Author: Hotcoin Research
Introduction
Recently, the market attention on the transfer of control of the WBTC project has been very hot. The news that Justin Sun (founder of Tron) announced his participation in the WBTC project quickly sparked widespread controversy in the crypto community. The focus of discussion was mainly on the security and degree of decentralization of WBTC and the potential impact of Justin Sun’s personal influence on the project.

Since its launch in 2019, WBTC has become an important bridge for Bitcoin's cross-chain applications. By anchoring Bitcoin as an ERC-20 token, WBTC has brought a wider range of DeFi applications to Bitcoin. However, WBTC's centralized custody model has also made it controversial for a long time. Sun Yuchen's entry has once again sparked discussions on this issue, especially in terms of cross-chain asset security and the importance of decentralized governance.
This article will explore the root cause of the controversy caused by Sun Yuchen's entry into WBTC through an overview of BTC anchor coins, mechanism principles, and in-depth analysis of representative projects, and look forward to the future development direction of BTC anchor coins.
I. Overview of BTC anchor coins
1.1 Definition and basic principles
BTC anchor coins are digital assets that map Bitcoin to other blockchain networks through specific technical means. This type of token is usually pegged to Bitcoin in a 1:1 manner, that is, for each BTC anchor coin issued, there will be an equal amount of Bitcoin as collateral behind it. This mechanism enables BTC anchor coins to have the value attributes of Bitcoin on other blockchains (such as Ethereum), and at the same time, they can participate in the decentralized applications DApps of these blockchains.
The creation of BTC anchor coins is mainly to make up for the shortcomings of Bitcoin's own network in smart contract functions, so that Bitcoin can play a role in a more complex financial ecosystem. Although Bitcoin is the earliest and most consensus-based cryptocurrency, its network lacks Turing completeness and cannot directly support smart contracts and other complex decentralized financial operations. For example, the ERC-20 standard token on Ethereum can be easily integrated into the DeFi protocol, and by mapping Bitcoin to ERC-20 or other standard token forms, it can be used on smart contract platforms such as Ethereum and participate in various DeFi scenarios such as lending, liquidity mining, and derivatives trading, thereby greatly expanding the scope of Bitcoin's application.
1.2 The Demand and Significance of BTC Anchor Coins
(1) The Demand for Cross-Chain Liquidity
As the world’s most liquid cryptocurrency with the highest market value, Bitcoin has far more users and holdings than other crypto assets. If Bitcoin can flow seamlessly to other blockchains, especially those with smart contract functions, it will greatly enhance its usage scenarios and value creation capabilities. BTC anchor coins are designed to meet this demand for cross-chain liquidity. Through BTC anchor coins, Bitcoin can leverage its asset advantages on other blockchains and participate in more diverse decentralized applications, such as lending, liquidity mining, and derivatives trading.
(2) Driving force for the development of decentralized finance (DeFi)
As "digital gold", Bitcoin has great potential in DeFi. However, due to the technical limitations of the Bitcoin network itself (such as the lack of smart contract functions), it is quite challenging to develop DeFi applications directly on the Bitcoin network. Therefore, "relocating" Bitcoin to a blockchain with smart contract functions (such as Ethereum) has become a key path to achieve this goal. BTC anchor coins enable Bitcoin to participate in the DeFi ecosystem by mapping it to blockchains such as Ethereum. This not only improves the utilization rate of Bitcoin, but also injects more liquidity and stability into DeFi applications.
(3) Asset appreciation and risk management tools
Through BTC-pegged coins, holders can obtain additional benefits by participating in the DeFi ecosystem without giving up long-term holding of Bitcoin. For example, users holding WBTC can pledge it on the DeFi platform, borrow stablecoins for other investments, or participate in liquidity mining to earn rewards. In addition, some decentralized exchanges also provide trading pairs between BTC-pegged coins and other assets, providing investors with more arbitrage opportunities. In addition, BTC-pegged coins can also be used as a risk management tool. Using BTC-pegged coins as collateral can effectively reduce the risk of the investment portfolio and play the role of a stabilizer.
(4) Improving the practical utility of the Bitcoin network
The Bitcoin network is the earliest blockchain and has a high degree of security and consensus strength. However, its own technical limitations make the application scenarios of Bitcoin relatively limited, mainly focusing on value storage and simple payment transfers. Over time, the market demand for Bitcoin is no longer limited to these basic functions, but hopes to be able to use Bitcoin in a wider range of financial services. The emergence of BTC anchor coins has provided a broader application stage for Bitcoin. By issuing anchor coins on other blockchains, Bitcoin is able to participate in more complex financial operations on these chains, which not only improves the practical utility of Bitcoin, but also consolidates its position as the world's preferred digital asset.
II. Principles of BTC Anchored Coins
2.1 Centralized Anchoring and Decentralized Anchoring
The core of BTC anchored coins lies in how to lock Bitcoin on its native chain and generate tokens of equal value through cross-chain technology. According to the difference of this core mechanism, the working mechanism of BTC anchored coins can be divided into two categories: centralized and decentralized.
Centralized anchoring mechanism relies on trusted third-party custodians, which are responsible for keeping the Bitcoin locked by users and minting corresponding anchored tokens according to the number of locked Bitcoins. For example, WBTC is a typical centralized anchored coin. Users send Bitcoin to custodians (such as BitGo), which are responsible for managing these Bitcoins and minting an equal amount of WBTC tokens on the Ethereum network. When the user wants to redeem Bitcoin, the custodian destroys the corresponding amount of WBTC and returns the Bitcoin to the user. The advantages of this model are simple operation and fast transaction speed, but due to its reliance on centralized institutions, there are trust risks and potential security risks of centralized management.
Decentralized anchoring mechanism uses distributed networks and encryption technology to achieve cross-chain transfer and tokenization of Bitcoin. Taking renBTC as an example, its working mechanism does not rely on a single institution, but manages and verifies the locking and token casting of Bitcoin through the distributed node network of Ren Protocol. Ren Protocol uses secure multi-party computing (MPC) technology to distribute the custody process of Bitcoin on multiple independent nodes to ensure that no single node can control the private key of Bitcoin. This mechanism greatly reduces the risk of centralization and enhances the security and transparency of the system. However, due to the high technical complexity, the casting and redemption process of decentralized anchor coins is usually more complicated and time-consuming.
2.2 Minting and Destruction Process
The minting and destruction process of BTC anchor coins is the core link of its working mechanism. These two processes represent the conversion between Bitcoin and anchor coins respectively.
Minting process: The process of minting BTC anchor coins usually involves locking the original Bitcoin in a multi-signature address or smart contract and generating an equal amount of anchor tokens on the target blockchain (such as Ethereum). Taking WBTC as an example, when users want to obtain WBTC, they need to send an equal amount of Bitcoin to the custody address managed by BitGo. Once the Bitcoin transaction is confirmed by the network, BitGo will mint an equal amount of WBTC on Ethereum through a smart contract and send it to the user's Ethereum address. Users can verify each step through the block browser.
Destruction process: When a user wants to redeem the BTC anchored currency back to Bitcoin, the destruction process needs to be triggered. The user first sends the anchored currency (such as WBTC) to the corresponding smart contract for destruction, and at the same time sends a request to the custodian to redeem the Bitcoin. Once the destruction transaction is confirmed, the custodian will release the originally locked Bitcoin and send it to the Bitcoin address specified by the user.
In a decentralized model, the minting and destruction process of renBTC is more complicated, involving the consensus and collaboration of distributed network nodes. After the user sends Bitcoin to the custodian address of Ren Protocol, multiple independent nodes will verify it and jointly generate renBTC through secure multi-party computing technology. The destruction process is through the reverse operation. After renBTC is destroyed, multiple nodes jointly decide to release the corresponding Bitcoin.
2.3 Decentralized Custody and Trust Model
Unlike centralized custody, decentralized custody ensures the safe management of Bitcoin through distributed networks and encryption technology, avoiding over-reliance on a single institution.
Multi-party signature mechanism: Taking tBTC as an example, it uses a multi-party signature (threshold signature) mechanism to randomly select multiple signers to jointly manage the private key of Bitcoin. These signers ensure the legitimacy of their actions by providing collateral (such as ETH). If the signer attempts to perform malicious operations, they will face financial losses. This mechanism can theoretically achieve higher security and decentralization.
Secure Multi-Party Computation (MPC): Ren Protocol uses MPC technology to allow multiple nodes to jointly participate in the management of Bitcoin without revealing private keys. This technology ensures that even if individual nodes are attacked, the security of the entire network will not be affected. In this way, Ren Protocol achieves decentralized management of BTC anchor coins.
2.4 Cross-chain communication and smart contract execution
The cross-chain operation of BTC anchor coins is inseparable from the cross-chain communication protocol and the execution of smart contracts. The cross-chain communication protocol is responsible for transmitting information between the Bitcoin network and the target blockchain (such as Ethereum), while the smart contract is used to automatically manage operations such as casting and destruction.
Cross-chain communication: Cross-chain communication usually relies on relayers or observers, which monitor transactions on the Bitcoin network and pass relevant information to the target blockchain. Taking Ren Protocol as an example, Ren's Darknodes nodes are responsible for monitoring transactions in the Bitcoin network and broadcasting their information to the Ethereum network, triggering corresponding smart contract operations.
Smart Contract Execution: Smart contracts are the automated core of BTC anchor coins. Both the centralized minting process of WBTC and the decentralized minting process of renBTC are inseparable from the execution of smart contracts. These contracts ensure that the minting and destruction of each token are transparent and tamper-proof, while automatically processing user requests, verifying transactions, and updating on-chain data.
III. Analysis of representative projects and current status of BTC anchored coins
The earliest attempts to anchor BTC focused on the exploration of cross-chain technology. Early attempts included the concept of Bitcoin's sidechain, such as Rootstock (RSK), which attempted to achieve interoperability between Bitcoin and other blockchains through sidechains. However, these early projects were not widely used in the market due to their technical complexity and difficulty in implementation.
3.1 The birth and market application of WBTC
In 2018, the WBTC (Wrapped Bitcoin) project was officially launched, becoming an important milestone in the development of BTC anchored coins. WBTC was jointly initiated by BitGo, Kyber Network, Ren Protocol and other institutions. It is the first ERC-20 token to achieve 1:1 Bitcoin anchoring on Ethereum. WBTC locks Bitcoin in BitGo's custody account through centralized custody and mints an equal amount of WBTC tokens on Ethereum. The emergence of WBTC has opened the door for the application of Bitcoin in the Ethereum ecosystem, allowing Bitcoin to participate in DeFi applications. Due to its transparency and high market acceptance, WBTC has quickly become one of the most popular BTC anchor coins in the market.
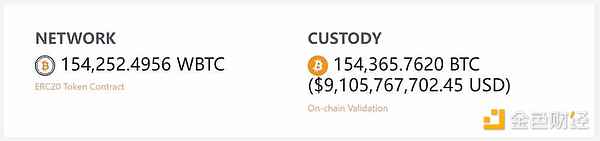
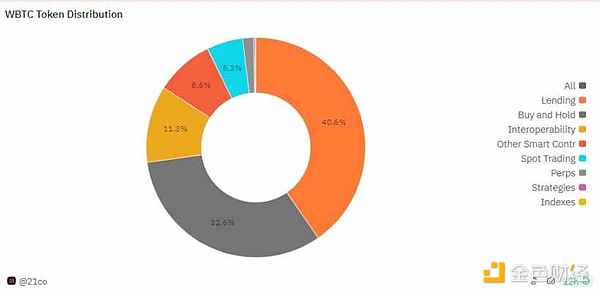
According to the official website of WBTC, the current issuance of WBT has reached 150,000, with a value of approximately US$9 billion. Among them, 40.6% is used for lending, 32.6% is for buying and holding, and 11.3% is used for cross-chain interoperability.
3.2 The rise of decentralized anchor coins
With the rapid development of the DeFi market, users' demand for decentralization and security is increasing. Some decentralized BTC anchor coin projects have emerged to avoid the trust risks brought by centralized custody.
renBTC: renBTC is launched by Ren Protocol and is a decentralized BTC-pegged coin. Ren Protocol enables cross-chain transfer and custody of Bitcoin by using secure multi-party computing (MPC) technology. Ren's network consists of a series of decentralized nodes (called Darknodes), which are jointly responsible for the custody of Bitcoin and the minting of renBTC. The main advantage of renBTC is its high degree of decentralization, which reduces the trust reliance on a single institution, but its technical complexity is also relatively high.
tBTC: tBTC is another decentralized BTC-pegged coin launched by Keep Network. tBTC uses a unique multi-party signature (threshold signature) scheme to randomly select multiple signers to jointly manage the cross-chain transfer of Bitcoin. The design goal of tBTC is to minimize dependence on centralized institutions and ensure that users have full control over their Bitcoin. However, tBTC also faces certain challenges in promotion due to its complex mechanism and high technical threshold.
3.3 Diversification and ecological expansion of BTC anchor coins
With the emergence of more blockchain platforms and the diversification of market demand, BTC anchor coins have begun to develop in the direction of diversification and multi-chain. Not only on Ethereum, other blockchain platforms such as Binance Smart Chain, Tron and Polygon have also begun to support the issuance and application of BTC anchor coins.
sBTC (Synthetix BTC): Issued by the Synthetix platform, as a synthetic asset, it simulates the price changes of Bitcoin through over-collateralization. sBTC provides users with more flexibility, especially in synthetic asset trading and DeFi applications.
BBTC (Binance Wrapped BTC): Launched by Binance, it strictly follows the 1:1 asset guarantee principle and realizes the seamless flow of BTC on Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain.
3.4 Analysis of the current status of BTC anchor coins
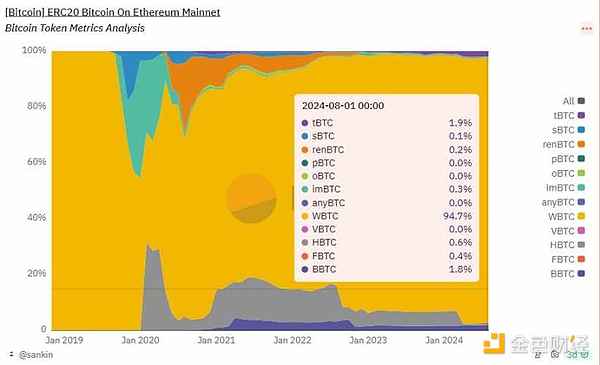
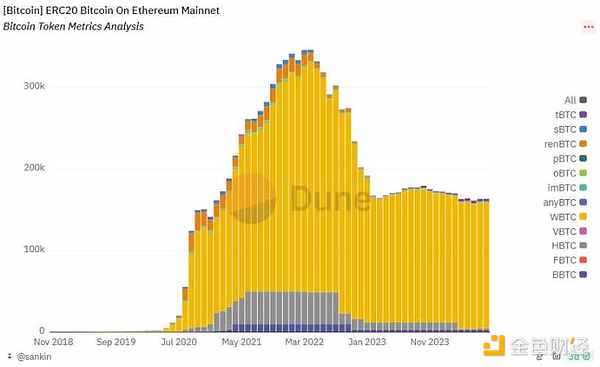
Dominance of WBTC: As of August 2024, WBTC is still the dominant BTC anchor coin in the market, accounting for 94.7%. This data shows that despite the existence of a variety of BTC anchor coins in the market, WBTC is still the first choice of users due to its earlier market entry time, extensive DeFi support and high trust.
Performance of other BTC-pegged coins: tBTC, BBTC and HBTC also have a certain market share, but the total amount is relatively small. Among them, tBTC accounts for 1.9% and BBTC accounts for 1.8%. These BTC-pegged coins are mainly used in specific application scenarios or supported by specific communities.
Fourth, the rise of BTC LSD tokens
The rise of the concept of pledge and re-pledge has brought new development directions for BTC anchor coins. Babylon launched a non-custodial Bitcoin pledge solution, which implements Bitcoin pledge through cryptography and generates liquid pledge tokens. This project has opened up a new track for BTC staking by improving the capital efficiency of pledged assets.
4.1 stBTC
stBTC is an important representative of BTC LSD tokens, launched by Lorenzo Protocol. The minting process of stBTC involves staking native Bitcoin in the escrow contract of Lorenzo Protocol, and then generating corresponding stBTC tokens based on the number of staked Bitcoins. Users can use stBTC for other financial activities and redeem native Bitcoin by destroying stBTC tokens when needed. stBTC not only improves the capital utilization of Bitcoin, but also allows holders to freely flow and increase value in the DeFi ecosystem.
4.2 LBTC
LBTC is a BTC LSD token launched by Lombard, which aims to provide Bitcoin holders with more secure and transparent staking returns through decentralized staking management. Similar to stBTC, users can participate in the DeFi ecosystem by minting LBTC and use LBTC to earn returns in decentralized exchanges, lending protocols, and yield strategy platforms. Users can also entrust LBTC to Babylon to obtain proof-of-stake (PoS) security benefits. In addition, Babylon also provides additional reward incentives for deposited BTC, including possible returns and other incentives.
4.3 SolvBTC
SolvBTC is a BTC LSD token launched by Solv, which aims to provide an efficient liquidity staking solution by integrating staking income on multiple chains such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. SolvBTC provides users with more flexible staking and liquidity management services through an innovative decentralized asset management architecture. Due to its integration of multi-chain staking income, SolvBTC provides users with a wider range of investment and arbitrage opportunities. Users can use SolvBTC for a variety of DeFi protocols, such as decentralized exchanges, lending protocols, and yield farms, and redeem the corresponding assets by destroying SolvBTC when needed.
V. Risk and Opportunity Analysis of BTC Anchored Coins
BTC anchored coins, as an innovative tool to introduce Bitcoin into other blockchain ecosystems, have shown great potential in improving Bitcoin liquidity and expanding its scope of application. However, like other financial innovations, BTC anchored coins are also accompanied by a series of risks and challenges in their development.
5.1 Risk Analysis of BTC Anchored Coins
(1) Centralization Risk:The security of the custodian is of paramount importance. Once the custodian is hacked or has poor internal management, it may lead to the loss or theft of Bitcoin, which will seriously affect the value and market confidence of the anchored coin. Centralized custody also means that if the custodian encounters operational problems, such as bankruptcy, regulatory intervention or other forms of failure, users may not be able to redeem their Bitcoin and face the risk of losing funds.
(2) Technical risks:Decentralized protocols usually involve complex technologies such as multi-party signatures and MPC (secure multi-party computation). The implementation of these technologies requires highly precise code and meticulous management. Once vulnerabilities or design flaws occur, they may lead to system crashes or security incidents. Decentralized anchor coins rely on consensus among multiple nodes. If these nodes are attacked, fail, or engage in malicious behavior, the stability and security of the anchor coins may be affected.
(3) Smart contract vulnerabilities:BTC anchor coins usually manage the minting and destruction process through smart contracts. Once deployed, smart contract code is difficult to change, and any undiscovered vulnerabilities may be maliciously exploited, resulting in financial losses. There have been many large-scale attacks caused by smart contract vulnerabilities in history, and the BTC anchor coin project is no exception. BTC-pegged coins often interoperate with other DeFi protocols, and this dependency may bring additional risks. If the protocol it interacts with fails or is attacked, it may affect the normal operation of the pegged coin.
(4) Regulatory uncertainty: With the development of the cryptocurrency market, regulators in various countries have gradually increased their supervision of crypto assets. BTC-pegged coins may face compliance pressure, especially in terms of KYC and AML regulations. Strict supervision may limit the liquidity of pegged coins or increase operating costs.
5.2 Analysis of opportunities for BTC-pegged coins
(1) Cross-chain liquidity and expansion of DeFi applications:The biggest opportunity for BTC-pegged coins is that they can bring cross-chain liquidity to Bitcoin, enabling it to participate in the DeFi ecosystem of smart contract platforms such as Ethereum. This capability has transformed Bitcoin from being limited to value storage and simple payments to a dynamic asset that can participate in complex financial activities such as lending, liquidity provision, and derivatives trading.
(2) The rise of multi-chain ecology:With the development of cross-chain technology, the application of BTC anchor coins is no longer limited to Ethereum, but has gradually expanded to multiple blockchain platforms, such as BSC and Solana. The rise of this multi-chain ecology has opened up new application scenarios and market space for BTC anchor coins. From DeFi to NFT markets, and then to decentralized governance, the potential application scope of BTC anchor coins is constantly expanding.
(3) The development of BTC LSD:BTC LSD tokens allow Bitcoin holders to maintain the liquidity of their assets while staking, thereby achieving higher capital efficiency in the DeFi ecosystem. The emergence of LSD tokens has made Bitcoin staking more flexible and efficient, attracting more Bitcoin holders to participate in staking and DeFi activities, and further promoting the market development of BTC-pegged coins.
(4) Participation of institutional investors:With the maturity of the cryptocurrency market and the improvement of infrastructure, more and more institutional investors have begun to participate in the BTC-pegged coin market. The entry of institutional investors has not only brought a large amount of funds, but also improved the trust and stability of the market. The demand of institutional investors has promoted the improvement of project parties in technical security and regulatory compliance, and improved the standards and credibility of the entire industry.
Summary
Sun Yuchen's entry into WBTC has caused controversy, mainly because WBTC has an absolute dominant position in the BTC-pegged coin market, with a market share of nearly 95%, and is widely used in the DeFi ecosystem. As a core asset of decentralized finance, the security and custody transparency of WBTC are of vital importance. Sun Yuchen's participation has aroused the community's concerns about the increase in centralized control and potential conflicts of interest, especially in the context of BitGo's transfer of custody rights, which has increased doubts about the management of WBTC and the security of underlying assets, and worried that it may affect the stability and trust of the DeFi market.
However, it is undeniable that BTC anchor coins have opened up new application scenarios and value space for Bitcoin. How to make full use of the potential of BTC anchor coins while ensuring security will be the key to future development. The rise of BTC LSD tokens reflects an important trend in the application of Bitcoin in the DeFi field: transforming static assets into dynamic assets with liquidity and yield attributes. This trend not only improves the capital efficiency of Bitcoin, but also provides users with more diversified investment opportunities. The success of BTC LSD tokens depends not only on its technical implementation and market application, but also on a balance between security, decentralization and user experience. With the further maturity of cross-chain technology, DeFi ecology and liquidity pledge derivatives, BTC anchor coins are expected to play a more important role in the future cryptocurrency market, providing Bitcoin holders with richer and more flexible asset management tools.
 Huang Bo
Huang Bo













