Written by: Tia, Techub News
It has been a very unusual year for Ethereum. There have been climaxes after the approval of the US spot ETF, as well as the crisis of facing competition from Solana and various "anti-Ethereum" remarks. In addition to personnel changes, a researcher joined Eigenlayer as a consultant and then resigned from the Eigenlayer position to better develop Ethereum. There are also the issues of Beam Chain and liquidity fragmentation raised at Devcon. All of these things highlight this unusual year.
Ups and downs in price trends
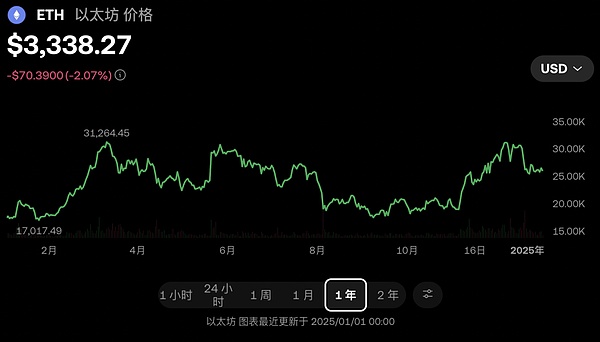
From the Ethereum price chart, we can already see how many ups and downs it has experienced. From more than 2,000 US dollars at the beginning of the year to more than 4,000 US dollars in March, back to the beginning of the two-word, and then rose to more than 4,000 US dollars again, it is full of drama and uncertainty.
On January 11, 2024, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) document showed that the SEC approved 11 spot Bitcoin ETFs to be listed. Riding on the east wind of ETFs and the expectation of Ethereum's approval of ETFs, Ethereum has soared all the way. In just over a month, the price has nearly doubled.
On July 23, the U.S. spot Ethereum ETF was launched. Although the trading volume of the spot Ethereum ETF was hot after it was launched, the trading volume exceeded 200 million US dollars in just 45 minutes. However, since the price increase in the first half of the year has already included the expectation of issuing Ethereum ETFs, the U.S. spot Ethereum ETF went online and did not achieve excessive growth.
Since there is no sustainable innovation in the industry to support high prices, after the Ethereum price has been running wild, in August, the price began to fall wildly again. Starting from July 30, the price of Ethereum began to fall for 7 consecutive days. It fell from a high of $3,366 to a low of $2,111. After that, it was a long sideways trend.
Until President Trump won the election, it rose all the way again, pulling Ethereum from the beginning of 2 to a high of $4,170.
The 7-day decline and 7-day rise, as well as the roller coaster-like multiples of ups and downs, reflect the extremely high volatility of the crypto market, and also show the emotions, expectations and external events of market participants. (Yes. This is crypto ?️)
Behind the ups and downs is a series of iron logic that must be admitted. For example, the sharp rise in the expectation of the listing of Ethereum ETF after the approval of Bitcoin ETF at the beginning of the year, the waterfall-like decline back to the starting point caused by the inability of ETF alone to continuously drive industries that lack real innovation and lasting market demand; and the crazy rise due to the optimistic attitude towards encryption after Trump took office... Looking back at the price trend of Ethereum, it is not difficult to find that its ups and downs are not only driven by external macro factors, but technological progress often plays an important role in it. From the launch of Ethereum 2.0, to the implementation of Layer2 scalability solutions, to the continuous optimization and update of the Ethereum network, every technological breakthrough has become the focus of the market. However, the gains brought about by these advances are not achieved overnight, but are often obscured by short-term market sentiment. Beam Chain, Dencun Upgrade, Pectra Upgrade and Other EIPs Beam Chain was proposed by Ethereum researcher Justin Drake at Devcon in Thailand. Beam Chain is Justin's proposal to redesign the Ethereum consensus layer. The proposal is a further upgrade of Beacon Chain. The main goals are related to MEV, lowering the threshold for staking, achieving fast finality single slot finality, and ZKing the entire consensus layer. Riding on the breakthrough of SNARK technology, this proposal is equivalent to an upgrade of the old Beacon Chain design from 5 years ago.
Dencun Upgrade
The Ethereum Dencun upgrade was launched on March 13, 2024. The hard fork combines two core improvements: the Deneb consensus layer and the Cancun execution layer update. The highlight of the upgrade is EIP-4844 Proto-danksharding, which allows Rollup to send data such as transactions and proofs to Layer1 in the form of Blobs. Since Blobs are temporary storage and access to off-chain data, using Blobs will make Rollup much cheaper than the original calldata. But this also caused a significant drop in Ethereum revenue.
EIP-4844 is a controversial EIP. In the short term, it is indeed the reason for the sharp decline in Ethereum's revenue and one of the main reasons why Ethereum is criticized; but some people also call this EIP "a small step for Sharding and a big step for Ethereum's expansion". In the long run, its specific impact is still unknown.
The Dencun upgrade also includes some EIPs that improve the efficiency of Ethereum, such as EIP-7516, EIP-6780, EIP-5656, EIP-1153, etc. The specific EIPs included in the Dencun upgrade are detailed in the table below.
EIP-4788 | Consensus layer | Improve the communication between the Ethereum execution layer and the consensus layer. Before EIP-4788, the EVM could not directly access the latest directory. It had to rely on indirect methods to understand what was happening in the beacon chain. EIP-4788 proposes to put the beacon block root (the hash tree root of the digest or parent block) into each EVM block. In this way, information and data can be transmitted without relying on a third party. |
EIP-7044 | Consensus layer | Improve the exit mechanism for Ethereum staking |
EIP-7045 | Consensus layer | Extend the maximum time for Attester to submit proofs. |
EIP-7514 | Consensus layer | Introduce restrictions on the "epoch churn limit" to limit the growth rate of the number of Ethereum validators. |
EIP-4844 | Execution layer | EIP-4844 is also known as the proto-danksharding proposal. It reduces the Gas cost of Layer2 data published on the Ethereum mainnet by realizing temporary storage and access to off-chain data. |
EIP-7516 | Execution Layer | is an opcode that returns the current data blob base fee. |
EIP-6780 | Execution Layer | is an opcode that allows a smart contract to remove itself from the blockchain. |
EIP-5656 | Execution layer | is an opcode that optimizes the process of copying data in memory |
EIP-1153 | Execution layer | is an opcode that allows smart contracts to use transient storage, that is, the storage is cleared at the end of the transaction execution. |
Pectra Upgrade
The Pectra upgrade combines two separate upgrades: the Prague execution layer upgrade and the Electra consensus layer upgrade. The Pectra upgrade is an upgrade before the Fusaka upgrade (specifically for implementing the Verkle transition). Since Ethereum developers agree that no other substantive changes can be combined with Verkle, the Pectra upgrade is a series of other changes before the Verkle transition. The Verkle transition represents the migration of all Ethereum state data from the Merkle Patricia tree structure to the Verkle structure. This will enable nodes to generate smaller proofs about state data, which can be more easily passed to other nodes, and is a prerequisite for achieving "stateless clients".
The Pectra upgrade is initially scheduled to be activated on the mainnet in early 2025. Among them, the more important one is the account abstraction EIP-7702, whose main function is to extend the smart account function to EOA.
EIP-7702 is an improvement of EIP-3074, proposed in May 2024. EIP-3074 is the community's first attempt to explore the extension of smart account functionality to EOA. Unlike ERC-4337 (which introduces a smart contract called EntryPoint so that the smart contract can behave like a user's account), if ERC-4337 is a way to implement account abstraction without changing the execution layer or consensus layer, EIP-3074 requires an Ethereum hard fork to implement. It mainly extends the smart account function to EOA by introducing two opcodes, AUTH and AUTHCALL.
EIP-7702 is a step further than EIP-3074. Unlike EIP-3074, which implements the smart account model of EOA with opcodes, with EIP-7702, EOA can now store an address called a "delegation indicator" that points to a smart contract. When a transaction is sent to EOA, it can execute the code at this specified address as if it were its own code, similar to how "delegated calls" work in smart contracts.
EIP-7702 brings smart account functionality to EOA while addressing many of the concerns raised by EIP-3074, providing full compatibility with ERC-4337 and a clear upgrade path, and is planned to be included in the Pectra upgrade.
Since the focus of the Pectra upgrade will shift to Verkle Tree, EIP-7702 may be the last EIP for account abstraction-related upgrades, as there may not be another 2-year window to include account abstraction-related upgrades after this.
So far, other code changes to Pectra have mainly involved improving the experience of users and smart contract developers. For a more detailed introduction to the Pectra upgrade, please refer to this article.
Other EIPs
Not all EIPs that have passed the review need to be used after the hard fork upgrade. Ethereum has also passed some major process/standard EIPs this year, such as the cross-chain intention standard ERC-7683 and the account abstraction standard ERC-4337 (ERC is a subset of EIP). Such changes rely more on the community's recognition of the EIP, that is, whether the community is willing to accept or actively implement it. Some EIPs that need to be used after the hard fork upgrade also need to wait for the acceptance of users, DApps, etc. before they can be widely adopted.
Interoperability: Cross-chain/Rollup Standards
With the Ethereum Rollup-centric roadmap and the growing number of various Layer1s, on-chain liquidity is fragmented and the composability, one of the biggest advantages of the chain, is gradually lost with the fragmentation.
Interoperability has two gradient problems to solve: one is how to achieve fast, low-cost and secure cross-chain of assets, and the second is how to achieve synchronous composability.
At present, there are many protocols that can solve the problem of the first gradient. Protocols like Across have greatly improved the cross-chain speed and have low handling fees. Due to its intent-based architecture, the security issues of user cross-chain have also been completely transferred to the solver. At present, some proposals related to cross-chain/Rollup are mainly committed to solving some preliminary standard issues.
Synchronous composability will be subsequently transferred to Based Rollup for implementation. The specific proposals related to cross-chain/Rollup are as follows:
ERC-7683
ERC-7683 is an intention cross-chain standard jointly proposed by Across and Uniswap. Through this standard, all intention interoperable orders can share the solver network.
ERC-7683 combined with ERC-3668 and ERC-3770 will bring a preliminary interoperability experience to L2. ERC-7683 creates a unified framework for cross-chain intentions that can be accessed by all solvers; EIP-3370 adds identification tags to blockchain addresses, clearly indicating the specific blockchain network to which the address belongs, preventing users from sending money to the wrong network; ERC-3668 CCIP Read has done a good job of off-chain verification, providing a secure mechanism for obtaining off-chain data without additional trust assumptions, and will effectively and automatically support light clients compatible with L2 blockchains without any additional configuration of wallets.
RIP-7755 (L2 Call Standard)
RIP-7755 is the L2 call standard. The POC was launched by the Base research team on October 17th, aiming to achieve seamless cross-chain interoperability between different Ethereum Layer2 networks, especially mainstream second-layer networks such as Optimism and Arbitrum. The proof of concept of RIP-7755 is applicable to blockchains that comply with the EIP-4788 standard, and the status of the OP Stack chain and Arbitrum has been verified.
Summary
The above is an overall review of the major events that Ethereum experienced in 2024. Of course, the journey of Ethereum in 2024 is far more than that. It also includes the dispute with Solana, the criticism of unclear positioning and centralization, large institutions began to hold Ethereum spot ETFs (Michigan Pension Fund disclosed that it holds more than $10 million in Ethereum spot ETFs), large institutions launched tokenized products on Ethereum (UBS launched uMINT, a tokenized money market fund based on Ethereum in Singapore, and Wall Street giant Guggenheim tokenized $20 million in commercial paper on Ethereum), and after facing the crisis, V God published 6 articles on the Ethereum roadmap, and Ethereum Research conducted AMA answers on Reddit, etc. ...
And in the end, everything points to an unresolved question, where is the future?
 Brian
Brian
 Brian
Brian Alex
Alex Kikyo
Kikyo Brian
Brian Brian
Brian Joy
Joy Alex
Alex Kikyo
Kikyo Brian
Brian Alex
Alex