Source: BlockSec
On January 10th, Eastern Time, the SEC officially approved 11 Bitcoin spot ETFs! This historic moment is destined to be recorded in the history of the encryption industry. And a brand new concept surrounding Bitcoin - Inscription, also frequently appears in front of investors around the world.
The addition of many myths of wealth and the continued influx of capital have made Inscription, a new concept that claims to be able to revolutionize the Bitcoin ecosystem, even more popular. Recently, as the market value of Bitcoin heats up, the popularity of inscriptions has also reached its peak.
But the vast majority of people are like looking at flowers in the fog, looking at the moon in the water. Although the price increase of inscriptions is dazzling, most people still have little understanding of inscriptions. What they see is the rise in prices, but they often ignore the technical implications behind it. This state of half-understanding undoubtedly increases the uncertainty of investment. Sowhat exactly is an inscription? How is it implemented? Don’t worry, this article will take you about 10 minutes to read and give you a comprehensive explanation of the inscription.
1. Origin - Bitcoin Inscription
In January 2023, the Ordinals protocol proposed by Casey Rodarmor announced the birth of Bitcoin Inscription. TheOrdinals protocol allows users to write data such as text, images, videos, and contracts directly to the Bitcoin blockchain.
In a rough view, isn’t this Bitcoin’s NFT? But the L2 network on top of Bitcoin, such as Stacks, has already realized this demand? Wait! Please note that Ordinals are written directly to the Bitcoin mainnet rather than the Layer 2 network. This change directly affects Bitcoin, a huge financial entity. The amount of funds affected by this change is completely different from that of Laryer2.
How is this agreement achieved? We must know that Bitcoin does not have a complete smart contract execution environment (EVM). How can we add new protocol support to Bitcoin?
This starts with the design principles of the entire BTC network and the repeatedly changed protocol. In the original design of Satoshi Nakamoto, the Bitcoin ecosystem has the smallest indivisible unit - Satoshi (1/100,000,000 bitcoin), and each Satoshi is minted by miners after proof of PoW, and naturally has different Unique serials number. With the help of this unique serial number, Bitcoin can be traced back to its minter and owner. In the 2021 upgrade, the Taproot protocol was added, allowing some complex information to be written into notes, and the upper limit of information that can be stored in a block was expanded from 1M to 4M, which allows more rich information to be written into Bitcoin. Blockchain offers technological potential.
The essential principle of the Ordinals protocol is that it extends the sequence number information on Satoshi. Specifically, theOrdinals protocol takes advantage of the unique characteristics of Satoshi and extends a single serial number to add data such as text, images, videos, and contracts. This makes each Satoshi a carrier of unique information and stores the data on the Bitcoin link, ensuring its non-tamperability.
For example, we take out a UTXO and prepare to engrave the inscription content "hello, world!" on it. We need to record the information content of Ordinals in the taproot remarks, and then engrave these records on the first inscription of UTXO during the transaction, thereby recording the content of the inscription on the chain. (Of course, these contents need to be serialized before being deployed on the link)

If there is no note for this transfer or the transaction fails due to special circumstances, the note message will not be considered valid content.
?In the early days when the Ordinals protocol was proposed, a large number of users used it as a carrier of NFT, but it was subsequently proposed on March 8, 2023 In the BRC20-protocol, a homogeneous currency protocol similar to ERC20 is proposed on the Ordinals protocol, thus allowing the inscription market to take shape.
We use a simple example on ordiscan to illustrate the ecological transaction process of this BRC20 currency:
First, the project party needs to deploy ( deploy) a series of inscribed assets so that subsequent people can mint this series of assets. How to do it specifically? First, the project party records the executable code (scription) that complies with the brc-20 rules on a Satoshi according to the Ordinals protocol, and then sends the Satoshi with the code engraved on it to the chain.
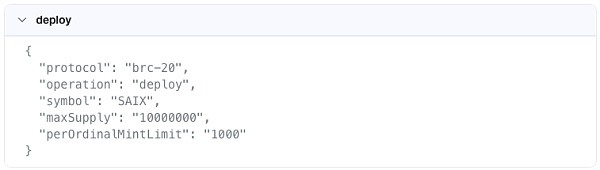
Specifically, the project Using the BRC20 protocol, a SAIX token series is deployed, and maxSupply is stipulated to be 10000000. The above is the information we have engraved on this Satoshi.
On-chain, this code-imprinted satoshi is sent and recorded on the Bitcoin blockchain. At the same time, off-chain, the server listening to the Ordinals protocol on the Bitcoin chain discovered this code that conforms to the protocol. As a result, the virtual machine off the chain executed this code. That is, a brc20 token is deployed on the off-chain virtual machine, named SAIX, and all attributes are configured. After this, other users can use the mint method to mint their inscribed assets.
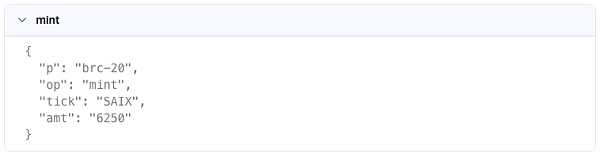
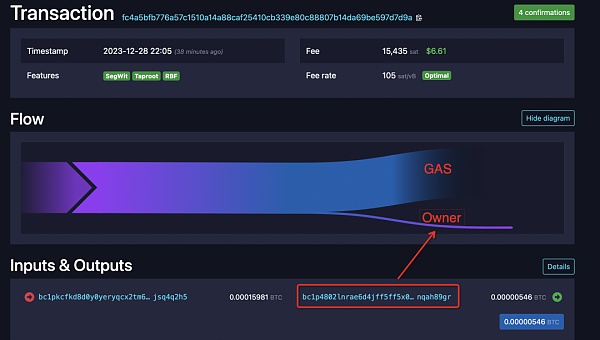
After that, you need to cast the inscription Property users can use the brc-20 protocol to mint inscribed assets belonging to the user in transactions. For example, the user called the mint action, thus minting 6250 SAIX. The owner of the inscription at this time is the payment address excluding the GAS fee after the transaction is initiated, such as bc1p4802...nqah89gr in the picture.
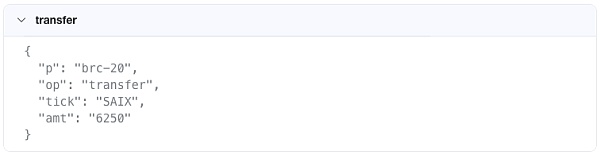
After successful casting, if The user needs to transfer his inscribed assets, then he can transfer 6250 BERUs by inscribing brc-20 on Satoshi as the above code says. Of course, the target address of this Bitcoin transaction naturally has these brc-20 tokens.
So we can roughly understand, The inscription of the Bitcoin ecosystem is actually another virtual asset generated by the Ordinals protocol and recorded on the Bitcoin blockchain. The project party will inscribe the information recorded in the inscription (including pictures, web pages, token names) on Satoshi in accordance with the agreement. Then the user performs financial attribute operations such as mint and transfer of assets based on the special codes in the transaction. Compared with the previous Layer2, the significance ofBitcoin Inscription is to directly expand the hugely funded Bitcoin mainnet, introduce the possibility of diversifying assets, improve the flexibility of the Bitcoin ecology, and thereby mine The potential of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
2. Derivative extension - EVM inscription
After Bitcoin inscription became popular, the EVM chain also proposed the concept of inscription. However, since the EVM chain has a smart contract design, the diverse information functions brought by the inscription design have already been realized by smart contracts. Therefore, the ecological story carried by theEVM inscription is slightly different than that of the Bitcoin inscription.
Due to the Gas design of smart contracts in Ethereum, the gas fee required for any successful contract interaction is at least greater than 21,000, which causes problems for users of the entire ecosystem Heavy gas fee pressure. Ethereum Inscription bypasses the design of smart contracts and aims to move the operations that need to be performed off-chain by sending data fields to EOA. When the off-chain Inscription virtual machine listens to the data field on the chain that complies with the protocol rules, the Inscription virtual machine will execute the result and match the execution result to the on-chain hash that sent the transaction at that time, thus saving the need to perform operations on the chain. handling fee.
Here we give an example of the ERC-20 inscription protocol. First, the user transfers 0ETH to his or her EOA address, thereby triggering the monitoring mechanism of ERC-20 inscription and triggering the inscription server to parse the content of the calldata. At this time, the content of calldata is similar to the BRC-20 protocol, which stipulates p-protocol, op-behavior, tick-token collection, id-the ID number of the current token and amt-the number of operations. According to the content in calldata, after the off-chain EVM inscription server monitors the transaction, it will execute the transaction content, mint the corresponding token to the current EOA account, and record this token in the off-chain index.
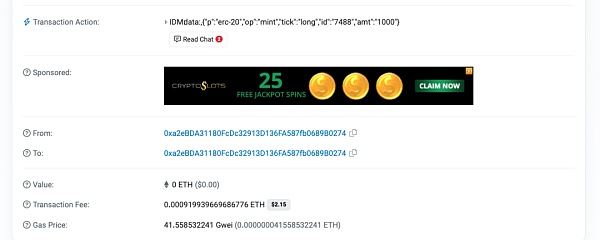
Currently,The inscription operation of EVM is mainly to reduce the expensive handling fees on some EVM links, thereby making transaction costs cheaper. Although this design will be easily reminiscent of Layer2. However, Layer 2 mainly expands the main network and has a complete smart contract execution environment, while EVM Inscription mainly reduces handling fees and does not have a complete smart contract execution environment. Therefore, the current design of EVM inscriptions mainly focuses on reducing the handling fees of EVM links as the ecological function it carries.
3. Common protocols for inscriptions
Oridinals protocol is The cornerstone of the Bitcoin Inscription protocol, in addition to the Ordinals protocol, many common Bitcoin Inscription protocols have been born.
Bitcoin Department-Well-known Project
BRC-20: Ordi, sats, rats
ARC-20: ATOM, Realm
Bitmap
Rune: Pipe
Ethereum Department-well-known project
Ethscription: eths, Facet
IERC-20: ethi
4. The current status of inscription ecology
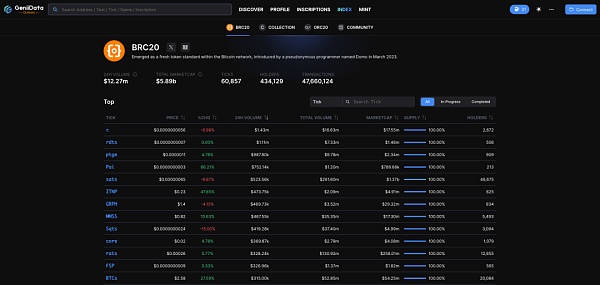
The current status of Inscription ecological transactions on BRC-20, on January 11, 2024, the 24-hour volume is close to $12.27M.
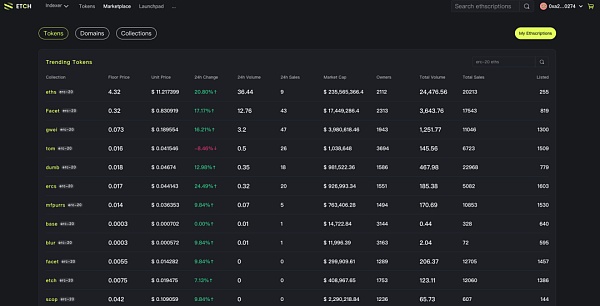
The inscription ecology on ETH The current trading volume, on January 11, 2024,the 24-hour volume is close to 53.66 ETH (139,516 U).
Generally speaking, the current inscription ecology is still dominated by the Bitcoin ecology, with increasing transaction popularity, huge transaction volume, and significant growth in total funds.
Conclusion
Through in-depth discussion Regarding the principle of inscription and its innovative role in the Bitcoin ecosystem, it is not difficult to find that the introduction of inscription technology is not a temporary gimmick or a simple technological iteration. It represents a major step forward in the security, scalability, and utility of the Bitcoin network. The implementation of the Ordinals protocol and the BRC20 protocol has opened new application scenarios for the Bitcoin blockchain. However, users still need to remain cautious. The market for inscription assets is still in its infancy, and its value and trading rules are constantly evolving. Therefore, a deep understanding of how these new technologies work is crucial for anyone looking to invest or innovate in this space.



