Author: Delphi Digital, Translation: Golden Finance xiaozou
“Unlike today’s tokens being associated with specific applications, in the future, tokens may increasingly be used to support possible participation in a Or specific solvers (solvers/solvers) of multiple independent applications to obtain income. Due to intent-based cross-chain value transfer applications (such as Across, deBridge’s DLN, @hashflow, Connext, CHAINFLIP LABS, Uniswap Labs, etc. ) requires solvers to have similar functionality, so it is reasonable to expect the same solvers to participate in multiple applications." - From "Infrastructure Outlook 2024".
Our Infrastructure Vision 2024 provides a comprehensive and in-depth exploration of the following 6 topics:
Topic1: The Battle for Level 2< /h2>Research and analysis of Blast L2, the biggest catalyst that may lead to the next market collapse, and The increasingly fierce competition among rollups.
The L2 ecosystem is becoming increasingly siled -- dissecting Arbitrum, Optimism, Base, zkSync, Mantle, Starknet, Polygon and more.
Ethereum Alignment: Fungible DA (data availability) is needed for scalability and a top protocol with competing products.
In-depth research on value accumulation: from ETH, L2 tokens to fungible DA – reflecting different fee generation designs and future rollup structures.
Entering the L1 competition landscape, the main competitors are Monad, Sei, Berachain, Sui and Aptos.
Theme2: Solana
A comprehensive overview of the state of Solana -- evaluating the pros and cons of Solana's architecture, the changing fee landscape, and the changing relationship between NFT and SOL prices.
Firedancer & Franendancer: A concise summary of Firedancer, the latest optimization and performance updates, and Franendancer architecture.
Payments: Solana’s area of expertise – assessment of payment activity and infrastructure, analysis of payment applications and integrations such as Sphere, Code, Sling, Shopify, and more.
OPOS: Only possible on Solana – An overview of Solana’s unique applications, including the Crankless Limit Orderbook DEX “Phoenix”, consumer-facing apps, and creator-facing apps cNFT platform DRiP, liquidation DAO sanctum focusing on Solana LST, and more.
Topic3: Intent-based cross-chain future, value will flow tosolvers
Profitable token bridges will decline, and a thorough review of the USDC full-chain standard CCTP will change the bridging landscape.
The main player in the future of intent-based bridges is Across, which is the most mature intent-based bridge.
Where does value come from?
Future Outlook: The ubiquity of intent and how the lines between applications are becoming increasingly blurred in an intent-centric world.
Topic4: SolverCentralization
The evolution of DEX (decentralized exchange) to an intent-based architecture, focusing on in-depth study of UniswapX.
Solver’s Fifty Shades of Decentralization: Solver’s Competition, Decentralization and Requirements.
Solver will dominate intent-based DEX trading volume.
Topic 5: THORChain & Chainflip – Scaling is Bitcoin’s decentralized highway
A comprehensive overview of THORChain and its development, Synths and the protocol’s own liquidity.
What are the benefits of Synths?
Future Outlook: What’s next for Thorchain in 2024?
In-depth study of Chainflip: used to evaluate the differentiating factors of THORChain such as JIT AMM and MEV in Chainflip.
Topic6: Ethereum Roadmap
Future Hard Forks – Study two major upcoming hard forks: Deneb-Cancun hard fork and Prague-Electra hard fork.
EIP-4844 and its impact on data publishing -- a case study in one of the most anticipated Ethereum upgrades since EIP-1559 and the Ethereum merger.
A key takeaway:“The future of cross-chain is based on intent, and value will flow tosolvers. ”
CCTP and Canonical Bridge have obvious advantages and disadvantages. First, they solve most liquidity/user experience fragmentation issues by increasing the share of canonically denominated assets. On the other hand, due to their conservative nature, they are slow. Authentication for Rollup bridges can take hours or weeks, while CCTP can take anywhere from tens of minutes to hours.
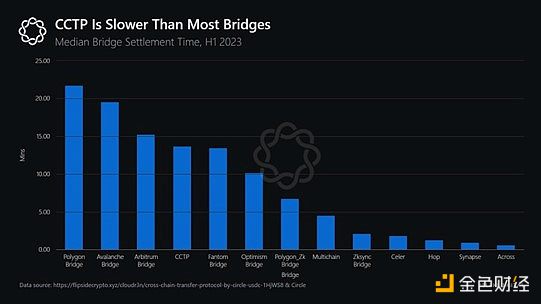
However, users want to Want faster speed. Therefore, adoption of backend services may come from user-facing applications that compete with each other in terms of speed, capital efficiency, and gas cost. As a result, we believe intent-based design will have a competitive advantage.
Across stands out as the most mature intent-based bridge. The area of connectivity between Ethereum and Ethereum rollups is particularly active, and coupled with the increasing adoption of rollups, Across has gained considerable market share.
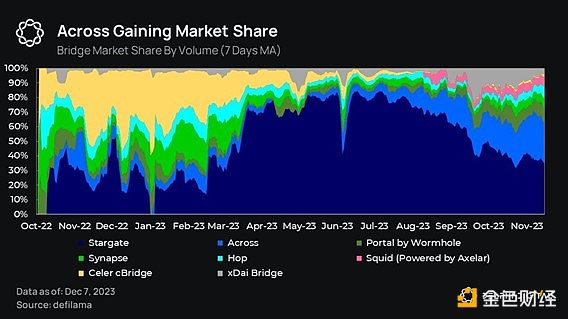
Our main points Yes, cross-chain will be based on intention in the future, which can be explained by taking Across as an example.
The intent-based liquidity network is unique in its ability to leverage off-chain liquidity through an open, permissionless off-chain main market of solvers.
The idea is: users outsource bridging risks to solvers. Solvers compete to realize cross-chain transfer intentions and capture value through fees.
The cross-chain transfer process through Across can be simplified into the following 3 steps:
Step 1, generate intent: user deposits assets into a custodial account , to express its intention of cross-chain transfer. After the intention is completed, the relayer (relayer/repeater) will receive the fee.
Step 2, intent completion: Relayers compete to identify and complete user intent on the target chain to earn fees, paying out of their own pockets using off-chain liquidity.
Step 3, Settlement: Completed transactions on the target chain are sent back to the source chain for verification. The winning relayer will unlock the assets in custody and verify them through Across’ UMA’s optimistic oracle to reduce on-chain gas costs.
Key aspects: Users’ cross-chain transfer intentions are provided by relayers immediately, and relayers will be compensated later. This guarantees users the fastest processing speeds while enabling relayers to minimize operating costs.
Transaction-based bridge transfer time is limited by the finality of the source and target chains. Intent-based bridging overcomes this problem by using relayers. Relayer can implement user intent on the target chain even before the transaction on the source chain is completed. This makes transactions faster as competition among relayers increases.
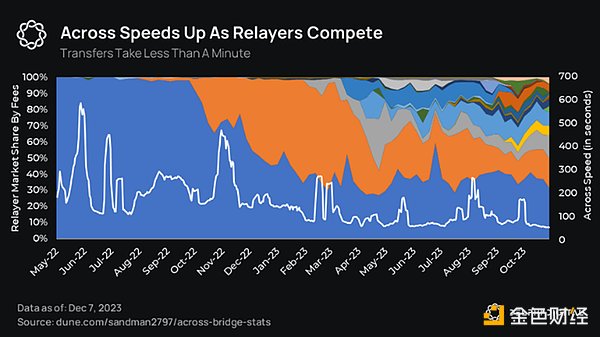
Across’s settlement is for Gas fee minimization is optimized, with periodic (every 2-4 hours) batch payments to reduce gas amortization costs. Across uses UMA's optimistic oracle for verification, further reducing gas costs.
Reliability is crucial for a liquidity network like Across. To ensure the continued availability of liquidity on the target chain, the protocol also helps relayers rebalance their liquidity. This is achieved through Across utilizing on-chain liquidity pooled by passive LPs (liquidity providers), using a hub-and-spoke (spoke) model, that is, there is a central pool on the Ethereum mainnet, and on the target chain There are some smaller radiant pools.
The protocol proactively manages rebalancing by periodically adjusting liquidity between the radiating pool and the central pool. This flexibility allows relayers to receive payments on the chain of their choice, regardless of the user’s deposit location. These pools also serve as backup for off-chain liquidity in case relayers fail to serve user intent.
Future Outlook:
Across currently uses canonical bridging and is planning to move to the Universal Bridge Adapter UBA to achieve rebalancing of liquidity. UBA will involve off-chain relayers, incentivize the balancing pool, and impose penalties on relayers who withdraw from the underbalanced radiation pool.
After UBS, Across will not bind a specific bridge method and will allow relayers to choose any bridge and compatible chain without using a canonical bridge.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Xu Lin
Xu Lin JinseFinance
JinseFinance Brian
Brian TheBlock
TheBlock Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Ftftx
Ftftx Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph