Author: YBB Capital Researcher Ac-Core
TLDR
The CryptoEconomic DVN framework combines LayerZero's cross-chain messaging with EigenLayer's economic security and incentives.
The DVN framework operates through a structured process divided into three stages: verification, rejection, and punishment.
LayerZero's collaboration with EigenLayer deepens the decentralization of DVN by accepting ETH, ZRO, and EIGEN as collateral, creating new growth opportunities for both tokens.
The CryptoEconomic DVN framework is expected to enhance the security of the entire blockchain ecosystem.
1. Understanding the narrative: Iterative upgrades of EigenLayer and LayerZero

Image source: LayerZero official
According to the announcement on October 2, 2024, LayerZero Labs and Eigen Labs have jointly launched the CryptoEconomic DVN Framework, which aims to provide cryptoeconomic security for cross-chain messaging. Under this framework, developers can deploy their own DVN on EigenLayer, while introducing incentive mechanisms to enhance the security and reliability of cross-chain messaging.
In short, the CryptoEconomic DVN Framework combines LayerZero’s cross-chain security mechanism with EigenLayer’s re-staking cryptoeconomic model. Its core goal is to leverage EigenLayer’s cryptoeconomic framework to provide greater security and incentives for decentralized validation networks (DVNs).
1.1 Phase 1: Laying the foundation for CryptoEconomic DVN and LayerZero V2
LayerZero is not just a cross-chain asset bridge, but also a trustless cross-chain communication protocol that separates trust layers through relayers and oracles. It uses ultra-light nodes to enable cross-chain messaging.
The LayerZero V2 architecture is divided into three core components: protocols, standards, and infrastructure.
1. Protocol
The protocol part of LayerZero remains consistent across all supported blockchains, maintaining immutability and permissionlessness to ensure censorship resistance and long-term stability. It consists of two main components:
Endpoints:Immutable and non-upgradeable smart contracts deployed on each blockchain that serve as the core of the LayerZero protocol. These endpoints provide a standardized interface for applications to manage security configurations and send/receive cross-chain messages.
MessageLibs: These libraries connect to the endpoints and handle the verification and communication of cross-chain messages. When updated, MessageLibs are appended rather than replaced, ensuring backward compatibility and allowing developers to use older versions if necessary.
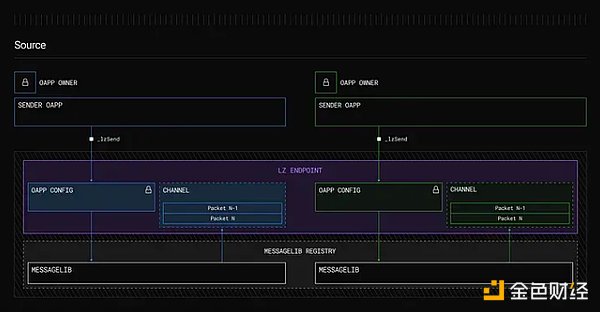
Image source: LayerZero endpoint description
2. Standards
LayerZero's standards enable developers to build unified applications and tokens across multiple blockchains. This ensures cross-chain consistency and scalability.
Contract standards:LayerZero provides standards such as OApp (full-chain application) and OFT (full-chain token), which extend existing smart contract standards and enable developers to quickly create applications and tokens that run on all LayerZero-supported blockchains.
Message Packets:These packets transmit data and commands between blockchains, including random numbers, source/target chain IDs, and payloads. This structure ensures the accuracy and security of cross-chain messaging, even across EVM and non-EVM chains.
Design Patterns:A collection of design patterns such as AB, ABA, and combined AB help developers build efficient cross-chain interactions and user experiences.
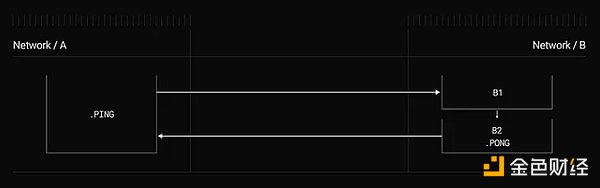
Image source: Combination ABA design pattern
3. Infrastructure
LayerZero's infrastructure is open and modular, allowing any entity to join the network to verify and execute transactions.
Decentralized Verification Networks (DVN):These networks verify cross-chain messages. Applications can choose the right verification network to meet their security needs and avoid being locked into a single validator network.
Executor:The entity responsible for ensuring that cross-chain messages are executed on the target chain. Executors simplify the user experience by allowing users to pay gas fees only on the source chain.
Security Stack:Each application can configure a unique security stack, including DVN, executor, and security preferences, providing a highly customizable security solution.
To understand the CryptoEconomic DVN framework, it is necessary to understand the role of DVN in LayerZero V2:
DVNis responsible for verifying cross-chain messages.
Openness:Anyone can create or develop a DVN, providing a variety of verification methods.
Customizable Security:Applications can choose a DVN based on their security needs.
DVN Combinations:Applications can configure multiple DVNs to authenticate messages, such as a "1 of 3 out of 5" configuration.
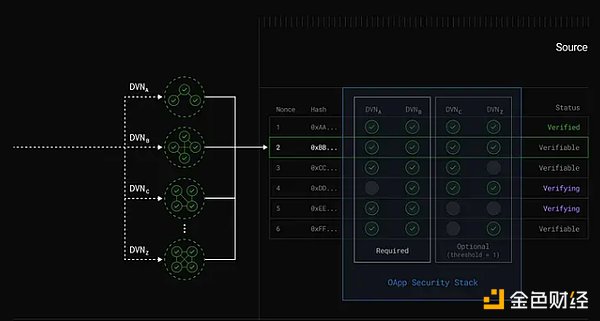
Image source: DVN's position in the V2 architecture
1.2 Phase 2: CryptoEconomic DVN protected by EigenLayer
EigenLayer consists of smart contracts that allow users to "re-stake" their ETH or Liquid Staked Tokens (LST), thereby enhancing the security and decentralization of the modular blockchain network. In essence, EigenLayer sells the security of Ethereum for use by the broader ecosystem. Key aspects include:
1. Native re-staking:Allows verification of multiple commitments to ensure that all commitments are solvent.
2. Liquidity re-staking:Provides tokenized representation of pledged assets to release liquidity.
3. AVS Economy:A decentralized system that combines technology with trust structure.
4. Massive Rollups:Achieve unlimited expansion through mechanisms such as EigenDA.
5. Trustworthy Applications:Maximize the delivery of commitments and provide decentralized services with Ethereum-level security.
Therefore, EigenLayer enhances the decentralized network by providing a modular, scalable solution to extend Ethereum's security model.
2. Token economic empowerment: LayerZero x EigenLayer cooperation, empowering ZRO and EIGEN as collateral assets
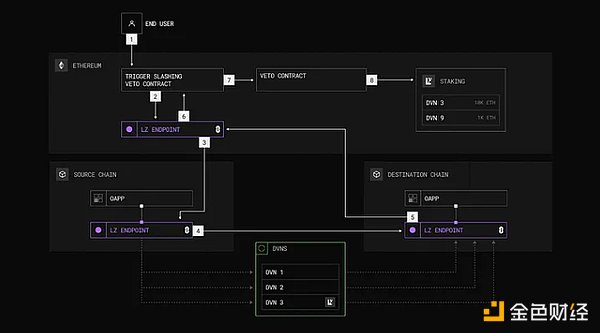
Image: Schematic diagram of the pledge, verification, rejection and penalty process
In short, the crypto-economic distributed verification network (DVN) enhances cross-chain security in three key ways:
1. Crypto-economic security:DVN introduces a penalty mechanism. If DVN acts maliciously or makes a mistake, its pledged assets may be fined. This economic model incentivizes DVN to act responsibly, as improper behavior can lead to significant financial losses, thus promoting accountability and security.
2. AVS-defined security:Each active verification service (AVS) defines the types of assets that can be staked and the penalty conditions. This flexibility allows different types of DVNs (such as those based on ZKP, intermediate chains, or authority proofs) to enhance security through additional collateral, thereby increasing the economic deterrent to malicious behavior.
3. Permissionless security:Anyone can contribute to the security of DVN by staking assets, making the system more open and inclusive. DVN can choose to accept any asset (such as ZRO, ETH, or EIGEN) as collateral, thereby expanding security options and promoting decentralization.
The CryptoEconomic DVN framework is an open source system designed to enhance the security of decentralized verification networks (DVNs) through token-based economic incentives. It leverages LayerZero's DVN for message verification and adds an additional layer of security. The framework operates through four key mechanisms: staking, validation, rejection, and slashing.
Staking: Validators (stakers) lock tokens such as ZRO, EIGEN, or ETH as collateral in the DVN Active Validator Set (AVS). These staked funds incentivize validators to act honestly, as misbehavior can result in penalties.
Validation: Users or applications can trigger a cross-chain round-trip message (e.g., Ethereum → source chain → target chain → Ethereum) to verify that the hash recorded by the DVN matches the hash on the chain. If it matches, the process ends.
Rejection: If there is a mismatch, the rejection process is initiated, allowing token holders to vote on whether to slash DVN’s staked assets. This step prevents erroneous penalties caused by non-malicious issues such as blockchain reorganizations.
Penalties: If rejection fails, confirms malicious behavior or validation errors, DVN’s staked assets will be slashed as a penalty.
The framework operates in three phases:
1. Verification - Messages are verified on multiple chains using independent DVNs to ensure fairness.
2. Rejection - If a discrepancy is found, a rejection contract is triggered, allowing token holders to vote on penalizing DVN.
3. Penalties - If the rejection process fails, DVN’s staked assets will be penalized for malicious behavior or validation errors.
The framework operates in three phases:
1. Verification - Messages are verified on multiple chains using independent DVNs to ensure fairness.
2. Rejection - If a discrepancy is found, a rejection contract is triggered, allowing token holders to vote on penalizing DVN.
3. Penalties - If the rejection process fails, DVN’s staked assets will be penalized for malicious behavior or validation errors.
3. CryptoEconomic DVN Framework Outlook

As Ethereum infrastructure matures and the multi-chain landscape is firmly established, cross-chain communication security remains a major challenge. The key innovation of the CryptoEconomic DVN framework is to use AVS to provide core components for DVN, define pledge assets and penalty conditions. In the long run, it can help improve security across blockchains. However, balancing security and flexibility remains a challenge that the entire industry must solve.
There is no doubt that the CryptoEconomic DVN framework represents a mutually empowering collaboration between LayerZero Labs and Eigen Labs. From a technical perspective, it introduces safeguards through staking, punishment, verification, and rejection mechanisms. But from an economic perspective, this collaboration remains an extended "stacking" operation of PoS staking rewards.
By partnering with EigenLayer, LayerZero deepens the decentralization of its DVN, accepting ETH, ZRO, and EIGEN as collateral, while creating a new growth cycle for both tokens. LayerZero provides the technical foundation, while EigenLayer provides funding, rewards validators, and encourages honest behavior within this economic system.
 Hui Xin
Hui Xin
 Hui Xin
Hui Xin Kikyo
Kikyo Brian
Brian Alex
Alex Joy
Joy Brian
Brian Alex
Alex Hui Xin
Hui Xin Kikyo
Kikyo Brian
Brian