Compiled by: Deng Tong, Golden Finance; Source: Golden Finance, Bloomberg, CoinDesk, Bankless, Blockworks,
In the early morning of November 8th, Beijing time, the Federal Reserve announced a 25 basis point interest rate cut, lowering the target range of the federal funds rate to 4.5%~4.75%. This is the second interest rate cut by the Federal Reserve this year, which is in line with market expectations. As early as September 18 this year, the Federal Reserve announced a 50 basis point cut in the target range of the federal funds rate to between 4.75% and 5%, officially opening this round of interest rate cuts.
Why did the Federal Reserve cut interest rates? What impact does the interest rate cut have on the crypto market? Will there be further interest rate cuts in the future? Golden Finance sorted out the relevant information as follows.
1. Why did the Federal Reserve cut interest rates?
In September, the Federal Reserve cut interest rates by 50 basis points, opening the so-called liquidity easing cycle, which is a positive development for risky assets including cryptocurrencies.
Before the rate cut results were announced, federal funds futures data showed that a 25 basis point rate cut was expected on Thursday, a similar move would be taken in December, a pause in January, and multiple rate cuts before 2025. In addition, many voices expected the Fed to cut interest rates: Wells Fargo believes that the Fed cuts interest rates by 25 basis points, and the risk is inclined to keep interest rates unchanged; Morgan Stanley expects the Fed to cut interest rates by 25 basis points in November and December, and the statement will raise its assessment of economic growth and continue to recognize inflation progress.
1. Employment data
The target range of the federal funds rate (benchmark borrowing cost) is 4.75% to 5%, which is much higher than the "neutral" level (expected to be 3%-3.5%). Therefore, Before the rate cut, the market generally believed that the Fed had enough room to normalize the overly tight monetary policy through rate cuts, especially since the labor market cooled sharply in October. So far this year, the United States has added an average of about 170,000 jobs per month.
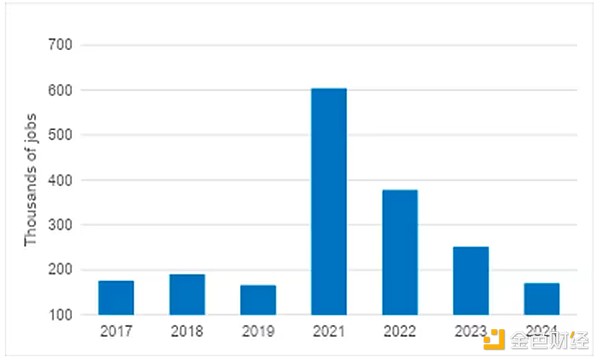
The Federal Reserve FOMC statement showed that the risks facing the goals remained "roughly balanced" and the labor market conditions "generally eased"; the scale of balance sheet reduction remained unchanged, and the discount rate was lowered from 5.00% to 4.75%; the overnight reverse repurchase rate was lowered from 4.80% to 4.55%, and the overnight repurchase rate was lowered from 5.00% to 4.75%.
2. Inflation
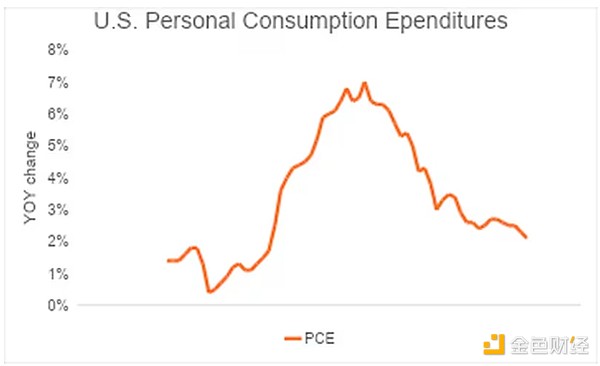
From 2020 to 2023, stimulus funds had a huge impact on prices. The chart below shows the change in the Bureau of Economic Analysis' Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) index over the past five years. The Fed prefers this metric to the Consumer Price Index (CPI) because it measures not only the dollars consumers pay, but also the dollars they pay for, such as health benefits. By looking at this metric, policymakers can get a better idea of what's happening with consumption. Currently, PCE has fallen back to pre-pandemic levels.
3. Economic Output
Last week, the Bureau of Economic Analysis reported that GDP grew 2.8% in the third quarter. That's a pretty impressive number. However, when we combine this with the 1.4% and 3% increases in the first and second quarters, we arrive at an average full-year growth rate of about 2.4%, slightly above the normal growth rate of 2.3% since the financial crisis.
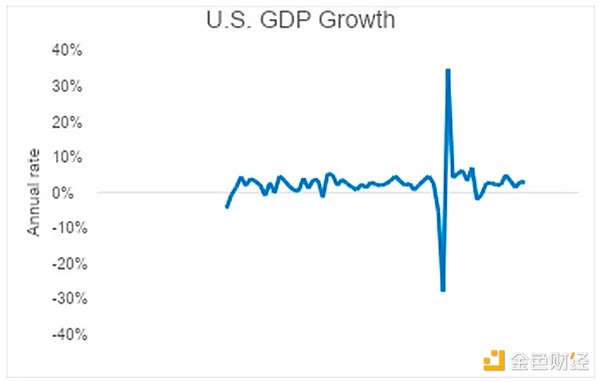 Based on the latest PCE data, the real interest rate (the effective federal funds rate minus PCE) is 2.8%. That means the central bank can cut rates by another 280 basis points before borrowing costs no longer weigh on inflation growth.
Based on the latest PCE data, the real interest rate (the effective federal funds rate minus PCE) is 2.8%. That means the central bank can cut rates by another 280 basis points before borrowing costs no longer weigh on inflation growth.
4. Loose fiscal policy
Trump already has a secure Senate majority, and potential control of the House will bolster his ability to deliver on his election promises of tax cuts and loose fiscal policy. Trump is a supporter of a weaker dollar, which he believes will help drive demand for U.S.-made goods and stimulate the domestic economy. Lower borrowing costs are a good way to achieve this goal, because lower interest rates mean the dollar will become more plentiful, depressing its value.
Some professionals pointed out that "Powell expressed multiple logics in different answers: First, the current monetary policy is still restrictive. The Fed started to cut interest rates in September, and this rate cut should be regarded as "another step"; Second, the Fed does not want and does not need to see a further cooling of the job market; Third, the Fed believes that inflation in some links such as rent mainly reflects the "catch up" effect, that is, it reflects past inflationary pressures rather than the present, so it tends to believe that inflation will continue to move towards 2%." For details, click on the article "Why insist on cutting interest rates? - Interpretation of the Federal Reserve's November 2024 interest rate meeting"
2. How does the Fed's interest rate cut affect the crypto market?
Asian stocks also rose on Friday, driven by the Fed's rate cut.
Stocks in Australia, Japan, South Korea and China all rose, supporting regional stock indexes to rise for a second day. Earlier, the S&P 500 rose 0.7% and the Nasdaq 100 rose 1.5%, both hitting new highs. U.S. Treasury prices fell slightly in Asian markets, while U.S. stock index futures were almost unchanged.
In the short term, the boost to the crypto market from the principal and interest rate cut is very limited: the crypto market has digested the expectation of further interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve; Trump's victory in the U.S. election has greatly boosted the trend of cryptocurrencies. In the short term, the crypto market seems to be facing the dilemma of running out of good news, but in the long term, the crypto market has a bright future.
Lower interest rates are expected to reduce pressure on the shrinking private sector and support housing affordability; rate cuts reduce borrowing costs, making it cheaper to borrow capital, which in turn increases liquidity across financial markets, which has a strong positive impact on cryptocurrencies as a liquidity-driven asset class.
This rate cut further opens the floodgates of liquidity, thereby encouraging capital to flow down the risk curve. This environment is particularly favorable for cryptocurrencies. Historically, Bitcoin and similar assets have thrived in periods of expanded liquidity, attracting investors seeking high returns at low borrowing costs. With the Fed focused on ensuring the resilience of the private sector, especially as inflation recedes, cryptocurrencies are the best asset class for more capital to enter the domestic and global system.
3. Expectations of future interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve
According to CME's "Fed Watch", the probability that the Federal Reserve will maintain the current interest rate unchanged by December is 32.6%, the probability of a cumulative interest rate cut of 25 basis points is 66.8%, and the probability of a cumulative interest rate cut of 50 basis points is 0.6%. The probability of maintaining the current interest rate unchanged by January next year is 17.9%, the probability of a cumulative interest rate cut of 25 basis points is 51.5%, and the probability of a cumulative interest rate cut of 50 basis points is 30.4%.
Powell's response to the expectation of interest rate cuts:
When asked whether the Federal Reserve is considering pausing interest rate cuts in December, Federal Reserve Chairman Powell said at a press conference that as officials shift their monetary policy stance to neutral, they have not yet decided what policy actions the central bank will take in December. He said: "In the face of uncertainty in the outlook, we are ready to adjust our assessment of the appropriate pace and ultimate goals of monetary policy. If the labor market deteriorates, the central bank will be ready to act faster. It may also be appropriate to slow down the pace of reducing the restrictive interest rate stance." Fed Chairman Powell said that the unemployment rate has fallen in the past three months and is still low. If there were no storms and strikes, the number of recruits would be "slightly higher." He also said that improved supply conditions support the economy and consumer spending growth remains resilient.
As the neutral interest rate approaches, it may be necessary to slow down the pace of rate cuts. The Fed has just begun to consider adjusting the pace of rate cuts. It is ready to adjust its assessment of the speed and target of interest rate changes. And said that the Fed is not in a hurry to reach the neutral interest rate, and the right way to find the neutral interest rate is to act cautiously. Raising interest rates is not the Fed's plan. The Fed's basic expectation is to gradually adjust interest rates to a neutral level. Powell said at a press conference that the central bank will not deliberately push inflation below 2% to make up for the excesses of the past few years. He said: "We believe it is inappropriate to deliberately go below the 2% target to make up for periods when it exceeds the target. The Fed currently operates under a policy called average inflation targeting, but is expected to change the system in next year's policy review."
In the short term, many industry insiders believe that the Fed will continue to cut interest rates in December:
U.S. interest rate futures price the Fed to cut interest rates by another 67 basis points in 2025.
LSEG data: After the Fed's interest rate decision, U.S. interest rate futures prices reflect expectations of another 25 basis point cut in December.
Diane Swonk of KPMG: The Fed may cut interest rates in December, but it looks like they want to keep their "options" in the future. One of the main challenges facing the Fed at present is "communication" because this is not a period when they can provide "a lot of forward guidance."
Whitney Watson, co-head of fixed income and liquidity solutions at Goldman Sachs Asset Management: The Federal Reserve will cut interest rates by 25 basis points in December. Watson said, "However, stronger data and uncertainty about fiscal and trade policies mean that there is an increasing risk that the Fed may choose to slow down the pace of easing. The word "skip" may enter our vocabulary in 2025."
Some analysts are also skeptical about expectations of future interest rate cuts:
Ben Vaske, senior investment strategist at Orion Portfolio Solutions: The FOMC announced a 25 basis point interest rate cut as scheduled today, marking a reduction in their aggressiveness relative to the September rate cut. It is worth noting that long-term interest rates have been on a sharp upward trajectory since the first rate cut and began to decline after the rate cut was announced today. Against the backdrop of a strong US economy, the road ahead for the Federal Reserve may be more complicated than steady rate cuts.
Quilter Investors analyst Lindsay James: The pace of future Fed rate cuts seems far less certain than the widely expected rate cuts before the resolution. "The volatile data in the job market cast a shadow on the outlook, as did Donald Trump's victory," the investment strategist said. "Expectations of future Fed rate cuts are being greatly reduced compared to what many initially hoped."
Jackson Garton, co-chief investment officer of Makena Capital Management: Powell remained silent on providing new forward guidance at his press conference, and he did not make any comments on changing the summary of economic expectations. Short-term U.S. Treasury yields barely changed when Powell spoke. Garton still believes that the Fed may choose to cut interest rates in December, but is uncertain. He said: "I think the probability of a further 25 basis point rate cut at the next meeting is more than 50%, but I am not 100% sure."
Affected by the dual positive factors of Trump's victory and the Fed's rate cut, as of press time, BTC was at $76,035.89, up 0.8% in 24 hours; ETH was at $2,919.63, up 3.7% in 24 hours; SOL was at $198.45, up 4.5% in 24 hours.
 Kikyo
Kikyo



 Based on the latest PCE data, the real interest rate (the effective federal funds rate minus PCE) is 2.8%. That means the central bank can cut rates by another 280 basis points before borrowing costs no longer weigh on inflation growth.
Based on the latest PCE data, the real interest rate (the effective federal funds rate minus PCE) is 2.8%. That means the central bank can cut rates by another 280 basis points before borrowing costs no longer weigh on inflation growth. 


