Author: Tanay Ved Source: Coin Metrics Translation: Shan Ouba, Golden Finance
Key Points:
Despite the overall sluggish performance of the cryptocurrency market, ETH, BTC and SOL have risen 48%, 44% and 38% year-to-date in the second quarter of 2024, respectively.
Bitcoin’s 30-day hash rate fell 7% to 580 EH/s after the halving, while the imminent Mt. Gox repayment and BTC sales by German authorities added to market pressure.
Ethereum stake reaches 33M ETH (27% of supply), while 13.7M ETH (11.5%) is locked in smart contracts and bridges, limiting liquidity.
Stablecoin transfer volume reaches a record $1.2 trillion in May 2024, with DAI on Ethereum and USDT on TRON leading with $345 billion and $388 billion, respectively.
Introduction
In this special edition of the State of the Network, we’ll take a data-driven look at the key developments impacting the digital asset industry in Q2 2024.
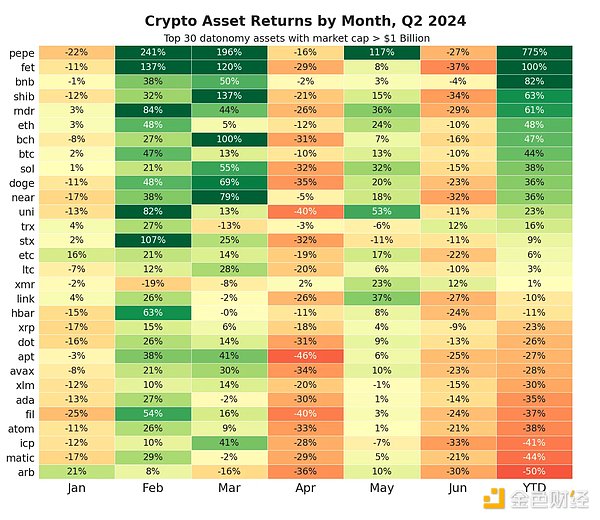
After a strong start to the year, the second quarter was a more muted market as the long-awaited launch of a spot Bitcoin ETF, Ethereum’s move toward scalability, and stablecoin and layer 1 ecosystems gained momentum. Among the largest crypto assets, Ethereum (ETH) is up 48% year to date, followed by Bitcoin (BTC) and Solana (SOL), up 44% and 38%, respectively. Memecoins, real world assets (RWA), and artificial intelligence (AI) computing sectors performed well, with tokens such as PEPE and Fetch.ai (FET) both rising sharply.
In May, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) unexpectedly approved an Ethereum spot ETF, bringing more opportunities to an otherwise challenging April and June. These months saw Bitcoin’s fourth halving, and the market was cautious about the issuance and distribution mechanisms of new tokens, resulting in mixed performance across sectors.
Macro Trends and Market Performance
The fate of the market is not limited to events within the crypto ecosystem, but is also influenced by external market conditions and developments. Studying the performance of major traditional market indices, ETFs and stocks, as well as the digital asset space, can provide important context for understanding the broader economic landscape.
In the second quarter of 2024, we witnessed a clear divergence between the crypto market and traditional risk assets, especially technology stocks. Artificial intelligence remains a focus for investors, with Nvidia valued at more than $3 trillion, making it the world's most valuable company, while single-handedly contributing more than a third of the S&P 500's gains through 2024. Apple's 24% gain, helped by the company's announcement of a partnership with OpenAI during its annual Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC), helped drive the seven-stock tech index up 14.8% in the second quarter. Along that theme, some publicly traded bitcoin miners positioned themselves as infrastructure providers for a wider range of computing applications, driving gains in the Valkyrie Bitcoin Miner ETF (WGMI).
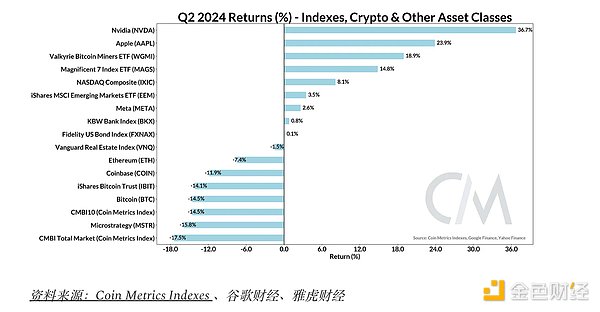
The digital asset market as a whole has lagged behind these bullish trends in tech and public miners - Coin Metrics' CMBI 10 Index (the performance benchmark of a basket of the 10 largest crypto assets) and the CMBI Total Market Index both posted double-digit declines in the second quarter. With the stock market reaching new all-time highs, crypto market participants may be looking for a reversal that is catalyzed by a rate cut, a favorable outcome to the presidential election, or a reduction in the pressure currently enveloping the market.
Bitcoin Prepares for Shock
As expected, Bitcoin entered its fifth epoch with the completion of the fourth halving in April. However, a number of developments could weigh on BTC prices in the near term. While the introduction of Runes after the halving has boosted transaction fee revenue, the reduction in block rewards from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC has squeezed miners’ profits, causing the 30-day moving average of Bitcoin’s hash rate to fall 7% to 580 EH/s. Although not as severe as previous halvings, BTC reserves held by miners have also fallen to their lowest level since April 2021, currently at 1.78 million BTC.
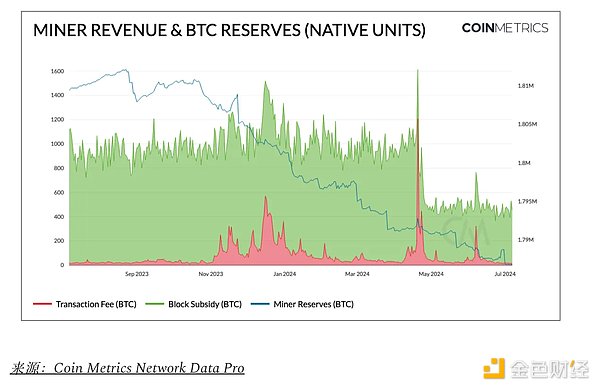
In addition, market sentiment has also been shaken by concerns about increased selling pressure caused by an impending supply glut. Notably, the long-defunct exchange Mt. Gox announced that it would redistribute approximately 142,000 bitcoins (worth approximately $8 billion), or close to approximately 65,000 bitcoins, as an initial payment to creditors in July this year. While former users will receive bitcoins at a much higher market price, the extent to which they will hold or sell bitcoins remains uncertain. However, recent wallet activity associated with the entity has raised concerns about a sell-off and may prompt some investors to sell preemptively.
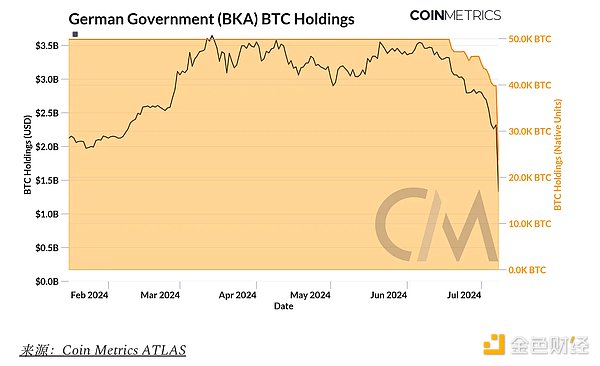
In addition, the German Federal Criminal Police (BKA) seized 50,000 Bitcoin from the operators of Movie2k.to, an online platform that provided viewing of copyrighted films before 2013. As of July 8, wallets associated with the entity still held approximately 27.4K Bitcoin. Recently, the movement of funds between intermediary addresses and exchanges such as Coinbase, Bitstamp and Kraken has sparked speculation about the entity's selling strategy and its impact on the market. As a result, these developments triggered liquidations, with open interest in Bitcoin futures contracts closing out around $8 billion. While these events could put short-term pressure on Bitcoin’s price, their one-off nature suggests the impact is likely to be temporary.
Ethereum ETF Coming Soon & Inflationary Pressures on ETH
A key development for Ethereum in Q2 was the unexpected approval of an Ether spot ETF. Prior to this, it was thought that the launch of an Ether ETF would take much longer than the expected summer deadline, largely due to regulatory uncertainty about ETH’s security status. However, these concerns were put to rest with the SEC’s approval of 19b-4s for eight issuers in May, providing clarity on ETH’s commodity status. The market reaction was swift, driving ETH and other ecosystem-related tokens higher, while the Grayscale Ethereum Trust’s (ETHE) discount to net asset value quickly compressed. With Ethereum ETFs on the horizon, attention has shifted to how much inflows these instruments could attract into assets like Ether relative to Bitcoin. Without delving too deeply into the size of the Ethereum ETF market, it may be helpful to understand the supply dynamics of Ether. With 33M ETH (~27% of supply) staked, and 13.7M ETH (~11.5% of supply) held in smart contracts and bridges, ~39% of ETH supply is “locked.” Meanwhile, supply on exchanges has trended down to 12M ETH (~10% of supply). This liquidity-constrained situation could increase price sensitivity in response to steady inflows from ETF-related demand.
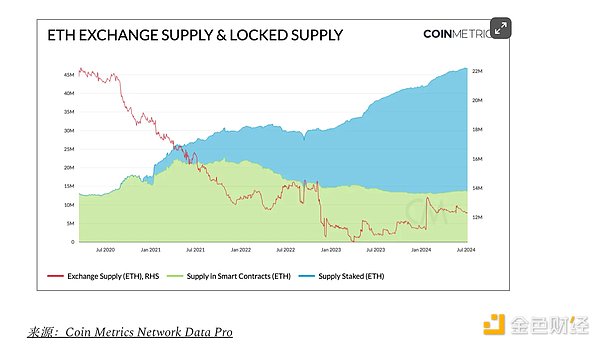
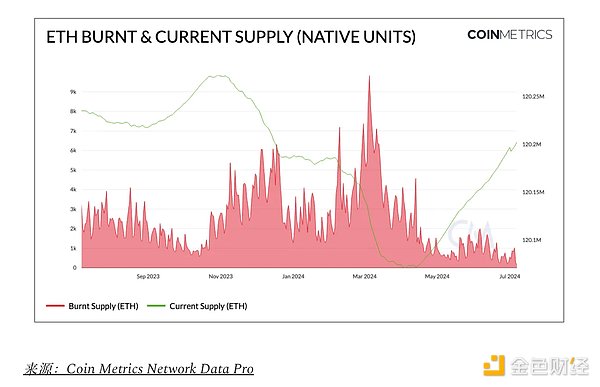
On the other hand, as Ethereum continues to advance on its scalability roadmap, the adoption of layer 2 blob space has continued to grow since EIP-4844 in March. As rollups become more accessible with lower operating costs and fees, user activity has shifted further to Ethereum layer 2, while the Ethereum mainnet has suffered as a result. As a result, total fees on Ethereum L1 have reached a yearly low of 460 ETH ($1.4 million) following EIP-4844, which has reduced the supply burn rate, resulting in a slight net inflation of ETH supply. This highlights the interplay between Ethereum scalability improvements and the monetary system, with increased Layer 2 usage needed to maintain deflationary pressure on ETH.
Outside of Ethereum, Solana’s fees have grown by more than 150% year-to-date to near Ethereum levels. While 50% below its March high, Solana’s high usage has resulted in significant fee revenue to date.
Pursuit of Quality: Altcoins Fall Out of Favor
Market participants’ attention has also been drawn to the surge in token issuance and its associated token economics. In particular, tokens with low circulating supply (public supply) relative to FDV (fully diluted valuation) and tokens with large supply unlocks are prevalent. Check out our report “Floating in the Air” where we explore this topic in more detail. As the barrier to issuing tokens and creating new chains has been lowered, projects like pump.fun have driven the rise of meme coins, and projects like Conduit have made it easy to deploy rollups, a large number of L1, L2, meme coins, and infrastructure tokens have emerged. As a result, the “altcoin” industry has become bloated, resulting in an oversupply of tokens. Arguably, this has led to a heightened focus on new token issuance, initial valuations, and distribution, making blue-chip assets with established demand more attractive.
The 14-day moving average of trusted spot volumes for majors (including BTC, ETH, and SOL) and altcoins (other assets in the datonomy universe) convincingly captures this dynamic. During the 2021 bull run, altcoin volumes easily outpaced majors, a trend that has reversed this time around. While majors volumes reached similar levels to their 2021 peak (around $42 billion), altcoin volumes fell 3x. The gap between the two baskets has also widened recently, with majors seeing an $11 billion increase in spot volumes.
Stablecoins Gain Regulatory Momentum
Since Q4 2023, the stablecoin industry has continued to grow and liquidity has continued to increase. The total supply of stablecoins increased by 3.8% in Q2, totaling $159 billion, of which $60 billion was hosted on Ethereum L1 and $30 billion was hosted on Tron. On a monthly basis, stablecoin (adjusted) USD transfer volume hit a new high of $1.2 trillion in May, mainly driven by Dai on Ethereum ($345 billion) and Tether on Tron ($388 billion).
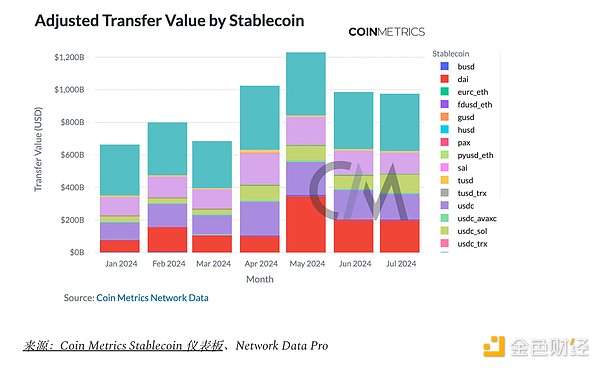
This growth coincides with major regulatory developments, notably the EU’s implementation of the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation. Circle, the issuer of USDC and EURC, became the first global stablecoin issuer to comply with MiCA, receiving an Electronic Money Institution Authorization. These measures are expected to promote a safer and more transparent stablecoin market, with implications beyond the EU and potentially influencing global regulatory standards. As a result, stablecoin issuers that adapt to these new requirements are likely to consolidate market share and capture growth opportunities in different jurisdictions.
Conclusion
Q2 2024 saw a complex digital asset landscape marked by evolving regulatory developments, technological milestones, and market dynamics. The approval of an Ethereum spot ETF and progress on stablecoin regulation point to growing institutional acceptance and regulatory clarity. However, challenges remain, including Bitcoin’s post-halving correction and potential selling pressure from the Mt. Gox offering.
Looking ahead, key areas to watch include the launch and adoption of an Ethereum ETF, the impact of Layer 2 scaling solutions on Ethereum’s sustainability, and ongoing regulatory developments in major markets. These factors, along with broader macroeconomic trends, will be critical in determining the direction of digital asset markets through the remainder of 2024 and beyond.
 Edmund
Edmund













