Author: Jagjit Singh, CoinTelegraph; Compiler: White Water, Golden Finance
1. Validiums Definition
Validiums is a Layer 2 scaling solution designed to process off-chain Transactions to optimize Ethereum performance.
Vailidiums are primarily responsible for reducing the load on the Ethereum blockchain by processing most transactions off-chain and only sending concise proofs to the mainnet for verification. The off-chain transaction processing method significantly increases throughput and reduces mainnet congestion, resulting in a more efficient and cost-effective Ethereum experience.
With this approach, even if most data is processed off-chain, the security and integrity of transactions can be maintained through repeated validity proofs verified on-chain. By validating the accuracy of off-chain calculations, these proofs ensure that state transitions follow Ethereum’s guidelines.
Validiums provide considerable scalability and transaction speed improvements by offloading transaction data from the mainnet. This is especially beneficial for high-throughput systems and decentralized applications (DApps).
2. How Validiums works: step-by-step process
Validiums batches and processes transactions off-chain, and submits validity certificates to the Ethereum mainnet for verification.
Validiums operates through a series of steps designed to optimize transaction processing and enhance scalability. These steps include:
Step 1: Transaction Submission
Users initiate transactions by submitting them to the validium operator, which manages off-chain transaction processing.
Step 2: Batch and off-chain processing
The operator collects multiple transactions and processes them into batches. Subsequently, processing of these batches is completed off-chain. This off-chain processing greatly increases transaction throughput compared to processing each transaction individually on the mainnet.
Operators are critical to managing validium. They are responsible for collecting transactions, batching them together, and generating zero-knowledge proofs to verify these batches of transactions.
Step 3: Generate proofs
Zero-knowledge (ZK) proofs are critical to the operation of validiums. Operators generate ZK proofs after transactions are processed. These cryptographic proofs demonstrate that the resulting state transitions follow Ethereum network rules and that off-chain computations are performed correctly. Crucially, ZK demonstrates that it achieves this while preserving privacy – i.e. not disclosing any details of the transaction itself.
Step 4: Proof Verification
The generated ZK proof is uploaded to the Ethereum main network together with the state commitment, which is an encrypted representation of the latest state of the off-chain system. The mainnet smart contract verifies the validity of the proof. This verification process ensures the security and finality of transactions by verifying that off-chain calculations are correct and that the modified state complies with the blockchain's regulations.
How Validiums relies on the Ethereum mainnet for security
Validiums are off-chain transaction processors, but they still rely on the Ethereum mainnet for security. The state commitments and ZK proofs generated by the operator are submitted back to the Ethereum mainnet. This commit ensures verifiability and security of off-chain operations.
Validiums leverages Ethereum’s strong security model by leveraging cryptographic proofs to link these off-chain operations to the mainnet. Combining the benefits of off-chain processing with mainnet security, this integration enables Validiums to achieve outstanding scalability while ensuring that the final state and integrity of transactions are protected by the Ethereum blockchain.
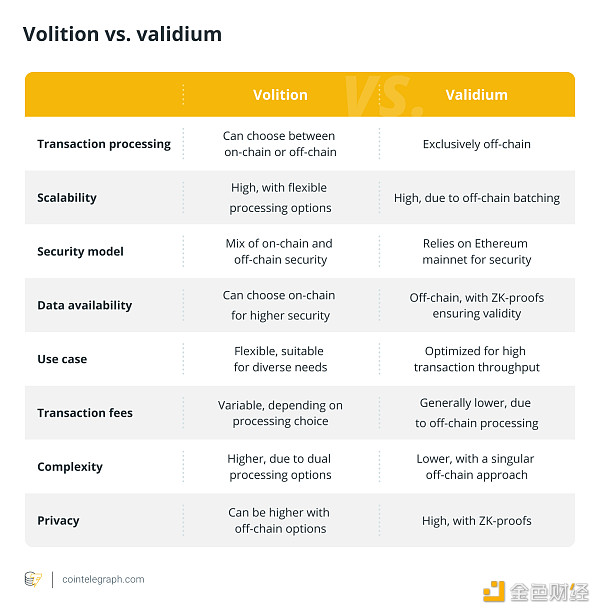
3. What is the difference between Volition and Validium?
Although validium and volition are both Layer 2 scaling solutions for Ethereum, they differ in terms of data availability.
Volition provides users with the flexibility to choose between off-chain and on-chain data availability in transactions, providing enhanced security and flexibility at a slightly higher cost. In contrast, Validium exclusively stores data off-chain, prioritizing scalability and cost reduction, but with slightly less security than on-chain solutions.
The following table shows the difference between volition and validium:
IV. Rollups vs. validiums
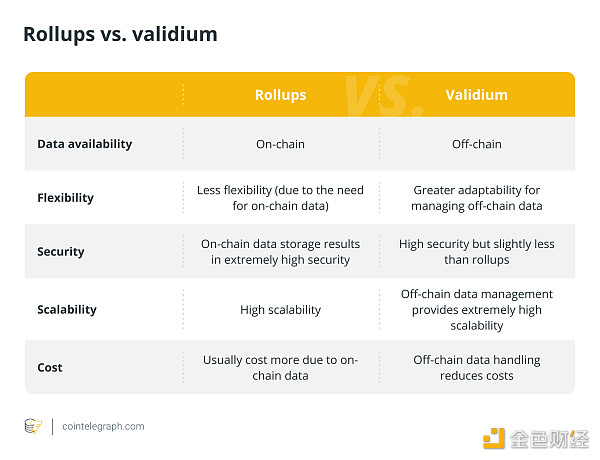
Validium and rollups are both L2 extension solutions for Ethereum; however, their security protocols and data can Accessibility is different.
Rollups provide enhanced security and simplified verification by processing transactions off-chain while storing data on-chain. Validium, on the other hand, optimizes for lower costs and higher scalability by keeping data off-chain, while maintaining slightly lower security. Their cost profile, flexibility and security are affected by this difference.
The following table shows the difference between rollups and validium:
5. Benefits of Validiums
Validium is an attractive L2 scaling solution for the Ethereum network, with several significant advantages, including Faster transaction speeds, lower fees, and the potential for enhanced privacy.
A key advantage is the ability to speed up transaction processing. By processing off-chain transactions, Validium reduces the computational load on the Ethereum mainnet, thereby reducing transaction times and increasing network efficiency. This feature is especially valuable for DApps and high-throughput platforms.
In addition, Validium significantly reduces gas fees. Since most transaction data and calculations are processed off-chain, the cost of executing transactions is significantly reduced. This cost-effectiveness makes validium ideal for users who frequently interact with the Ethereum network but are concerned about high transaction fees.
In addition, Validium has the potential to enhance privacy. Since validium handles data off-chain, transaction details do not need to be publicly disclosed on the Ethereum mainnet. Instead, they are verified using zero-knowledge proofs, which verify transactions without revealing sensitive information. This enhanced privacy is critical for users and businesses that prioritize confidentiality in blockchain interactions.
6. Challenges faced by the Validium system
Potential disadvantages of Validiums include data availability issues and centralization risks related to the operator role.
An important issue is data availability. Because validiums stores transaction data off-chain, there is a risk of losing or being unable to access this data if the off-chain storage solution fails or is compromised. This could hinder the ability to verify transactions and maintain the historical integrity of the blockchain.
Another potential disadvantage is the centralization risk associated with operators. In the validium system, operators play a crucial role in collecting transactions, generating zero-knowledge proofs, and submitting state commitments to the Ethereum mainnet. This core role can create a single point of failure if an operator acts maliciously or fails to perform their duties properly, potentially compromising the system. Relying on a limited number of operators also concentrates power and trust in the hands of a few entities, which could undermine the decentralized ethos of blockchain technology.
These challenges highlight the importance of implementing strong security measures and risk mitigation strategies for validium systems to ensure that they can successfully balance scalability and security while maintaining decentralization and trust.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance







