Source: Hive Tech
The Federal Reserve has finally completed its first interest rate cut since March 2020, and monetary policy has shifted from a tightening cycle to an easing cycle.
On September 18, local time, the Federal Reserve announced that it would lower the target range of the federal funds rate by 50 basis points to a level between 4.75% and 5.00%. Federal Reserve Chairman Powell said that the 50 basis point rate cut was a "powerful action."
The crypto market is like ushering in the dawn of dawn. On September 19, Bitcoin's trend fluctuated more, from $59,000 to $63,000, a daily increase of 6%. On September 23, it further broke through to around $64,600; Ethereum also rose from $2,200 to $2,400, and stood above the $2,600 mark on September 23. The overall market value of the crypto asset market also rose by 6% to $2.3 trillion five days after the rate cut.
After the first rate cut, the market generally expected that the rate cut would continue in the fourth quarter. In addition to the emergency rate cut during the crisis, it is rare for the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates by 50 basis points at a time. The last major rate cut occurred in 2020. In the face of the impact of the new crown epidemic, the Federal Reserve implemented an aggressive rate cut policy, lowering interest rates to near zero. At that time, the price of Bitcoin did not immediately soar, but broke through the $30,000 mark at the end of the year.
From a cyclical historical perspective, rate cuts usually drive Bitcoin prices up. After this rate cut, will the crypto asset market repeat history again?
The "boot" of rate cuts has landed
Since the second half of this year, Bitcoin has repeatedly staged a roller coaster ride with the crypto asset market. After entering August, it has continued to fluctuate at a low level, and the U.S. federal funds rate has become the focus of attention in the crypto market.
The so-called rate cut refers to the Federal Reserve lowering the federal funds rate, which is the benchmark interest rate for interbank lending in the United States. Lowering interest rates means lower borrowing costs, making it easier for businesses and individuals to get loans, thereby stimulating economic activity, increasing employment and controlling inflation. Lowering interest rates reduces the cost of capital, stimulates economic activity and investment, and makes investors more inclined to high-risk, high-return assets, such as stocks, as well as other crypto assets such as Bitcoin.
From 2008 to 2022, the U.S. federal funds rate has remained in an extremely low range of 0-0.25%. Since 2016, there has been a wave of moderate increases, but the highest has not exceeded 2.25%.
In the United States' more than two years of anti-inflation, the Federal Reserve has continuously raised the federal funds rate. In the 2022 interest rate hike cycle, from March to the end of the year, a total of 7 interest rate hikes were made, with a cumulative increase of 425 basis points; by December 2022, the Federal Reserve raised the federal funds rate target range to 4.25%-4.50%, the highest level since the 2008 international financial crisis.
As of September 8, 2024, the Fed's target range for the federal funds rate is 5.25%-5.50%. Judging from the chart, the current US federal funds rate is at its highest level in more than a decade.
The pace of interest rate hikes finally stopped in September. On September 18, local time, the Federal Reserve announced that it would cut the target range of the federal funds rate by 50 basis points to a level between 4.75% and 5.00%. Federal Reserve Chairman Powell said that the 50 basis point rate cut was a "powerful action". He emphasized that a large rate cut does not mean that a recession is imminent in the United States. The rate cut is more of a preventive action aimed at maintaining the current sound economic and labor market situation.
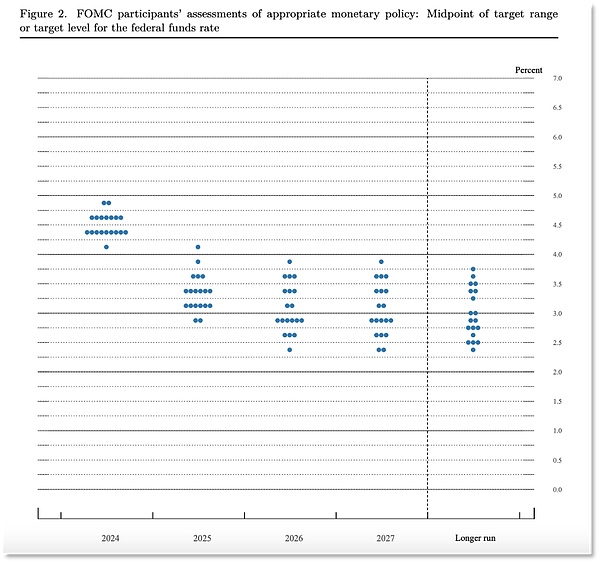 US Federal Funds Rate Dot Chart
US Federal Funds Rate Dot Chart
The interest rate dot chart shows that the median of 19 policymakers' expectations for the Fed's interest rate at the end of 2024 is between 4.25% and 4.5%. This means that they generally believe that by the end of the year, there will be a cumulative interest rate cut of 50 basis points on the current basis.
ETH rebounds better than BTC
After the Fed cut interest rates, the three major U.S. stock indexes collectively closed down on the 18th local time, and the interest rate cut did not meet expectations to boost U.S. stocks. In contrast, the performance of the crypto asset sector is more optimistic, especially Bitcoin and Ethereum, which rank first and second in market value. These two assets also entered the U.S. stock ETF asset target sequence last year and this year respectively.
As soon as the interest rate cut news came out on September 19, Bitcoin (BTC) rose, from $59,000 to $63,000, with a daily increase of 6%. Ethereum (ETH) also rose from $2,200 to $2,400, and broke through $2,600 on September 22.
However, Ethereum's overall performance was better than Bitcoin, with a 7-day increase of 16.3%, far higher than Bitcoin's 7-day increase of 9.7%.
In addition, SOL also achieved an increase of more than 20% on the day of the interest rate cut news, Meme coin DOGE increased by 3%, and the inscription tokens ORDI and SATS of the Bitcoin ecosystem achieved a nearly 10% increase.
While the prices of crypto assets rose collectively, Bitcoin spot ETFs also ended eight consecutive days of net outflows. Since September 12, Bitcoin spot ETFs have achieved four consecutive days of net inflows, and the confidence of OTC funds is gradually recovering.
Many market professionals are optimistic about the Fed's interest rate cut, believing that it will boost the Bitcoin and crypto markets. Anthony Scaramucci, founder of the hedge fund Sky Bridge, believes that this is good for asset prices in the United States and the world. Driven by a series of interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve and clearer US crypto asset regulation, Bitcoin will hit a record high of $100,000 by the end of the year.
In terms of theory and historical laws, the interest rate cut is indeed reflected in the rise in Bitcoin prices.
In 2019, the Fed cut interest rates in July, September and October, lowering the target range of the federal funds rate to 1.5%-1.75%. Before the rate cut, the price of Bitcoin had risen from about $4,000 at the beginning of the year to $8,000. After the news of the rate cut was announced, the price of Bitcoin reached a high of $10,000 in July, but then fell back.
In 2020, facing the impact of the new crown epidemic, the Federal Reserve implemented a more aggressive rate cut policy, reducing interest rates to near zero. Despite this, the price of Bitcoin did not immediately soar, but broke through the $30,000 mark at the end of the year.
However, although the rate cut brought the effect of "flooding", it also cast a shadow of recession. Some Fed officials are worried that cutting interest rates too quickly may lead to a rebound in demand and keep inflation high. Republican presidential candidate Trump believes that this shows that the US economy is very bad. "Assuming they are not playing politics, such a large drop shows that the economic situation is very bad." Peter Cardillo, chief market economist at Spartan Capital Securities, said that the Fed's move was clearly dovish, mainly because of concerns about the excessive weakness of the labor market. Although the U.S. stock market reacted positively to the news of the rate cut, market sentiment may change in the next few days, and investors may begin to worry about the economic outlook.
Compared with traditional financial markets such as stocks, CryptoSea founder Crypto Rover is more optimistic about the future development of Bitcoin. He said: "The last time this happened, the bull market for Bitcoin began." Wealth Mastery founder Lark Davis is also more optimistic about the long-term trend of Bitcoin. He emphasized: "If history repeats itself, the next 6-12 months will be crazy."
In any case, the interest rate cut cycle has begun. Among the 19 officials within the Federal Reserve, 7 officials believe that the interest rate should be cut by another 25 basis points in 2024, 9 officials believe that the interest rate should be cut by another 50 basis points in 2024, and 7 officials believe that the interest rate should be cut by another 75 basis points in 2024. Only 2 officials believe that the interest rate should not be cut further in the remaining meetings in 2024.
Employment market data will shape the pace and end point of future interest rate cuts. As time goes by and interest rate cuts continue, market liquidity will become more active, and some funds are likely to flow out of bonds and banks and flow into stocks, crypto assets and other markets.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Sanya
Sanya Xu Lin
Xu Lin Coinlive
Coinlive  decrypt
decrypt Beincrypto
Beincrypto Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Ftftx
Ftftx Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph