Author: BiB Exchange
I believe you have recently seen a project EigenLayer. What kind of project is this? I believe everyone understands it more or less. In this article, BiB Exchange will give you a comprehensive explanation of this upstart project that Ethereum loves and hates - EigenLayer.
EigenLayer is a token economic security rental market platform. Its main services include retake of LSD assets, node operation pledge and AVS services. EigenLayer is an Ethereum-based Restake protocol that provides Ethereum-level security for the entire future Ethereum-based crypto-economy. It allows users to re-stake native ETH, LSDETH and LP Token through EigenLayer smart contracts and obtain verification rewards, allowing third-party projects to obtain more rewards while enjoying the security of the ETH main network, thus achieving a win-win situation.
1. Principle
1.1 Starting from the virtual machine
Ethereum was conceived in 2013 and launched in 2015, completely changing the blockchain landscape with the introduction of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Ethereum pioneered the concept of programmability, enabling distributed applications (DApps) to be built on top of it without permission. This innovation eliminates the need for DApp developers to be trusted because security and liveness are guaranteed by the underlying blockchain, and trust is provided by the blockchain.
This kind of decoupled innovation greatly promotes the development of the anonymous economy, because innovators do not need reputation or trust, DApp can be used by anyone who trusts, and the underlying Blockchain can verify the code of DApp. The value stream provides trust to the DApp through the blockchain and collects fees in exchange. With development and entering the Layer2 era, its scale has expanded significantly. Rolllup outsources execution to a single node or a small group of nodes, while EVM contracts can absorb the trust of Ethereum through Ethereum-proof computation.
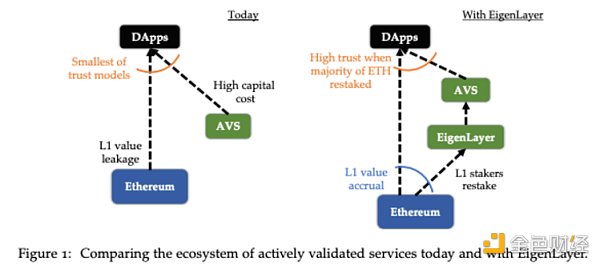
However, traditional verification services obviously lack a trust mechanism. Any module that cannot be deployed or proven on top of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) cannot absorb Ethereum’s collective trust. These modules involve processing input from outside Ethereum, so their processing cannot be verified within the protocol inside Ethereum.
Examples of these modules include side chains based on new consensus protocols, data availability layers, new virtual machines, management networks, oracles, cross-chain bridges, and thresholds Cryptographic schemes and trusted execution environments. These modules require an active verification service, which has its own distributed verification semantics for verification. Typically, these Active Validation Services (AVS) are either secured by their own native token or are permissioned in nature.
1.2 AVS
EigenLayer directly connects the security and liquidity of Ethereum; AVS plays a crucial role here. AVS (Actively Validated Services) usually refers to a service used to verify an individual's identity or specific information. AVS can be applied in many fields, such as finance, telecommunications, online services, etc., to ensure that the information provided is accurate, valid and legal.
So the essence of Eigenlayer is to combine various middleware, data availability layers, side chains, oracles, sequencers, etc. to enjoy Ethereum-level security at a low cost The security verification of sexual demand projects is entrusted to Ethereum’s node operators, a process called Restake. EigenDA is a decentralized data availability (DA) service built on Ethereum using EigenLayer Restake, and will be the first Active Validation Service (AVS) layer.
1.3 Business logic
EigenLayer's business logic involves multiple key concepts, including middleware , LSD, AVS, and DA layers. These concepts are intertwined and constitute the complex and specific business logic of EigenLayer. EigenLayer effectively exports the security of ETH to the entire Ethereum ecosystem through its business logic, especially node operations, AVS services and other functions. Through the provision and staking of LSD (Liquid Staking Derivatives) assets, users provide additional security support for the Ethereum network.
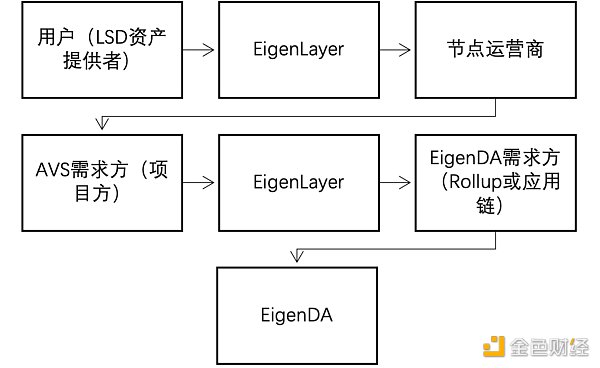
According to the diagram, we can simply sort out the business logic:
i. LSD asset provider: The user passes the Tokens such as stETH, rETH, cbETH are retaken to provide AVS services for node operators to obtain additional income.
ii. Node operator: Obtain LSD assets through EigenLayer, provide node services for projects that require AVS services, and obtain node rewards and handling fees from the project parties .
iii. AVS demander (project party): The project party purchases AVS services through EigenLayer without building AVS by itself, thus reducing costs.
iv. EigenDA demand side (Rollup or application chain): Rollup or application chain can obtain data availability services through EigenDA.
v. The role of EigenLayer: The main role of EigenLayer is to reduce the cost of the project party to independently build a trust network, expand the use scenarios of ETHLSD, and improve the capital efficiency of LSD assets. and earnings, while increasing demand for ETH.
1.4 Relationship between the parties
At the same time, we can see that this The required participants for a block are as follows: We can see that according to the official white paper, the role of EigenLayer in the block is as follows:
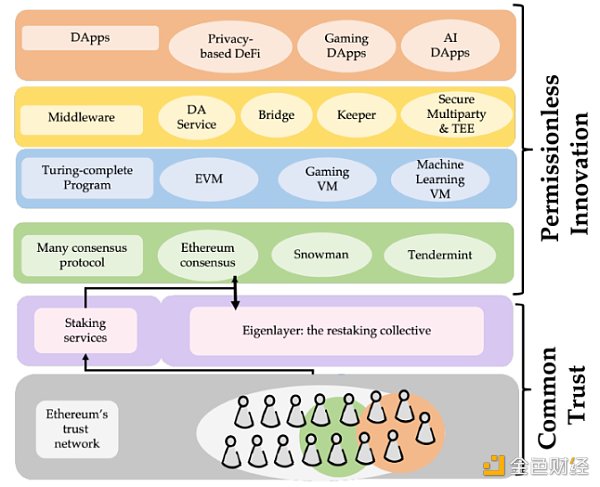
So the relationship between the main participants here is as follows:
< p style="text-align:center">
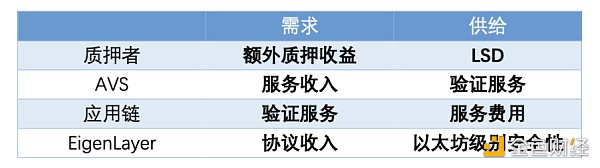
LSD asset provider: Hope to obtain additional income and are willing to provide LSD assets as pledge to node operators.
Node operator: Obtain LSD assets from EigenLayer, provide AVS services for the project, and obtain node rewards and handling fees.
AVS demander: The project party needs AVS services and purchases them through EigenLayer. There is no need to build AVS by itself.
EigenDA demand side: Rollup or application chain requires data availability service.
2. Concerns from L2 DAs
The 11th AMA from the Ethereum Foundation research team focused on why EIP-4844 is being made and how Ethereum will solve the liquidity fragmentation and composability issues on L2. This is also something that V God has always wanted to emphasize.
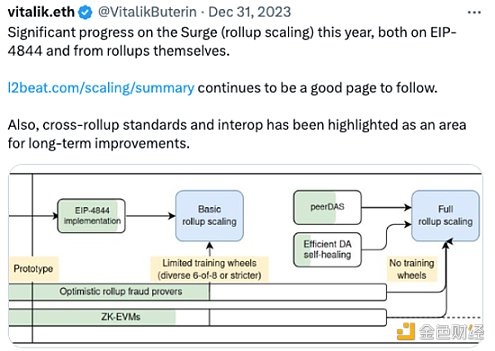
This is the biggest test facing Ethereum. What if layer2 doesn’t have one? Choose Ethereum as DA, or something else? But it can be felt that Ethereum is quite helpless in this regard, and may face competition from Celestia. Once other L2s do not use Ethereum as DA, Ethereum may "slowly die." Therefore, Ethereum must promote the Cancun upgrade as soon as possible and reduce the cost of Layer 2.
Vitalik said: "The key to Rollup is unconditional security: even if you are targeted by everyone, you can still take away the assets. If DA relies on external Systems (outside Ethereum) cannot do this."
As for the above sentence, some people have raised questions and feel that V God is based on Ethereum. The logic of Fangzhu.com does not go beyond the framework. At the same time, similar opinions have appeared in the market - Layer 2 does not have to publish DA data to Ethereum in order to avoid "data withholding" by the sequencer. It can be placed on other similar Celestia third-party DAs.
We can issue DA at four important levels of ETH's external system through the figure below.
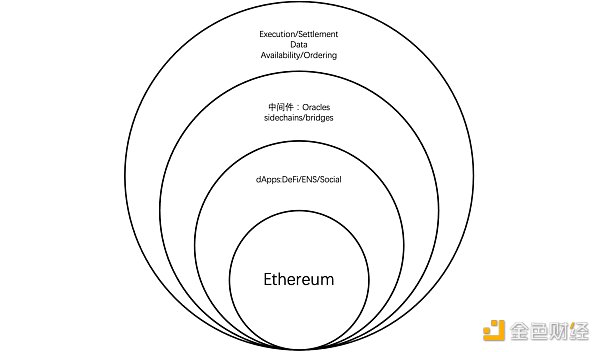
So a major feature of the Cancun upgrade focuses on EIP-4844. After completion, all Ethereum nodes will automatically lose part of the historical data, so that the historical data of Layer 2 for more than 18 days will no longer be used by the entire ETH node network. Backups, when user withdrawals are censorship-resistant, will no longer be as close to Trustless as they are today. Previously, users could prove their Layer 2 asset status through Merkle Proof and achieve unnecessary withdrawals on Layer 1.
2.1 Data Availability
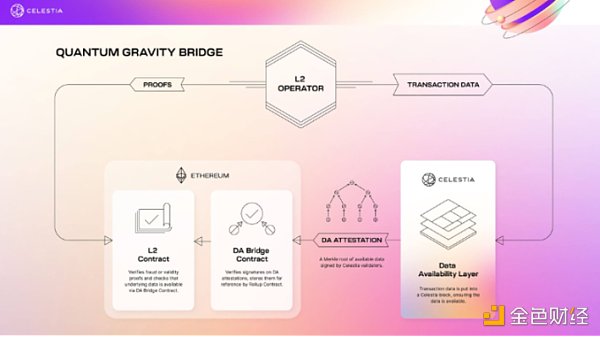
First, let’s take a look at the structure of Celestia’s DA ?
Quantum Gravity Bridge is an Ethereum Layer 2 solution that greatly reduces the number of transactions on the Ethereum main chain through data availability (DA) verification provided by Celestia. The cost of storing DA on. The specific process includes L2 Operator publishing transaction data to the Celestia main chain, Celestia validator signing the Merkle Root of DA Attestation, and sending it to the DA Bridge Contract on the Ethereum main chain for verification and storage. The Celestia chain achieves consistent propagation of Data Blobs through the P2P network and Tendermint, but full nodes have high requirements for high-speed downloads and uploads, and the actual throughput is relatively low. Celestia's Quantum Gravity Bridge uses this approach to reduce costs while ensuring data availability.
At this time, EigenLayer as a platform is, at its core, dedicated to the security of output Ethereum (ETH) and has made important innovations in data availability (DA). By introducing the new data structure of Blob space, it iterates the limitations of relying on calldata to store data in the past, and at the same time improves the data availability capability of the Ethereum main network. Pure Rollup refers to a solution that simply puts DA on the chain, which requires a constant payment of 16 gas for each byte, which will account for 80%-95% of the cost of Rollup. After the introduction of Danksharding, the cost of on-chain DA will be significantly reduced.
Compared with the full node storage structure of calldata, Blob is designed as temporary storage for some nodes, which can greatly increase the upper limit of data submitted by Layer2 to the main network at a time. Its TPS can be expanded. At the same time, since it is only temporary storage, data storage efficiency will increase and data storage costs will plummet. The improvement of DA capability is due to the temporary storage of 1 month, which is more than enough to cope with the 7-day fraud proof time window of OP-Rollup.
Layer2’s single transaction volume submitted to the main network will increase significantly, and the cost shared to a single user will also decrease significantly. Before the Cancun upgrade, no matter how high TPS Layer 2 boasted, it was mostly a test environment. On the contrary, the bad experience of gas consumption and wear and tear intuitively felt by users will make everyone feel that Layer 2 is not worthy of its name.
2.2 Sequencer centralization problem
Sequencer’s decentralization problem has always been a market problem Focusing on the focus, everyone found that in the strong OP Rollup on the Layer 2 track, the decentralized Sequencer has become a social consensus of the nature of the alliance "soft decentralization".
Layer2 decentralized Sequencer solution provider Metis’s TVL lock-up amount has ranked third in L2. The issue of Sequencer decentralization is related to the credibility of transactions submitted by Layer 2, as well as the security of the main network interaction of Layer 2 transactions. If we put aside the issue of "foundation", the TPS and Gas rates after Cancun's upgrade It seems that everything has become a "castle in the air", and Sequencer's decentralization problem will always be solved by other game-breakers.
2.3 Layer2 gradually evolves into modularization, and its orthodoxy will be broken
When the Layer2 market becomes large At a certain scale, the pure narrow-sense Ethereum Layer 2 legitimacy may be broken. After the Cancun upgrade, third-party DA solutions will invade Layer 2, including the third-party DA solution of Celestia mentioned earlier.
The focus of the OP Stack stack is to realize the shared Sequencer, and the ZK Stack stack is focused on realizing the shared Prover system, its own DA capabilities and third parties such as Celestia DA capabilities, as well as the limited DA capabilities of the main network, will fall within ZK's strategic enclosure.
2.4 EigenLayer provides DA
So this time Eigenlayer comes forward. Given that many ecological applications are currently deployed on Layer 2, their smart contracts need to interact with EigenLayer for data or obtain data availability services. Its integrated Layer2 solutions include Celo, which transitions from L1 to Ethernet L2, Mantle and its supporting products outside the BitDAO ecosystem, Fluent which provides the zkWASM execution layer; Offshore which provides the Move execution layer; and Optimism's OP Stack, which is currently Used on the EigenDA test network.
EigenDA is a generalized DA solution, in the same category as Celestia and Polygon Avail. However, there are some differences in the solution ideas between EigenDA and the other two. EigenLayer has a unique reimagining of data availability, creating a new data availability model. By introducing AVS services, project parties can obtain the required services without building their own AVS. This innovation not only reduces project costs, but also provides a more efficient and scalable data availability solution for the entire Ethereum ecosystem. EigenLayer’s innovation in this field brings new possibilities to the development of the blockchain ecosystem.
3. Competition and Challenges
3.1 Competition of Polygon+Celestia
< p style="text-align: left;">Competition not only comes from within, but also from the outside. Polygon+Celestia has begun to compete with Ethereum. In the past 18 months, the explosion of Rollup technology has largely made the DeFi field Advanced users can experience an unprecedented user experience, including faster confirmations and cheaper transactions
Polygon's Customizable Development Kit (CDK), The ability to rapidly develop modular blockchains. CDK’s modular approach allows developers to select specific components to enable personalized design of blockchain use cases, and enables interoperability between blockchains through interconnection. The four main parts of Polygon CDK include ZK Provers, Data Availability, Virtual Machines (VMs), and Sequencers. The combination of these parts gives developers the option to flexibly build a blockchain based on their project needs.
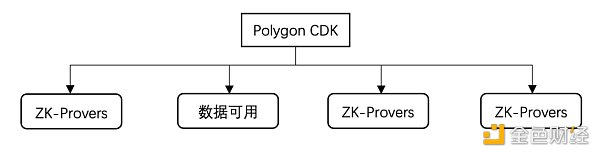
Celestia and Polygon Labs announce a collaboration to integrate Celestia's data availability layer with Polygon CDK. This collaboration will further improve the efficiency of Ethereum L2 transactions and reduce transaction fees. DeFi users will experience a better user experience. The integration with Celestia is expected to significantly reduce Ethereum L2 transaction fees, allowing users to conduct transactions in a better execution environment with fees potentially below $0.01.
3.2 Ambiguity of Cosmos
Fragmentation of liquidity and composability across Rollup (across L2 more generally, including validation) is a problem. Each Rollup (such as Arb or Optimism) is an execution "silo": isolated pre-confirmation, isolated ordering, isolated state, and isolated settlement. The universal synchronous composability of Ethereum contracts, which is the fundamental driver of network effects, has been lost.
Recently, EigenLayer announced that it will provide services for the application chain of the Cosmos ecosystem. When new network projects are launched in the future, they will be able to enjoy the flexible architecture of the Cosmos SDK and Ethereum at the same time. security provided. Many innovations in Cosmos involve leveraging sets of validators to perform complementary work. However, maintaining a quorum of validators with strong economic security is a well-known challenge. EigenLayer solves this problem by providing an economic staking platform - allowing any stake holder to contribute to any PoS network. By reducing cost and complexity, EigenLayer effectively paves the way for innovation in the L2 mining Cosmos stack.
Cosmos is mainly based on its modular nature to integrate interoperability, which is the shortcoming of Ethereum, with the ecosystem as the center, through the Tendermint consensus and IBC protocol Enable interoperability between independent blockchains, each using Tendermint to reach consensus and execute transactions. Integration simplifies the blockchain development process and provides a cohesive environment, but may limit flexibility to meet different application needs.
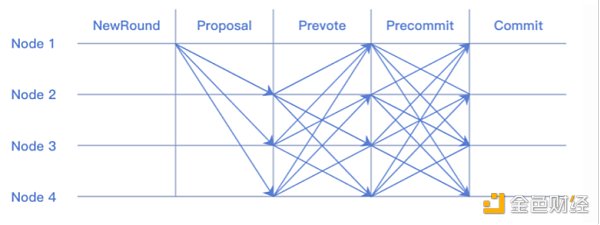
Through the Tendermint integration diagram above (if it is not easy to understand, it can be understood as a Byzantine agreement), an interconnected blockchain network is formed, running uniformly under the protection of Cosmos, emphasizing blocks collaboration and interaction between chains. The application-specific innovations launched by Cosmos are therefore a perfect complement to EigenLayer’s sophisticated staking community and capital base. So expect deeper collaborations that will be highly creative, expand Ethereum’s capabilities, and create an environment for Cosmos builders to apply their talents to the world’s largest on-chain programmable staking economy.
Ethereum and Cosmos initially pursued different goals, but their technical development gradually converged. Both face common technical challenges such as MEV, liquidity fragmentation, and widespread decentralization. Cosmos continues to evolve as a nexus of experimentation, and Ethereum is validated as a composable settlement layer. Until the emergence of EigenLayer. EigenLayer solves this problem by providing an economic staking platform - allowing any stake holder to contribute to any PoS network. By reducing cost and complexity, EigenLayer effectively paves the way for expressive innovation in L2 mining within the Cosmos stack.
MEV (Maximum Extractable Value) has always been a core issue of concern in Ethereum, which has a profound impact on the future roadmap and protocol design. In order to deal with the centralization pressure caused by MEV, Ethereum adopted the proposer-builder separation (PBS) approach. In Ethereum, PBS is currently implemented through the MEV-Boost off-protocol design, which uses a trusted commit-reveal scheme. Ethereum plans to integrate the fixed PBS (ePBS) design into the base layer to eliminate dependence on trusted third parties and achieve a more decentralized PBS.
Cosmos also faces the problem of MEV, and in order to solve this problem, it is implementing a more advanced ePBS solution. For example, Osmosis is experimenting with mechanisms for arbitrage profit sharing, while Skip is testing the Block SDK, a decentralized block builder and proposer commitment design. The separation of individual components in a blockchain architecture, such as consensus, data availability, and execution, contrasts with traditional integrated blockchains. Modularity allows each component to be developed, optimized and expanded independently, providing a customizable and efficient framework. Handle large amounts of data The modular architecture enhances scalability and can effectively handle large amounts of data, especially suitable for applications with high transaction throughput requirements.
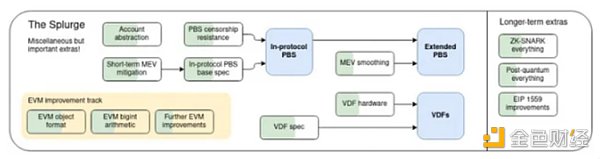
Vitalik Buterin’s Ethereum roadmap as of December 2021
EigenLayer introduces new A wave of innovation. The Cosmos community can leverage Ethereum’s decentralized security and liquidity, and Ethereum can learn from innovative experiments in Cosmos. This convergence brings new possibilities to both ecosystems. On a technical level, MEV is an important issue for both Ethereum and Cosmos, and both are exploring solutions. Interoperability is also a key focus, especially the modular nature of Cosmos. As their designs converge, they begin to learn from each other and adopt some of each other's design elements.
EigenLayer lowers the barriers for Ethereum to leverage Cosmos innovation, specifically by providing an economic staking platform that enables L2 to leverage the validator set for complementary work. This paves the way for more innovation and collaboration between the two ecosystems. EigenLayer merges the technology stacks of Ethereum and Cosmos, creating a symbiotic relationship with endless possibilities. This integration will not only drive the growth of Ethereum and Cosmos, but will also hopefully create a more creative and resilient ecosystem.
3.4 Competitive products based on LSDFi platform
Competitor and partner Restake
This project is based on EigenLayer and provides a modular liquidity staking solution. Through innovative ways, users can reap staking rewards on Ethereum and EigenLayer without locking up assets or dealing with complex infrastructure. Governed by a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO), it focuses primarily on revenue-generating strategies.
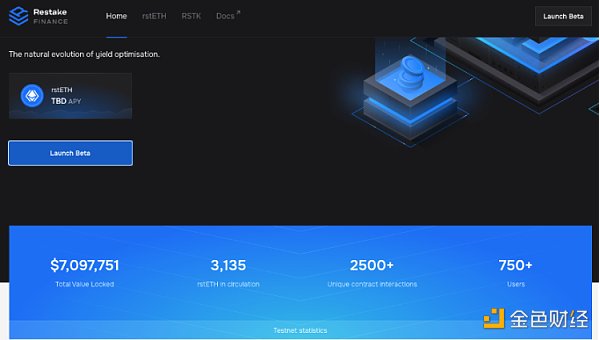
Promote the liquidity and re-pledge of LSTs (such as stETH) within EigenLayer through the newly launched re-pledged Ethereum token (rstETH). Holding rstETH seamlessly earns Ethereum and EigenLayer staking rewards, estimated to be between 3%-5% and over 10%.
Its token RSTK (maximum supply 100 million) is used for the utility and governance of the ecosystem. Directly tied to EigenLayer success and revenue, reflecting platform growth. The fee is fixed at 10%, of which 5% goes to the stakers and 5% goes to the platform treasury.
The project focuses on promoting decentralization and community governance of cryptocurrency transactions. Through its unique Stake & Yield mechanism, Restake provides holders with substantial returns and implements governance through community voting. The project focuses on security and sustainability, providing users with a reliable trading ecosystem.
Prisma Finance

This project focuses on Ethereum liquidity collateral derivatives. Users can use a variety of LSD (wstETH, rETH, cbETH, sfrxETH) to fully mortgage and mint the stable currency mkUSD. Multiple LSD collaterals: wstETH, rETH, cbETH and sfrxETH are available for mkUSD minting. Get the LSD payoff. Depositing into the stability pool earns you a higher APR. Additional weekly PRISMA rewards for maintaining mkUSD debt. mkUSD is a relatively stable asset that provides users with additional income.
Its PRISMA (total supply 300 million); ways to earn PRISMA include depositing into the pool, minting mkUSD, maintaining mkUSD debt, and staking Curve/Convex LP. Locking PRISMA can earn protocol fees and increase voting rights, with a maximum locking period of 52 weeks.
Lybra.finance

Lybra is an LSDFi platform focused on stabilizing the cryptocurrency market through Liquidity Collateralized Derivatives (LSD).
The project provides a unique stablecoin eUSD, backed by ETH assets, generating stable interest for holders. With LSD income, users receive a stable income in eUSD. Also launching is peUSD, the Omnichain version of eUSD, adding the option of liquid staking tokens. rETH and WBETH serve as collateral for eUSD and peUSD, adding flexibility.
LBR (total supply 100 million) is an ERC-20 token based on the Arbitrum and Ethereum networks. Token uses include governance, revenue enhancement, and ecosystem incentives. esLBR esLBR is a managed LBR that has the same value and is limited by the total LBR supply and is not tradable. However, voting rights and a share of the proceeds of the agreement are granted. esLBR holders actively participate in shaping the direction and development of the Lybra protocol. esLBR holders receive 100% of the protocol’s revenue, increasing their potential earnings. Compared to the previous two projects, Lybra stands out because of its ability to work across chains, allowing it to reach a larger market.
4. Development and Prospects
Just like when discussing the DA chapter above, in On the demand level, the Cancun upgrade and the opening of OP Stack have promoted the rapid development of small and medium-sized rollups and application chains, increasing the demand for low-cost AVS. The modularization trend increases the demand for cheap DA layers, and the expansion of EigenDA increases the demand for EigenLayer. On the supply level, the Ethereum pledge rate has increased and the number of pledge users has increased, providing abundant LSD assets and holder scale, and they are willing to improve the capital efficiency and income of LSD assets.
4.1 Product Progress
The first is the product progress. To be honest, EigenLayer's own product page is a bit Not very user-friendly and flexible. From a user perspective, users cannot obtain any substantial staking benefits in the short term, and the unclear staking rewards may affect the subsequent increase in the number of users.
EigenLayer establishes an open marketplace where validators can choose whether to join each module and decide which modules deserve the additional collective security assigned to them. This provides a free market structure that allows new blockchain modules to take advantage of resource differences among validators. Therefore, the current open market product external promotion page has not yet been developed, and most of them are promoted through the operational perspective of the project party. Of course, if you participate in some activities, you can find that by integrating the Restake function: users can restake tokens such as stETH, rETH, and cbETH to participate in the EigenLayer ecosystem.
4.2 Business Model
Both LSD asset deposit activities attracted users, Deposits reached limits quickly and users showed interest in potential airdrop rewards. EigenLayer has accumulated about 150,000 staking ETH, and the entire TVL can be seen on the official website.
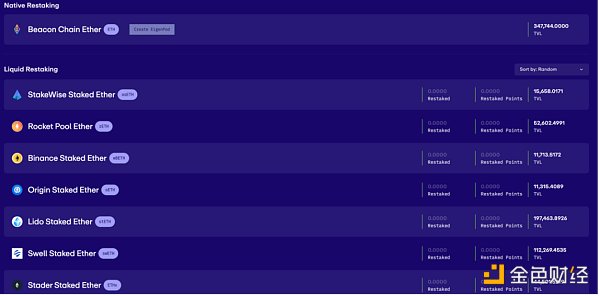
eigenlayer official website pledge status as of January 27, 2024 (5:am, UTC)
EigenLayer mainly charges AVS service users Commission on security service fees, of which 90% is given to LSD depositors, 5% is given to node operators, and the EigenLayer commission rate is 5%.
4.3 Future Development
The value of ETH pledged on Ethereum is approximately US$42 billion , the scale of funds on the entire chain is 300-400 billion US dollars. Project size for EigenLayer services is expected to be in the $10-10 billion range in the short term. All projects that require token pledges, use gaming mechanisms to maintain network consensus, and maintain decentralization are potential users. The market's evaluation of EigenLayer is quite high. Taking Lido's current PS of 25 times as an anchor, newer narratives may enjoy a higher premium when they first debut, with a value of 20-40 times. We can simply calculate that EigenLayer’s valuation will be a project of US$1-2 billion in the conservative future.
EigenLayer has completed three rounds of financing, totaling more than $64 million. Among them, the latest Series A financing was led by Blockchain Capital, with participation from Coinbase Ventures, Polychain Capital, IOSG Ventures, etc., with a valuation of up to US$500 million. It is difficult to estimate the market size accurately, but under optimistic circumstances it may reach tens of billions of dollars within 3 years. If the market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 37%, revenue will exceed $25 billion by 2030.
5. Risks and Challenges
EigenLayer also faces technical complexity and uncertainty in market adoption sexual challenges. While EigenLayer currently holds an unchallenged position in the AVS market, potential competition and the additional risks that come with being a middleware layer cannot be ignored.
Re-pledge collective security issue: The current AVS has the challenge of re-pledge collective security. EigenLayer establishes a new mechanism by allowing validators to use restaking tokens instead of their own tokens to obtain security, and validators earn additional income by providing security and verification services.
Open market mechanism issue: EigenLayer introduces an open market mechanism that allows validators to choose whether to join each module and decide which modules deserve to be assigned additional collective security . This selective and dynamic governance provides a free market structure for launching new additional features.
New AVS launch issues: Innovators must build a new trust network to ensure security when launching a new AVS, which can be a difficult task .
Value dispersion problem: As each AVS develops its own trust pool, users must pay fees for these pools, which leads to a dispersed loss of value.
The burden of capital costs: Verifiers who protect new AVS must bear capital costs, which include opportunity costs and price risks. AVS must provide a high enough return on staking to cover this cost, and this is a challenge for many AVS.
The problem of reduced trust model of DApps: The current AVS ecosystem has led to the reduced trust model of DApps, because applications that rely on specific modules may become targets of attacks. However, the security disadvantages brought by the Restaking mechanism may affect the entry of AVS to a certain extent.
Risks of LSD collateral: Project parties that use LSD collateral as security collateral need to consider the credit and security risks of the LSD platform itself, which adds a layer of risk.
Although EigenLayer demonstrates the advantages of the innovative re-staking protocol, the overall risks need to be considered. At the same time, EigenLayer's centralized governance model may lead to governance deficiencies or negative impacts such as complexity of governance and slow decision-making process.
Summary
EigenLayer’s concept of exporting ETH security emphasizes the importance of the blockchain ecosystem Interoperability. This interoperability helps build a more powerful and secure blockchain network, laying a solid foundation for future development. Provides security and trust layers and supports multiple modules, such as consensus protocols, data availability layers, etc. It has completed three rounds of funding and is valued at $500 million. As an innovative protocol, it has great opportunities for future development.
I believe you have also learned about the methods of early participation in this project in major news, social platforms and various KOL recommendations, so this article will not go into details. BiB Exchange believes that EigenLayer is not just an independent platform, but a part of the entire Ethereum network. It is also a unique project that can compete with Celestia and Polygon, and also chat with Cosmos. Of course, there are also many voices of criticism and questioning. This article elaborates on the relevant principles in detail. We also hope that readers will make more active judgments and pay more attention to the re-staking ecosystem.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance

















