Author: Gryphsis Academy Source: medium Translation: Shan Oppa, Golden Finance
< h2 style="text-align: left;">Abstract:
By the end of 2022, Commercial applications of generative AI are sweeping the world, but as the novelty wears off, some current issues with generative AI are surfacing. The increasingly mature Web3 field leverages the transparency, verifiability, and decentralized properties of blockchain to provide new perspectives on solving these generative AI problems.
Generative artificial intelligence is an emerging technology in recent years, based on the deep learning neural network framework. Its application in image generation models and ChatGPT language models has shown great commercial potential.
In Web3, the architecture for implementing generative AI includes infrastructure, models, applications and data. The data component, especially when integrated with Web3, is critical and has huge potential for growth. It is worth noting that blockchain-based data models, artificial intelligence agent projects, and applications in professional fields may become key areas for future development.
The Web3 AI protocol currently on the market has fundamental flaws and limited ability to capture token value. Look forward to new trends or updates in the token economy in the future.
Generative artificial intelligence has huge potential in the Web3 field, and its integration with other software and hardware technologies is expected to bring People are excited about future developments.
1. Why do generative AI and Web3 need each other?
2022 is a watershed for generative artificial intelligence. Before that, generative artificial intelligence was mainly an auxiliary tool for professionals. That changed dramatically with the advent of DALL-E 2, Stable Diffusion, Imagen, and Midjourney. These technologies have pushed artificial intelligence-generated content (AIGC) to the forefront of technology trends, creating a wave of popular content on social media. The release of ChatGPT shortly after was a game-changer that took this trend to the top.
As the first artificial intelligence tool that can answer almost any question with only simple text prompts, ChatGPT has quickly become a daily work assistant for many people. It can handle a variety of tasks such as document writing, homework tutoring, email assistance, essay editing and even emotional counseling, triggering heated discussions on the Internet about optimizing results through "magic tips", allowing people to truly feel the "intelligence" of artificial intelligence.
A report from the Goldman Sachs macro team shows that generative artificial intelligence can promote the growth of U.S. labor productivity, potentially boosting global GDP within ten years (or nearly 7 trillion) by 7% and increase productivity growth by 1.5 percentage points.
p>
The Web3 field is also feeling the positive impact of AIGC (Artificial Intelligence Generated Content). In January 2023, Web3’s AI sector rose across the board.
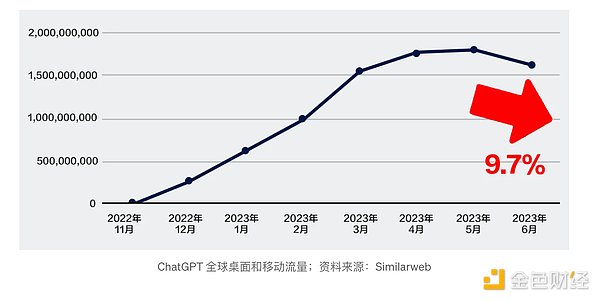
However, as the initial excitement began to fade, ChatGPT's global traffic fell in June 2023 for the first time since its launch (data from SametimeWeb) . This recession marks a timely opportunity to rethink the importance and limitations of generative AI.
The current challenges faced by generative artificial intelligence include but are not limited to: the ubiquitous unauthorized and untraceable AIGC flooding social media platforms; the high maintenance of ChatGPT Cost has forced OpenAI to reduce output quality as a measure to cut costs and improve efficiency; while global large-scale models such as ChatGPT are still biased in some aspects due to uneven data distribution.
p>
As the initial enthusiasm for generative AI like ChatGPT fades, the maturing and growing field of Web3, with its decentralization, transparency, and verifiability, is Challenges faced by generative AI provide new solutions:
1. Web3’s transparency and traceability can solve the problem of artificial intelligence-generated content Related Copyright and Privacy Issues
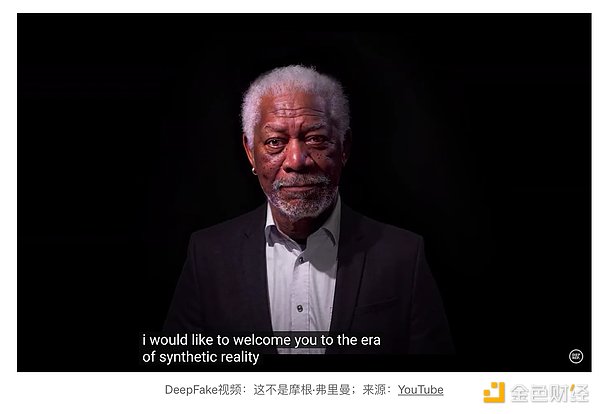
Web3’s transparency and traceability can effectively verify the source and authenticity of content, thereby significantly improving production fraud or The cost of infringing AI-generated content, such as copyright-obfuscated TikTok remixes or privacy-invading DeepFake videos. Smart contracts in content management can resolve copyright issues and ensure creators are fairly compensated.
p>
2. The decentralization of Web3 reduces the risk of centralized AI computing
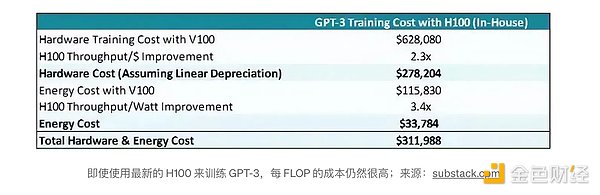
Developing generative AI requires significant computing resources. For example, training ChatGPT based on GPT-3 costs over $2 million, with daily electricity costs of approximately $47,000, and these costs are expected to grow exponentially as technology and scale advance.
Currently, computing resources are heavily concentrated in the hands of large companies, resulting in high development, maintenance and operation costs, centralization risks, and difficulty for small companies to compete. While the training of large models may still require centralization due to their extensive computing requirements, Web3’s blockchain technology enables distributed model inference, community voting governance, and model tokenization.
Taking decentralized exchanges as an example, we can imagine a community-driven decentralized artificial intelligence model inference system, where the community owns and manages large models.
p>
3. Use Web3 to achieve diversified AI data sets and interpretable AI models
Traditional data collection methods are often limited by geography and culture, resulting in subjective biases in AI-generated content and ChatGPT responses, such as changing the skin color of the target task. Web3’s token incentive model optimizes data collection, collecting and weighting data from around the world. Additionally, Web3’s transparency and traceability enhance model interpretability, encouraging diverse outputs to enrich the model.

p>
4. Unique AI model for massive Web3 on-chain data
AI model design and training are often built around the target data format (text, speech, image, or video). A unique future direction for the integration of AI and Web3 is the development of large-scale models for on-chain data, similar to natural language models.
This approach can provide unique insights that cannot be obtained with traditional data analysis (such as intelligent fund tracking, project funding flow), and artificial intelligence has the ability to process large amounts of data simultaneously. ability.
p>
5. Generative artificial intelligence as a catalyst to reduce barriers to entry in Web3
Currently, mainstream participation in Web3 Projects require an in-depth understanding of complex on-chain concepts and wallet operations, which increases learning costs and the risk of errors. In contrast, Web2 applications are designed around the "laziness principle", allowing users to get started easily and securely.
Generative AI can assist intent-centric projects by acting as an "intelligent assistant" between users and protocols in Web3, significantly empowering users experience.

p>
2. Summary of Generative AI Technology
2.1 Technical Background of Generative AI< /h3>
Since the concept of artificial intelligence was proposed in the 1950s, it has experienced several peaks and troughs, and each key technological innovation has triggered a new wave.
Generative AI (Generative AI), as an emerging concept proposed in the past decade, has been widely used in various artificial intelligence applications with its impressive technology and product performance. The research direction stood out and attracted global attention overnight. Before delving into the technical architecture of generative artificial intelligence, it is necessary to first define the meaning of generative artificial intelligence in this article and briefly review the core technologies of recently popular generative artificial intelligence.
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence used to create new content and ideas, including conversations, stories, images, videos, and music. It is built on the deep learning neural network framework and trained using large datasets containing a large number of parameters.
The generative AI products that have recently entered the public eye can be roughly divided into two categories: one is image (video) generation based on text or style input, and the other is image (video) generation based on text or style input. One category is products similar to ChatGPT based on text input. Both categories rely on the same core technology: pretrained large language models (LLMs) based on the Transformer architecture.
The former category combines text input with a diffusion model to generate high-quality images or videos, while the latter uses reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF) to generate Output very similar to human logic.
2.2 Current technical architecture of generative AI:
There are many excellent articles from different The impact of generative artificial intelligence on existing technology architecture is discussed from the perspective of For example, A16z’s comprehensive article titled “Who Owns the Generative AI Platform” comprehensively summarizes the current technical architecture of generative AI.
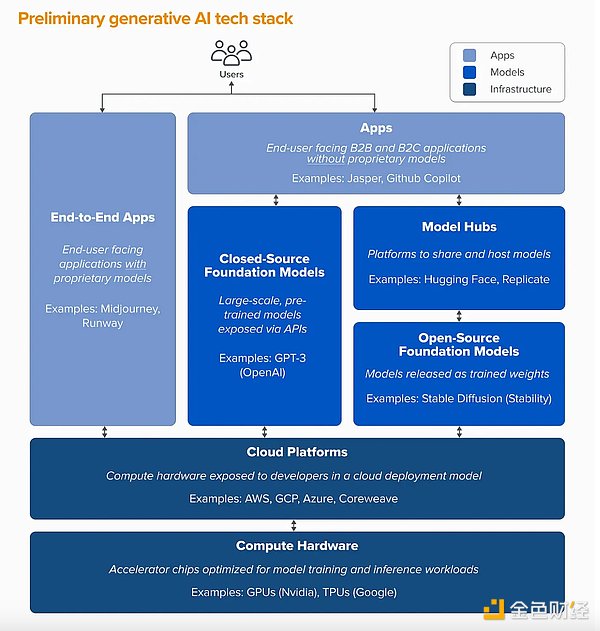
p>
According to this research, the current generative AI architecture in the Web2 era is divided into three levels: infrastructure (computing power), model, and application. The article also provides insights into current developments at these three levels.
Infrastructure: At present, the focus is still mainly on Web2 infrastructure logic, and there are few projects that truly integrate Web3 and AI. Infrastructure gets the most value at this stage. The Web2 giant, which has been involved in the storage and computing fields for decades, made huge profits by "selling shovels" during the exploration stage of artificial intelligence.
Model: Ideally, the model should be the true creator and owner of the AI. However, there are currently few business models that enable the authors of these models to capture the corresponding business value.
Apps: Applications developed across multiple verticals have generated over hundreds of millions of dollars in revenue. However, high maintenance costs and low user retention rates pose challenges to sustaining these applications as viable long-term business models.
2.3 Application of generative artificial intelligence in Web3
2.3.1 Using AI to analyze Web3 massive data
Data is the cornerstone of building technical barriers to future artificial intelligence development. To understand its importance, we first look at research on the sources of performance in large AI models.
This study demonstrates the unique emergent power of large artificial intelligence models: when the model size exceeds a certain threshold, model accuracy suddenly surges. As shown, each graph represents a training task, and each line represents the performance (accuracy) of a large model.
Experiments on various large-scale models have consistently concluded that after exceeding a certain threshold, model performance will experience breakthrough growth on different tasks.
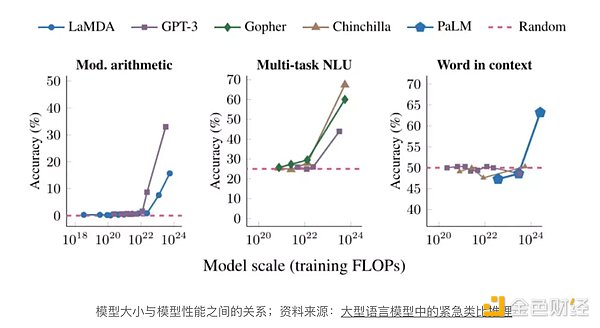
p>
Essentially, quantitative changes in model size will lead to qualitative changes in model performance. This size is related to the number of model parameters, training duration, and the quality of the training data. Currently, without significant differences in model parameters (designed by top research teams of each company) and training time (most computing hardware is purchased from NVIDIA), there are two main paths to developing leading products.
The first is to identify and solve the specific pain points of the niche area, which requires in-depth understanding and insight into the target area. Second, it is more practical to collect more comprehensive data than your competitors.
This opens an excellent entry point for large-scale generative AI models to enter the Web3 field. Existing artificial intelligence large models or basic models are trained on massive data from various fields, and the uniqueness of on-chain data in Web3 makes on-chain data models an exciting and feasible approach.
In Web3, there are currently two product logics at the data level: the first is to incentivize data providers and encourage users to share data usage rights while protecting the privacy of data. and ownership. The Ocean Protocol provides an effective data sharing model in this regard. The second approach involves projects that integrate data and applications to provide task-specific services to users. For example, Trusta Lab collects and analyzes users' on-chain data and provides services such as witch account analysis and on-chain asset risk analysis through its unique MEDIA scoring system.
2.3.2 Application of AI Agent in Web3
As mentioned earlier, the application of on-chain artificial intelligence agents is booming. Leveraging large language models and prioritizing user privacy, they provide quantifiable on-chain services. According to a blog post by Lilian Weng, chief AI researcher at OpenAI, an AI agent can be divided into four parts: Agent = LLM (Large Language Model) + Planning + Memory + Tool Usage.
LLM, as the core of AI Agent, handles external interactions, learns from large amounts of data, and uses natural language for logical expression. The planning + memory aspect is similar to the concepts of action, strategy, and reward in the reinforcement learning techniques used to train AlphaGo.
It involves breaking down tasks into smaller goals and learning optimal solutions through repeated training and feedback, storing information in various types based on functionality in memory. Tool usage refers to the agent's ability to utilize tools such as modular tools, Internet information retrieval, and access to proprietary information sources or APIs. It is worth noting that most of this information is difficult to modify after pre-training.
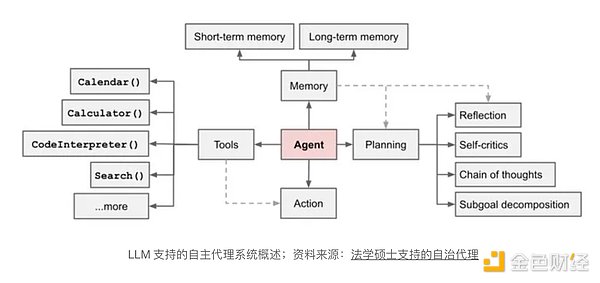
p>
Considering this logic of AI Agent, we can imagine the infinite possibilities of combining Web3 and AI Agent. For example:
In current trading applications, integrating AI Agent models can provide customers with natural The language interface provides a variety of trading functions including price prediction, trading strategy, stop loss strategy, dynamic leverage adjustment, intelligent following opinion leaders, borrowing and lending, etc.
When executing a quantitative strategy, the strategy can be further decomposed into subtasks and assigned to different AI Agents for execution. Collaborative AI agents can enhance privacy and enable real-time monitoring to prevent exploitation by adversaries.
Many NPCs in blockchain-based games naturally align with AI agents. There are already projects that use GPT to dynamically generate game character dialogue. Future developments may move beyond preset text to create more realistic real-time NPC (or even digital human) interactions that operate independently of player intervention. Stanford University's "Virtual Town" is a good example of such an application.
Although the current Web3+AI Agent project is mainly focused on the primary market or AI infrastructure, a killer consumer application has not yet emerged. But the potential of the game-changing Web3+AI project is huge. By integrating various blockchain features such as distributed on-chain governance, zero-knowledge proof inference, model distribution, and improved interpretability, these projects have great prospects in the future.
2.3.3 Web3+AI potential vertical field applications
A. Application in the field of education
The integration of Web3 and artificial intelligence heralds the development of the field of education A revolution in which generative virtual reality classrooms are a noteworthy innovation. By embedding artificial intelligence technology into online learning platforms, students can get a personalized learning experience. The system generates customized educational content based on each student's learning history and interests. This personalized approach is expected to improve students' learning motivation and efficiency, making education more personalized.

p>
In addition, token-based credit incentives represent innovative practices in the education field. Using blockchain technology, students' credits and grades can be encoded into tokens to form a digital credit system. This incentive mechanism encourages active participation in learning activities and creates a more engaging and motivating learning environment.
Inspired by the recently popular SocialFi project FriendTech, similar key pricing logic can be applied to establish a peer review system among students to add more socialization to education element. Leveraging the immutability of blockchain, peer evaluations become more fair and transparent. This peer review mechanism is not only conducive to cultivating students' teamwork skills, but also allows for a more comprehensive and multi-dimensional evaluation of students' performance, introducing a diversified and holistic evaluation method into the education system.
B. Application in the medical field
In the medical field In the field, the integration of Web3 and AI promotes federated learning and distributed reasoning. By combining distributed computing with machine learning, medical professionals can share data at scale, enabling deeper and more comprehensive group learning. This collective intelligence approach can accelerate disease diagnosis and treatment plans, driving progress in the medical field.
Privacy protection is also an important aspect of applications in the medical field. With the decentralization of Web3 and the immutability of blockchain, patient medical data can be stored and transmitted more securely. Smart contracts can achieve precise control and permission management of medical data, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive patient information, thereby maintaining the privacy of medical data.
C. Application in the insurance field
In the insurance industry , the integration of Web3 and AI is expected to bring more efficient and intelligent solutions to traditional operations. For example, in auto and home insurance, the application of computer vision technology helps insurance companies more effectively assess property values and risk levels through image analysis and assessment. This provides insurance companies with more refined and personalized pricing strategies and enhances risk management in the insurance industry.
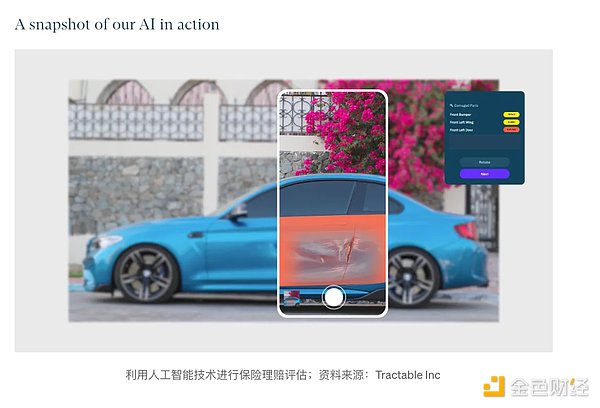
p>
At the same time, automated claims processing on the chain is an innovative advancement in the insurance industry. Using smart contracts and blockchain technology, the claims process becomes more transparent and efficient, reducing cumbersome procedures and the possibility of human intervention. This not only speeds up the claims process, but also reduces operating costs and provides a better experience for both insurance companies and customers.
Dynamic premium adjustment is another area of innovation. Through real-time data analysis and machine learning algorithms, insurance companies can adjust premiums more accurately and timely, and conduct personalized pricing based on the actual risk profile of the insured. This approach not only makes premiums fairer, but also encourages healthier and safer behaviors among insureds and promotes risk management and preventive measures across society.
D. Application in the field of copyright
In the field of copyright , the combination of Web3 and artificial intelligence introduces a new paradigm for digital content creation, management, and code development. Through smart contracts and decentralized storage, the copyright information of digital content can be better protected, making it easier for creators to track and manage their intellectual property rights. Blockchain technology can also establish a transparent and immutable record of creation, providing a more reliable means of tracking and verifying works.
Innovation in working models also represents a major change in the copyright field. Token-incentivized collaborative work combines work contributions with token rewards to encourage creators, curators, and developers to participate in projects together. This not only promotes collaboration between creative teams, but also gives participants the opportunity to benefit directly from the success of the project, leading to more great work.
On the other hand, using tokens as proof of copyright has reshaped the profit distribution model. Through the dividend mechanism automatically executed by smart contracts, all participants of the work can obtain their share of the profits in real time when the work is used, sold or transferred. This decentralized benefit distribution model effectively solves the opacity and delay problems in the traditional copyright model and provides creators with a fairer and more efficient benefit distribution mechanism.
E. Application in the field of virtual universe
In Yuan In the universe, the integration of Web3 and AI opens up new possibilities for creating low-cost AIGC to enrich blockchain-based game content. AI-generated virtual environments and characters can enrich game content, provide users with a more vivid and diverse experience, while reducing production manpower and time costs.
Creating vivid digital people is an innovation in Metaverse applications. Digital humans have detailed physical appearances down to the hair and psychological logic built on large language models, and can play various roles in the Metaverse. They can interact with users and even participate in digital twins of real-world scenarios. This provides a more realistic and profound experience for virtual reality and promotes the widespread application of digital human technology in entertainment, education and other fields.
Automatically generating advertising content based on blockchain user portraits is a smart advertising application in the Metaverse. By analyzing user behavior and preferences within the Metaverse, AI algorithms can create more personalized and engaging ads, thereby increasing click-through rates and user engagement. This method of advertising creation is not only more in line with user interests, but also provides advertisers with a more efficient promotion channel.
Generative interactive NFTs are a compelling technology in the Metaverse. By combining NFT with generative design, users can participate in the creation of their own NFT artwork in the Metaverse, giving it interactivity and uniqueness. This opens up new possibilities for the creation and trading of digital assets and promotes the development of digital art and virtual economy in the virtual universe.
3. Signature Web3 protocols
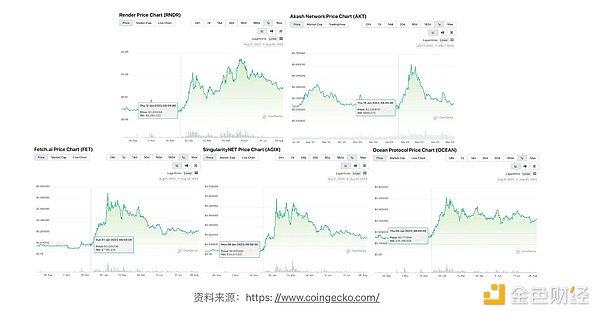
In this section, the author selects five representative protocols to gain an in-depth understanding of the current status of generative AI in the Web3 field: Render Network and Akash Network was highlighted as a universal AI infrastructure protocol and a leader in the AI category in Web3; Bittensor was identified as a hot project in the current model training field; Alethea.ai was selected for its close relevance to generative AI applications; Fetch.ai demonstrates the potential of artificial intelligence agents in a decentralized Web3 world.
3.1 Render Network ($RNDR)
Render Network is founded by the founder of the parent company OTOY Founded in 2017 by Jules Urbach. OTOY, whose core business is cloud-based graphics rendering, is advised by Google and Mozilla co-founders, has contributed to Oscar-winning film projects, and has collaborated on projects with Apple.
Render Network is OTOY's move into the Web3 field. It aims to use the distributed characteristics of the blockchain to combine small-scale rendering and artificial intelligence needs with decentralization. Resources are connected. This initiative is intended to provide cost savings for small studios that would otherwise rent expensive centralized computing resources (such as AWS, MS Azure, and Alibaba Cloud), and to provide revenue generation opportunities for those with idle computing resources.
Backed by OTOY, which released its proprietary renderer Octane Render, Render Network launched with inherent demand and a solid business model and was quickly recognized as a A Web3 project with solid foundation and potential.
With the rise of generative AI, the demand for distributed verification and reasoning tasks continues to increase, which perfectly fits with Render's technical architecture, making it a future development A promising direction. Render has been leading the AI circuit in the Web3 space, evolving into a somewhat meme-like entity that has benefited from the upward trend and demonstrated its versatility every time the narrative surrounding AI, the metaverse, and distributed computing heats up. .
In February 2023, Render Network announced a roadmap to update its pricing tier system and introduce a community-voted price stabilization mechanism for $RNDR (although the release Date has not yet been announced). The project also announced a migration from Polygon to Solana (upgrading the $RNDR token to the Solana SPL-based $RENDER token, completed in November 2023).
Rendering Network’s new pricing system divides on-chain services into three levels, from high to low, with each level corresponding to a different price point and rendering service quality. . These layers provide customers with options based on their specific rendering needs.
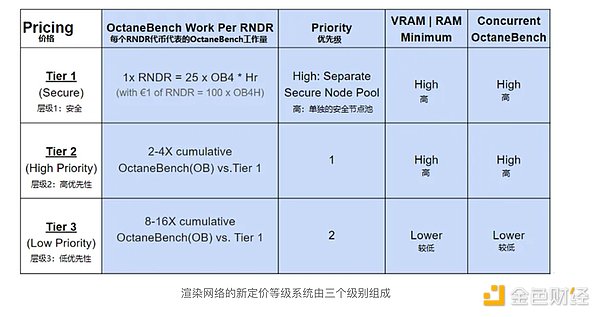
p>
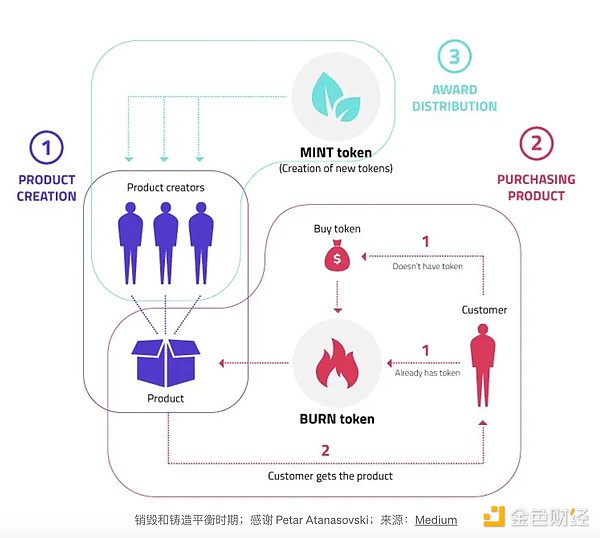
The community-voted $RNDR price stabilization mechanism has transitioned from irregular buybacks to a "Burn and Mint Equilibrium (BME)" model. This change emphasizes $RNDR as a stablecoin for trading rather than a long-term holding asset. The specific business process of a BME Epoch is as follows:
Product creation: Product creator on Render , that is, the provider of rendering resources, packages idle rendering resources into products (nodes) and puts them online, waiting to be used.
Purchase products: Customers with rendering needs can directly destroy $RNDR tokens as service fees. If they don’t have $RNDR tokens, they first buy them on the DEX with fiat currency and then burn the tokens. The price paid for the service is publicly recorded on the blockchain.
Sponsored Business Content
Minting tokens: Minting new tokens according to preset rules.
Note: Render Network charges 5% of the project operating transaction fees paid by product buyers.
p>
In each BME Epoch, a preset number of new tokens are minted (the number decreases over time). These new tokens are distributed to three parties:
Product creators: the rewards they receive are :
A. Task completion: Rewards will be awarded based on the number of rendering tasks completed by each product node.
b. Online rewards: Encourage resource providers to complete tasks online and give rewards based on market standby time.
2. Product buyers: Similar to product coupon rebates in shopping malls, buyers can receive up to 100% $RNDR token rebate to encourage future use Render Network.
3. DEX Liquidity Provider: Provider in cooperative DEX to ensure that $RNDR tokens are provided at a reasonable price for necessary destruction, which will be based on The amount of $RNDR staked is rewarded.
p>
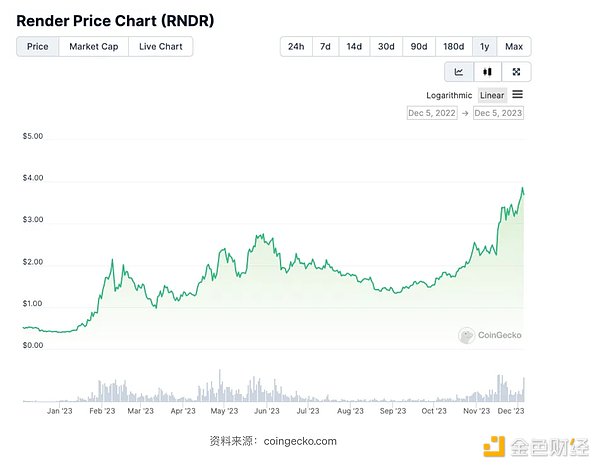
Judging from the price trend of $RNDR in the past year, as the leading AI track project in Web3, $RNDR will benefit from the popularity driven by ChatGPT at the end of 2022 and early 2023. AI craze. With the introduction of the new token mechanism, the price of $RNDR will peak in the first half of 2023.
After a period of stability, with the resurgence of AI triggered by the new version of OpenAI, the migration of Render Network to Solana, and the expected implementation of the new token mechanism, $ The price of RNDR reached recent highs. Given that $RNDR's fundamentals have changed little, future investments in $RNDR will require careful position management and risk control.
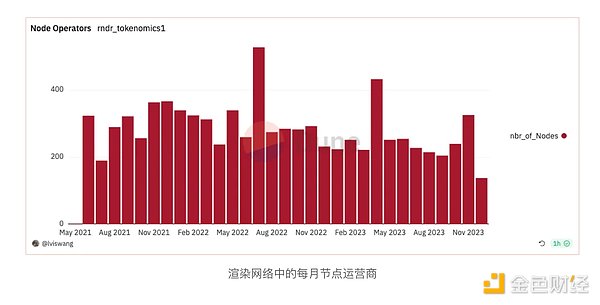
p>
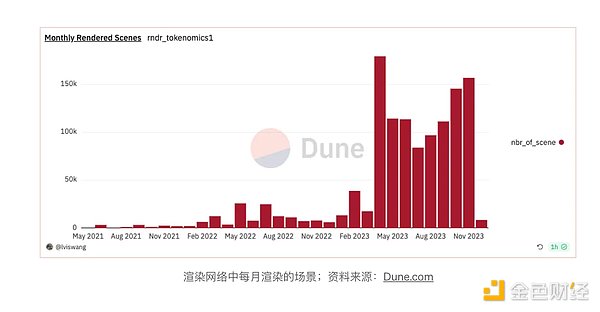
Data from the Dune Analytics dashboard shows that the total number of rendering tasks has increased since the beginning of 2023, but the number of rendering nodes has not. This suggests that the new users causing the increase in workload are those with rendering needs rather than those providing rendering resources.
Given that generative AI will proliferate by the end of 2022, it is reasonable to infer that additional rendering tasks will be related to generative AI applications. Whether this increase in demand represents a long-term trend or a temporary surge remains to be seen and requires further observation.
3.2 Akash Network ($AKT)
Akash Network is a decentralized cloud The computing platform aims to provide developers and enterprises with more flexible, efficient and cost-effective cloud computing solutions.
The project's "super cloud" platform is based on distributed blockchain technology and takes advantage of the decentralized nature of blockchain to provide users with global, decentralized services. Centralized cloud infrastructure includes diverse computing resources such as CPU, GPU, and storage.
Akash Network was founded by Greg Osuri and Adam Bozanich, experienced entrepreneurs with rich project backgrounds. Its mission is clear: reduce cloud computing costs, improve availability and Give users greater control over computing resources. By incentivizing providers to open idle computing resources through a bidding process, Akash Network enables more efficient resource utilization and provides competitive prices to resource demanders.
In January 2023, Akash Network launched the Akash Network Economics 2.0 update to address various shortcomings in the current token economy, including:
$AKT Market price fluctuations lead to mismatches in long-term contract price and value.
Insufficient incentives for resource providers to release large amounts of computing power.
Insufficient community incentives hinder the long-term development of the project.
$AKT’s insufficient value capture poses a risk to project stability.
According to the official website, the solutions proposed in the Akash Network Economy 2.0 plan include introducing stable currency payments and increasing order fees to increase Agreement income, enhanced incentives for resource providers, and increased community incentives, etc. It is worth noting that the stablecoin payment function and order fee function have been implemented.
As the native token of the Akash network, $AKT has multiple uses within the protocol, including for verification (security), incentives, network governance, and payment of transaction fees of pledge. According to the official website, the total supply of $AKT is capped at 388 million coins, and as of November 2023, approximately 229 million coins (59%) have been unlocked. The creation tokens allocated at the launch of the project will be fully unlocked and enter the secondary market in March 2023. The distribution of genesis tokens is as follows:
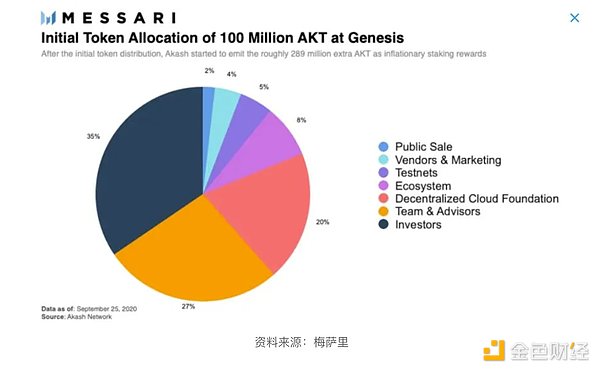
Regarding value capture, a noteworthy yet-to-be-implemented feature mentioned in the white paper is that Akash plans to charge a fee for each successful lease." cost". These fees will be sent to the revenue pool to be distributed to holders.
The plan provides for a 10% fee on AKT transactions and a 20% fee on transactions using other cryptocurrencies. Additionally, Akash intends to reward holders who lock up their AKT holdings for the long term, thereby incentivizing long-term investment.
p>
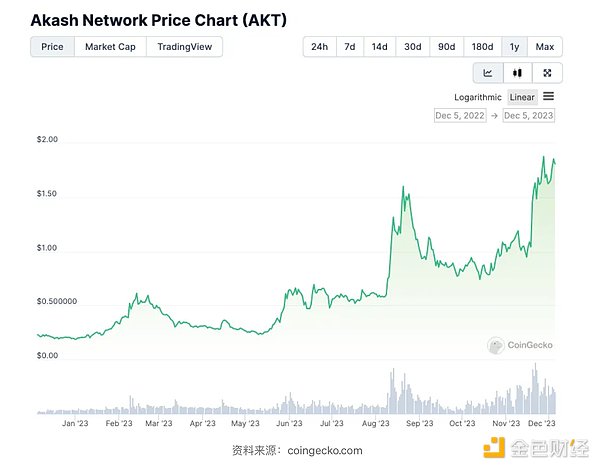
CoinGecko’s price trend shows that $AKT experienced increases in mid-August and late November 2023, although the increase was not as large as other projects in the artificial intelligence space, which may be Due to current market sentiment.
Overall, Akash Network is one of the few high-quality projects on the AI track, and its fundamentals are better than most competitors. Its potential business revenue can bring future profitability to the protocol. As the artificial intelligence industry develops and the demand for cloud computing resources continues to increase, Akash Network is expected to make significant progress in the next wave of artificial intelligence.
3.3 Bittensor ($TAO)
For those familiar with the technical architecture of $BTC That said, it is very simple to understand the design of Bittensor. In fact, when designing Bittensor, its creators drew inspiration from several characteristics of cryptocurrency pioneer $BTC.
This includes a total token supply of 21 million, which is halved approximately every four years, and involves the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, etc.
To conceptualize this, imagine the initial Bitcoin production process, then replacing the computationally intensive "mining" process with training and validating AI models , the process does not create real-world value. Miners receive incentives based on the performance and reliability of their AI models. This forms a brief summary of the Bittensor ($TAO) project architecture.
Bittensor was founded in 2019 by artificial intelligence researchers Jacob Steeves and Ala Shaabana based on a white paper written by mysterious author Yuma Rao. In short, it is an open source, permissionless protocol that creates a network architecture connected by many subnetworks, each responsible for different tasks (machine translation, image recognition and generation, large language models, etc.). Excellent task completion is rewarded, and subnetworks can interact and learn from each other.
As far as the current major artificial intelligence models are concerned, they are the result of technology giants’ massive investment in computing resources and data. While these AI products perform well, this approach also brings high centralization risks.
Bittensor's infrastructure allows a network of communicating experts to interact and learn from each other, laying the foundation for decentralized training of large-scale models. Bittensor’s long-term vision is to compete with closed-source models from giants like OpenAI, Meta, and Google, maintaining decentralized characteristics while aspiring to match their inference performance.
The core of Bittensor’s technology is Yuma Rao’s uniquely designed consensus mechanism, also known as Yuma Consensus, which mixes elements of PoW and Proof of Stake (PoS). The supply side mainly involves "servers" (miners) and "validators" (validators), while the demand side consists of "clients" (clients) who use the models in the network. The process is as follows:
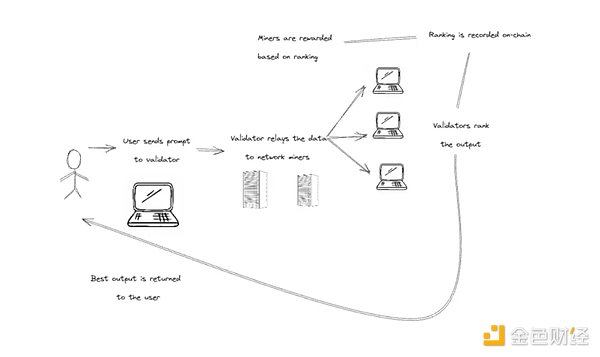
The client sends the request and data to the validator for processing.
Validators distribute data to miners under a specific subnet.
Miners use their models and the data they receive to make inferences and return results.
Verifiers rank the inference results by quality and record them on the blockchain.
The best inference results are returned to the client, and miners and verifiers receive rewards based on ranking and workload.
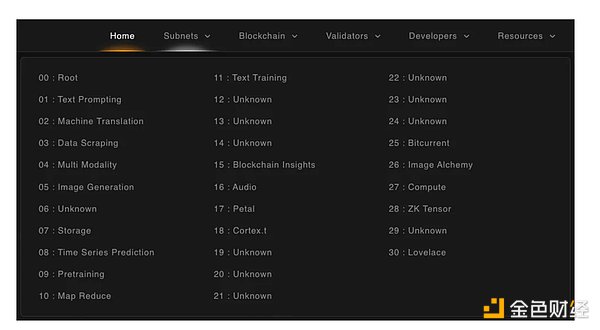
It is worth noting that Bittensor itself does not train any models in most sub-networks; it is more like a model provider and users, further improving the performance of various tasks through interactions between smaller models. Currently, there are (or already have) 30 subnetworks online, each subnetwork corresponding to a different task model.
p>
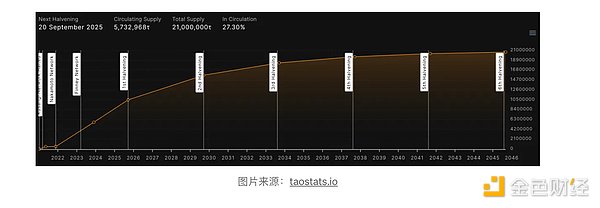
$TAO, as the native token of Bittensor, plays a vital role in creating subnetworks, registering in subnetworks, paying service fees, and staking to validators within the ecosystem. crucial role. Following the spirit of BTC, $TAO opts for fair release, meaning all tokens are generated through contributions to the network.
Currently, the daily production of $TAO is approximately 7,200 tokens, evenly distributed among miners and validators. Since the launch of the project, approximately 26.3% of the 21 million tokens have been produced, with 87.21% used for staking and verification. The project also follows BTC’s pattern of halving production approximately every four years, with the next halving scheduled for September 20, 2025, expected to be a significant price driver.
p>
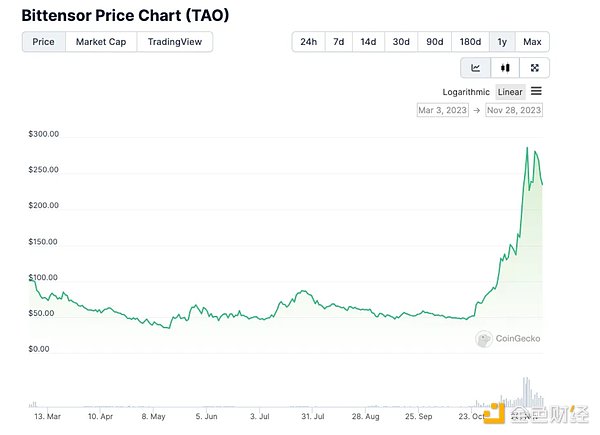
Starting from late October 2023, the price trend of $TAO has increased significantly, which was mainly driven by a new wave of enthusiasm for artificial intelligence after the OpenAI conference and the shift of capital to the field of artificial intelligence. promote.
The emergence of $TAO as a new project in the Web3+AI track, its quality and long-term vision have also attracted investment. However, it must be admitted that, like other AI projects, although the combination of Web3+AI has great potential, it has not yet found an application in actual business to support long-term profitable projects.
3.4 Alethea.ai ($OR)
Alethea.ai was established in 2020. is a project dedicated to bringing decentralized ownership and governance to generated content using blockchain technology.
The founders of Alethea.ai believe that generative artificial intelligence will lead us into an era of information redundancy caused by generative content, in which, through A large amount of digital content can be easily replicated or generated with a simple copy-paste or click, but it is difficult for the original creator to reap the benefits. By connecting blockchain primitives such as NFTs with generative AI, they aim to ensure ownership of generative AI and its content, with community governance on top of it.
Driven by this concept, Alethea.ai initially launched a new NFT standard, iNFT, which uses Intelligence Pods to integrate AI animation, speech synthesis and even generative AI is embedded in the image. Alethea.ai also works with artists to create iNFTs from their artwork, one of which sold at a Sotheby’s auction for $478,000.

p>
Alethea.ai subsequently launched the AI protocol, allowing any generative AI developer or creator to create using the iNFT standard without a license. To demonstrate the AI protocol, Alethea.ai developed CharacterGPT, a tool based on the theory of large models like GPT for creating interactive NFTs. Recently, they released Open Fusion, which allows any ERC-721 NFT to be combined with Intelligence and published on the AI protocol.
Alethea.ai’s native token is $ALI, which has four main uses:
Lock a certain amount of $ALI to create iNFT.
The more $ALIs locked, the higher the level of the intelligence module.
$ALI holders participate in community governance.
$ALI as a credential for interaction between iNFTs (no practical use case yet).
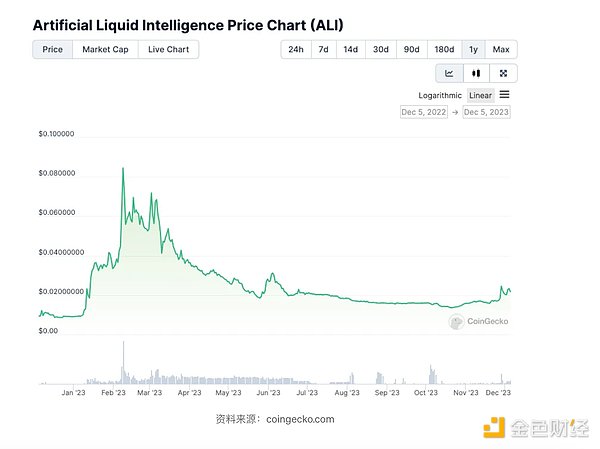
Looking at $ALI’s use cases, it’s clear that the token’s value capture is still primarily narrative-based. Token price trends over the past year confirm this: $ALI has benefited from the generative AI boom led by ChatGPT starting in December 2022. Additionally, when Alethea.ai announced new Open Fusion capabilities in June, it triggered a price spike. However, aside from these instances, the price of $ALI has been trending downwards, not even responding to the late 2023 AI hype like similar projects.
In addition to native tokens, the performance of Alethea.ai's NFT projects (including its official collection) in the NFT market is also worthy of attention.
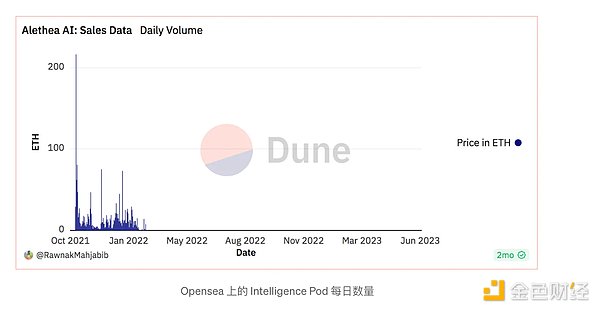
p>
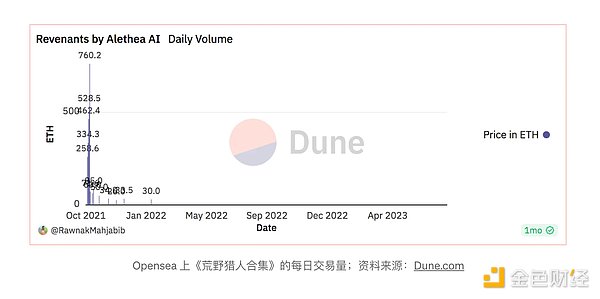
According to data from the Dune dashboard, third-party-sold Intelligence Pods and Alethea.ai's line of first-party Revenants faded into obscurity after their initial release. The author believes that the main reason is that the initial novelty wears off and there is no substantial value or community engagement to retain users.
3.5 Fetch.ai ($FET)
Fetch.ai is a community dedicated to promoting A project integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology. Its goal is to build a decentralized smart economy by combining machine learning, blockchain and distributed ledger technology to support economic activities among smart agents.
Fetch.ai was founded in 2019 by British scientists Humayun Sheikh, Toby Simpson and Thomas Hain, and its founding team has impressive backgrounds.
Humayun Sheikh is an early investor in DeepMind, Toby Simpson has held executive positions in various companies, and Thomas Hain is a professor in the field of artificial intelligence at the University of Sheffield. The founder's diverse experience spans traditional IT companies, blockchain star projects, medical care, and supercomputing fields, providing Fetch.ai with rich industry resources.
Fetch.ai's mission is to build a decentralized network platform composed of autonomous economic agents (AEA) and artificial intelligence applications to enable developers to Create autonomous agents to complete preset goal-directed tasks. The core technology of the platform is its unique three-layer architecture:
Bottom layer: based on PoS- uD (permissionless proof of stake) consensus mechanism, this base layer supports smart contract networks, facilitating miner collaboration and basic machine learning training and inference.
Middle layer: The Open Economic Framework (OEF) provides a shared space for interactions and underlying protocols between AEAs, and supports Search, discover and trade.
Top-level: AEA is the core component of Fetch.ai. Each AEA is an intelligent agent software that can perform various functions through skill modules and perform user-defined tasks. These agents do not run directly on the blockchain, but interact with the blockchain and smart contracts through OEF. Smart agent software can be purely software-based or tied to physical hardware such as smartphones, computers, and cars. Fetch.ai provides a Python-based development suite, the AEA framework, which is modular and enables developers to build their intelligent agents.
On top of this architecture, Fetch.ai launched Co-Learn (sharing machine learning models between agents) and Follow-up products and services such as Metaverse (agent cloud hosting service) to support users in developing agents on its platform.
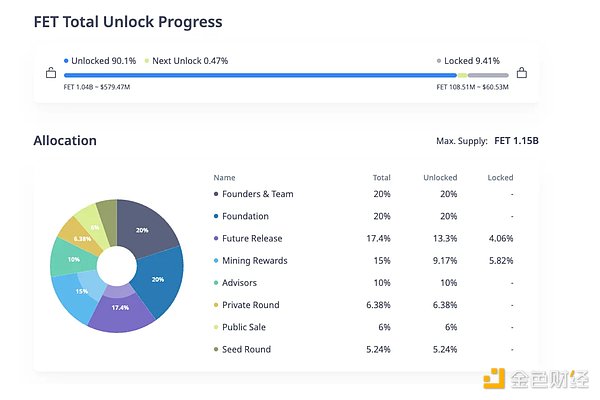
Regarding tokens, $FET, as the native token of Fetch.ai, covers standard functions such as paying gas, verifying pledges, and purchasing services within the network. More than 90% of $FET tokens have been unlocked and are allocated as follows:
Since its inception, Fetch.ai has experienced multiple rounds of token dilution financing, the most recent of which was in 2023 On March 29, 2019, it received a US$30 million investment from DWF Lab. Given that the $FET token cannot capture value from project revenue, its price momentum relies primarily on project updates and market sentiment towards the AI space. In fact, during two waves of the AI market boom, Fetch.ai’s price experienced more than 100% surges in early and late 2023.
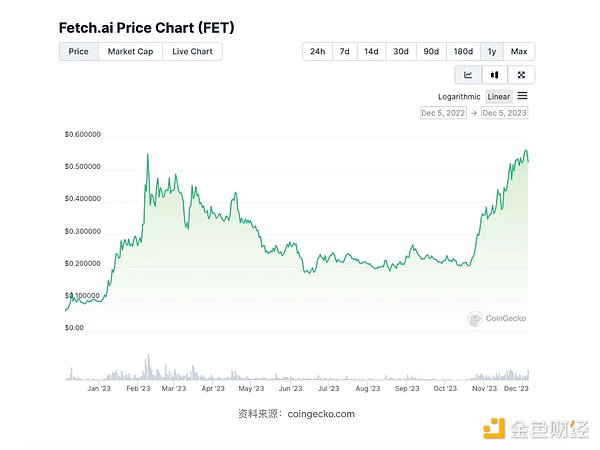
p>
Fetch.ai's development trajectory is more like a Web2.0 artificial intelligence startup, focusing on perfecting its technology. It seeks recognition and profitability through ongoing fundraising and extensive collaboration.
This approach leaves plenty of room for future applications developed on Fetch.ai, but also means it could be useful for other blockchain projects. Not as attractive, potentially limiting the vitality of the ecosystem. One of the founders of Fetch.ai even tried to launch a DEX project, Mettalex DEX, based on Fetch.ai, but it ultimately failed. As an infrastructure-focused project, the weakening of the ecosystem also hinders the growth of Fetch.ai’s intrinsic value.
4. The bright future of generative AI
NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang compared the launch of large-scale generative models to the "iPhone moment" of artificial intelligence, indicating the changing role of artificial intelligence. In a key shift, high-performance computing chips have become the core of scarce resources for artificial intelligence.
The AI infrastructure projects that lock most of the funds in the Web3 AI sub-track are still the long-term focus of investors. As chip giants gradually upgrade their computing capabilities, AI capabilities will expand, which is likely to spawn more AI infrastructure projects in Web3, and may even be chips specifically designed for AI training in Web3.
Although consumer-focused generative AI products are still in the experimental stage, some industrial-grade applications have shown great potential. One such application is “digital twins” that transfer real-world scenes into the digital realm.
Given the untapped value in industrial data, NVIDIA’s Metaverse digital twin platform positions generative AI as an essential component of industrial digital twins. In Web3, including virtual worlds, digital content creation and real-world assets, digital twins influenced by artificial intelligence will play an important role.
The development of new interactive hardware is also crucial. Historically, every hardware innovation in computing has brought revolutionary changes and opportunities, such as the now-ubiquitous computer mouse or the iPhone 4’s multi-touch capacitive screen.
Apple Vision Pro is announced to be released in the first quarter of 2024. It has attracted global attention with its impressive demonstration and is expected to bring meaning to various industries. Unexpected changes and opportunities. The entertainment industry, known for rapid content production and wide distribution, is often the first to benefit from hardware updates. These include Web3’s metaverse, blockchain games, NFT, etc., which are worthy of long-term attention and research.
In the long run, the development of generative artificial intelligence represents a quantitative change leading to a qualitative change. The core of ChatGPT is a solution to the long-researched academic problem of reasoning question answering. It was only through extended data and model iteration that the impressive levels of GPT-4 were achieved. AI applications in Web3 are similar, and are currently in the stage of adapting the Web2 model to Web3. A model based entirely on Web3 data has yet to emerge. Future visionary projects and vast resources dedicated to researching Web3-specific problems will bring Web3 its own ChatGPT-level killer app.
There are many promising ways to explore the technical basis of generative artificial intelligence, such as thought chain technology. This technology allows large language models to make significant leaps in multi-step reasoning. However, it also highlights or even exacerbates the limitations of large models in complex logical reasoning. Interested readers can explore the original author's paper on Chain-of-Thought.
After ChatGPT, various GPT-themed projects have appeared in Web3, but simply combining GPT with smart contracts cannot meet user needs. About a year after ChatGPT was released, there is still huge potential for the future. Future products should start from the real needs of Web3 users. As Web3 technology becomes increasingly mature, the application of generative AI in Web3 will surely be broad and exciting.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance





































