The current status of the three blockchain abstraction giants: Axelar, Wormhole, and LayerZero
“Interoperability is the future” — Vitalik Buterin.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
Author: First.VIP; Source: First Class Warehouse
Axelar is a cross-chain interoperability project. Based on cross-chain technology, on top of the concepts of cross-chain and multi-chain, an inter-chain concept is proposed, aiming to provide a unified development environment for all Web3 applications. To this end, Axelar developed the Axelar Virtual Machine (AVM) in 2024 and launched a variety of development tools, allowing Axelar to evolve from a cross-chain layer responsible for message and asset transfer to a layer that can program and deploy smart contracts to execute more complex Cross-chain layer of operations. The project is currently developing well, with transaction volume and the number of users growing steadily. If we can rely on the concept of inter-chain to expand an entire ecosystem in the future, we will have a good competitive advantage in this track.
Axelar is a cross-chain interoperability project.
From the perspective of team and funding, the Axelar team has a good academic background and development capabilities, and has completed multiple rounds of financing, with a total financing amount of US$113.8 million. , investors include Binance, Polychain Capital, Coinbase Ventures, Dragonfly Capital, Crypto.com Capital, etc. The project is currently in good development, with the number of code submissions and developers showing a clear upward trend.
From a product and technology perspective, Axelar is based on cross-chain technology and is based on the concepts of cross-chain and multichain. In this concept, all Web3 applications will have a unified development environment. This development environment will accommodate different logic on multiple chains and support data from multiple chains. User. To this end, in 2024, Axelar developed the Axelar Virtual Machine (AVM) based on CosmWasm, and launched tools such as Interchain Amplifier and Interchain Maestro, allowing Axelar to move from a cross-chain layer responsible for message and asset delivery. Evolved into a cross-chain layer that can program and deploy smart contracts to perform more complex operations. To a certain extent, Axelar's inter-chain concept is an upgrade to the cross-chain and multi-chain concepts. Its core lies in taking advantage of the Axelar network and using it as the central interactive node in a multi-chain network. Developing and deploying applications in this central node and then extending them to other networks can greatly improve efficiency, reduce costs, and provide users with a smoother experience. Therefore, the inter-chain solution proposed by Axelar has very good potential in the future.
From the perspective of project development, Axelar is currently developing well. In terms of data, the growth in the number of GMP cross-chain messages reflects the growth and improvement of the cross-chain ecosystem. At the same time, the number of active users has remained relatively stable, which also shows the user stickiness of the Axelar ecosystem. In addition, Axelar’s ecological landscape is also constantly expanding. Currently, it has been connected to 60 chains and has interacted, cooperated and integrated with more than 600 smart contracts, including many leading projects in DeFi, public chains, second-tier and other tracks. With the development of eco-related projects in the future, Axelar will also achieve certain results.
From the perspective of token economics, AXL tokens are mainly used as network application tokens to play a role in network consensus, governance, development, payment, etc. functions. In the future, AXL tokens will turn deflationary, which will further promote the healthy development of the network.
From a track perspective, the cross-chain interoperability track that Axelar is in is still in the growth stage. In the future, with the development of the public chain track and DeFi There will be a lot of room for growth in the development of the track. In the competition on the track, the solutions proposed by Axelar and the concept of inter-chain give it unique advantages in scalability. In the future, if we can rely on this concept to attract enough projects to build a prosperous ecosystem, Axelar will have a great competitive advantage in this track.
1.1 Project Introduction
Axelar is a cross-chain interoperability project based on cross-chain technology. On top of the concepts of cross-link and multi-chain, it also proposes an inter-chain concept and is committed to providing services for all Web3 applications provide a unified development environment. To this end, Axelar developed the Axelar Virtual Machine (AVM) in 2024 and launched a variety of development tools, allowing Axelar to evolve from a cross-chain layer responsible for message and asset transfer to a layer that can program and deploy smart contracts to execute more complex Cross-chain layer of operations.
1.2 Basic information [1]
< /p>

2.1 Team
According to currently available information, Axelar’s development team Interop Labs is located in Canada, with a total headcount estimated at Around 50 people, currently 33 employees on LinkedIn:

Sergey Gorbunov — Co-founder, Bachelor's and Master's degrees in Computer Science from the University of Toronto, Ph.D. in Computer Science from MIT. After graduation, he founded StealthMine, a company that helps companies encrypt data. In 2018, Gorbunov joined Algorand as chief cryptographer. In June 2020, Gorbunov co-founded Axelar.

Georgios Vlachos — Co-founder, B.S., M.S. in computer science from MIT. After graduation, he joined Algorand as the head of mathematical research. In June 2020, Vlachos co-founded Axelar.

Christian Gorenflo — Development team leader, holds a bachelor's degree in physics from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology in Germany and a Ph.D. in computer science from the University of Waterloo. After graduation, he joined Axelar's development team Interop Labs as a blockchain engineer and was promoted to the development team leader in July 2023.

Milap Sheth — Engineering Team Leader, Bachelor of Science in Computer Science from the University of Waterloo. After graduation, he joined ISARA, a network security solutions company, to engage in software development. In July 2021, Sheth joined Interop Labs as the leader of the engineering team.

Talal Ashraf — DevOps team leader, holds a bachelor's degree in electrical and computer engineering from the University of Toronto. After graduation, he joined Symantec, an enterprise cloud service development company, as a full-stack back-end engineer. Then he joined two software development companies, Flywheel and Pixlee, in 2019 and 2020 to engage in DevOps development. In August 2021, Ashraf joined Interop Labs. Serve as DevOps team leader.
Generally speaking, the development team members of the Axelar project all have good academic backgrounds, and the founder has also participated in the research and development of the Algorand public chain. Therefore, The project itself has good development capabilities.
2.2 Funds
 < /p>
< /p>
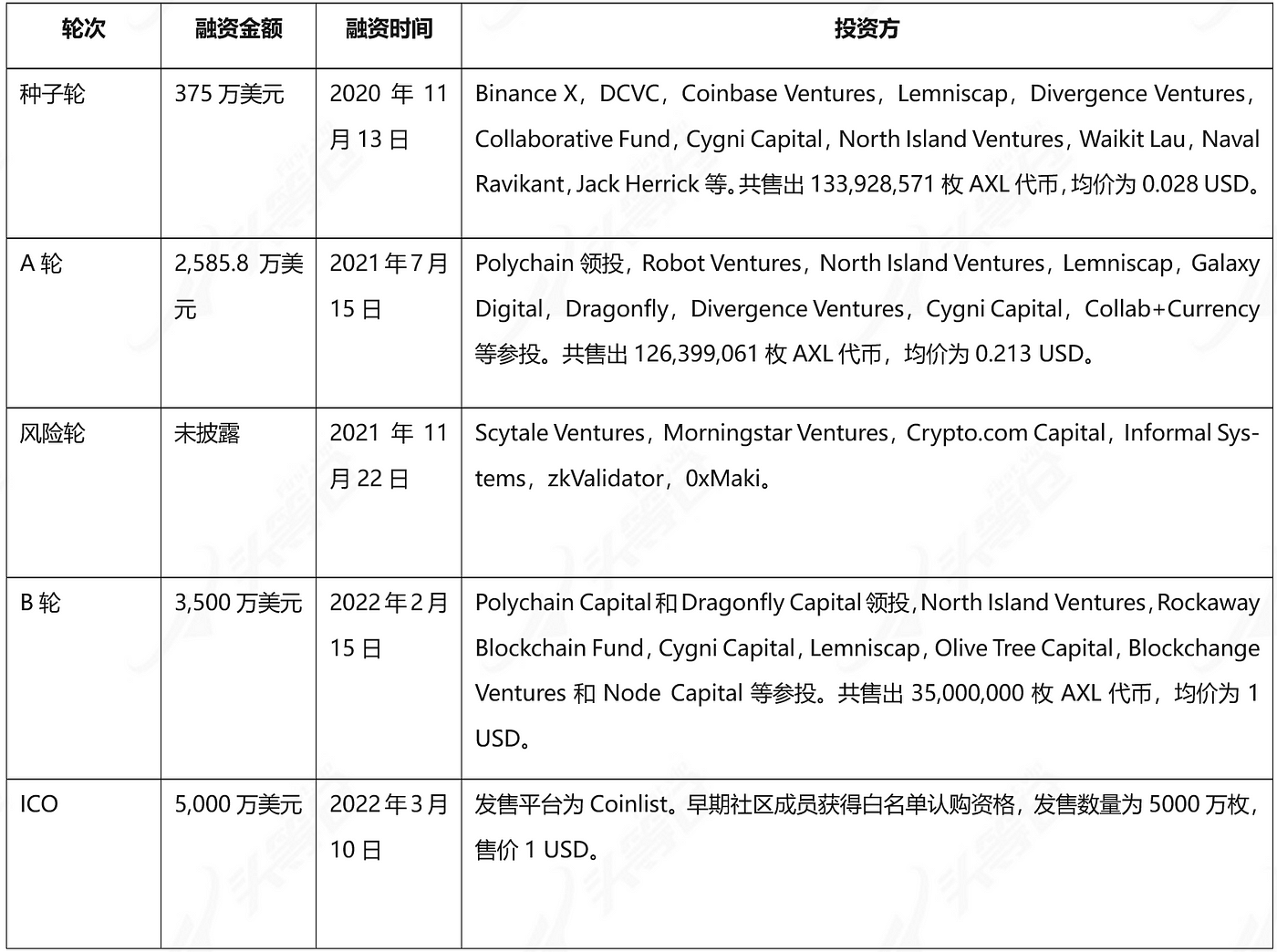
As of March 5, 2024, Axelar has completed 5 rounds of financing. According to the disclosed financing information, the total financing amount reaches raised US$113.8 million, and at the time of Series B financing, the total project valuation had reached US$1 billion. Investors include Binance, Polychain Capital, Coinbase Ventures, Dragonfly Capital, Crypto.com Capital, and others. However, the latest round of financing was completed on March 10, 2022, nearly two years ago. The actual funding situation of the project is currently unknown, but because it can still maintain the scale of the team and is still advancing the development and operation plan, it is estimated that the project itself Funds are still relatively abundant.
2.3 code
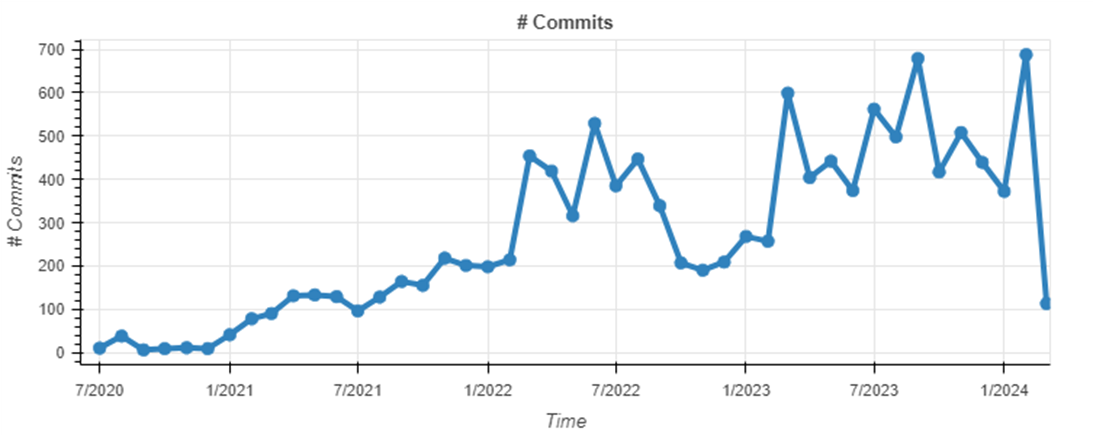

Axelar’s source code is open source on Github. As of March 4, 2024, as can be seen from the picture above, the Axelar code is continuously updated, with a total of 12,110 Commits submissions. The number of developers was more than 50 at the peak, and the current number of developers is about 50. There have been no obvious peaks and troughs in Axelar's development rhythm. Since entering 2023, Axelar's code updates and the number of developers have shown a steady upward trend, indicating that the current project development is in good condition.
2.4 Products and Technology
Axelar is a cross-chain platform developed with Cosmos SDK Cross-chain interoperability projects for major core businesses.
2.4.1 Cross-chain layer
In the cross-chain solution, Axelar chooses to use the gateway as the point, the verifier as the line, and the Axelar network as The above-mentioned "Trinity" cross-chain layer serves as a cross-chain solution. Among them:
The gateway is mainly responsible for communication and cross-chain execution functions. On the source chain of cross-chain initiation, the gateway is responsible for initiating corresponding requests, and on the target chain of cross-chain reception, the gateway is responsible for receiving and executing corresponding messages to complete cross-chain operations. On the EVM chain, the gateway exists in the form of a smart contract, while on Cosmos and other non-EVM chains, the gateway exists in the form of a Dapp. The multi-signature key controlling the gateway is jointly held by all validators, and each validator owns the key. The shared key share held is determined by the number of AXL tokens staked by it, and the key will only become effective when the key share submitted by the verifier who confirms the message exceeds the threshold.
The cross-chain messages sent by users on each chain will first interact with the gateway. After receiving the message, the gateway will generate an event in the background, and then These events are picked up by the relay and submitted to the Axelar network for processing.
Verifiers are mainly responsible for message verification and network consensus. When a cross-chain event is submitted to the Axelar network, the verifier node will start working by querying its RPC port on the source chain node to check whether the submitted event can be observed, and then confirm the existence of the event and vote to approve the event. The event is legal. Validators then package these events into blocks, and these blocks are confirmed through proof-of-stake consensus.
Axelar network is mainly responsible for processing all cross-chain requests and paying the corresponding Gas fees. When the block is packaged and the cross-chain requested messages are authorized, another set of relays will pick up these messages and periodically send these messages to the gateway on the target chain. In this process, Axelar needs to use tokens on the target chain to pay gas fees. In order to facilitate users and eliminate the need to prepare tokens on the target chain and Axelar to pay Gas fees, Axelar created and deployed a smart contract called Gas Receiver. The Gas Receiver contract will estimate the total Gas fees required on the source chain, Axelar network and target chain, charge the user one-time native tokens on the source chain as Gas fees, and then convert these native tokens into AXL, target chain tokens and Other required tokens are used to complete Gas fee payment on behalf of the user. During this process, the Gas Receiver will generally collect more tokens than the actual payment amount, and return the excess Gas fees to the user's account after the transaction is completed.
Compared with common cross-chain bridges, the Axelar network as a cross-chain layer has more advantages in many aspects.
1) First of all, in terms of security, Axelar's security is guaranteed by multi-signature keys and network consensus layers. First, when transmitting cross-chain information and performing cross-chain operations, a threshold number of verifier nodes are required to confirm the authenticity of the message and submit the shared key before the gateway can function, and Axelar has also added a rate limiting function at the gateway level. , there will be an upper limit on the number of transactions for each asset class within a given time interval. Secondly, after all cross-chain events are packaged, they need to be confirmed through the Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism before a new block can be generated. In addition, in order to reduce the risk of voting rights being concentrated in a small number of stakeholders due to different AXL pledge shares, Axelar also introduced a "square voting" mechanism at the consensus level, that is, when a validator votes, it obtains a share of voting rights. One unit of AXL tokens needs to be pledged, but if it needs to obtain the voting rights of two shares, it needs to pledge the square of two, that is, four units of AXL tokens, and so on, the share of tokens owned by the validator node , it is necessary to complete the square calculation to obtain the corresponding number of voting rights. After restricting the validator nodes with high pledge shares, the decentralization of the network has been greatly improved. The existence of the above two mechanisms ensures that Axelar has better security than common cross-chain bridges.
2) Secondly, in terms of scalability, Axelar, as a public chain, can execute smart contracts. This means that Axelar can integrate with other public chains and Dapps more conveniently, quickly and at low cost, and even act as their "cross-chain layer" in the concept of modular blockchain to help these projects complete cross-chain operations. At the same time, it can also effectively improve the user experience. For example, an API released by Axelar can help integrated Dapps generate a one-time deposit address. These addresses can receive cross-chain funds of any token from any wallet on any integrated chain, allowing users to obtain cross-chain funds during the process. No less interactive experience than a centralized exchange. Secondly, by expanding the General Message Passing (GMP) function, Axelar can not only realize cross-chain assets, but also support complex cross-chain function calls and cross-chain status synchronization, which greatly improves Dapps that cooperate with Axelar. scalability.
In addition, in 2023, Axelar proposed another concept based on the concepts of cross-chain and multi-chain. The concept of interchain. In this concept, all Web3 applications will have a unified development environment. This development environment will accommodate different logic on multiple chains and support users from multiple chains to further implement Axelar. The ideal of full-stack interoperability. To this end, in 2024, Axelar developed the Axelar Virtual Machine (AVM) based on CosmWasm, allowing Axelar to evolve from a cross-chain layer responsible for message and asset transfer to a layer that can program and deploy smart contract execution. Cross-chain layer for more complex operations.
2.4.2 Axelar Virtual Machine (AVM)
AVM is a Turing-complete The significance of the virtual machine is not only that it can deploy smart contracts, but also that it completely changes the logic of traditional Dapp implementation of cross-chain. Because for Dapp developers, applications developed on AVM are equivalent to having cross-chain functions innately, without having to integrate with other cross-chain projects the day after tomorrow. Their cross-chain functions are provided by the lower-level Blockchain is implemented by Axelar. This is the concept of interchain proposed by Axelar. In Axelar's own words, it is "Build once, run everywhere".
Specifically, by developing Dapps on AVM, DeFi projects will be able to use liquidity on multiple chains at the same time for transactions or lending; stablecoin projects It will be able to expand the application space and allow users to obtain a seamless experience on multiple chains; game projects can choose to issue the same asset or token on multiple chains; NFT projects can also be integrated into cross-chain games, or Fully enjoy higher transaction liquidity; wallet projects can log in to any blockchain to provide services to users above; DAO projects can govern and act across multiple chains, and allocate assets more easily.
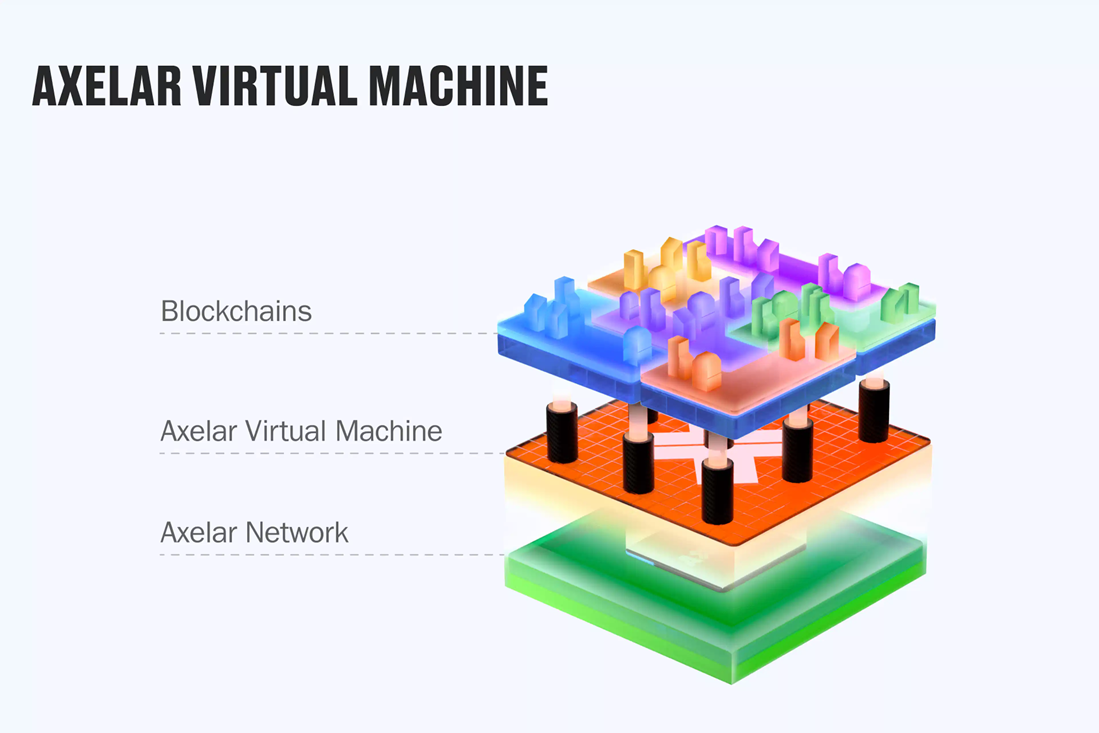
To help developers deploy their projects on AVM more efficiently and cost-effectively, Axelar has launched two tools that developers can use to build applications: Interchain Amplifier and Interchain Maestro.
Interchain Amplifier is a tool for developers to connect and use the Axelar network. It is mainly used to help developers establish connections with the Axelar network without permission and at low cost. connect. Developers only need to pay the cost of joining the Axelar network, and can enjoy the links between Axelar and other ecosystems and networks to add new functional attributes to improve Dapp security and scalability, so it is called Amplifier. ). Its use cases include the ability to easily integrate components developed on Ethereum, such as ZK proof components, into Dapps on the Axelar network.
Interchain Maestro is a tool for developers to deploy and manage multi-chain Dapps. Developers can deploy their own contracts on multiple chains through the following simple process. :
1) Specify the contract you want to deploy, set the key parameters of the contract and the chains you want to involve.
2) Store parameters and content in Axelar’s smart contract, and deploy the smart contract on the relevant chain.
3) Extend or clone these contracts to other chains.
4) When a Dapp needs to be upgraded, developers only need to initiate a transaction on Axelar to upgrade their contract code, and the upgrades of these codes will be sent to other connected chains without having to do it separately on other chains. Smart contract upgrades.
Developers can greatly improve the efficiency of Dapp deployment and reduce the cost of Dapp deployment through Interchain Maestro. Among them, Interchain Token Service, an important component of Interchain Maestro, has been released to the main network. Through this function, project parties can easily issue and manage inter-chain tokens, and retain the cross-chain functionality of the tokens during this cross-chain deployment process. Interchangeability as well as some custom features.
Through the deployment of AVM, the concept of "Interchain" proposed by Axelar can be truly practiced, thus laying a solid foundation for the development of the Axelar ecosystem. . To a certain extent, Axelar's inter-chain concept is an upgrade to the cross-chain and multi-chain concepts. Its core is that it establishes a central interactive node in a multi-chain network. By developing and Deploying applications can greatly improve efficiency and reduce costs, and users will also have a smoother experience. Therefore, the solution proposed by Axelar has good potential in the future.
Summary
From the perspective of team and funding, the Axelar team has a good academic background and development capabilities, and has completed multiple rounds of financing, with the total financing amount reaching US$113.8 million. Investors include Binance, Polychain Capital, Coinbase Ventures, Dragonfly Capital, Crypto.com Capital, etc. The project is currently in good development, with the number of code submissions and development The number of participants has shown a clear upward trend.
From a product and technology perspective, Axelar is based on cross-chain technology and is based on the concepts of cross-chain and multichain. In this concept, all Web3 applications will have a unified development environment. This development environment will accommodate different logic on multiple chains and support data from multiple chains. User. To this end, in 2024, Axelar developed the Axelar Virtual Machine (AVM) based on CosmWasm, and launched tools such as Interchain Amplifier and Interchain Maestro, allowing Axelar to move from a cross-chain layer responsible for message and asset delivery. Evolved into a cross-chain layer that can program and deploy smart contracts to perform more complex operations. To a certain extent, Axelar's inter-chain concept is an upgrade to the cross-chain and multi-chain concepts. Its core lies in taking advantage of the Axelar network and using it as the central interactive node in a multi-chain network. Developing and deploying applications in this central node and then extending them to other networks can greatly improve efficiency, reduce costs, and provide users with a smoother experience. Therefore, the inter-chain solution proposed by Axelar has very good potential in the future.
3.1 History

3.2 Current Situation
3.2.1 Operational data
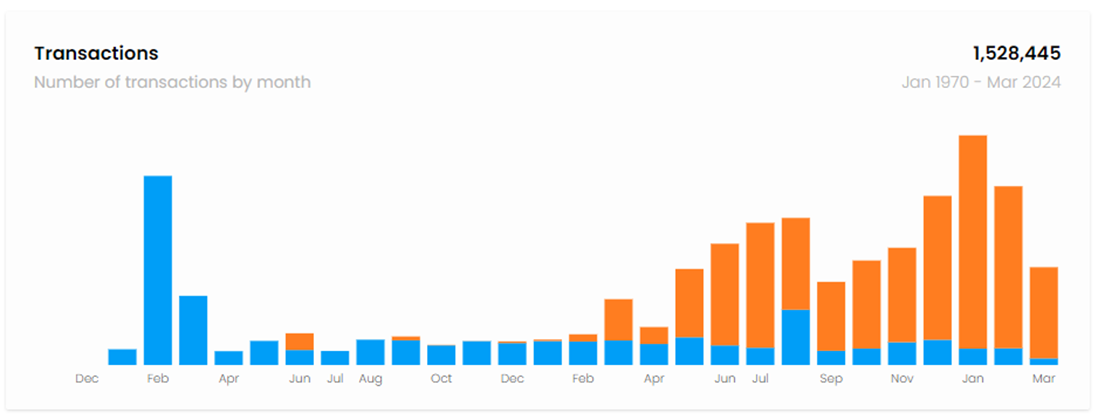

According to Axelar’s block explorer, as of 11:00 on March 11, 2024, a total of 1,528,445 transactions, including 962,300 GMP (General Message Passing) transactions, accounting for approximately 62.96%. GMP transactions are mainly used on one chain to call smart contracts on other chains connected by Axelar. The difference between them and ordinary cross-chain transactions The reason is that the designated object is a smart contract, while ordinary cross-chain transactions are only responsible for transferring an asset from the account of the source chain to the account of the target chain. Therefore, after 2023, the rapid increase in the number of GMP transactions reflects the continuous improvement and activity of Axelar's cross-chain ecosystem. In addition, the number of active users of Axelar has also increased significantly since 2023, and has remained relatively stable since then, which reflects that Axelar has good user ecological stickiness.
3.2.2 Ecological project
As a project that can program and deploy smart contracts to execute updates A cross-chain layer for complex operations, Axelar's ecosystem includes not only other chains connected to it, but also Dapps developed on top of it.

Axelar currently has 60 blockchains connected to it, and these blockchains can be divided into 3 levels according to the active level of user and Dapp interaction.
T1 level public chains include: Polygon, Osmosis, BNB Chain, Arbitrum, Avalanche, Ethereum, Fantom, Moonbeam, Celo, Terra Classic, Terra, Base, Optimism, Kujira.
T2 level public chains include: Kava, Sei, Mantle, Linea, Neutron, Umee, Juno, Crescent, Secret-SNIP, Cosmos, Filecoin, Evmos, Scroll, Comdex, XPLA.
Among them, there were approximately 290,330 transactions initiated from Polygon, accounting for approximately 19.00%, and approximately 189,880 transactions initiated from BNB Chain, accounting for approximately 12.42% , there were approximately 166,120 transactions initiated from Osmosis, accounting for approximately 10.87%, approximately 151,400 transactions initiated from Arbitrum, accounting for approximately 9.91%, and approximately 135,840 transactions initiated from Avalanche, accounting for approximately 8.89%, from Ethereum initiated approximately 95,540 transactions, accounting for approximately 6.25%. It can be seen that the participation of various public chains in the Axelar cross-chain ecosystem is relatively dispersed, and there is no special dependence on a certain public chain. The overall development situation is relatively healthy.
At the application level, as of March 11, 2024, the number of Dapps deployed or preparing to be deployed on Axelar has reached 635[7].
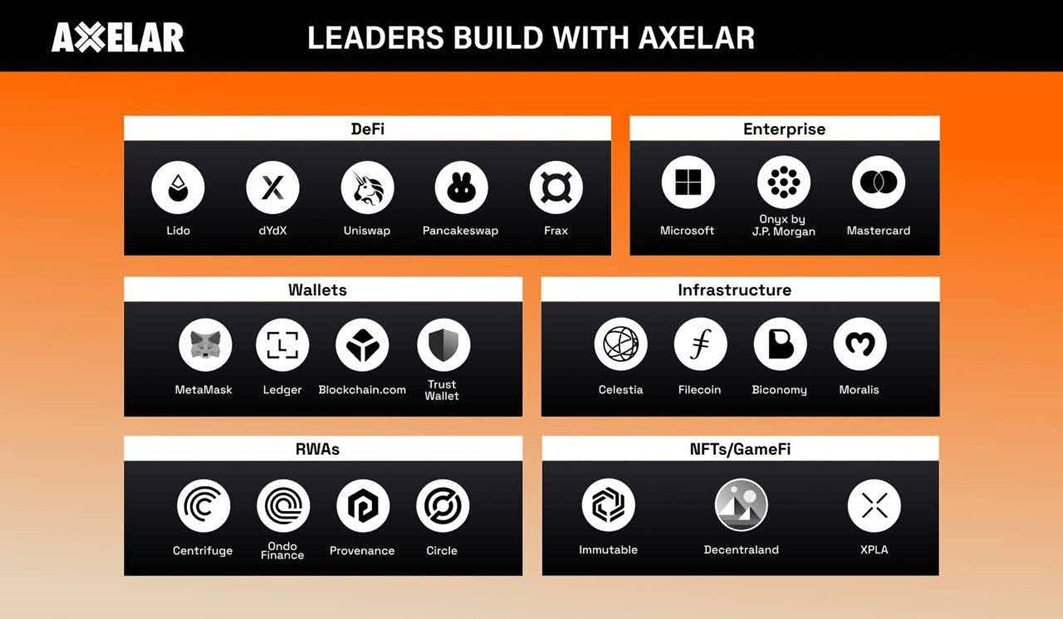
Projects that have been deployed so far include wallet projects such as MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Keplr; infrastructure projects such as Biconomy; game projects such as Decentraland; DeFi projects such as dYdX, Lido, PancakeSwap, SushiSwap, QuickSwap , KyberSwap.
In addition, there are some projects that integrate or cooperate with Axelar, including Uniswap, Ripple, Immutable, Frax Finance, Vertex, Ondo Finance, Fantom, Band Protocol, Sommelier, Filecoin, Umee, Polygon, Sui, Circle, etc.
At present, projects related to Axelar's ecology are mainly DeFi and public chains. This is inseparable from the cross-chain nature of Axelar itself. It will follow With the prosperity of DeFi ecology and public chain ecology, Axelar has good development potential.
3.2.3 Social media scale
As of March 11, 2024, Axelar’s social media platform is larger in scale and has a larger number of fans, but less interaction. The community has a large number of people, but its activity level is average. The communication content mainly focuses on the problems encountered in project interaction. The governance forum is generally active, and the communication content mainly focuses on the technical upgrade and development direction of subsequent projects.
3.3 Future
According to the roadmap announced by Axelar on January 30, 2024, The next development of Axelar will revolve around AVM. Specifically, it will include the following sub-items:
1) Let AVM become a development platform for open source tools and carry out Development of various Dapps.
2) Use Interchain Amplifier to achieve permissionless links to any chain, extending potential network effects to hundreds of blockchains such as Ethereum Layer2.
3) Expand the use cases of Interchain Tokens and expand their availability on the native chain across all connected chains.
4) Add a Gas burning mechanism to the AXL token to achieve deflation to protect the Axelar network.
5) Integrate consensus mechanisms on different chains, including Solana, Stellar and Move-based chains such as Aptos and Sui.
6) Improve the Gas pricing mechanism and improve the accuracy of cross-chain Gas estimation services on the Axelar network.
Summary:
From the perspective of project development, Axelar is currently developing well. In terms of data, the growth in the number of GMP cross-chain messages reflects the growth and improvement of the cross-chain ecosystem. At the same time, the number of active users has remained relatively stable, which also shows the user stickiness of the Axelar ecosystem. In addition, Axelar’s ecological landscape is also constantly expanding. Currently, it has been connected to 60 chains and has interacted, cooperated and integrated with more than 600 smart contracts, including many leading projects in DeFi, public chains, second-tier and other tracks. With the development of eco-related projects in the future, Axelar will also achieve certain results.
4.1 Supply
4.1.1 AXL Token Allocation [9]
AXL is the project token of Axelar. It will be launched on the main network in September 2022. The initial supply is 1,000,000,000. New AXL tokens will be issued using inflation. As of March 5, 2024, the supply of AXL tokens There are 1,137,455,595 pieces, and the total circulation is 587,380,415 pieces.
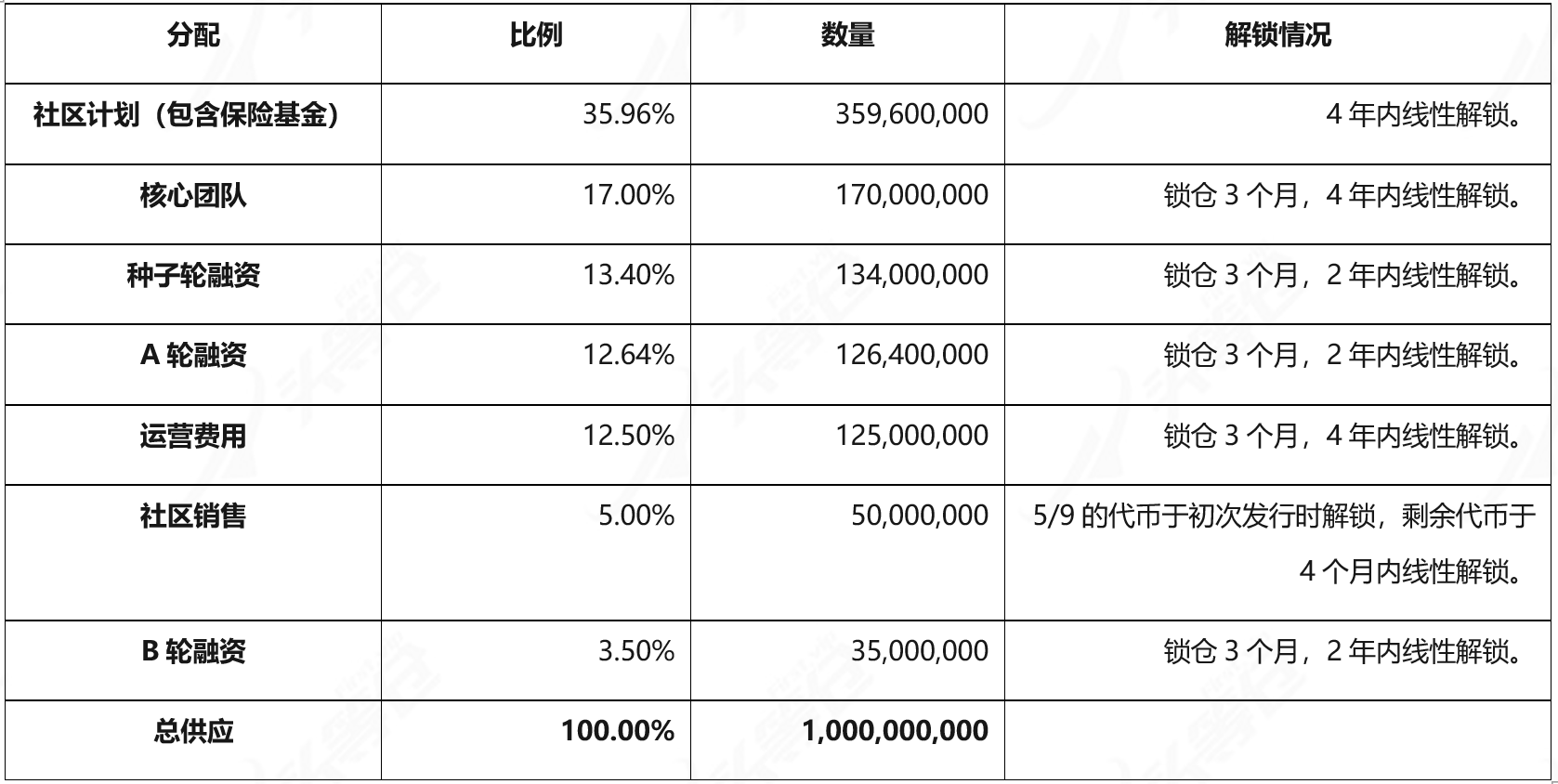
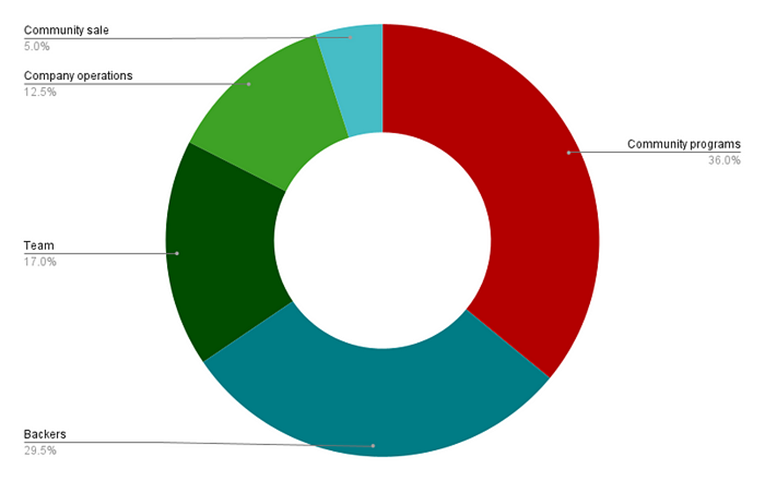

From the perspective of token distribution, among the 1 billion AXL initially distributed, both team and financing accounted for At about 30%, community and ecology account for 40%, which is a relatively reasonable proportion. As of March 5, 2024, it has been nearly 17 months since the initial issuance of the token, and the unlocked tokens among the 1 billion tokens initially issued are approximately US$452[1.1] million.
4.1.2 Analysis of currency holding addresses

As shown in Figure 4–2 above, according to Axelar’s browser, as of February 2024 On the 22nd, there were a total of 849,110 AXL currency holding addresses, with the top 100 holdings accounting for 86.94%. Among the top 20 currency holding addresses, there are 10 contract addresses, accounting for approximately 62.37%. Among them, there are 273,740,417 tokens in the locked contract of AXL tokens, 62,683,244 tokens in the reserve contract, and 40,063,641 tokens in the stable currency reserve. After deducting these contracts and reserve tokens, the overall holdings of AXL tokens are relatively dispersed.
From the perspective of the token issuance method, the current AXL token is still an inflation token, and the calculation formula of its token inflation rate is, 1 % base inflation rate plus each externally supported blockchain (EVM chain) provides an inflation rate of 0.3% (0.75% until December 5, 2023), there are currently 20 externally supported blockchains, so currently The inflation rate is 7% (14.5% before December 5, 2023).
In order to promote the healthy development of the network, Axelar plans to change the AXL token from an inflationary token to a deflationary token by implementing a Gas burning plan. Currently, Axelar costs about 0.2 AXL tokens to process a cross-chain message. If calculated based on processing 100,000 transactions per day, it will collect approximately 104 [1.3] million AXL a year. By burning these AXL tokens as gas fees, Axelar will be able to offset up to 10% of the inflation rate and achieve deflation of the token.
Although the proposal has been passed, the plan for burning AXL as a network Gas token has not yet been deployed on the main network. This will be the next step. One of the focuses of Axelar's efforts this year.
4.2 Requirements
AXL token, as the native token of the Axelar network, mainly includes the following Functions:
1) As the basis for DPoS to conduct network consensus, and as the block reward that validator nodes can obtain.
2) As a governance token, it is used to vote on governance proposals, including network parameters and the marketing, development and technical upgrades of the protocol.
3) Pay transaction fees on the network, which will be the main Gas fee in the Axelar network ecosystem in the future.
4) Used to reward ecosystem participants and community contributors.
4.2.1 Network Node
Axelar network adopts Tendermint’s consensus algorithm for DPoS form of network consensus. The number of validator nodes is currently fixed at 75, and the nodes with the top 75 token pledges will be able to register as validators. This number of validators can be adjusted through governance in the future.
A validator on the Axelar chain needs to first configure a node on the external chain of its choice, and then submit the RPC endpoint of the external chain to the Axelar validator node, and Register as the maintainer of these external links to submit the status of these external links for voting at any time, so there is a certain operational threshold.
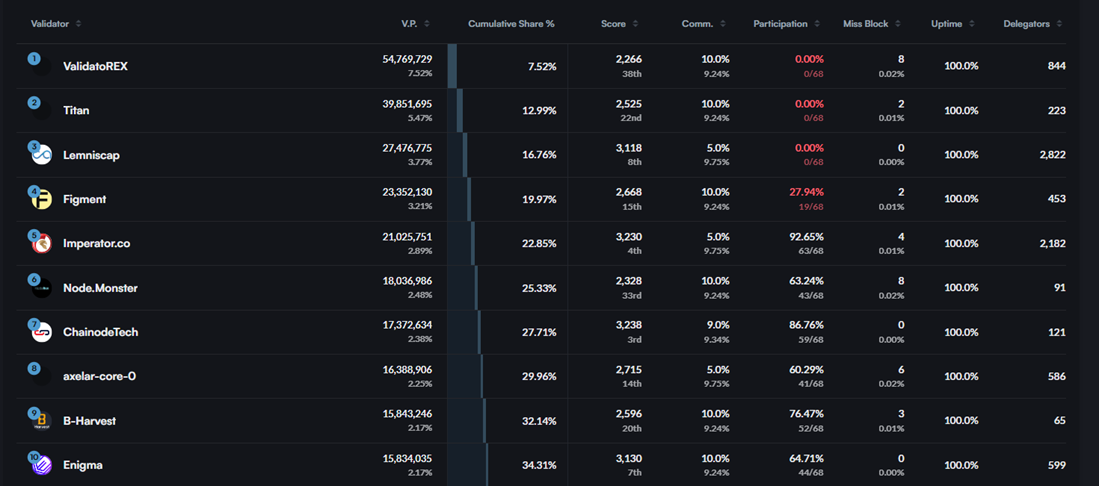
Each node will receive block rewards during the block consensus process. Currently, the expected APR of block rewards for each validator node is between 5% and 10%, depending on the number of nodes deployed on the external chain. is fixed, and the actual APR is around 9%. Axelar network users can share the block rewards they receive by staking their AXL holdings to the corresponding validator nodes. In addition, canceling the pledge will take 7 days to complete.
At present, ValidatorREX, the validator node with the highest share of AXL, accounts for about 7.52%, and the share of the top ten validator nodes is about 34.31%, and The top three validator nodes by share hardly participate in the governance of the protocol. Therefore, it can be seen that although Axelar has a relatively small number of validator nodes, it still has a certain degree of decentralization.
Summary:
From the perspective of token economics, the AXL token’s The design is quite satisfactory and is mainly used as the application token of the network to play the functions of network consensus, governance, development, payment and other aspects. In the future, AXL tokens will turn deflationary, which will further promote the healthy development of the network.
5.1 Track Overview
Axelar, as a cross-chain layer that can carry out message cross-chain and asset cross-chain, can be classified into the cross-chain interoperability track.
In the past, the public generally understood that the cross-chain track refers to projects that carry out cross-chain assets. After the information transfer plan was proposed, , the cross-chain interoperability track came into being. As the name suggests, the purpose of cross-chain interoperability is to achieve interoperability between multiple chains. For example, users can complete operations on chain B on chain A. The completion of this operation depends on the interaction between data on different chains, including The exchange of information such as assets, chain status, contract calls, etc. To a certain extent, cross-chain interoperability has certain similarities with side chains. Both emphasize the realization of interoperability between the main chain and side chains, that is, the sharing of assets and information. The difference is that the cross-chain interoperability project is committed to realizing an interoperable network. When the main chain is connected to this network, all other chains connected to the network can theoretically become the main chain. side chain".
Projects in the current cross-chain interoperability track generally follow a similar implementation architecture, which is "observation-confirmation-transmission/interaction". Because in essence, all cross-chain projects perform functions similar to "intermediaries". They need to obtain the source chain information first, confirm and process it, and then interact with the target chain. In this process, how to obtain the source chain information? Chain information, how to confirm and process the obtained information and how to interact with the target chain have become the focus of product and technology competition among various cross-chain interoperability projects.
At present, there are not many projects in the cross-chain interoperability track. The overall development of the track is still in the growth stage, and there is still great development potential in the future. In the following comparison of competing products, we will select LayerZero and Wormhole as Axelar's competing products, and compare the implementation plans of the three to a certain extent.
5.2 Competitor Comparison
5.2.1 LayerZero
LayerZero is a full-chain interoperability protocol.
From the perspective of team and funding, LayerZero’s team has relatively rich development experience, and the team has a long-term cooperative relationship with each other and has a high degree of integration. It has completed multiple rounds of financing, with the total financing amount reaching US$293.3 million. Investors include Binance Labs, Delphi Digital, A16z, Sequoia Capital, Coinbase Ventures and other star capitals.
From a product and technology perspective, LayerZero focuses on achieving "lightweight" data transmission, so it chooses to use oracles and relay networks to complete data transmission. transmission. After the user completes the operation on the endpoint of the LayerZero source chain, the oracle, as an external component, will forward the block header of the transaction on the source chain to the target chain. At the same time, the relay will obtain the transaction proof on the source chain and transmit it. to the target chain. There are three benefits of doing this:
1) Reduce the cost of information transmission. Because LayerZero does not need to run its own nodes on each chain, it outsources the function of information verification. At the same time, the oracle sends information to the target chain in one direction, which also avoids the cost of interaction with verification nodes.
2) Safety is guaranteed. The functions of the oracle and the relay are separated and independent from each other, and the information transmitted by the two can be mutually verified, reducing the threat to the network caused by the oracle or relay acting alone.
3) Increased scalability. Because oracles and relays are only responsible for transmitting information, and all verification is done on the respective source and target chains, the speed and throughput of transactions will entirely depend on the properties of the two transaction chains.
In January 2024, LayerZero launched the V2 version, which divided message verification and execution into two independent stages. Developers can set different settings according to their needs. security configuration and independent execution, thus having more autonomy and improving the programmability of the protocol.
From the perspective of token economics, although LayerZero has not yet issued tokens, the team has released some information in the code of its official document. It is expected that in the future LayerZero’s token will undertake functions such as paying Gas.
From the perspective of project development, LayerZero is currently developing well, especially since March 2024, user usage has increased significantly. The ecosystem has supported the interconnection of more than 20 chains, among which the source chains with the most transactions are Arbitrum, Optimism, Polygon, Avalanche, Binance, Fantom and Ethereum. The number of integrated and cooperative Dapps has reached 95 and is still increasing.
5.2.2 Wormhole
Wormhole is a general messaging protocol.
From the perspective of team and funding, Wormhole was born out of the cooperation between Solana and Certus.One. It was initially only a cross-chain established for the two networks of Ethereum and Solana. Bridge, so it has rich development experience. In November 2023, Wormhole completed US$225 million in financing at a valuation of US$2.5 billion, and established a new company, Wormhole Labs, to be responsible for the development of new protocols.
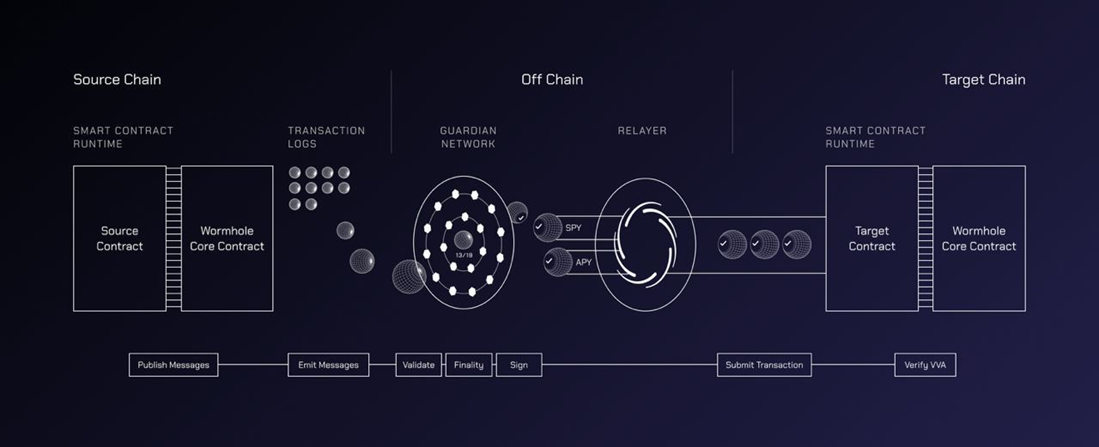
From a product and technology perspective, Wormhole's implementation solution is relatively "simple and crude". The overall architecture consists of on-chain components and off-chain components.
The components on the chain mainly include the emitter (Emitter), Wormhole core contract and transaction log.
The emitter includes the xAsset contract (a smart contract that converts ordinary tokens into xAsset and bridges them), and a relay contract (which allows cross-chain applications to pass It consists of smart contracts such as a decentralized universal cross-chain relay network that sends messages to a specific blockchain) and a Worm Router contract (a smart contract that allows developers to build Dapps into cross-chain applications), which is responsible for calling core contracts. Send messages.
The core contract of Wormhole is a contract that interacts with off-chain components and is mainly responsible for the verification and confirmation of messages.
Transaction logs are specific logs on the blockchain that allow off-chain components to observe messages sent by core components.
The off-chain components are mainly composed of guardian nodes and message transmission networks.
The guardian nodes are composed of 19 guardians. They hold VAA (Verifiable Action Approvals) multi-signatures, which run on each connected chain. A complete node dedicated to listening for any messages from the core contract. When two-thirds or more of the guardians verify the message and sign it, the verified message will be relayed to the target chain, where the message will be processed and cross-chain transactions completed.
The external verification solution adopted by Wormhole has the advantage of being faster, lower cost, and can be expanded to multiple chains very quickly. , but its disadvantage is that it sacrifices a certain degree of security and needs to rely on a few validator nodes, and there is also a certain risk of centralization.
From the perspective of token economics, Wormhole's tokens will be mainly used for the development of future projects and ecosystems, and will have certain governance functions. However, in general, the link between W tokens and project development is not close enough, and the dividends of project development cannot be fully shared and it cannot bring more empowerment to the project.
From the perspective of project development, Wormhole is currently developing well. Although after the FTX thunderstorm, it was affected by the Solana ecology and experienced a low period for more than a year, but Starting from mid-2023, the project will regain a certain vitality. Currently, Wormhole is connected to more than 40 networks (including verification networks). From the perspective of transaction volume, the source chains with the most transactions are Ethereum, Solana, Sui, and Arbitrum. The transactions between these four constitute the main transactions on Wormhole. Currently, there are more than 100 Dapps integrated and cooperated with Wormhole, and the number is still increasing.
 < /p>
< /p>
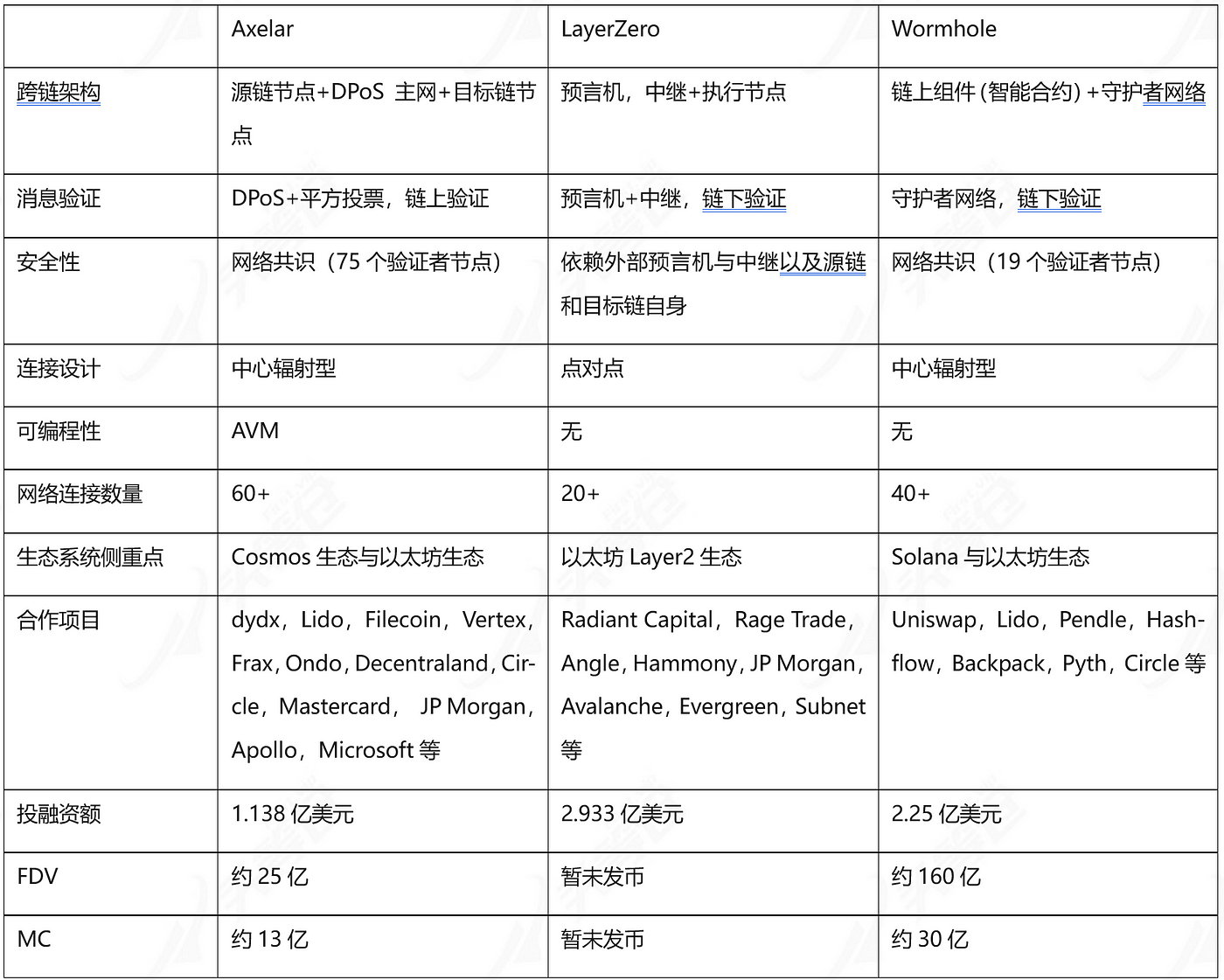
After comparing with LayerZero and Wormhole, we can find that because Axelar requires node verification and network consensus, Therefore, Axelar's architecture is not as efficient as LayerZero. In terms of security, both LayerZero and Axelar have merits. LayerZero simplifies the process of cross-chain information interaction. It is not responsible for the verification of information. There is no collusion between oracles and relays. In this case, the source chain and the target chain themselves ensure cross-chain security, while Axelar relies on the consensus of the network to ensure cross-chain security. Axelar is similar in architecture to Wormhole, but compared to Wormhole, Axelar has a larger number of validator nodes and is therefore more decentralized.
But in terms of scalability, as a cross-chain layer that can program and deploy smart contracts to perform more complex operations, Axelar has unique advantages. The inter-chain concept proposed can also further lay the foundation for the subsequent development of the ecosystem. At the same time, from the perspective of token economics, the integration of AXL tokens and Axelar is undoubtedly closer. After the application of the new token economic model, it can bring new empowerment to the development of the project. Judging from the current specific project development, we can see that the development of LayerZero focuses on the interaction between the second-layer ecology of Ethereum, the development of Wormhole focuses on the interaction between the Solana ecology and the Ethereum ecology, and the development of Axelar focuses on The focus is on the interaction between the Ethereum ecology and the Cosmos ecology. The three compete with and complement each other. This means that the current market competition environment is still in a blue ocean. In the future, with the development of the public chain track and the DeFi track, the cross-chain interoperability track will still have broader market growth space.
To sum up, we are optimistic about Axelar’s potential to compete in the cross-chain interoperability track.
Summary
From a track perspective, Axelar is in a cross-chain interaction The operational track is still in the growth stage, and there will be a lot of room for growth in the future with the development of the public chain track and the DeFi track. In the competition on the track, the solutions proposed by Axelar and the concept of inter-chain give it unique advantages in scalability. If we can rely on this concept to attract enough projects to build a prosperous ecosystem in the future, Axelar will have a great competitive advantage in this track.
1) Code security risk: despite completing multiple audits , Axelar still has the possibility of system risks and vulnerabilities. At the same time, the cross-chain track is the hardest hit area by hackers, so users need to be more vigilant.
2) Market competition risk: Currently, Axelar has many competing products, and its strength is not weak.
3) Centralization risk: Currently, Axelar only has 75 network nodes, and there is still a certain degree of centralization risk.
“Interoperability is the future” — Vitalik Buterin.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceAxelar is a cross-chain interoperability project based on cross-chain technology. On top of the concepts of cross-chain and multi-chain, it also proposes an inter-chain concept and is committed to providing a unified development environment for all Web3 applications. .
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceBinance listing propels Axelar's AXL token up 81%, reflecting market excitement for its Web3 interoperability role. Partnership with Ripple further boosts prospects.
 Xu Lin
Xu LinAXELAR, cross-chain bridge, why is Axelar said to be a dark horse in the cross-chain track? Golden Finance, what does the future of cross-chain look like?
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceAxelar and Microsoft have teamed up to develop and offer blockchain interoperability products. As part of the deal, Axelar’s cross-chain stack will be available to Microsoft customers via the Azure cloud marketplace.
 TheBlock
TheBlockDeGods will bridge over to Ethereum while its sister project Y00ts will move to Polygon with a grant from the layer 2's partnership fund.
 Coindesk
CoindeskAxelar is partnering with leading infrastructure company Mysten Labs to enable decentralized applications built on Mysten’s Sui blockchain.
 Others
OthersSeveral activities are taking place in the crypto industry amid the current market situation. One of such activities is the ...
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistWith less than 24 hours remaining until the debut of the Chains (CHA) token presale, time is running out to ...
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistMicrosoft CEO Satya Nadella said: “The Metaverse allows us to embed computing in the real world, and the real world in computing. Bringing a sense of real presence to any digital realm.”
 Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph


Please enter the verification code sent to