Bitcoin cycle theory, especially its connection with the Bitcoin halving event, has long been regarded as an important tool for predicting Bitcoin price trends. Historically, Bitcoin halvings have typically resulted in price increases, but current market performance and the factors behind it suggest that the validity of this theory may be waning.
This article will review the four Bitcoin cycles from 2011 to 2024, and deeply explore the market changes in the current cycle.
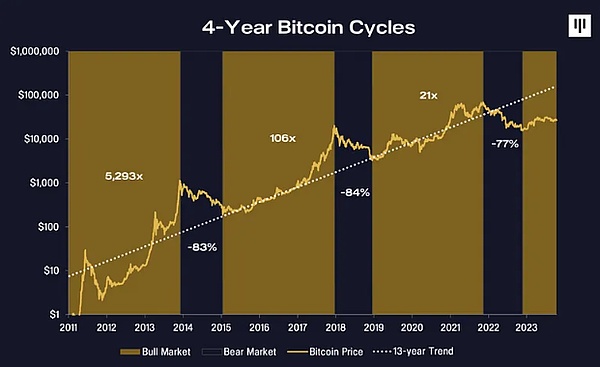
01 Basics of Bitcoin Cycle Theory
Bitcoin’s mining rewards are halved every 210,000 blocks, which happens approximately every four years. This mechanism is designed to control the supply of Bitcoin, thereby increasing its scarcity. Historically, halving events are usually accompanied by significant increases in Bitcoin prices, forming cycles. For example:
2012 Halving: Bitcoin price surged from about $12 to over $1,000 by the end of 2013.
2016 Halving: Bitcoin price rose to nearly $3,000 shortly after the halving and reached an all-time high of nearly $20,000 in late 2017.
2020 Halving: After the halving in May 2020, the price of Bitcoin quickly rose to a record high in 2021.
After the halving events in 2012, 2016 and 2020, the price of Bitcoin has experienced significant increases, forming an obvious bull market cycle. These historical data have allowed the Bitcoin cycle theory to gain widespread recognition and trust.
This cycle completed the fourth Bitcoin halving on April 20, 2024, but the performance after the halving was not as expected.
02
Price data after halving
If we pull the date of Bitcoin halving in history to the same starting point on the axis, and then Comparing the price with the currency price on the day of halving, we can find that the performance of the current cycle is the worst.
Although the market broke through a new cyclical historical high for the first time before the April halving event, this did not change the relatively sluggish performance of the current cycle.
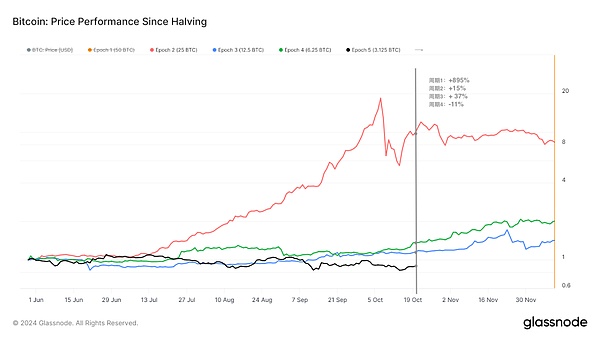
Source: Glassnode
The following is the price rise and fall around 144 days after each cycle of halving (compared to the day of halving Price comparison):
Period 1: +895%
Period 2: +15%
Period 3: + 37%
Period 4: -11%
The price reaction after the current cycle halving is weaker than before, and Bitcoin's price performance is poor. Why is this? How is this cycle different from previous ones?
03 Bitcoin stabilizing
The 2023-2024 Bitcoin cycle is similar to previous cycles in some ways, but there are also significant differences.
After the collapse of FTX at the end of 2022, the market experienced about 18 months of steady price increases. With the passage of the Bitcoin ETF, new funds continued to pour in, and after reaching a high of $73,000, the market entered a three-month range-bound period.
During this period, from May to July, Bitcoin prices experienced the deepest cyclical correction, with a correction of more than 26%. Although this decline is significant, it is significantly shallower and less volatile than in previous cycles, reflecting the relatively stable market structure of Bitcoin and its greater maturity as a financial asset than before.
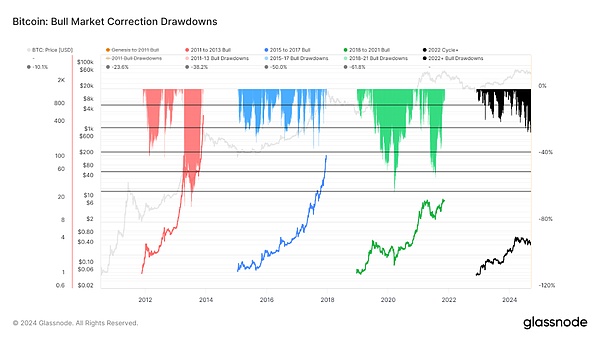
Source: Glassnode
Let’s take a look at another technical indicator MVRV Z-score, which can also see different cycles Differences in Bitcoin market performance.
First of all, the MVRV-Z score is a relative indicator, and the calculation formula is: (circulation market capitalization - realized market capitalization) / standard deviation (circulation market capitalization). When this metric is too high, it means that Bitcoin’s market value is overvalued relative to its true value, which can be detrimental to the price. On the other hand, if the indicator is low, it means that Bitcoin’s market value is undervalued.
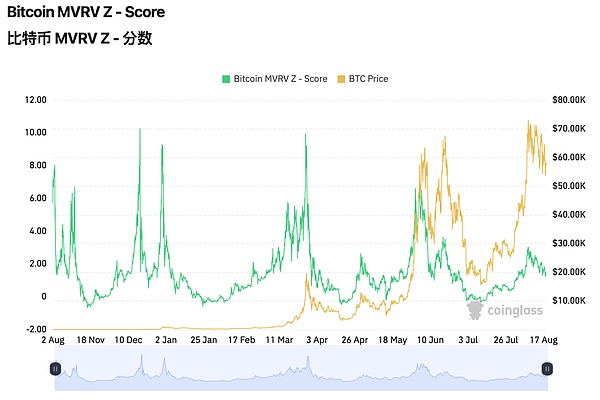
Source: Coinglass
From the 2010-2024 data in the above figure, we can see that compared with the previous cycle, MVRV-Z score (green line) fluctuations, spikes and returns are relatively mild and not as dramatic as in the early days.
Bitcoin has begun to trend towards a stable and gradual upward trend, rather than the violent price surges in the past. This gradual growth model has More attractive in the long run.
04 Reasons for reduced volatility
We can use a data indicator to intuitively explain why the volatility of Bitcoin has weakened and stabilized.
Bitcoin 5+ Years HODL Wave indicator, showing the percentage of Bitcoins that have not moved on the chain for at least 5 years, sometimes also referred to as last active 5 years ago of Bitcoin supply. To some extent, it reflects the behavior of long-term participants in the market.
Of course, it is also possible that some of these Bitcoins have been lost, that is, the user no longer has access to the private key of the wallet containing the Bitcoins, but this proportion is smaller .
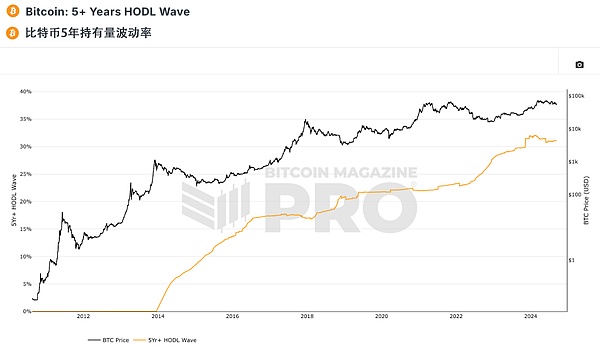
As can be seen from the figure, currently more than 30% of Bitcoins have not changed hands in the past five years, and this proportion may continue to rise.
This phenomenon has led to a reduction in the number of Bitcoins circulating in the market, and its impact has exceeded the reduction in supply increment caused by the halving event.
This means that the trend of long-term holding of Bitcoin is significantly increasing, making the market better able to withstand short-term fluctuations, while also potentially weakening Bitcoin cyclical fluctuations, which is one of the reasons for the weakening of Bitcoin volatility.
Other factors can also be attributed to: For example, as the market matures, more and more investors choose to hold Bitcoin for a long time, reducing the circulating supply. , reducing violent price fluctuations.
In addition, the supply and demand relationship of Bitcoin is also changing, and the continued inflow of funds has provided support for the price.
Furthermore, global economic uncertainty, policy changes, market sentiment and other factors will have an impact on the price of Bitcoin.
In this case, Bitcoin's price may become more correlated with movements in traditional financial markets, thereby reducing its stand-alone volatility.
These reasons work together to make Bitcoin price volatility appear relatively mild in the current cycle.
05 Summary
Compared with historical cycles, the price correction in the current cycle is smaller, the market structure is relatively stable, and Bitcoin price volatility has weakened.
Therefore, when trading Bitcoin, analysis of market cycles alone is not enough. On the one hand, historical data cannot predict future trends. On the other hand, the encryption market will gradually move towards market standardization, ushering in enhanced liquidity and larger-scale applications, which is a natural result of financial development.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Catherine
Catherine Beincrypto
Beincrypto Beincrypto
Beincrypto Beincrypto
Beincrypto Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Nulltx
Nulltx Nulltx
Nulltx