Why the Bitcoin Reserve Act could break the four-year cryptocurrency cycle
Bitcoin Reserve Act could break the halving cycle. Would this four-year cycle unfold differently? Are we entering a mythical supercycle?
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
Author: Climber, Jessy, cryptonaitive, Golden Finance
One day in the cryptocurrency world is like one year in the human world. Bitcoin has completed its fourth halving in history, and in a sense, one cycle is a hundred years.
Bitcoin has evolved over a four-year period, and each stage has refreshed people's cognition. From the initial payment currency to value storage and digital gold, or to the subversion and impact on sovereign currencies, mainstream financial systems and other fields, it has been questioned again and again to the moon, and has gained a mythical increase.
Just as science came to Europe in the Middle Ages, theology was shrouded and ignorance was rampant. But it could not stop the pace of truth after all. Adam Back, Nick Szabo, Satoshi Nakamoto, Hal Finney, Vitalik... batches of evangelists have come one after another, pioneers have benefited, and believers have eternal life.
Bitcoin is a virtual currency and a digital currency, but it is also the Noah's Ark when the financial tsunami hit. For this giant ship, let's take a look at how it was built bit by bit from the beginning.
Bitcoin halving, also known as "Halving", refers to a pre-coded event set in the Bitcoin protocol that occurs once every 210,000 blocks (about once every four years). Block halving refers to the process of reducing the amount of digital currency generated per unit time, mainly achieved by reducing block rewards.
The supply of Bitcoin is limited to 21 million units, and once that total is reached, the generation of new BTC will stop. Bitcoin halving ensures that the number of Bitcoins that can be mined per block will decrease over time. By 2140, all Bitcoins will have been mined, with the total expected to be just under 21 million.
The process is designed to control the issuance of new Bitcoins and maintain their scarcity, thus ensuring a limited supply of Bitcoin. Essentially, halving is the reduction of the reward given to miners in half.
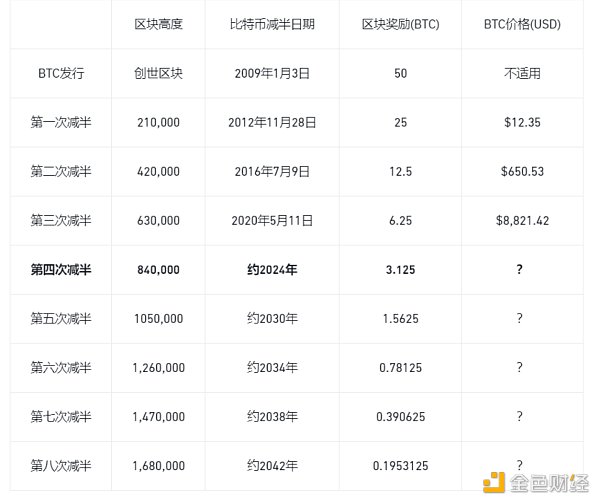
Bitcoin halved at block height 840,000 on April 20, and the block reward will drop from 6.25 bitcoins to 3.125 bitcoins after the halving.
Public data shows that miners currently bring about 900 bitcoins to the market every day. After the halving, this number will drop to around 450 BTC.
Halving has a large impact, mainly because the event usually causes market volatility and increases speculation in the cryptocurrency field; reshapes the mining industry, miners' profit points decrease; and stimulates technological innovation and community development within the blockchain ecosystem. However, the halving event may also hedge against inflation and enhance Bitcoin's attractiveness as a long-term investment asset.
Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin white paper on October 31, 2008, and the Bitcoin Genesis Block was born on January 3, 2009. Halving is to control the supply of Bitcoin in circulation. By reducing block rewards, the speed at which new Bitcoins enter the market will slow down, which will help prevent inflation and ensure that the value of Bitcoin remains stable.
By the halving on April 20, 2024, Bitcoin's inflation rate is expected to drop from about 1.75% to only 0.85%.
The reason why Bitcoin was born was mainly because some countries would issue more money without limit. Satoshi Nakamoto hoped that there would be a currency that would not be controlled by anyone and that value could be transferred between any two nodes, so he designed this peer-to-peer trading system.
The law of market supply and demand in economic theory shows that if the circulation of a certain commodity is not restricted, hyperinflation will easily occur and the price of the commodity will be greatly reduced. Conversely, when supply decreases and demand remains unchanged or increases, the value of the asset may rise.
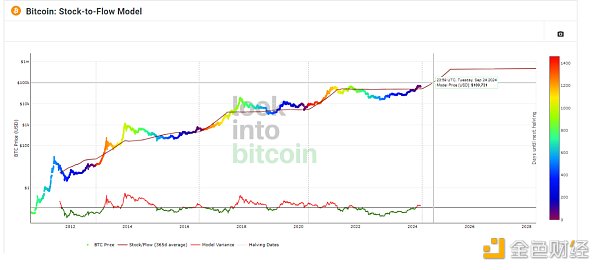
This halving mechanism is also studied by institutions. The figure above shows the Bitcoin stock/flow ratio model, which studies the annual mining volume and total inventory to try to predict the future value of Bitcoin. Backtesting has proved that it can simulate past price curves very accurately.
According to the conclusion drawn by the model, the scarcity of Bitcoin is the main driving force of price. After clarifying the potential relationship between price and scarcity, holders will realize the value of Bitcoin as a value storage tool.
In terms of block time, the Bitcoin mining algorithm is programmed to find a new block every ten minutes. As more miners join the network and add more hash power, the time required to find a block will decrease. In order to restore the 10-minute target, the mining difficulty is recalculated every two weeks or so. As the Bitcoin network has grown dramatically over the past decade, the average time to locate a block has remained around 10 minutes (about 9.5 minutes).
A block is produced in about 10 minutes in the Bitcoin network, and a certain amount of Bitcoin will be continuously mined. Setting the Bitcoin reward to halve every 210,000 blocks can effectively gradually reduce the inflation rate of Bitcoin, thereby preventing the occurrence of hyperinflation.
Satoshi Nakamoto wrote in 2009: "From this perspective, Bitcoin is more like precious metals. Instead of adjusting the supply to maintain its value, the supply cap is set in advance, allowing the value to change accordingly. As the number of users grows, the value of each token will also increase. This can form a positive feedback loop; as the number of users increases, the value will gradually increase, thereby attracting more users to profit from the upward trend of the currency price."
Market participants often regard Bitcoin halving as a precursor to a bull market. This is because the price of BTC has hit new highs without exception after the previous three halvings, and many investors have the same expectations for the halving on April 20, 2024.
Basically, BTC will halve every time miners add a total of 210,000 blocks to the BTC blockchain. In the past, after each BTC halving, the price of BTC has risen sharply for a long time.
Halving Schedule:
First Halving (2012): The first Bitcoin halving occurred on November 28, 2012, and the mining reward was reduced from 50 bitcoins per block to 25 bitcoins.
Second Halving (2016): The second halving, which took place on July 9, 2016, further reduced the block reward to 12.5 bitcoins.
Third Halving (2020): The third halving, which took place on May 11, 2020, reduced the reward to 6.25 bitcoins per block.
Fourth Halving (2024): The fourth halving, which took place on April 20, 2024, reduced the reward to 3.125 bitcoins per block. Future halvings will continue until the maximum supply of 21 million bitcoins is reached, which is expected to be achieved around 2140.
As of today, Bitcoin has undergone four halvings, which are called halving cycles in the industry. In the past, BT prices rose sharply before and after almost every BTC halving.
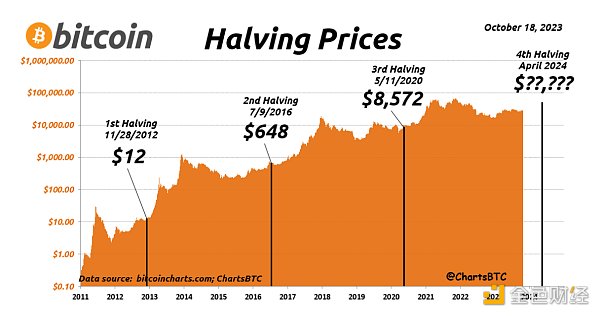
From the above figure, we can see that since the birth of Bitcoin, its cycle has been very stable.
The first halving cycle: 2012.11.28-2016.07.10. This halving cycle led to two bull markets in April and November 2013. In the first bull market, the price of Bitcoin rose from $12 to $288, a price increase of 2,300%; in the second bull market, the price of Bitcoin rose from $66 to $1,242, a price increase of 1,782%.
Second halving cycle: 2016.07.10-2020.05.12. This halving cycle led to a bull market in December 2017. In the 2017 bull market, the price of Bitcoin rose from $648 to $19,800, a price increase of 4,158%.
Third halving cycle: 2020.05.11-2024.04.20. The halving cycle resulted in two bull runs in April and November 2021, with the first bull run seeing the price of Bitcoin rise from $8,572 to $69,000, a 741% increase. The second bull run saw the price of Bitcoin rise from $15,476 to $737,770, a 376% increase. Given the current price of Bitcoin, the crypto market is still in a bull run.
Historically, Bitcoin prices often fluctuate significantly before and after halving events. In the months leading up to the halving, market expectations and speculation about possible price increases from future supply cuts often drive prices higher. After the halving event, Bitcoin typically experiences a significant bull run.
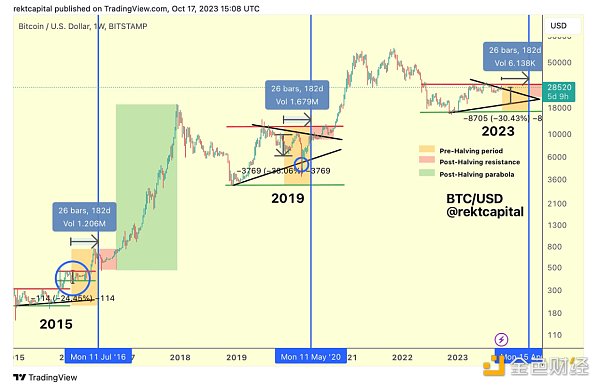
As can be seen from the above figure, before each BTC halving, the market will have a bear market trough period of about 1.3 years. After that, the market will take about 1.3 years to reach its peak. In view of this, the entire ups and downs of the market will take about 2.6 years. In addition, based on the BTC halving events that have occurred in the past, the BTC price bottomed out about 477 days before the BTC halving occurred. In addition, it takes an average of 480 days from the date of halving to the peak of the next bull market cycle.
For example, after the 2012 halving, the BTC price rose from $12.25 to $127 in 150 days. Similarly, after the 2016 halving, the BTC price rose from $650.63 to $758.81 in 150 days. Finally, after the 2020 halving, the BTC price rose sharply from $8821.42 to $10,943.00 in 150 days.
At the same time, looking back at previous halving events, Bitcoin will also encounter a retracement period. In 2016, the market experienced a sharp sell-off from around $760 to $540 before and after the halving, with a retracement of about 30%. The event in 2019 saw a larger retracement of about 38%.
This year is no exception. As of writing, the price of Bitcoin has retreated by about 14%.
However, according to the Bitcoin stock-to-flow ratio model mentioned above, after the BTC halving in 2024, the price of BTC may rise to more than $100,000. Crypto research institutions PlanB and Glassnode both predict that the price of BTC will rise and exceed $100,000 in 2024. Pantera Capital more specifically predicts that after the entire bull market cycle is over, the price of BTC will reach about $149,000 in 2025.
Historically, the Bitcoin cycle usually starts 12 to 18 months after the peak of the previous bull market, and the new historical high appears a few months after the halving. However, unlike in the past, this halving event is accompanied by the development of the US Bitcoin spot ETF, so the impact of the halving in this cycle may be weakened.
Investors should also note that the rise in Bitcoin prices after the halving is also associated with major macroeconomic events. For example, in 2012, the European debt crisis highlighted the potential of Bitcoin as an alternative value storage in economic turmoil, causing its price to rise from US$12 to US$1,100 in November 2013.
During the ICO boom in 2016, more than $5.6 billion was pumped into altcoins, which indirectly benefited Bitcoin, raising its price from $650 to $20,000 in December 2017.
It is particularly noteworthy that during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, massive stimulus measures have exacerbated inflation concerns, which may push investors into Bitcoin as a safe haven, causing its price to rise from $8,600 to $69,000 in November 2021.
The above information shows that although halving helps to strengthen Bitcoin's scarcity narrative, macroeconomic factors can also have a significant impact on Bitcoin prices. The risk of the crypto market is already high, and investors should be more cautious.
In order to more fully grasp the crypto cycle triggered by each round of Bitcoin halving, it is necessary to review the development epic of Bitcoin.
Like countless great things, Bitcoin did not come out of thin air, it also stands on the shoulders of predecessors.
It requires both technical reserves and ideological reserves.
The birth of Bitcoin requires a technological breakthrough in cryptography and digital currency.
The birth of asymmetric encryption in 1976: On November 1, 1976, cryptographers Whitfeld Diffie and Martin E. Hellman published the paper "New Directions in Cryptography". This breakthrough paper moved cryptography from symmetric encryption (the same key is used for encryption and decryption) to asymmetric encryption. This innovation paved the way for secure digital signatures, implementing public and private key pairs in encrypted transactions, and became an integral part of Bitcoin's functionality.
1977RSA Algorithm: One of the first viable public key cryptosystems, RSA comes from the initials of three founders, Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman.
1989DigiCash: David Chaum founded DigiCash, one of the first attempts at a completely anonymous and secure digital payment system. DigiCash was based on blind signature technology, built on public and private key pairs. Despite its innovative approach, its centralized model led to its failure. But DigiCash was an important forerunner to the development of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin.
With the development of the Internet, the late 1990s and early 2000s ushered in a period of innovation in digital currencies.
1996 e-gold (digital currency): e-gold was a platform created by Douglas Jackson and Barry Downey that allowed users to transfer gold ownership electronically. Its centralized structure became the focus of legal challenges, especially in terms of money laundering. This, combined with security issues, led to its eventual dissolution.
1997 Hashcash (proof of work mechanism): Adam Back invented HashCash in 1997 and proposed a proof of work system. Hashcash is a proof of work mechanism used to prevent spam and denial of service attacks. The proof-of-work principle was later introduced into the Bitcoin consensus mechanism by Satoshi Nakamoto.
1998 B-money (distributed ledger): Dai Wei, a Chinese-American scientist, proposed the B-Money electronic currency protocol. B-Money was envisioned as a decentralized, anonymous electronic cash system. One of the methods is that all participants keep a copy of all transactions, thereby ensuring collective and transparent verification. This protocol is the prototype of a distributed ledger, and Satoshi Nakamoto cited B-money when he created Bitcoin.
1998 Bit Gold: Nick Szabo invented Bit Gold, which was inspired by the real-world gold mining process and introduced a proof-of-work mechanism. Bit Gold requires participants to show proof of work to create a new unit of currency called "bit". Once this work is verified, the new "bit" will be added to a chain, linking it to the previous bits to form a public, tamper-proof record. And the Byzantine algorithm is proposed to prevent double spending. This system is the first prototype close to the Bitcoin architecture. Although Nick Szabo elaborated on the principles of Bit Gold, a fully operational model has never been fully developed or launched.
2004 RPOW (Reusable Proof of Work): Developed by Hal Finney inspired by Hashcash, Hal Finney believed that RPOW could serve as the basis for some kind of payment system. RPOW will promote the use of POW tokens as a form of P2P electronic cash by allowing tokens to be transferred and exchanged between people. This is why Hal Finney was interested in Bitcoin from the beginning when Satoshi Nakamoto shared the Bitcoin white paper on the cypherpunks mailing list. Hal Finney was the first person to run a Bitcoin node, the first miner, and the recipient of the first Bitcoin transaction.
Monetary issues have always been thought-provoking. If money is the crown of social science, then the business cycle is the jewel in the crown of social science.
In the classical period, countless sociologists such as Cantillon, John Law, and Hume have thought about the origin of inflation and the pursuit of sound money.
After entering modern times, in the process of pursuing explanations for capitalist economic crises and business cycles, a school of economists, the Austrian school, was born. The Austrian school believes that inflation is mainly a monetary phenomenon. It is inflation caused by the increase in the issuance of credit currency, which in turn distorts market price signals and causes companies in the market to make generally wrong decisions until a market liquidation, i.e. an economic crisis, occurs.
After entering the 20th century, with the credit era, especially the central bank's gradual expansion, the inflation caused by legal currency is finally like a tiger returning to the mountain. Humanity has witnessed countless cases of hyperinflation, such as the German mark and the Kuomintang gold yuan coupons.
There have also been notorious cases in the United States, starting with the Great Depression in 1929. Because the central bank's legal currency is afraid of competition from sound money. During the Great Depression, on April 5, 1933, US President Roosevelt issued Executive Order No. 6102, prohibiting the American people from owning gold. Executive Order No. 6102 was not repealed until 1975.
Satoshi Nakamoto must be quite familiar with this dark history of the United States. Perhaps this is why Satoshi Nakamoto entered April 5, 1975 as his date of birth when registering the pseudonym for the P2P Foundation.
In 1974, the Austrian economist Hayek won the Nobel Prize in Economics, and in 1976, Hayek published "The Denationalization of Money". In addition, in the 1980s and 1990s, Friedman, the American monetary school's criticism of inflation, and the revival of the Austrian school in the United States promoted by libertarians and the American Liberal Party.
Looking back, if Satoshi Nakamoto grew up in the 1980s and 1990s, he must have been deeply influenced by the Austrian school of economics and accepted its monetary proposition of "separation of money and state".
After the experiments of Adam Back, Dai Wei, Nick Szabo, Hal Finney and others in the previous section, Satoshi Nakamoto began to stand on their shoulders, integrate the strengths of each, and make original contributions.
In early 2007, Satoshi Nakamoto began to write code for Bitcoin. On November 17, 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto wrote in an article on the cryptography mailing list: "I believe that I have solved all these small details in the past year and a half when writing code."
Then came 2008, and the financial crisis that shocked the world in 2008. The financial crisis made people all over the world think about business cycles and inflation again.
And in this crisis, Satoshi and humanity were ready.
August 18, 2008, Bitcoin.org domain name registration: The domain name "bitcoin.org" was registered by an unidentified person using a privacy protection service to hide his identity. The identity of the person remains unknown, but many believe that he is Satoshi Nakamoto, the pseudonymous creator of Bitcoin. The website is a central hub for information about Bitcoin, including beginner's guides, technical documentation, and news and updates about the Bitcoin ecosystem. The domain is currently maintained by the open source community.
October 31, 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin white paper "Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System" on the Cryptography Mailing List: The most important contribution of the Bitcoin white paper is that it solves the double-spending problem through a decentralized mechanism called blockchain. Blockchain is a distributed public ledger that records all transactions in a secure and transparent manner. The Bitcoin network will rely on a PoW network to verify transactions and maintain the integrity of the blockchain.
On January 3, 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto mined the Bitcoin Genesis Block on a server in Helsinki: The Genesis Block contained a message in the coinbase parameter that read: "The Times January 3, 2009 Chancellor of the Exchequer is about to give banks a second bailout." This was the headline of the Times that day, reporting on the British government's plan to rescue bankrupt banks.
January 12, 2009, the first BTC transfer: 9 days after the launch of the Bitcoin network, Satoshi Nakamoto sent 10 Bitcoins to Hal Finney's Bitcoin address.
February 2009, the first Bitcoin wallet Bitcoin-Qt: Its user-friendly interface allows early Bitcoin adopters to create and manage digital wallets to send and receive Bitcoin. Starting from version 0.9.0, Bitcoin-Qt was later called the Bitcoin Core wallet.
March 17, 2010, the first recorded Bitcoin price ever: Bitcoin's price is first recorded at $0.003 on the now-defunct bitcoinmarket.com.
May 2, 2020, the first Bitcoin transaction: Laszlo Hanyecz buys two Papa John's pizzas for 10,000 Bitcoins, which are worth just a few dollars.
December 12, 2010, Satoshi's last post: Satoshi posts his last post on bitcointalk.org, adding some DoS restrictions and removing the previously introduced alarm system safety mode.
July 18, 2010, programmer Jed McCaleb founded Mt.Gox: Mt.Gox was originally a project initiated by programmer Jed McCaleb, who purchased the mtgox.com domain in 2007 with the intention of creating a platform for trading virtual cards for the game Magic: The Gathering. By 2010, McCaleb had repurposed the domain as a Bitcoin exchange, and less than a year after the platform was founded, he sold the platform to French-born developer Mark Karpelès, and in 2013, at its peak, Mt.Gox handled approximately 70% of the world's Bitcoin trading volume.
November 1, 2010, the Bitcoin logo was created: an unknown artist used the name "Bitboy", and to this day, the identity of "Bitboy" remains unknown.
February 2011, Silk Road went online
June 2011, the first Bitcoin bubble: Although Bitcoin was born in 2008, it was not until 2011 that its price really began to soar. In early 2011, the trading price of Bitcoin was less than $1 per coin, but by June 2011, the price of each Bitcoin had risen to more than $31. However, due to the theft of 25,000 Bitcoins in a large-scale hacking incident at the Mt. Gox exchange, the price of Bitcoin fell to $2 by November 2011.
June 2011, the first Bitcoin hacker attack: Allinvain posted on the BitcoinTalk forum that someone had hacked into his computer and stole 25,000 bitcoins directly from his hard drive. In June 2011, each bitcoin was worth around $20, which means that the value of Allinvain's bitcoins was about $500,000.
June 20, 2011, Mt. Gox was hacked for the first time: In June 2011, Mt. Gox experienced its first major crisis when hackers targeted the exchange and exploited a vulnerability that caused the price of Bitcoin on the platform to plummet from $17 to just cents in a matter of minutes. A leaked Mt. Gox document showed that hackers had been stealing Bitcoin from the exchange for years, resulting in the disappearance of more than 850,000 Bitcoins.
On April 18, 2011, the first altcoin Namecoin was born: Namecoin is a cryptocurrency and decentralized domain name system (DNS). As a fork of the Bitcoin protocol, it has some similarities with Bitcoin (including the use of a proof-of-work mechanism). It aims to provide a decentralized, censorship-resistant system for registering and managing domain names, as well as storing and transmitting arbitrary data.
On November 18, 2012, Bitcoin's first halving: The first Bitcoin halving event occurred at block height 210,000, and the block reward was reduced from 50 bitcoins to 25 bitcoins.
On May 2, 2013, the first Bitcoin ATM was installed in Vancouver, Canada
On March 18, 2013, the market value of Bitcoin exceeded $1 billion for the first time
On July 3, 2013, the first ICO: Mastercoin Initial Coin Offering (ICO), participants of the ICO sent Bitcoin to a designated address and in return received the newly created Mastercoin token MSC. This method demonstrated the potential of token sales as a means of financing blockchain development, setting a precedent for countless subsequent ICOs. Mastercoin was later renamed Omni.
On December 18, 2013, HODL was born:A user posted a post titled "I'm HODLING" on the bitcointalk.org forum. This misspelling later became a popular term.
On February 25, 2014, Mt. Gox filed for bankruptcy protection:due to a hacker attack, it lost 850,000 bitcoins, worth about $450 million at the time.
2015 was a year of Bitcoin expansion and block size issues: two expansion conferences, Scaling Bitcoin Montreal in September and Scaling Bitcoin Hongkong in December.
On January 14, 2016, the Lightning Network white paper was released: Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja released the Lightning Network white paper, which provides an expansion solution for Bitcoin by speeding up transaction time through state channel off-chain payments.
July 9, 2016, Bitcoin's second halving: Bitcoin's second halving occurred at block height 420,000, with the block reward falling from 25 bitcoins to 12.5 BTC.
BCH fork on August 1, 2017: Bitcoin's block size limit is 1MB (upgraded to 4MB due to SegWit), while BCH's block size limit is 32MB.
On August 23, 2017, Segregated Witness SegWit was activated at height 481,824 of the Bitcoin mainnet: SegWit aims to solve several long-standing problems of Bitcoin, such as transaction ductility and scalability. In terms of scalability: By separating witness data from transactions, the block size limit is effectively raised to 4MB, allowing more transactions to be included in each block. SegWit also improves the security of Bitcoin transactions by solving certain vulnerabilities, such as transaction ductility. The activation of SegWit marks the end of the Bitcoin block size dispute.
In November 2017, the Lightning Network was launched on the Bitcoin mainnet and completed the first transaction. Please refer to Jinse Finance's previous article "Explanation of the Principles of Lightning Network".
In November 2017, CME Group officially launched Bitcoin futures trading, and Bitcoin hit a high of $19,000.
In January 2018, the legendary Lazlo Hanyecz successfully purchased pizza again through the Lightning Network.
In January 2019, the Lightning Torch Event
On March 12, 2020, affected by the COVID-19 pandemic and the U.S. stock market, Bitcoin plummeted, falling to below $3,800.
On May 25, 2020, Bitcoin's third halving occurred at block height 630,000, and the block reward was reduced from 12.5 bitcoins to 6.25 bitcoins.
In January 2021, Stacks was launched: Stacks was originally named Blockstack and was co-founded by Muneeb Ali and Ryan Shea. This layer has its own programming language Clarity and a consensus mechanism called Proof of Transfer (PoX), which together allow smart contracts to be executed on the Bitcoin blockchain.
On February 8, 2021, Tesla announced that it would accept Bitcoin payments
On February 19, 2021, the market value of Bitcoin exceeded 1 trillion US dollars
In April 2021, the price of Bitcoin reached 65,000 US dollars
In June 2021, China banned Bitcoin mining, and Bitcoin fell below 30,000 US dollars. Bitcoin computing power migrated to the United States
On September 7, 2021, Bitcoin became the legal currency of El Salvador
On November 14, 2021, Taproot upgrade was successfully activated: This is the biggest progress of Bitcoin since the activation of SegWit in 2017. The Taproot upgrade introduced improvements to Shnorr signatures and smart contract functions. See Golden Finance's previous article "What is Taproot".
In November 2021, the price of Bitcoin reached the previous round of ATH of $69,000
In December 2022, ICP mainnet integrated Bitcoin
In 2023, the year of Bitcoin ecological development: Ordinals, Inscriptions, BRC20, Atomical, ARC20, Bitstamp, SRC20, Rune, Taproot Assets, RGB and other new concepts emerge in an endless stream. The development in 2023 is the sum of the development in the previous few years. Refer to the previous article of Golden Finance "Bitcoin Ecosystem 2023 Inventory".
In January 2024, the US SEC approved the listing of 11 Bitcoin spot ETFs.
In March 2024, stimulated by the Bitcoin spot ETF, the price of Bitcoin rose to $73,000, breaking the previous high for the first time before the halving.
Since 2024, the rise of Bitcoin layer 2. According to Golden Finance statistics, there are currently more than 50 Bitcoin L2s.
With the development and evolution of Bitcoin and the cycle of encryption, the leaders of the encryption industry are also updated very quickly. It can be said that there are talented people in every generation, and each leads the trend for one or two years.
The following are the leaders in the history of crypto development.
Satoshi Nakamoto: The creator of the Bitcoin protocol and its related software Bitcoin-Qt, whose real name is unknown and who claims to be Japanese-American, released the first Bitcoin software in 2009 and officially launched the Bitcoin financial system. In 2010, he gradually faded out and handed over the project to other members of the Bitcoin community.
Vitalik Buterin: Known as V God, the founder of Ethereum. When he first came into contact with cryptocurrency, he was also a supporter of Bitcoin. In 2011, he founded "Bitcoin Magazine". The most comprehensive Bitcoin Python library is pybitcointools written by him. Vitalik is a supporter of Bitcoin's large blocks. He wanted to make Bitcoin an extensible thing at first. For example, he and his team made Colored Coins, which supports users to issue coins on the BTC ecosystem. Anyone can build assets based on the Bitcoin protocol and trade. Ethereum inherits the idea of large blocks. Unlike Bitcoin's digital gold, it is a "computer".
Australian Satoshi: Formerly known as Craig Steven Wright, the founder of BSV, a fork of BCH, is an Australian who claims to be Satoshi Nakamoto. He became famous because he claimed to be Satoshi Nakamoto in 2016, and even got confirmation from Gavin Anderson, a member of the Bitcoin core team. But later, because Australian Satoshi could not provide enough evidence, he finally gave up, but got the title of "Australian Satoshi Nakamoto".
During the Bitcoin fork, Craig Wright was also very active, and even threatened to destroy Bitmain with money. In the end, BCH was forked, and BSV was born.
Chang Jian: Real name Liu Zhipeng, founder of China's largest blockchain forum and media "Babbitt", and also a science fiction writer. He plays a pivotal role in the Chinese blockchain world, has long been committed to the promotion and theoretical research of blockchain technology, is the originator of the blockchain "impossible triangle" theory, and published the first Bitcoin monograph in China "Bitcoin: A Real and Illusory Financial World".
Kaomao: Real name Jiang Xinyu, another name that cannot be ignored in the history of Bitcoin development. He is the first person in the Chinese Bitcoin circle to successfully launch an ICO project, and one of the earliest Chinese geniuses in manufacturing Asic mining machines. As early as 2013, he had a net worth of over 100 million yuan and held 20% of the computing power of the entire network. From the end of 2014 to the beginning of 2015, he suddenly lost contact and never showed up again.
Wu Jihan: Miner, founder of Bitmain, Bitmain once controlled more than 50% of the computing power of Bitcoin mining. In 2017, in the dispute between large and small blocks of Bitcoin, he supported large blocks, then forked Bitcoin, and BCH was born. He even wanted to usurp the power of BTC, but he tried his best but failed in the end.
Li Xiaolai: Formerly a teacher at New Oriental, he is known as the richest Bitcoiner in China. He bought Bitcoin for the first time in 2010 and decisively increased his position during the bear market in 2014. So far, he has accumulated 100,000 Bitcoins. In 2017, Li Xiaolai cashed out all his Bitcoins, earning about 13.5 billion yuan, and publicly stated that Bitcoin is a scam.
Casey Rodarmor: As the developer of the Ordinals protocol, he made NFTs possible on Bitcoin. This is another attempt to issue NFTs on Bitcoin since the colored coins in 2012 and the derivative Counterparty in 2014. Then he proposed the Rune protocol, which will be launched on the day of Bitcoin's fourth halving.
Larry Fink, CEO of BlackRock: As early as 2017, Fink said he was a "faithful believer" in cryptocurrency, and in 2023, BlackRock submitted an application for a Bitcoin ETF. Fink said that cryptocurrency is expected to surpass global currencies. This move by the global financial giant is undoubtedly a shot in the arm for the mainstreaming of Bitcoin. Later, BlackRock did become one of the first people in the United States to try out Bitcoin spot ETFs.
Salvadoran President Nayib Bukele: He is the first president in the world to publicly support Bitcoin and made Bitcoin the legal currency of his country. Since then, the country has been buying one Bitcoin every day. This is undoubtedly an innovative attempt for the current financial system.
MicroStrategy CEO Michael Saylor: Michael Saylor is the company with the most Bitcoin holdings, and Michael Saylor is also one of the most influential figures in the field of cryptocurrency. It is said that he holds more than 120,000 Bitcoins.
Changpeng Zhao: Founder of Binance, in 2014, he used the money from selling his house to buy Bitcoin at a price of $600. In 2017, he founded Binance, the exchange with the largest trading volume at present. After clearing out the exchange in China, he decisively chose the direction of global development. Facts have proved that decisively going overseas has indeed made Binance successful. However, it has also been involved in a lawsuit with the US government.
The reason why Zhao Changpeng has always been praised in the industry is that he is not just running an exchange. Binance has invested in and incubated many projects and has been working hard to make the industry bigger.
In the history of Bitcoin's development, countless people have come and gone, and some have persisted, from actively preaching in the early days to participating in the construction of the industry on the front line later. The history of crypto development will remember those active practitioners, and their belief in Bitcoin has also given them a sufficiently rich return on wealth.
Bitcoin has been born for nearly sixteen years since 2008. Bitcoin was born after the financial crisis in 2008. At that time, Satoshi Nakamoto wanted to create a financial system independent of the country in the face of inflation caused by excessive currency issuance. Bitcoin was originally created as an electronic cash, and Satoshi Nakamoto originally hoped that it could be used by people like currency.
However, in the first two years, Bitcoin was almost worthless. The price of a Bitcoin was less than half a cent, and no merchant was willing to accept Bitcoin as payment. It was not until May 2010 that Bitcoin was being used to buy food. An early miner, Laszlo Hanyec, exchanged 10,000 Bitcoins for two pizzas.
Since then, Bitcoin has been widely used as a payment method, especially on the dark web. In 2011, the dark web Silk Road was established, and Bitcoin became its hard currency. In addition to its anonymity, it was also largely because its difficult-to-trace characteristics highly met the needs of the dark web.
From early data, it can also be found that in the first three years of Bitcoin's birth, 30% of transactions pointed to the dark web; by 2014, the average daily transaction volume of Bitcoin in the six major dark webs reached 650,000 US dollars. Money laundering, drug trafficking, trafficking of women and children, Bitcoin is tied to these words. According to statistics, as of January 2018, about 25% of Bitcoin users and nearly half of Bitcoin transactions are related to illegal activities.
Some dark webs have disappeared, and the most commonly used virtual currency for money laundering has also changed from Bitcoin to Tether because of its constant price. With the surge in Bitcoin prices and its large price fluctuations, Bitcoin's function as an exchange currency is gradually weakening, and it is becoming more and more a tool for storing value. After the dispute over large and small blocks in 2017, Bitcoin has firmly established its position as digital gold, and in practice, Bitcoin is constantly fulfilling this position.
With the collapse of the monetary system of some sovereign countries, Bitcoin has become a choice for people in some countries to surpass legal tender.
In September 2021, Bitcoin became the legal currency in circulation in El Salvador. El Salvador has also become the country of Bitcoin.
And Argentina's new president has promoted the benefits of Bitcoin and cryptocurrency in many public occasions. The Argentine people, who have suffered from inflation in Argentina for a long time, are also actively buying Bitcoin. Argentina is one of the countries with the highest cryptocurrency adoption rate in the world. Inflation data shows that Argentina's inflation rate has risen from 254.20% in January 2024 to 276.20% in February.
From the examples of the above countries, we can see that Bitcoin is indeed playing the role of anti-inflation that Satoshi Nakamoto originally envisioned. However, some sovereign countries are indeed actively embracing Bitcoin, but the original intention of being independent of the mainstream financial system can no longer be realized. Today, some governments are actively regulating and embracing Bitcoin, and Bitcoin has become part of the mainstream financial system. The most direct manifestation is that some countries have passed Bitcoin spot ETFs, especially the United States, which has a profound impact.
Looking at the development of Bitcoin over the years, we can see that Bitcoin has gradually changed from a payment method to a gold-like investment product, and the attitudes of various countries towards it have also changed from crackdowns to having to study regulation, or actively embracing it.
Previously, Bitcoin was a toy for a handful of geeks, but after nearly 16 years of development, the narrative of Bitcoin has also changed from a payment currency to digital gold, and from a confrontation with the national financial system, it has finally been incorporated into the mainstream financial system.
Bitcoin itself is also changing. There have been disputes over large and small blocks, forks, and now there are endless new things such as inscriptions and runes on it.
All parties have staged various disputes on Bitcoin for their own interests, but these have never really shaken Bitcoin, and Bitcoin is still great.
Bitcoin Reserve Act could break the halving cycle. Would this four-year cycle unfold differently? Are we entering a mythical supercycle?
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceAs the digital asset market matures, it’s time for founders and investors to move away from the concept of a four-year Bitcoin halving cycle.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceAlthough Bitcoin’s four-year cycle is still in operation, the impact of the halving event is gradually weakening and the market may follow more traditional economic cycles.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceAfter investors “dumped” on news of the launch of a Bitcoin ETF, market watchers are looking for the next event that could drive market prices.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceAs the start of 2024 approaches, the possibility of a US ETF becomes more real, and with the upcoming Bitcoin halving in April, it’s shaping up to be a very positive year ahead!
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceCrypto market cycles could be lengthening.
 Beincrypto
BeincryptoObserving history is to understand the future to the greatest extent. This article gives a good review angle. The potential energy brought about by these extremes provides the ability for subsequent reversals.
 Ftftx
FtftxBitcoin price action this year is a case of "same, same, but different" but historically, nothing out of the ordinary.
 Cointelegraph
CointelegraphBitcoin avoided another 'Bart'-style price surge this weekend, but what's the sentiment ahead? Here are five potential bitcoin price talking points to consider.
 Cointelegraph
CointelegraphThe Bitcoin hash rate hit another all-time high and the 105,000th block since the last halving was mined, marking the halfway to the next halving.
 Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph