Source: web3 Chinese
In the past three months, the first batch of inscription projects such as Ordinals have sparked a fire in the entire track, and the increase in star tokens related to inscriptions has also continued. Setting a new record has also given rise to the popularity of SATS, RATS and even other public chain inscription concepts.
At the same time, Bitcoin Core core developer Luke Dashjr’s fierce criticism of inscriptions such as ORDI poured cold water on the entire inscription market, and also made the market question the relationship between inscriptions and Bitcoin. Healthy and sound development generates new thinking and exploration.
Against this background, the wave of "L2ization" of the Bitcoin ecosystem seems to be unstoppable, especially since L2 not only solves the much-criticized "junk transaction" problem of Bitcoin, but also creates a new digital currency with the help of programmability. A series of DeFi applications such as Swap, lending, and liquidity mining have broad prospects. So what is the current development trend of the Bitcoin L2 track, and what early passwords are hidden in it that are worthy of attention?
The "L2" trend of Bitcoin
As the Bitcoin inscription track continues to gain popularity, manual participation in new inscription projects on the chain has been quickly involved. It has become a red sea. From a narrative perspective, Inscription is indeed different from many previous large-scale investment and financing projects and the traditional narrative logic led by VC, giving more opportunities for the general public besides OG and Giant Whale to participate.
But the Bitcoin network at the center of the inscription craze is also facing many problems. The most intuitive one is "network congestion and surge in handling fees" - because inscriptions are similar to NFTs, allowing users to record various data to the blockchain, but overall since Bitcoin transaction fees are paid based on data size, Inscription users tend to set relatively low transaction fees.
This also means that they are willing to wait longer for confirmation, which can easily lead to inscription transactions being replaced by more urgent Bitcoin transfers.
In this context, these massive inscription transactions, which are all willing to queue up, have overwhelmed the Bitcoin memory pool (the place where all valid transactions that have not been officially added to the network are stored).
According to statistics from crypto KOL bitrabbit.btc, Bitcoin has accumulated 87 million UTXOs in the past 14 years, but after BRC20 started trading on April 24, it soared to 140 million in about 7 months - and the new Of the more than 50 million UTXOs added, 40 million are extremely small transactions of 100-1000 satoshis.
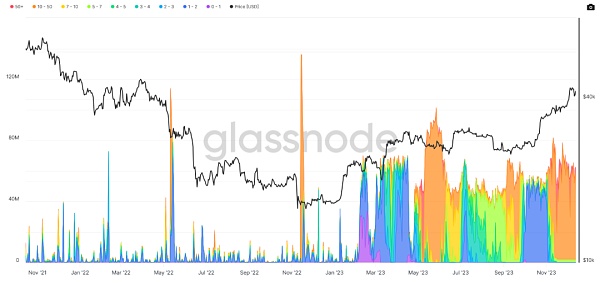
As can be seen in the picture above, since being launched in February 2023, the inscription has been It is the main consumer of Bitcoin block space, and the Bitcoin memory pool began to be fully loaded in February and continues to this day.
This has also resulted in the Bitcoin network being unable to clean up its memory pool. As of the time of publication, it is also at the highest level in BTC history since data records are available.
According to the current actual situation of the Bitcoin network, especially in order to prevent dust attacks, the Bitcoin transaction in a single UTXO is limited to no less than 546 satoshis, which means that tens of millions of inscription transactions The vast majority of pending small-value transactions are actually equivalent to spam transactions in DDoS attacks, and may not be packaged and broadcast on the chain for a lifetime.
“Most of these small-amount UTXOs will never be spent, but will always lie in Bitcoin nodes. In the next few decades or hundreds of years, they will cause tens of billions of dollars to the BTC network. Dollars of hardware and power resources wasted”.

This is also Bitcoin client Bitcoin Core developer Luke Dashjr’s public comment on ORDI, The main reason for the sharp criticism of Inscription and BRC20 - "Inscription is using the Bitcoin Core vulnerability to send spam information to the blockchain."
Therefore, with the inscription market exceeding billions of dollars and growing unabated, the inscription projects issued by the traditional Bitcoin main chain are limited by network congestion and "junk transactions" According to accusations, the distribution model will become increasingly unsustainable, which will be a key obstacle to limiting its further expansion.
The advantages of the Bitcoin L2 track are highlighted - it not only solves the problems of network congestion and "junk transactions" by packaging transactions into L2, but also uses new smart contracts. Its programmability creates a series of DeFi application scenarios for the Bitcoin ecosystem including Swap, lending, liquidity mining, and staking.
Bitcoin L2 Project Inventory
In general, building a prosperous DeFi application layer on the current Bitcoin ecosystem has become a new hot narrative , the Bitcoin L2 project has become a key track that carries the new expectations of Bitcoin supporters. In addition to familiar old projects such as Stacks, RSK, and Liquid, new solutions such as BitVM and BEVM also provide brand-new ideas.
Stacks: Bitcoin Smart Contract Layer
As the second layer of Bitcoin, Stacks is anchored on the Bitcoin blockchain on the one hand, and On the one hand, it introduces smart contract functions similar to Ethereum as an independent protocol and permanently settles transactions on the BTC blockchain to unlock the programmability of Bitcoin as Bitcoin L2, opening up new applications such as DeFi and NFT. possibility.
If you look at the overall system, Stacks actually has its own chain, compiler and programming language, and runs synchronously with Bitcoin to ensure its transactions and integrity.
However, because it uses the "hook" method to achieve BTC cross-chain - by issuing sBTC on the Stacks network, it is essentially a centralized mapping method, and there is a certain center Eliminate single point risks.
At the same time, its network Gas uses its main network token STX instead of BTC. Miners participating in Stacks' network mining will consume the pledged BTC to mine its network tokens. Through this system, miners earn STX coins and transaction fees, while STX stakers earn Bitcoins, which will also cause miners to be hesitant to participate in the choice.
As of the time of publication, compared with the popular ETH L2 Arbitrum’s 200,000 daily active users, the gap is still large, and the current response from both users and funds has been mediocre.
RSK: A universal smart contract platform based on Bitcoin
RSK (Rootstock) is a universal smart contract platform secured by the Bitcoin network. Its smart contracts were moved from Ethereum to RSK, making all Ethereum applications compatible with the Bitcoin blockchain. Since RSK creates a new block approximately every 33 seconds, it is much faster than Bitcoin’s 10-minute block time. RSK can also process approximately 10-20 transactions per second, which is also faster than Bitcoin’s processing capacity of approximately 5 transactions per second. More efficient.
Compared with other Bitcoin layered solutions, the most unique design of RSK is merged mining - the RSK blockchain uses the same proof-of-work (PoW) consensus algorithm as Bitcoin, but the miners Blocks can be generated faster than the Bitcoin base layer. These RSK blocks are mined through a process called “merged mining.”
Since both blockchains use the same consensus, miners can merge mining and mine for both the Bitcoin and RSK blockchains simultaneously, but have both Bitcoin and RSK consume the same amount of mining. Computing power, so the computing power contributed by miners can also mine RSK blocks, which allows merged mining to significantly increase miners' profitability without investing additional resources.
Merge mining allows RSK to verify transactions, generate blocks and send them to Bitcoin. Through this mining process, users can rest assured that RSK’s smart contracts benefit from Bitcoin blocks. chain security.
However, because RSK uses smartBTC (RBTC), which is to lock the tokens issued by BTC on Bitcoin at a 1:1 ratio and bridge it through the vault and smart contract on RSK, so The entire bridging process is still difficult to avoid smart contract security risks on RSK.
BitVM: A new star of Bitcoin smart contracts to be verified
BitVM is designed to implement Turing-complete Bitcoin without changing the operating code. Contract, key innovations include:
Introduce status between different UTXOs or different scripts through Bit Commitments.
Verifiability through logic gates: Execution can be verified by deconstructing any problematic program in the virtual machine, and the validity of the execution verified by the prover. This ensures that any false claims can be quickly proven wrong.
Keeping the Bitcoin network lightweight: Similar to Optimistic Rollup on Ethereum, BitVM does not perform a large number of calculations on Bitcoin. Instead, it minimizes on-chain activity and only refutes incorrect executions, acting more as a solver and validator. Only the output of the BitVM program is used in Bitcoin transactions.
However, the current functions of BitVM are extremely limited, and more of them are only in the paper stage. There is only one feasible function called the zero-check function, which is a potential use case in the future. Although a two-way hook with a side chain is included to achieve scalability, the implementation is similar to the Rollup logic on Ethereum:
Run an OPR-like fraud proof on the BTC script, that is, when a If there is any objection to an asset transaction, the user can initiate a report. If there is a problem with the transaction, the assets of the dishonest party will be confiscated. Generally, the effective report time is within 7 days (which can be simply understood as unconditional return within 7 days). ), however, if the report initiated by the user after 7 days is invalid, even if there is a problem with the asset transaction, it will be automatically saved on the blockchain and continue to run.
The smart contract layer of BitVM runs off-chain, and each smart contract does not share state. BTC cross-chain uses traditional Hash locks for asset anchoring, and does not achieve truly decentralized BTC cross-chain. chain, it is impossible to avoid the asset security risks of centralized arbitration nodes.
BEVM: Completely decentralized Bitcoin L2 solution
BEVM is a BTC Layer2 that uses BTC as Gas and is compatible with EVM. The core goal is Expand the smart contract scenario of Bitcoin, help BTC break through the constraints of the Bitcoin blockchain being non-Turing complete and not supporting smart contracts, so that BTC can build decentralized applications with BTC as the native Gas on BEVM Layer 2.
When a user transfers BTC from the Bitcoin main network to BEVM, the user's BTC will enter the contract address hosted by 1,000 nodes, and then at the same time be transferred to BEVM, the BTC Layer2 network, at a ratio of 1:1 Generate new BTC.
When a user issues an instruction to transfer BTC from BEVM back to the main network, the BEVM network node will trigger the Mast contract, and the 1,000 nodes that manage assets will automatically sign according to the established rules and return the BTC to the user's address. , the entire process is completely decentralized and trustless.
This means that all transactions are transferred from the Bitcoin main chain to run on the Layer2 network. At the same time, because BEVM is fully compatible with EVM, it can also easily enable BTC to implement various decentralized applications. Empowering Bitcoin ecological sub-projects from L2:
Ethereum DApp developers can directly and seamlessly migrate to BEVM, and quickly build Swap on BEVM and even on-chain DeFi such as lending and liquidity staking. Scenarios bring more possibilities to the Bitcoin ecosystem, and are the most decentralized and convenient compared to the first two.
MAP Protocol: Bitcoin L2 network for point-to-point cross-chain interoperability
MAP Protocol is a Bitcoin Layer 2 network for point-to-point cross-chain interoperation. , which utilizes the security mechanism of Bitcoin to enable assets and users of other public chains to interact seamlessly with the Bitcoin network, thereby enhancing the security of the network and achieving BRC20 cross-chain capabilities.
Compared with the Bitcoin main chain, MAP Protocol can provide lower gas transaction fees, which can even be as low as 35% of the cost of Unisat and OKX Ordinals platforms.
So using MAP Protocol’s Bitcoin L2 technology, users can trade inscribed BRC20 tokens on SATSAT with low Gas and zero congestion, and can also roll back to Bitcoin through Rolluper Main chain for trading on Unisat, OKX and other Bitcoin L1 trading platforms.
Summary
As the broader cryptocurrency community recognizes the importance of Layer 2 solutions in shaping the future of Bitcoin , also means that the entire Bitcoin L2 track will usher in new development opportunities, and the entire Build cycle will be very long. Now is the time for early layout.
Especially the most imaginative L2 solutions and a series of derivative application scenarios, such as Ethereum Layer 2 solutions such as Arbitrum and Optimism in 2021, are destined to eventually generate billions of dollars. Level Bitcoin L2 leading project.
Therefore, Bitcoin L2, as a new problem-solving idea, naturally has new enough imagination space. It is still in the early stage of the blue ocean and is in the dividend period of wealth cryptography waiting to be mined. It deserves long-term attention.
As such, ETF approval is currently the biggest catalyst for the cryptocurrency market, promising huge upside potential and limited downside. Although there is some liquidity risk, if investor appetite increases significantly, ETFs could improve market conditions across the board.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance




