Author: Lindabell, Source: Chainfeeds
The Dencun upgrade will take place on March 13th. As an important node in the development of Ethereum, the EIP-4844 introduced in this upgrade will significantly improve the efficiency of the Ethereum L2 network and help Ethereum achieve higher performance on Rollup by introducing a new Blob space data structure. throughput and lower costs.
In this context, ChainFeeds invited Ethereum OG Gulu to discuss key issues in the Ethereum ecosystem, including the understanding of the chain and the importance of decentralization in the development of the blockchain. As well as the potential development in areas such as DeFi, stablecoins and value storage, etc.
Gulu is the Chinese compiler of the Ethereum white paper and has participated in the Ethereum crowdfunding. In addition, he created the blockchain education platform Bihu and the multi-chain smart wallet MYKEY, and is also the evangelist of DeGate.
Key points:
1) The endgame of the blockchain industry is Modular Blockchain, that is, Layer1 + Layer2 , Layer 3 may appear in the future;
2) Blockchain provides a "non-state independent space", promotes the development of global financial infrastructure, and enables any user to conduct transactions freely through private keys. And will derive unexpected applications;
3) When the throughput of the underlying infrastructure is not a problem, the blockchain trading paradigm will change, and the order book trading model may become the final form;
p>
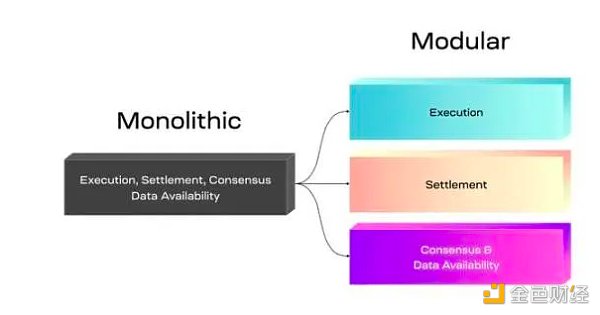
Blockchain Endgame: Who is better, modular blockchain or monolithic blockchain?
The debate between modularity and monolith in the blockchain field has never stopped, and each camp firmly believes that its own solution is superior. Twitter is filled with a lot of controversy about these two solutions, involving many issues such as cost, speed, decentralization and scalability. In this Spaces, Gulu also expressed his views. He believes that the endgame of the entire blockchain industry is a modular blockchain, that is, a combination of Layer1 and Layer2, and elaborated on his views from the perspectives of Gas cost and decentralization.
Gas Cost
In a single blockchain, each consensus node must verify every transaction in every block. This means that each node will bear a huge computational burden when processing a large number of transactions. For example, if the transaction demand of the blockchain grows to 100,000 transactions per second, then each consensus node must process 100,000 transactions per second, which will be a huge challenge.
In contrast, Gulu believes that the gas cost of modular blockchain is lower. Taking the Ethereum Rollup expansion route as an example, Layer 1 provides computing and data storage services, and Layer 2 handles actual transactions, which will eventually evolve into application transactions occurring on the second layer. Gulu gave an example. Assume that there will be 50 Layer2s in the future. Each Layer2 can process 2,000 transactions per second. The entire modular ecosystem can process 100,000 transactions per second. The verification of transactions is ultimately completed on the Layer1 node. Such a model is more economical for the entire ecosystem because every node does not need to verify and calculate every transaction, but only pays the hardware cost of 2000 transactions per second. In addition, after the Cancun upgrade is completed, Layer 2 will become very cheap to use BlockData, and the gas price at the data level is expected to drop by at least one order of magnitude, and possibly even two orders of magnitude. Taking the cost and Gas cost into consideration, for different Layer2, the Gas cost can be reduced by at least 80%.
Degree of decentralization
From a decentralization perspective, there may ultimately be only a dozen or so individual blockchains left. Even fewer nodes, which are likely to be operated by data centers. In this case, governments or other entities can interfere with the operation of the blockchain by controlling these nodes, thereby affecting its decentralized nature. Taking Bitcoin as an example, the government may limit its issuance quantity or control transaction rules. Guru said,In this case, blockchain will lose its core value, which is independence. As a result, a monolithic blockchain may not be truly decentralized and its ecosystem may become fragile and vulnerable to attack.
In contrast, in the modular blockchain, Layer 2 actually does not have strong independence, because the purpose of the overall design is to make Layer 2 lose some of its independence and manage it The rights belong to Layer1. In other words,While Layer2 still retains a degree of autonomy, final power control lies with Layer1. Gulu said that this design pattern can retain the decentralized nature of Layer1’s entire network. Arbitrum, for example, has implemented trustless and permissionless features, namely Trustless and Permissionless.
On the "non-state space" of blockchain: trust, expansion and financial revolution
The term "non-state space" historically refers to the early stage of the formation of a country, most of which The region has not yet been ruled by the state, so a large "non-state space" is formed between the points where the state is distributed. Various primitive forms of human organization exist in these spaces, such as tribes. In this concept, breaking away from national borders means gaining independence and freedom. In the early days, the scope of the state was usually limited to a radius of about 48 kilometers, which was the area over which the state had effective control.
Mapping this concept into the blockchain is the so-called independent space, which means independence from the national system. This independent space provides an environment of decentralization, autonomy and freedom, allowing individuals to better control their own data and assets. Similar to the early "non-state space", the "non-state space" on the blockchain is a network composed of decentralized nodes without a centralized governing body.
Gulu pointed out that Bitcoin is the earliest application in the "non-state space" of blockchain, demonstrating the perfect fit between the decentralization characteristics and the currency market. Subsequently, more and more flexible applications have emerged based on blockchain technology architecture, such as DeFi, NFT, and lending. The essential block of these applications and Web2 is to utilize the "non-state space" of the blockchain. So why should we choose to build applications on the blockchain? What advantages can the "non-state space" of the blockchain bring? Gulu also interpreted:
Trust:Blockchain applications increase users’ trust in applications. Because its data is publicly visible and cannot be tampered with. For example, the contract for issuing tokens can be made public on the chain, and anyone can verify its validity;
Expansion space:Gulu said in "< a href="https://www.jinse.cn/blockchain/3675562.html" target="_self">Ending Interpretation (Part 1): Ethereum is winning" The article also mentioned that blockchain The "non-state space" will gradually develop into an Internet financial center, covering various DeFi applications on Bitcoin and Ethereum, decentralized transactions, mortgages, stable coins, etc., providing users with more financial options and services; < /p>
Product-market fit:Gulu especially mentioned the product-market fit of stablecoins in the "non-state space" of the blockchain, especially in Cross-border payments. Unlike traditional international remittances, which are expensive, it provides low transfer fees and efficient transaction speeds, providing convenience for global economic activities.
Dollarization process: Although the US dollar consensus is stronger, there are national border issues, resulting in a slow dollarization process. However, with the popularization of blockchain technology, a second wave of dollarization may emerge, allowing products like the U.S. dollar to be more widely used in the blockchain "non-state space";
Asset blockchainization:Gulu believes that the demand for asset blockchainization is inherently attractive. Blockchain technology makes it possible to put assets on the chain, further expanding application scenarios. For example, the real estate certificate is uploaded to the chain and becomes an NFT token, which can be used as a pledge to provide users with convenient lending services. From a long-term perspective, on-chain assetization is an exciting track that will lead to many innovations and applications;
Evolution of blockchain transaction paradigm
As the Evangelist evangelist of the ZK Rollup order book DEX DeGate, Gulu also shared his views on the future form of the exchange in Spaces.
DeGate is an Ethereum ecological decentralized order book protocol based on ZK Rollup, which requires no trust and supports permissionless currency listing. It has officially entered the mainnet stage on January 9 this year. So far, its TVL has reached US$64.67 million, and its cumulative transaction volume has exceeded US$200 million.
Gulu believes that decentralized transactions are crucial to the blockchain ecosystem. He said,When the blockchain throughput is enough to support 100,000 transactions per second, the cost of intra-chain transactions is the lowest and the most convenient for users. However, high GAS fees currently limit applications like DeFi, causing most transactions to still occur on centralized exchanges. But Gulu believes that as the throughput of the chain increases, more transactions will be completed on the chain in the future. He stresses that this will take some timebut once the throughput of the underlying infrastructure is no longer an issue, order books will eventually become the form of trading adopted by exchanges.
Gulu also mentioned that the earliest decentralized exchanges on the blockchain were actually based on order books, such as EtherDelta. However, as the number of users increases, gas fees rise, resulting in inefficiencies in the entire order book-based decentralized exchange. As a result, the AMM model came into being, and its biggest advantage is its high gas efficiency. However, in terms of the form of trading products, it has the disadvantage of low capital efficiency. Gulu pointed out thatThe reason why traditional exchanges such as the New York Stock Exchange and the Shanghai Stock Exchange choose the order book model is because the order book has the advantages of flexibility, high capital efficiency, and the ability to implement various complex trading strategies through APIs.
In addition, Gulu also summarized the characteristics of DeGate:
Asset autonomy Characteristics:Like all DEXs, DeGate private keys are kept by users, and assets are fully owned by users. No one can use or freeze users’ assets without authorization;
Order Book Trading: Provides a better experience, higher capital efficiency and greater flexibility;
No permissions Listing:Users only need to pay the Gas fee to list any ERC20 token that is compatible with the protocol
Decentralized grid trading:
strong>Similar to Uniswap V3, users can provide funds within a specified price range, and the protocol will automatically help users buy low, sell high, and earn the difference in a decentralized manner;- < p>Decentralized Fixed Investment: Allows users to set regular time intervals for buying and selling assets to smooth the impact of market fluctuations;
Free pending order transactions:Users do not need to pay gas fees and transaction fees.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance




