressure.
Once the liquidation threshold is reached, Ethena will be forced to realize losses.
(2) Financing Interest Rate Risk
While Ethena’s gains may seem staggering from the outset, it is important to note that two previous protocols have attempted to scale synthesis The scale of US dollar stablecoins, but due to the occurrence of yield inversion, all ended in failure.
In order to combat negative financing Ethena uses staked ETH as collateral, a strategy that reduced the number of days USDe generated negative returns from 20.5% to 10.8% over the three-year data backtest.
While it is 100% certain that funding rates will invert at some point, the natural state of the crypto market is to trade in contango, putting upward pressure on funding rates and providing a favorable environment for Ethena to engage in basis trading .
(3) Counterparty risk
Many people unfamiliar with Ethena’s design believe that deploying user collateral to centralized exchanges is a major risk, but using the OES custody account mentioned above This risk is significantly mitigated.
While unsettled hedging profits against bankrupt exchanges may result in losses, Ethena conducts PnL (profit and loss) settlements at least daily to reduce capital exposure to the exchange.
If one of Ethena's exchanges goes bankrupt, the protocol may be forced to leverage positions on other exchanges, making its portfolio delta neutral until open positions are settled, impacting The custodian of the OES account can release funds.
In addition, if one of the custodians of Ethena's OES account goes bankrupt, access to funds may be delayed, requiring the use of leverage on other accounts to hedge the portfolio.
(4) General Crypto Risks
As is the case with many early crypto protocols, it is important to remember that depositors of Ethena are at risk of the protocol team defrauding users of their funds, because The ownership of project keys is not yet decentralized.
While the vast majority of crypto projects face substantial hacking risks regarding potential vulnerabilities in their smart contracts, Ethena’s use of OES escrow accounts mitigates this risk by eliminating the need to use complex smart contract logic.
3. Summary
In the event of the bankruptcy of the exchange or custodian, Ethena has protected the safety of assets and formulated an emergency plan. In the event that assets are frozen and cannot be traded, Make their portfolio delta neutral!
With many exchanges enforcing a zero-collateral haircut rate on their stETH collateral value and offering a 50% margin requirement for accounts the size of Ethena, the protocol may result in a liquidation of its collateral market value The loss is as high as 65% !
Negative financing rates may lead to compression of yields and loss of TVL, but negative financing rates themselves will not cause the dollar to depreciate. Calculated at the highest annualized financing interest rate of -100%, Ethena’s nominal loss per 8-hour financing period is only 0.091%!
On top of that, Ethena also has an insurance fund that can be used to replenish margin accounts to avoid liquidation, offset long-term negative financing yields, or act as a buyer of last resort for USDe in the open market !
Although Ethena can bear a certain degree of loss through the insurance fund, we must not forget Murphy's Law, which reminds us that anything that can go wrong will go wrong, still at the worst time.
Imagine a situation where LST starts to decouple.
Centralized exchanges responded by reducing the collateral weight of liquid pledged ETH tokens, thereby reducing the maximum loss that Ethena could suffer in the market value of the collateral before liquidation.
Assuming that the entire market is also selling off during this period, funding rates will become negative, putting further pressure on Ethena's collateral and pushing the protocol closer to liquidation and having to realize losses!
In normal operations, Ethena may not use leverage, but an unexpected bankruptcy event of an exchange or custodian may temporarily freeze funds, so leverage is needed to neutralize portfolio delta.
Theoretically, a deep discount, coupled with leveraged accounts and smaller liquidity staked ETH collateral weights, could put Ethena's collateral within liquidation range.
Now that basis trading is available to anyone in crypto, Ethena could easily swell to billions of dollars under management, meaning liquidation of its massive staked ETH portfolio could further depress LST market value , exacerbating Ethena’s paper losses and opening the door to the ensuing death spiral!
There is no doubt that the above series of events can only be the result of a black swan disaster event, but you must know what potential risks you may face when participating in the crypto world.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance Sanya
Sanya Weiliang
Weiliang JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Joy
Joy Beincrypto
Beincrypto Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph