Author: Riyue Xiaochu, member of Huzi Guanbi Source: X, @riyuexiaochu
We have heard many names related to cross-chain: cross-chain bridge, chain interoperability, full chain, account abstraction, chain abstraction, intention transaction, etc. It sounds very headache.
One phenomenon we can all observe is that there are more and more public chains. Before, the goal of the new public chain was to increase TPS and reduce GAS fees, and adopt different technical directions, such as solana, aptos, conflux, major layer2, etc. Now, the purpose of the new public chain has changed, and it is more for the development of its own ecology, such as the ecological Layer2 launched by Treasure, Aveo public chain, Loot public chain, etc., or want to use its own users and resources to create a successful public chain, such as base, blast, etc.
In this bull market, there will definitely be more and more public chains. Therefore, the demand for cross-chain has also surged. In fact, there is no need to be afraid of these. It is developing step by step.
Cross-chain bridges emerged in the bull market in 21 years, and their main function is the cross-chain of assets. The situation at that time After the Defi explosion in ETH, public chains such as BSC, Avalanche, and Fantom appeared and exploded one after another. Therefore, there was a relatively large demand for cross-chain assets. Famous projects at that time included multichain (formerly Anyswap) and celer bridge.
Public chains are like islands. With the increase of public chains and the rise of non-EVM systems, isolated islands have been formed and splits have been formed. Therefore, the cross-chain of assets alone cannot meet the needs of the multi-chain era.
The first thing to solve is the wallet problem. For each public chain, a wallet must be configured. It is easy to configure EVM. If you configure 100 or 80 chains, it will take more time to find them. However, each non-EVM chain needs a wallet, and none of them can be missing. The experience is more than bad. So, abstract accounts appeared. Abstract accounts are wallets that can handle all public chains, such as the OK wallet that has a good reputation recently. In essence, an abstract account is a contract account. It can also use social accounts to retrieve lost accounts and use gas tokens and other functions in a unified way.
After solving the problem of wallets being split in each chain, it is also necessary to solve the problem of Dapps being split in each chain. Then, the bottom-line demand is cross-chain information transmission. We hope that chain A can read the status of chain B, chain B can read the information of chain A, or the status of chain A and chain B at the same time. This is the interoperability of the chain. When information can be transmitted across chains, many things can be done, such as full-chain lending, cross-chain voting governance, etc. For dex and defi protocols, the benefits are even greater. The liquidity on different chains is no longer separated, and can be used in a unified way to achieve liquidity aggregation.
Imagine that with cross-chain assets, cross-chain information transmission, and abstract wallets, when we operate on the chain, we don’t need to know what chain is behind it. For example, if we want to mortgage the USDT in the wallet to borrow ETH, we don’t need to care whether the USDT is on the BNB chain or the Arbtrum chain. It can be used to mortgage the loan agreement and pay gas in a unified way. And the ETH that is loaned does not need to care which chain it comes from. Dapp will make its own agreement based on liquidity. This is chain abstraction.
The cross-chain protocols launched in this cycle are basically chain abstract protocols. They all have functions such as cross-chain information transmission and cross-chain assets. The difference between them is that the implementation methods and technologies used are different. So let's focus on the different ones below.
In this track, the top players are LayerZero, Wormhole, and Axelar
Sponsored Business Content
1.Axelar
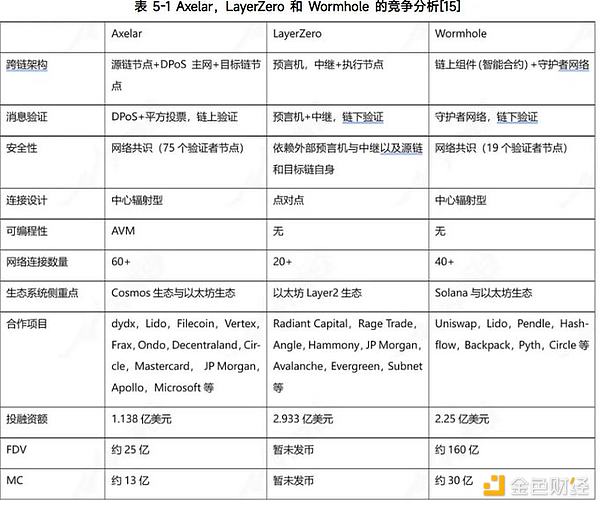
Axelar's biggest advantage lies in full-chain deployment. Axelar proposed the concept of interchain, in which all Web3 applications will have a unified development environment that will accommodate different logics on multiple chains and support users from multiple chains. Simply put, Dapps developed on Axelar can be deployed on all public chains it supports. Axelar also supports the most public chains among the three.
2.LayerZero
LayerZero should be a household name. Its feature is lightweight cross-chain information transmission, so it chooses to use oracles and relay networks to complete data transmission. LayerZero simplifies the process of cross-chain information interaction. It is not responsible for information verification itself, but the security is guaranteed by both parties across the chain. Therefore, in terms of efficiency, LayerZero is higher.
3. Wormhole
Wormhole originated from the cross-chain bridge established by the Ethereum and Solana networks. It consists of on-chain components and off-chain components. The on-chain components mainly include the emitter, the Wormhole core contract, and the transaction log. The off-chain components mainly consist of 19 guardian nodes and the message transmission network. Thanks to Solana's powerful ecosystem, Wormhole has the highest cross-chain amount.
In addition to the head, there are several very important members in this track, and there is hope that they will grow into giants in the future
4.ZetaChain
ZetaChain, although it also provides cross-chain information transmission, it mainly focuses on full-chain smart contracts, using ZetaChain to create truly interoperable decentralized applications that can span multiple chains such as Ethereum and Bitcoin. This is very similar to Axelar, and it also uses Cosmos SDK. And in terms of full-chain deployment, ZetaChain has more advantages than Axelar. However, due to resources and popularity, ZetaChain's ecology is slightly inferior to the three giants.
Axelar's structure is more similar to Zeta, but there are also obvious differences. Like ZetaChain, Axelar is also developed based on the Cosmos SDK. The difference is that it does not directly host EVM, so it does not support the same full-chain smart contracts as Zeta. So Axelar's target market is cross-chain messaging, which is similar to LayerZero.
5.Polyhedra
The core highlight of Polyhedra is zk zero-knowledge proof, which has the fastest zero-knowledge proof (ZK) algorithm. Its core product zkBridge guarantees strong security without adding additional trust assumptions. Through concise proofs, it not only guarantees correctness, but also significantly reduces the cost of on-chain verification. Its workload is several orders of magnitude faster than existing solutions. LayerZero now uses zkBridge as the default decentralized verification network (DVN) for many paths. Poyhedra supports 25 public chains.
6. Particle Network
Particle Network positions itself as a module that provides chain abstraction Layer1. Users can manage accounts and liquidity on different chains under a unified interface without downloading various wallets and conducting complex cross-chain transactions. Particle Network was originally a mainstream provider of wallet abstraction services. Particle has newly upgraded to wallet abstraction, chain abstraction, liquidity abstraction, Gas abstraction and other functions. Therefore, in the chain abstraction track, its strength is still the abstract wallet.
Under the rule of giants, Particle has focused on new directions, such as BTC layer2, GameFi's abstract wallet, SocaiFi's smart wallet, etc. Particle has laid the foundation for the 4 billion TVL of Bitcoin layer2 network Merlin.
 Anais
Anais










