Author: Veronika Rinecker Source: cointelegraph Translation: Shan Ouba, Golden Finance
Once hailed as the next frontier of human interaction, the metaverse seems to have lost momentum after an initial burst of enthusiasm.
Vague promises, unclear financial benefits and expensive hardware have hindered its mass adoption. But in Germany, a second wave of interest is brewing. State governments and research institutions see the potential of metaverse technology to revolutionize entertainment, social interaction, public administration and industrial processes.
The metaverse is an emerging virtual space built on blockchain, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), big data, spatial computing and digital twin technologies. It promises to create a new era of connectivity and innovation in many fields, bridging the gap between the physical and digital realms.
Will it be different this time? By focusing on practical applications within public services and industry, Germany aims to understand the true potential of the Metaverse.
Can the Metaverse transform government services?
Public administration and government can benefit from the Metaverse and its services integrated with it, according to Günter Wenzel, head of the research group on building culture innovation at the Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Engineering IAO in Germany.
The group is currently exploring the potential of the Metaverse in many areas, especially in public administration.
"We understand the Metaverse as the next evolutionary stage of the Internet and the superposition of real and virtual space, where citizens can get open but secure data exchange and communication with authorities in various Metaverse ecosystems (business, leisure, work, mobile, etc.) through connections to public administration services," said Wenzel.
Citizens will be able to access these services from anywhere via smartphone, desktop computer, VR or AR glasses, using cryptography to protect transactions, operations, access rights and role configurations.
In this case, government agencies will no longer communicate with citizens at physical counters, but rather through the virtual universe, and will be able to provide the vast majority of services regardless of where they are, Wenzel said.
In order to manage the real estate and infrastructure of a municipality or city, governments can create digital twins of buildings that can be used to perform AI-assisted processes for monitoring and maintenance, as well as demolition, renovation and new construction.
Testing VR and XR for public administration
For Wenzel, it is still difficult to say whether this will make government services more efficient, as this depends on the use case.
However, a collaborative initiative between the Lower Saxony Ministry of the Interior and Sports, the University of Münster and PwC has already demonstrated the advantages of using immersive technologies in public administration.
During a series of multi-day events in 2022, managers and stakeholders developed quarterly strategies, with 11% of participants more satisfied with the outcomes of the workshops, 16% seeing improved communication and 58% experiencing stronger camaraderie among colleagues.
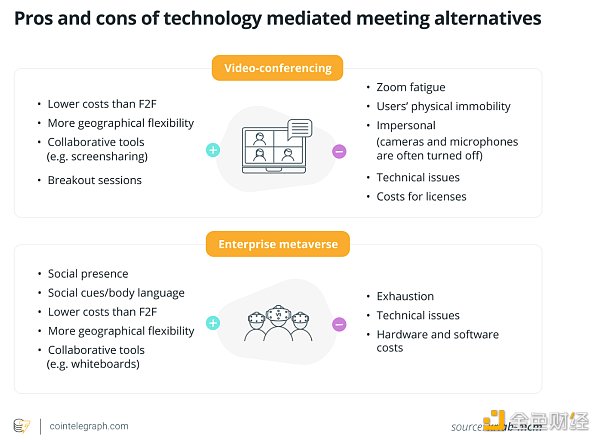
In addition to the VR Collaboration Room, the Lower Saxony government is also working on another project testing immersive technology.
The new project, called "Extended Reality", aims to explore the potential of extended reality (XR) technologies for public administration services. Lower Saxony also plans to conduct further scientific research to provide information on the added value of virtual reality and mixed reality (MR) collaboration in project work and communication with citizens.
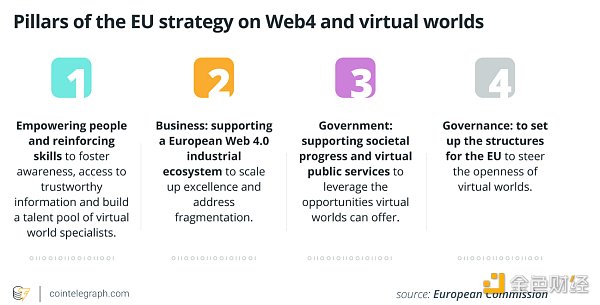
The projects are inspired by the “Web4 and Virtual Worlds Strategy” adopted by the European Commission on July 11, 2023, which aims to “lead the next technological transformation and ensure an open, secure, trusted, fair and inclusive digital environment for EU citizens, businesses and public administrations.”
The results of the upcoming extended reality projects will serve as the basis for determining the performance requirements for future headsets, a spokesperson for the Lower Saxony Ministry of the Interior and Sports told Cointelegraph.
“In 2024 and 2025, Lower Saxony will continue to focus on pilot projects using these technologies, as the market is developing very rapidly and framework conditions such as full compliance with the GDPR need to be clarified first in particular.”
Metaverse risks and challenges
Despite the positive signs, there is still some uncertainty regarding the use of immersive technologies in public administration in Lower Saxony. As the spokesperson puts it, recognizing not only the potential of these technologies but also their limitations and dangers “requires a careful and meticulous approach to integrating them into the planning process.”
Internal risks require special attention. Implementing the necessary hardware and software requires strong cybersecurity and data protection.
The state government also aims to assess the impact of the technology on employee health and the way data is processed.
The availability and suitability of headsets also pose further challenges. While the market offers various solutions, not all of them meet administrative needs, mainly due to the above-mentioned security and data concerns.
Finally, educating employees and citizens and providing them with the necessary skills for the long-term and sustainable use of immersive technologies is fundamental to successfully harnessing the potential of the Metaverse. But this is also not an easy task.
"Public administrations will have to learn for which application areas immersive technologies are best suited. On this basis, governments can also support technological developments and thus ensure an open, secure, trusted, fair and inclusive digital environment for citizens, businesses and public administrations."
Regional initiatives drive innovation
Lower Saxony and other German state governments are trying to explore Metaverse technologies.
In 2023, the Fraunhofer Institute for Information Technology and Automation (IAO) and the Fraunhofer Institute for Production Engineering and Automation, in cooperation with the Virtual Dimension Center (VDC) of Baden-Württemberg, launched a large-scale metaverse project called CyberLänd.
The project, which is funded by the Baden-Württemberg Ministry of Economics, Labor and Tourism, aims to explore the political, industrial and social potential of the metaverse for the South German state.
Above all, the project team wants to contribute to a deeper understanding of this complex topic: What role will the metaverse play in Baden-Württemberg? What actions should the government and companies take? How can public involvement be promoted?
According to CyberLänd, the metaverse is an important opportunity for Germany to maintain its position as a technological powerhouse. In the future, extended reality, software solutions for industrial business processes and public services, the virtualization and combination of 3D content, and decentralized, interoperable data platforms will play an important role.
However, building a robust ecosystem requires better cooperation between German industry and its digital technologies.
Another successful example of a regional initiative that is piloting with Metaverse and AI technologies is the AI Innovation Campus in Heilbronn. The planned Metaverse Lab will offer individuals and companies a variety of educational opportunities and practical use cases to learn about and experience the Metaverse.
Large companies invest in industrial Metaverse
The German industrial sector is also recognizing the benefits of Metaverse for development and production. Siemens Energy is already using the Metaverse to model power plants, predict maintenance needs and save operators $1.7 billion per year by minimizing downtime. Siemens will also invest more than $1.1 billion in Germany by 2023, half of which will be invested in a new campus in Erlangen. The campus will serve as a global development and manufacturing center and a hub for technical activities related to industrial virtual worlds.
In 2024, Siemens is also collaborating with Sony to create another solution for the Industrial Metaverse, combining Siemens’ Xcelerator industrial software portfolio with Sony’s new system for creating spatial content. The new solution will enable designers and engineers to create and explore design concepts in a limitless, immersive workspace.
Similarly, BMW is developing a digital factory powered by the Nvidia Omniverse platform, with physical construction starting only after extensive design and validation of the digital model.
The Metaverse is Dead – Long Live the Metaverse?
Metaverses offer a wide range of valuable applications. Germany is experiencing a second wave of interest, driven by a shift towards exploring their practical applications in public administration and industry.
Public administration sees the potential to improve citizen engagement, service delivery and collaboration between employees, as evidenced by early initiatives such as Lower Saxony’s VR Collaboration Room and Baden-Württemberg’s CyberLänd project. Similarly, industry giants such as Siemens and BMW use the Metaverse to enhance design, testing and production processes.
Of course, challenges such as data security, legal uncertainties and hardware limitations remain and require careful consideration. Fraunhofer-IAO's Wenzel said planning, employee training and cooperation between government, industry and researchers are essential to successfully overcoming these obstacles, adding:
"Strictly speaking, metaverses are still a promise for the future, as not all necessary sub-technologies have yet reached the required maturity. However, sub-technologies and business models are already available in smaller bundles and should always be developed and implemented from the perspective of use cases."
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance









