Author: Kyle Ellicott , Yan Ma, Darius Tan, Melody He, Spartan Group; Translation: 0xjs@金财经
"Bitcoin Layer: No Trust in the Financial Era" Tapestry is a research report on the development of the entire Bitcoin ecosystem. The report was written by Kyle Ellicott of the Spartan Group team and multiple experts who provided feedback and insights and generously gave their time to review the final version of this article. This part is the third in a series of four articles.
The concept of “Bitcoin Layers” introduced in 2018 represents a key shift in the development of Bitcoin and solves its scalability challenges. Historically, various efforts to enhance Bitcoin L1 have had a common goal: facilitating off-chain transactions to increase the scalability of the network. These efforts are underpinned by the secure settlement layer provided by L1. The Bitcoin layer has become a suite of solutions spanning L2, L3, data and application layers, etc., drawing insights from Ethereum’s layered architecture. These innovations reflect the network’s adaptive response to its inherent limitations, demonstrating a path toward a more robust and versatile blockchain infrastructure.
The emerging Bitcoin layer introduces a variety of features that change the capabilities of the network. These layers provide:
Smart contract programmability: implemented directly on the Bitcoin network Complex financial and contractual transactions.
Increased throughput speed: Significantly reduces transaction processing time, reaching speeds of less than 30 seconds on some tiers.
BTC trust-minimized movement to L2: Promote safe and efficient movement of BTC between layers, providing solutions to the centralization problem of the federated approach solution.
Reduced costs: Lower transaction costs, making Bitcoin transactions more accessible to a wider user base.
Asset Issuance and Rollup: Provide new ways for asset creation and transaction bundling to improve efficiency.
Interoperability and Privacy Measures: Enhance the network’s ability to interact with other blockchain systems and protect user privacy.
Virtual Machine (VM) and specific features:Supports a variety of applications including gaming, finance, media and decentralized science (DeSci) .
These layers are strategically built on top of Bitcoin’s L1, utilizing L1 as the underlying platform, similar to the “cold storage” of BTC assets. This layered structure not only allows for seamless asset movement across different layers, it also frees up Bitcoin’s $850 billion in idle capital. As a result, applications that leverage these layers benefit from Bitcoin’s renowned security and stability.
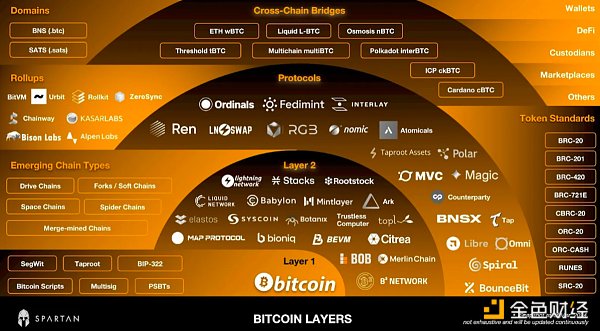
Bitcoin layers map (March 2024)
As of the fourth of 2023 During the quarter, significant progress was made in Bitcoin layer development, with L2 solutions making significant progress. The ecosystem has expanded to include sidechains, drivechains, merged mining chains, and PoS chains. This period also marked the emergence of various protocols, token standards, cross-chain bridges, rollups and other innovative solutions.
These developments are not only technological improvements; They represent a paradigm shift in Bitcoin’s utility, opening up new avenues for user adoption and application deployment. This layered approach emphasizes Bitcoin’s ability to evolve and adapt, solidifying its place in a rapidly evolving digital world. The following sections detail key innovations in these categories, illustrating the dynamic and forward-looking nature of Bitcoin’s layered ecosystem.
The Big Four Bitcoin L2
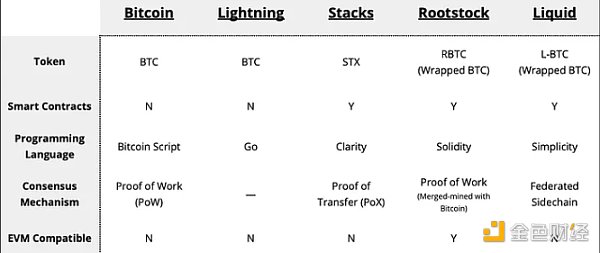
The existing main Bitcoin layers are dominated by the "Big Four" - Stacks, Lightning, RSK and Liquid. Together, these four entities conduct the majority of L2 transactions, shaping the landscape of scalable solutions for Bitcoin. Each of these L2 solutions has unique features and capabilities that uniquely contribute to the growth and scalability of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
 < /p>
< /p>
1. Stacks
The Bitcoin L2 project was launched in 2017 by Princeton computer scientists Ryan Shea and Muneeb Ali to provide smart contracts for Bitcoin. The initial version of the Stacks network launched in January 2021, allowing smart contracts and decentralized applications to use Bitcoin as a secure L1. Stacks Bitcoin L2 activates the Bitcoin economy with its Proof-of-Transfer(PoX)consensus mechanism, which is identical to the Bitcoin Proof-of-Work(PoW)consensus < /strong>Run in parallel and reuse its computing power.
The network is further secured through "Stacking", where Stacks token holders submit the native token STX (currently Stacking $252.87 million per cycle) to verify transactions, secure the Stacks network and earn BTC rewards.
Smart contracts on Stacks are coded in Clarity, a human-readable native language that responds to Bitcoin transactions and atomic swaps of assets with BTC.
The STX token is used as Gas on L2 and was the first SEC-qualified token issuance in 2019. It was later launched in 2021. Before the launch of the network, it was decentralized and filed with the SEC as a non-securities.
STX is a top 50 project and the only Bitcoin L2 with a native token, and is also ranked in the top of CoinMarketCap at the time of writing. Out of 100. In the 2022 Electric Capital Developer Report, the company ranked 38th in developer activity across the industry, with monthly active developers increasing since 2015 and as of October 2023, active developers 175 people.
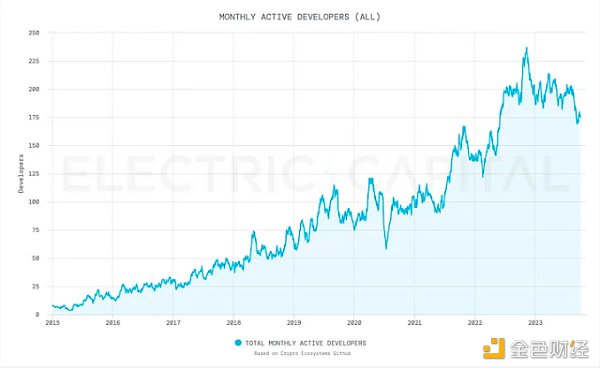 Monthly active developers on Stacks. Source: Electric Capital
Monthly active developers on Stacks. Source: Electric Capital
Upcoming Catalysts:
< strong>NakamotoThe network upgrade (Q2 2024) will enable Stacks to enable fast and cheap BTC transfers on L2 with 100% Bitcoin security (reorg resistance). Additionally, transaction speeds on the network will be reduced by a factor of 1,000 from the current settlement times of over 10-30 minutes for Bitcoin to approximately 5 seconds. As of December 2023, two major milestones in the development of the upgrade have been achieved, v0.1 (called " Mockamoto") and Neon (v0.2) "controlled" testnet with single miner, single Stacker and Stacker signature.
sBTC is a decentralized 1:1 Bitcoin-backed asset that can be traded on Bitcoin and Stacks Deploy and move BTC between (L2) and use it as Gas in transactions without the need for additional assets. sBTC transfers are 100% guaranteed by Bitcoin computing power. To reverse the transaction, an attack must be carried out on Bitcoin itself.
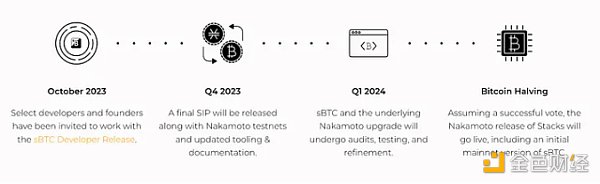
sBTC release roadmap. Source: sBTC
The resulting Stacks layer makes Bitcoin a fully programmable asset in a decentralized manner. If successful, it will drive more demand for Stacks and Bitcoin. This could provide an environment for the Bitcoin economy to accelerate, unlock hundreds of billions of dollars in passive Bitcoin capital, and make Bitcoin the backbone of a more secure network.
2. Lightning Network
Released in 2018 (white paper in 2016), the Lightning Network supports Bitcoin micropayments and can be made instantly anywhere Shipping costs next to nothing. The Lightning Network’s powerful transaction processing capabilities and its growing popularity highlight its role in enhancing Bitcoin’s scalability and transaction efficiency.
The protocol uses smart contracts to create payment channels that combine on-chain settlement and off-chain processes.
When the channel is closed, transactions are merged and sent to the Bitcoin network. The native asset of the Lightning Network is Lightning Bitcoin (BTC).
In August 2023, the network was processing approximately 6.6 million routing transactions, or approximately 213,000 transactions per day, accounting for approximately 52% of the network's public capacity. These approximate figures represent a 1,212% increase compared to K33’s estimated 503,000 Lightning payments in August 2021.
Additionally, on average, the Lightning Network handles at least 47% of Bitcoin’s on-chain transactions every day.
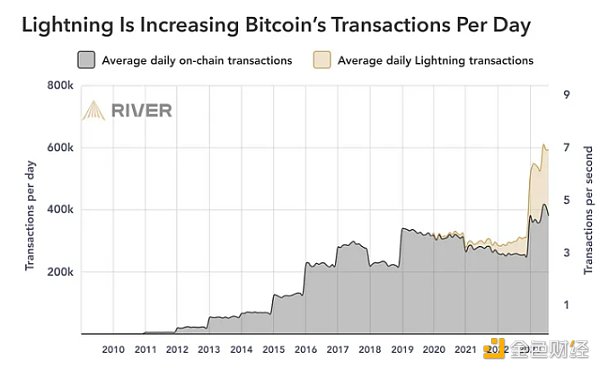 The Lightning Network is increasing Bitcoin’s daily transaction volume. Source: River
The Lightning Network is increasing Bitcoin’s daily transaction volume. Source: River
3, Rootstock (RSK)
Founded in 2015 by RSK Labs, the network is ItsRSK Virtual Machine (RVM) brings EVM-compatible smart contracts to Bitcoin. With RVM, developers can port Ethereum contracts to Bitcoin. RSK’s native asset is Smart Bitcoin (RBTC). RBTC maintains a 1:1 peg to BTC, but is not trustless. Since its block security is based on “merged mining,” it continues to rely on centralized custodians, which highlights the trade-off between security and decentralization in L2 solutions.
4. Liquid Network
Released by Blockstream in 2018, the Liquid Network sidechain enables users to perform fast, secure and confidential transactions on Bitcoin. trade. Liquid operates independently of Bitcoin, has its own ledger, and has abandoned utilizing Bitcoin’s PoW consensus mechanism in favor of the Liquid Alliance of approximately 60 members who serve as the creators of new blocks. Liquid’s native asset is Liquid Bitcoin (L-BTC), which is a “wrapped” version of BTC. This independent operation of Liquid Network demonstrates the diversity of approaches within the Bitcoin L2 ecosystem.
Today, while no Bitcoin L2 holds more than 10,000 BTC or has a user base in the millions, the potential for exponential growth is still huge, highlighting the future scalability of these solutions in Bitcoin and key role in function. As Bitcoin L2 technology advances, they have begun to open up multiple avenues to enable rapid experimentation around BTC while maintaining the stability of the core network. The success of future L2 solutions depends on their ability to provide a complete execution environment similar to the EVM, address current limitations, and foster a more inclusive development environment.
Coping with the L2 Dilemma
In the pursuit of unlocking scalability in the Bitcoin layer, a new problem has arisen: the L2 Impossible Trilemma. Revisiting blockchain’s Impossible Triangle and applying it to Bitcoin L2, we see that it’s still the same, but with slightly different trade-offs. For the L2 Impossible Triangle, the choices are limited to:
A. Become an open network or federation.
B. Whether to introduce new Token.
C. Have a full/global virtual machine (VM) or have limited off-chain contracts.
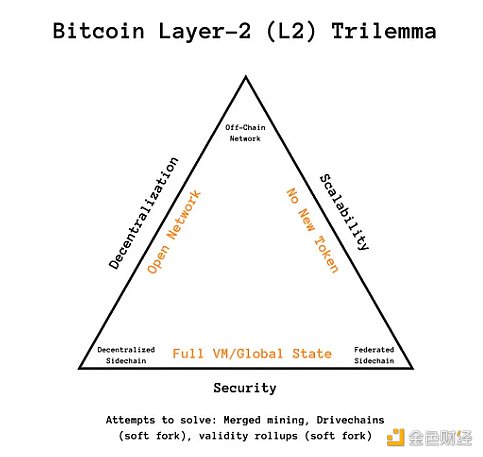
The industry has witnessed Try turning this triangle into a square to repurpose existing Bitcoin mining rigs to mine L2. RSK (formerly Rootstock) and Drivechains are examples of these attempts. In this approach, incentives for miners become an open issue, and similar gas fees (especially in the early days) may not be enough to handle the incentive issue.
Lightning selects A and B, but does not have the global state of the full VM.
Stacks chose A and C using the new token (STX).
Liquid chose B and C to operate as an alliance.
Early discussions among developers revolved around new opcodes for Bitcoin (L1), which, in theory, could help eliminate today's triangles. New opcodes, such as op-snark-verify , can be used with Bitcoin (L1) to verify L2 computations. However, the historical challenges of implementing soft or hard forks in Bitcoin suggest that this solution may not be feasible in the short term.
Going forward, the Bitcoin ecosystem will likely expand beyond the current handful of L2 solutions and require hundreds of solutions to fully explore and develop the network's potential. Currently, developers are considering these options to balance the trade-offs in the L2 dilemma. There is an emerging trend of leveraging open networks, where anyone can mine and enter/exit freely, providing a complete virtual machine (VM) environment for smart contracts, with global state as an essential attribute. This approach mirrors the successful structure of other blockchain ecosystems such as Ethereum and Solana and is expected to shape the future trajectory of Bitcoin L2 progress.
Emerging Innovation
In addition to the four established L2s, rapid experimentation continues with numerous infrastructure tools, standards, and protocols project. These innovations are actively introducing new classification definitions as technology stacks take shape to fill existing technology gaps in application requirements.
Ark is an experimental L2 protocol launched in May 2023. Ark allows users to make low-cost and anonymous off-chain, scalable Bitcoin payments by providing liquidity to the network through its always-on, trustless intermediary, the Ark Service Provider (ASP). Because transactions are conducted on the protocol, recipients can receive payments without accessing incoming liquidity while protecting recipient privacy at a lower cost than the Lightning Network.
Babylon Released during Cosmoverse 2023, Babylon is a PoS network powered by two secure sharing protocols between Bitcoin and other PoS networks, Bitcoin Timestamps and Bridgeless Pledge composition.
Botanix (Spiderchain L2) is a PoS Bitcoin EVM that utilizes a multi-signature distributed network to facilitate two-way pegs with Bitcoin and enhance its interoperability .
Interlay is a modular programmable network between Bitcoin and the multi-chain ecosystem, running as a Polkadot parachain. Interlay has created a decentralized Bitcoin bridge that can mint iBTC, or “valuable BTC,” its multi-chain 1:1 Bitcoin-backed asset.
MintLayer is a PoS network designed to serve as a sidechain for Bitcoin, optimized for DeFi related activities including atomic swaps. With MintLayer, there is no need to use a wrapped version of Bitcoin or a smart contract language (i.e. Solidity, etc.) to create tokens, as the network is UTXO-based and requires the creation of transactions that embed additional data. The network aims to generate a block every 120 seconds using a verifiable random function, with finalization after 1,000 blocks.
Ordinals. The innovative Ordinals theoretical framework was released in June 2022, triggering a cultural revolution based on Bitcoin. In December 2023, just months after the release of Ordinals (Ord), developers started using Ordinals, which does not require separate sidechains, tokens or Bitcoin Core updates and supports Bitcoin Inscription. Inscriptions are immutable Bitcoin NFTs that contain original file data (video, audio, images, executable software, etc.) addresses, wallets, etc. that are permanently recorded on Bitcoin and can be transferred or sent to Bitcoin.
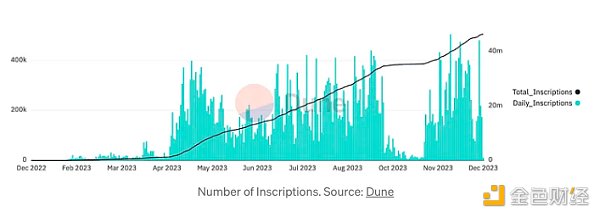
The number of inscriptions. Source: Dune
Ordinals' dramatic growth will only increase exponentially as new experiments, infrastructure tools, and standards emerge. In the year since the first inscription on December 14, 2022, the total number of inscriptions in the first 90 days has exceeded 460,000 and has exceeded 46.2 million so far this year, generating approximately 3,365 BTC (approximately $148.8 million) in fees during that period.
RGBNetwork (Really Good Bitcoin) is a Bitcoin-based protocol that utilizes the Lightning Network, rather than a token protocol.
Threshold Network is a privacy-centric convergence network between Keep and NyCypher, allowing users to leverage Keep Network to protect private data through off-chain containers and NuCypher's privacy tools capabilities for key management and dynamic access control. Threshold is the creator of the tBTC Bitcoin Bridge, a decentralized and permissionless bridge between Bitcoin and Ethereum.
These protocol experiments represent only a small portion of what developers release each week. The constant introduction of new protocols and standards shows that the Bitcoin technology stack is dynamic and constantly evolving. The momentum generated by these developments, especially in the context of the upcoming Bitcoin halving event in Q2 2024, indicates a bright future for further innovation and adoption within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
The Rise of Token Standards
Following several emerging protocols, the community has also begun to try new token standards, providing solutions that can take advantage of Bitcoin’s unique architecture An early preview of the token design. In its infancy, it is important to highlight those that have been introduced to developers and note its similarities to its peers in the Ethereum ecosystem.
BRC-20 is an experimental token standard created by DOMO and released in early March 2023 to create fungible tokens on Bitcoin. The standard leverages Ordinals inscriptions and JSON data, mirroring Ethereum’s ERC-20 standard but tailored for the feature-limited Bitcoin ecosystem. Several platforms quickly followed suit, rapidly developing tools and launchpads for experimental token standards (ALEX, Bitget, Leather, OrdinalsBot, UniSat Wallet, Xv erse, etc.). Notably, the ORDI token was the first token to be deployed under the standard and by May 2023 it had a market cap of over $1 billion, ranking 52nd on CoinMarketCap and with a market cap of over $1.3 billion at the time of writing. Dollar.
BRC-721E is an experimental token standard similar to the widely adopted ERC-721, implemented by a collaboration between Bitcoin Miladys, Ordinals Market and Xverse. In its initial state, the experimental standard allows users to connect NFTs from Ethereum to Bitcoin, documenting a less detailed version of the NFT with links back to the original Ethereum version and airdrop functionality. Once the NFT is bridged, it will automatically appear on the Ordinals Market. This experiment opens up many possibilities for cross-chain interactions between the two networks.
ORC-20 is an experimental open token standard designed to improve the BRC-20 experiment and achieve backward compatibility and flexible namespace between BRC-20 As well as the introduction of UTXO to prevent double spending in future developments.
ORC-CASH is an experimental token standard based on the Ordinals protocol, designed to best fit the UTXO security model and serve as a simplified version of the ORC-20 standard.
RUNES is an experimental fungible token protocol proposed by Ordinals creator Casey Rodarmor in September 2023 as an alternative to the BRC-20 standard. Runes does not intend to rely on off-chain data or require native tokens, instead holding balances via UTXO and using specific script conditions to identify transactions.
SRC-20 is a token standard created by Mike In Space, known as Bitcoin Stamps (Bitcoin Secure Tradeable Art Maintenanceed Securely), which is stored directly in the Bitcoin block Digital artifacts on the chain that cannot be pruned because they exist in the UTXO set (unsent transactions).
STX-20 is an experimental inscription protocol standard released in December 2023 for embedding protocol information in the metadata transmitted by STX tokens (34 only symbol limit) to create and share digital artifacts on the Stacks blockchain. The release of STX-20 resulted in one of the largest blocks on the Stacks network, with over 10,000 transactions.
Privacy and Security Solution
In addition to the extension, the developers have also made a huge effort to bring Rollup to Bitcoin and add an important layer of security s hard work. In the early stages of development, some of the notable experiments in this category include Urbit, Rollkit, ZeroSync, Alpen Labs, Bison Labs, Chainway, Kasar Labs, and many more.
Other experiments in the ecosystem include purpose-built protocols such as 1btc, BNSx and Rooch Network, as well as emerging classification definitions such as Drivechains, Spiderchains, Federated Chains, Spacechains and Softchains, each witness Projects are developed with the intention of contributing to a broad technology stack.
These innovations enhance the intrinsic value of the network and position Bitcoin as a more versatile and secure platform. They are critical to expanding the network and improving its ability to support a variety of applications. As these technologies continue to evolve, they are expected to greatly improve the network's ability to handle increasing transaction volumes and diverse applications, while maintaining the fundamental principles of privacy and security. The ultimate goal is to create a user experience that is smooth enough without having to worry about supporting infrastructure.
The future of Bitcoin finance
The Bitcoin layer, marked by advances in Layer 2 solutions and privacy-enhancing technologies, is shaping a trustless finance ecosystem. These developments represent a major shift in Bitcoin’s functionality and potential impact on the financial sector. With its enhanced privacy, security, and scalability, Bitcoin is expected to support a wide range of financial applications, from traditional transactions to innovative DeFi solutions. This shift highlights Bitcoin’s growing role not just as an asset but as a fundamental element of a safer, more efficient and inclusive financial landscape. As these technologies gain popularity, Bitcoin’s contribution to the trustless financial system becomes increasingly important, cementing its position as a key pillar of the future of finance.
PS: Latest Bitcoin L2
The Bitcoin ecosystem has grown significantly since our initial report. Notably, Bitcoin’s value surged above $63,000 for the first time since November 2021, marking a significant market rally. Meanwhile, the Bitcoin L2 landscape is rapidly expanding, highlighted by DWF’s tracker, which now lists 28 new Bitcoin L2 projects. How do we accurately assess the potential of these L2s?
Bitcoin Magazine has an editorial policy that defines true Bitcoin L2 based on three criteria: the use of Bitcoin as a native asset, the use of Bitcoin for transaction settlement execution, and the functionality of Bitcoin Dependence, which sparked discussion.
This definition classifies many emerging platforms, especially those that use their own tokens for decentralized scaling, as "meta-protocols" or "parasitic chains" rather than true L2 solutions .
Despite these classifications, the broader goal is to enhance the entire ecosystem. Notable innovations that piqued our interest include:
Merlin Chain: Led by the team behind BRC-4 20 and Bitmap, this asset-centric L2 aims to transform the famous L1 The assets and their user base are tied to L2, with total value locked (TVL) exceeding $2 billion as of the end of February.
B-squared Network: The platform introduces a modular approach, combining zk-rollup as an execution layer with B² Hub, integrating decentralized storage with the Bitcoin network , thus forming a comprehensive ecosystem including consensus, data availability and settlement layer.
BounceBit: This is a Bitcoin re-mortgage chain where users can earn original CeFi returns while utilizing LSD for BTC mortgage and on-chain farming, basically on Bitcoin The currency is “remortgaged”. With the successful financing, TVL also surged to more than $500 million this month.
BOB: The project utilizes the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) to create and execute smart contracts.
BEVM: Through the combination of Bitcoin light nodes and the POS consensus of the Taproot threshold contract, decentralized interaction between Bitcoin and BEVM is achieved.
Citrea: This is zkEVM on Bitcoin, where the proofs are engraved in Bitcoin and optimistically verified via BitVM.
It is worth noting that the rise of the new Bitcoin L2, mainly promoted by the Chinese team and supported by the large Chinese community, brings a large amount of TVL, which shows that the Bitcoin ecosystem is undergoing major changes to the east. change.
These projects have successfully improved Bitcoin’s cross-chain capabilities, leveraging their previous building experience to achieve substantial growth. However, this surge has also raised concerns about the potential for liquidity fragmentation in L2 solutions, as seen with Ethereum.
Instead, there are opportunities to expand the use of Bitcoin assets and allow more Bitcoin users to participate in these new platforms. Despite the similarities between many of these products, the future of Bitcoin L2 remains uncertain and dynamic, pending further development.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance


 < /p>
< /p>







